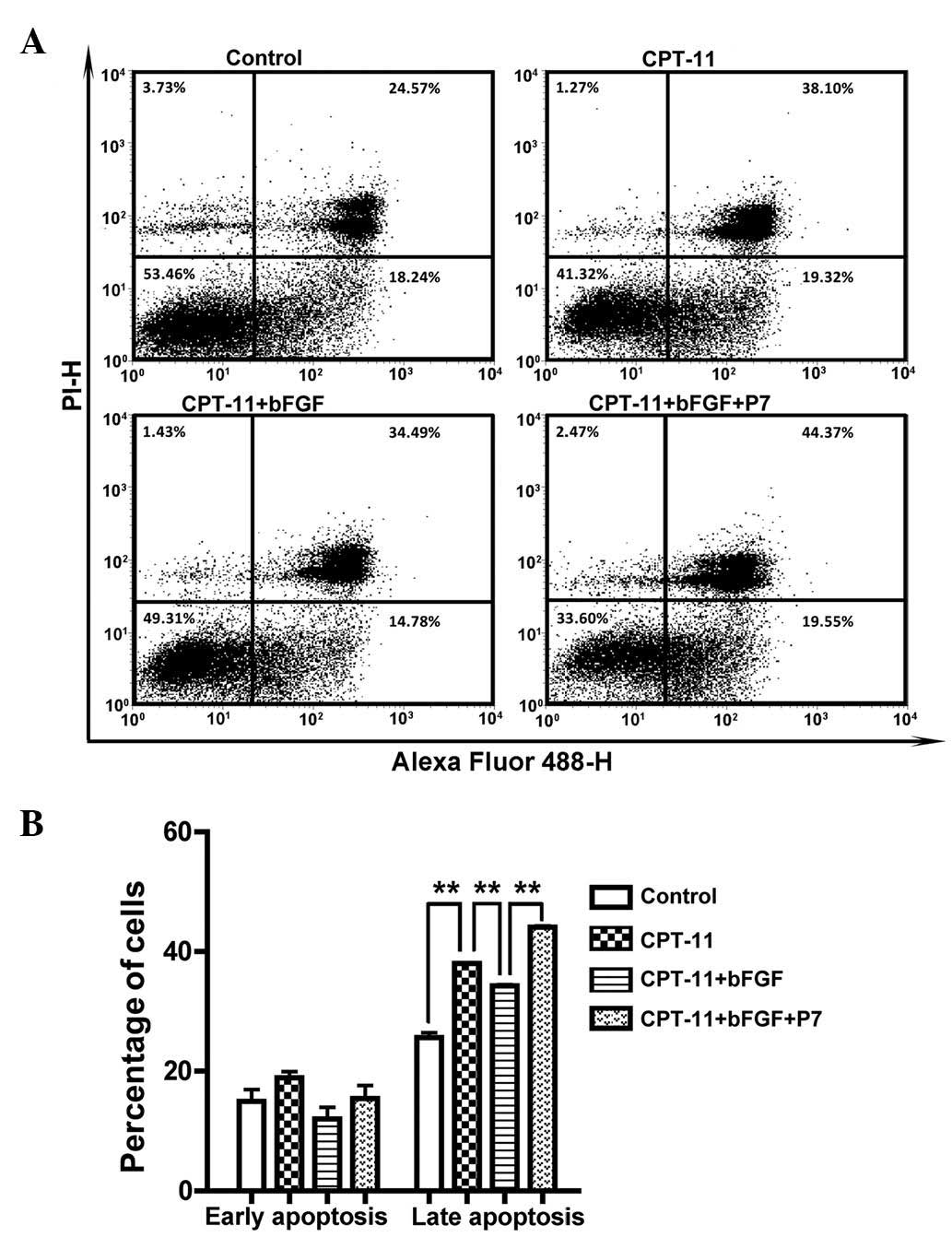
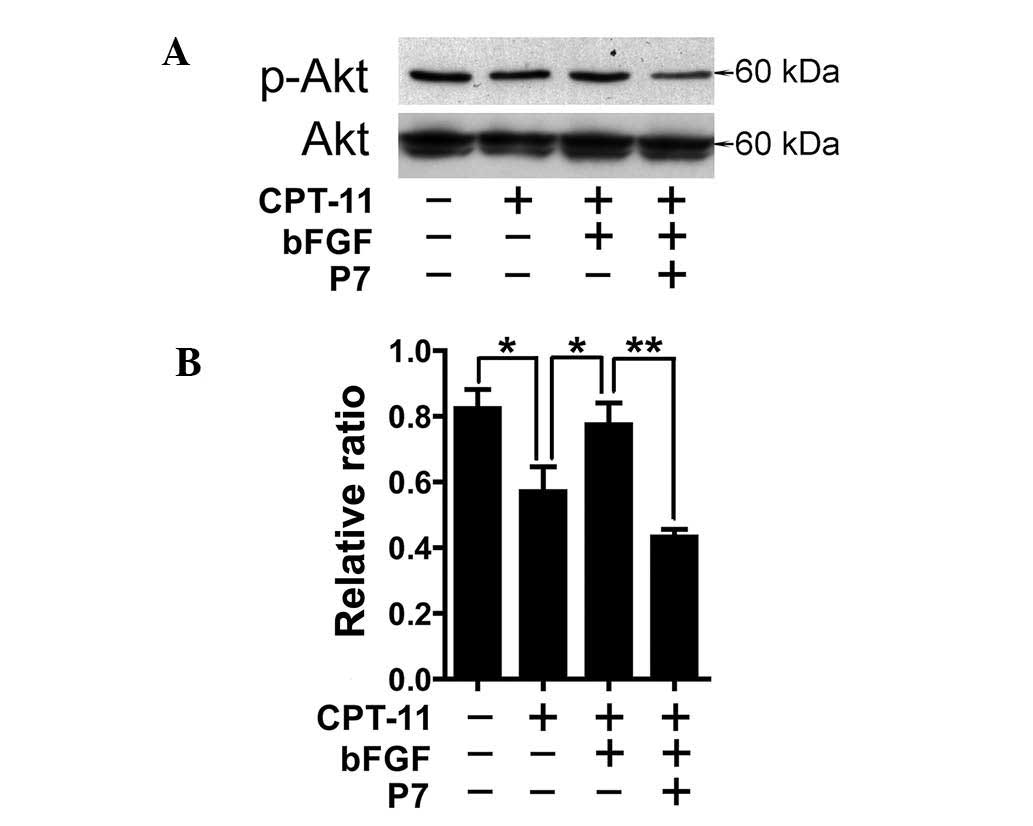
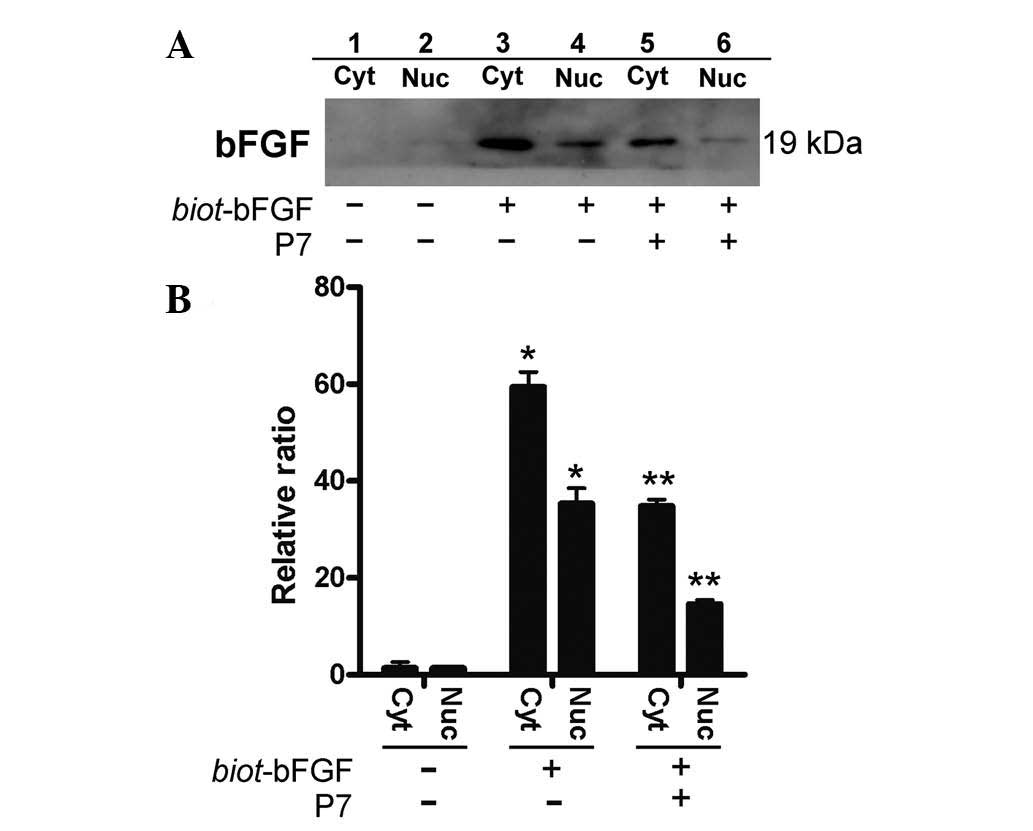
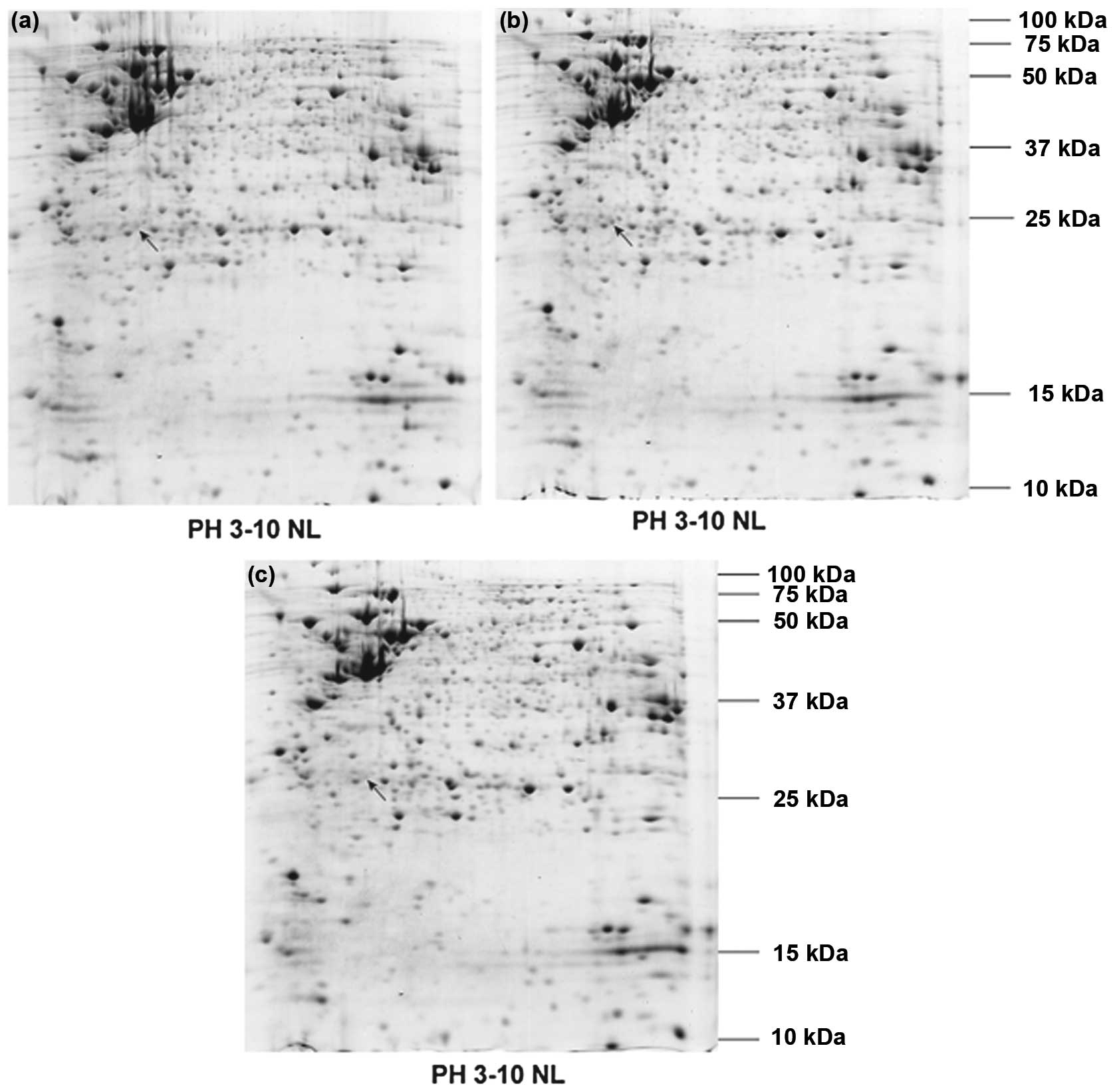
|
1
|
Kronborg O, Ugstad M, Fuglerud P, Johne B,
Hardcastle J, Scholefield JH, Vellacott K, Moshakis V and Reynolds
JR: Faecal calprotectin levels in a high risk population for
colorectal neoplasia. Gut. 46:795–800. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lum BL, Fisher GA, Brophy NA, Yahanda AM,
Adler KM, Kaubisch S, Halsey J and Sikic BI: Clinical trials of
modulation of multidrug resistance. Pharmacokinetic and
pharmacodynamic considerations. Cancer. 72(Suppl 11): 3502–3514.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Barrand MA, Bagrij T and Neo SY: Multidrug
resistance-associated protein, a protein distinct from
P-glycoprotein involved in cytotoxic drug expulsion. Gen Pharmacol.
