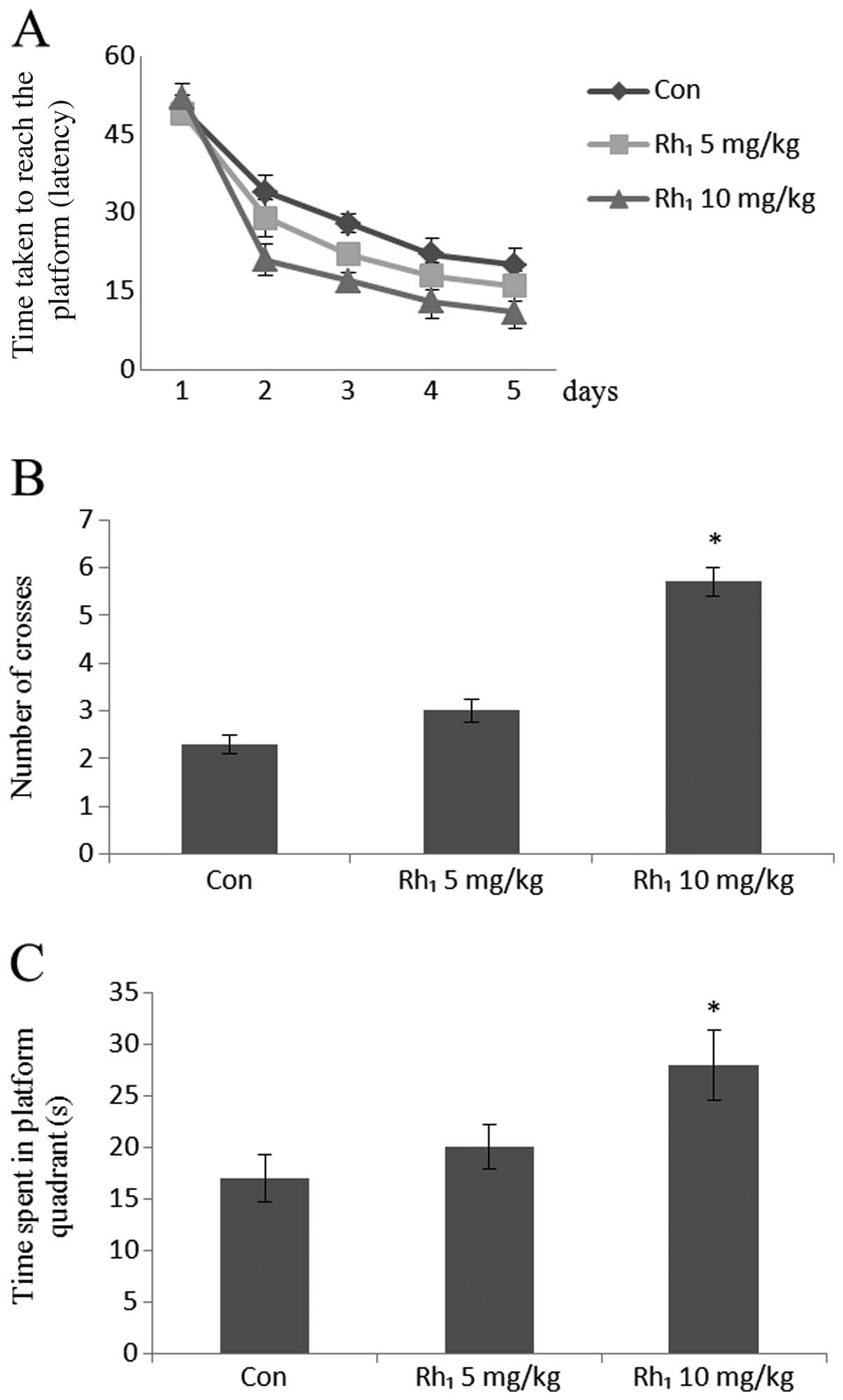
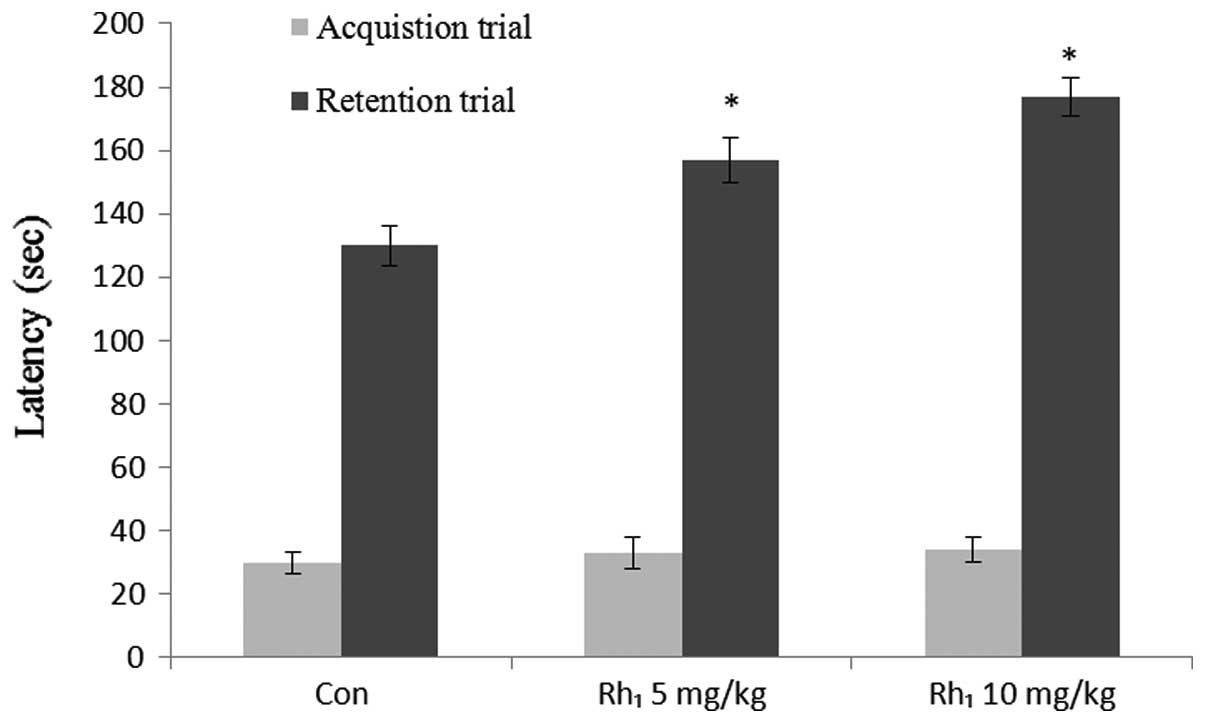
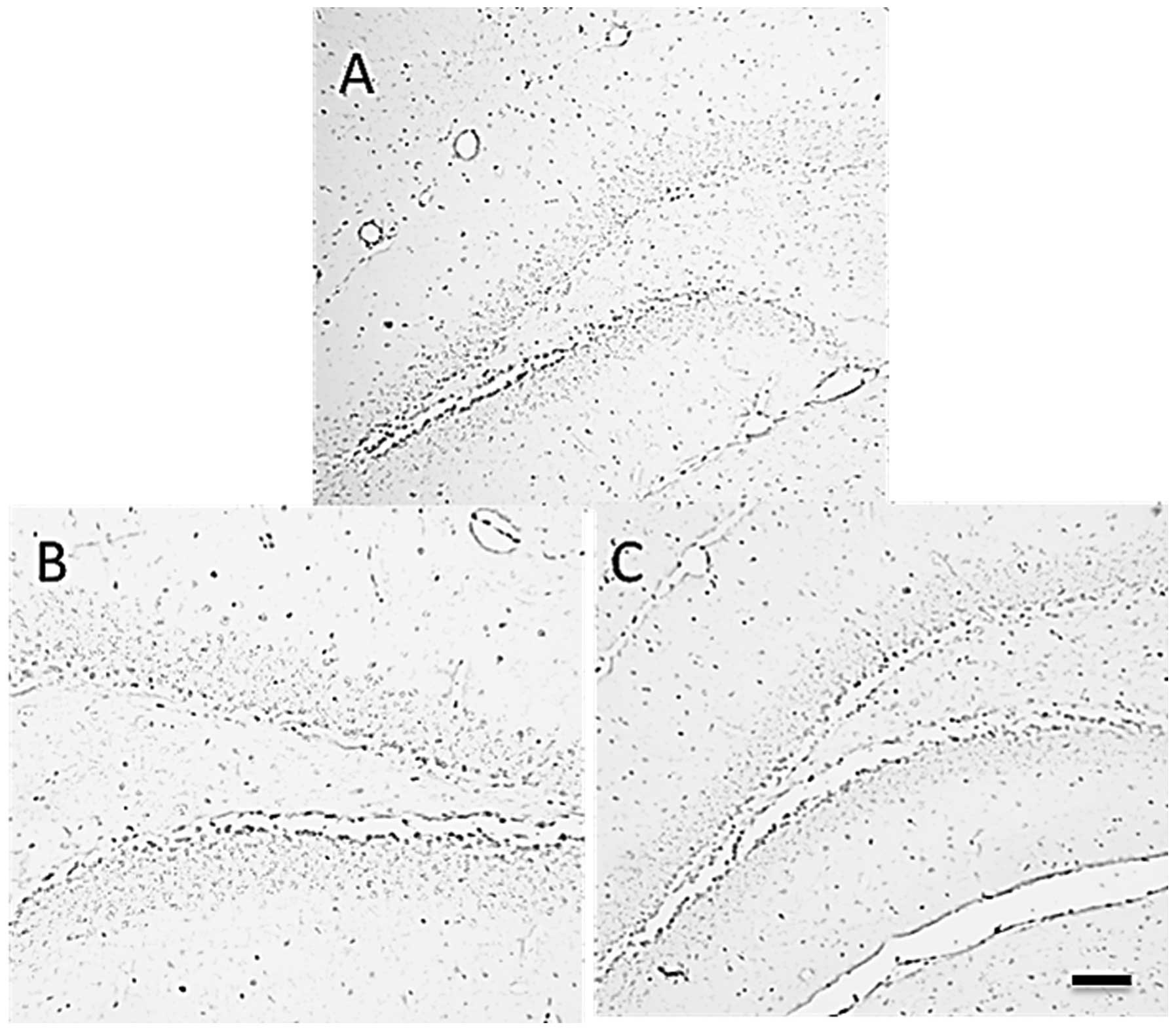
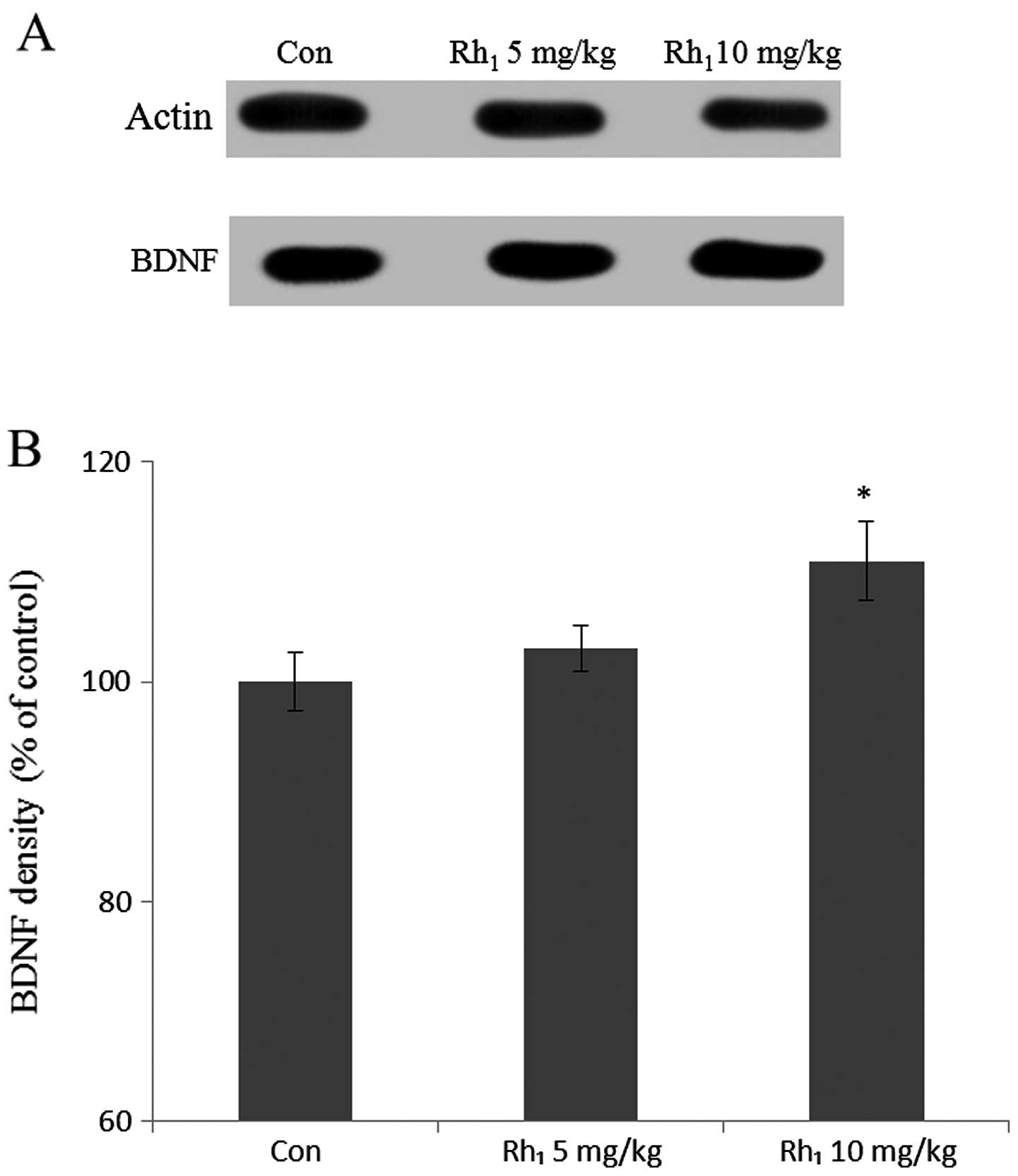
|
1
|
Christensen LP: Ginsenosides chemistry,
biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects. Advances in
Food and Nutrition Research. Taylor S: 55. Academic Press; New
Yotk: pp. 1–99. 2008
|
|
2
|
Van Kampen J, Robertson H, Hagg T and
Drobitch R: Neuroprotective actions of the ginseng extract G115 in
two rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol. 184:521–529.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kennedy DO and Scholey AB: Ginseng:
potential for the enhancement of cognitive performance and mood.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 75:687–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reay JL, Scholey AB and Kennedy DO: Panax
ginseng (G115) improves aspects of working memory performance and
subjective ratings of calmness in healthy young adults. Hum
Psychopharmacol. 25:462–471. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim EJ, Jung IH, Van Le TK, Jeong JJ, Kim
NJ and Kim DH: Ginsenosides Rg5 