28:639–645. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fidler IJ: Critical determinants of cancer
metastasis: rationale for therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
43:S3–S10. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Broxterman HJ, Lankelma J and Pinedo HM:
How to probe clinical tumour samples for P-glycoprotein and
multidrug resistance-associated protein. Eur J Cancer.
32A:1024–1033. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ferry DR, Traunecker H and Kerr DJ:
Clinical trials of P-glycoprotein reversal in solid tumours. Eur J
Cancer. 32A:1070–1081. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hertzberg RP, Caranfa MJ and Hecht SM: On
the mechanism of topoisomerase I inhibition by camptothecin:
evidence for binding to an enzyme-DNA complex. Biochemistry.
28:4629–4638. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Saltz LB, Cox JV, Blanke C, Rosen LS,
Fehrenbacher L, Moore MJ, Maroun JA, Ackland SP, Locker PK, Pirotta
N, Elfring GL and Miller LL: Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and
leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. Irinotecan Study
Group. N Engl J Med. 343:905–914. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ichiki M, Gohara R, Rikimaru T, Kitajima
T, Fujiki R, Shimada A and Aizawa H: Combination chemotherapy with
irinotecan and ifosfamide as second-line treatment of refractory or
sensitive relapsed small cell lung cancer: a phase II study.
Chemotherapy. 49:200–205. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takeuchi S, Takamizawa H, Takeda Y, Ohkawa
T, Tamaya T, Noda K, Sugawa T, Sekiba K, Yakushiji M and Taguchi T:
An early phase II study of CPT-11 in gynecologic cancers. Research
Group of CPT-11 in Gynecologic Cancers. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho.
18:579–584. 1991.(In Japanese).
|
|
11
|
Wall ME: Camptothecin and taxol: discovery
to clinic. Med Res Rev. 18:299–314. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fukuoka M, Niitani H, Suzuki A, Motomiya
M, Hasegawa K, Nishiwaki Y, Kuriyama T, Ariyoshi Y, Negoro S and
Masuda N: A phase II study of CPT-11, a new derivative of
camptothecin, for previously untreated non-small-cell lung cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 10:16–20. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ohno R, Okada K, Masaoka T, Kuramoto A,
Arima T, Yoshida Y, Ariyoshi H, Ichimaru M, Sakai Y and Oguro M: An
early phase II study of CPT-11: a new derivative of camptothecin,
for the treatment of leukemia and lymphoma. J Clin Oncol.
8:1907–1912. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shimada Y, Yoshino M, Wakui A, Nakao I,
Futatsuki K, Sakata Y, Kambe M, Taguchi T and Ogawa N: Phase II
study of CPT-11, a new camptothecin derivative, in metastatic
colorectal cancer. CPT-11 Gastrointestinal Cancer Study Group. J
Clin Oncol. 11:909–913. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shirao K, Shimada Y, Kondo H, Saito D,
Yamao T, Ono H, Yokoyama T, Fukuda H, Oka M, Watanabe Y, Ohtsu A,
Boku N, Fujii T, Oda Y, Muro K and Yoshida S: Phase I-II study of
irinotecan hydrochloride combined with cisplatin in patients with
advanced gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 15:921–927. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takeuchi S, Dobashi K, Fujimoto S, Tanaka
K, Suzuki M, Terashima Y, Hasumi K, Akiya K, Negishi Y and Tamaya
T: A late phase II study of CPT-11 on uterine cervical cancer and
ovarian cancer. Research Groups of CPT-11 in Gynecologic Cancers.
Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 18:1681–1689. 1991.(In Japanese).
|
|
17
|
Rusnati M and Presta M: Fibroblast growth
factors/fibroblast growth factor receptors as targets for the
development of anti-angiogenesis strategies. Curr Pharm Des.
13:2025–2044. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cronauer MV, Schulz WA, Seifert HH,
Ackermann R and Burchardt M: Fibroblast growth factors and their
receptors in urological cancers: basic research and clinical
implications. Eur Urol. 43:309–319. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gross JL, Herblin WF, Dusak BA, Czerniak
P, Diamond MD, Sun T, Eidsvoog K, Dexter DL and Yayon A: Effects of
modulation of basic fibroblast growth factor on tumor growth in
vivo. J Natl Cancer Inst. 85:121–131. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu X, Yan Q, Huang Y, Huang H, Su Z, Xiao
J, Zeng Y, Wang Y, Nie C, Yang Y and Li X: Isolation of a novel
basic FGF-binding peptide with potent antiangiogenetic activity. J
Cell Mol Med. 14:351–356. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang C, Lin S, Nie Y, Jia X, Wang J, Xiao
J, Wu J, Li X and Wu X: Mechanism of antitumor effect of a novel
bFGF binding peptide on human colon cancer cells. Cancer Sci.
101:1212–1218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bonnet H, Filhol O, Truchet I, Brethenou
P, Cochet C, Amalric F and Bouche G: Fibroblast growth factor-2
binds to the regulatory beta subunit of CK2 and directly stimulates
CK2 activity toward nucleolin. J Biol Chem. 271:24781–24787. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sorensen V, Nilsen T and Wiedlocha A:
Functional diversity of FGF-2 isoforms by intracellular sorting.
Bioessays. 28:504–514. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gan Y, Wientjes MG and Au JL: Expression
of basic fibroblast growth factor correlates with resistance to
paclitaxel in human patient tumors. Pharm Res. 23:1324–1331. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Walsh CT, Wei Y, Wientjes MG and Au JL:
Quantitative image analysis of intra-tumoral bFGF level as a
molecular marker of paclitaxel resistance. J Transl Med. 6:42008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Q, Maloof P, Wang H, Fenig E, Stein
D, Nichols G, Denny TN, Yahalom J and Wieder R: Basic fibroblast
growth factor downregulates Bcl-2 and promotes apoptosis in MCF-7
human breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 238:177–187. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Burchill SA and Westwood G: Mechanism of
basic fibroblast growth factor-induced cell death. Apoptosis.
7:5–12. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Coleman AB: Positive and negative
regulation of cellular sensitivity to anti-cancer drugs by FGF-2.
Drug Resist Updat. 6:85–94. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maloof P, Wang Q, Wang H, Stein D, Denny
TN, Yahalom J, Fenig E and Wieder R: Overexpression of basic
fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) downregulates Bcl-2 and promotes
apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 56:153–167. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raisova M, Hossini AM, Eberle J, Riebeling
C, Wieder T, Sturm I, Daniel PT, Orfanos CE and Geilen CC: The
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio determines the susceptibility of human melanoma
cells to CD95/Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Invest Dermatol.
117:333–340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Y, He QY, Tsao SW, Cheung YH, Wong A
and Chiu JF: Cytokeratin 8 silencing in human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells leads to cisplatin sensitization. Cancer Lett.
265:188–196. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jaquemar D, Kupriyanov S, Wankell M, Avis
J, Benirschke K, Baribault H and Oshima RG: Keratin 8 protection of
placental barrier function. J Cell Biol. 161:749–756. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Caulin C, Ware CF, Magin TM and Oshima RG:
Keratin-dependent, epithelial resistance to tumor necrosis
factor-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 149:17–22. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gilbert S, Loranger A, Daigle N and
Marceau N: Simple epithelium keratins 8 and 18 provide resistance
to Fas-mediated apoptosis. The protection occurs through a
receptor-targeting modulation. J Cell Biol. 154:763–773. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fortier AM, Van Themsche C, Asselin E and
Cadrin M: Akt isoforms regulate intermediate filament protein
levels in epithelial carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 584:984–988. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang C, Yu Y, Li Q, et al: P7 peptides
suppress the proliferation of K562 cells induced by basic
fibroblast growth factor. Tumour Biol. 33:1085–1093. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu Y, Gao S, Li Q, et al: The FGF2-binding
peptide P7 inhibits melanoma growth in vitro and in vivo. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 138:1321–1328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|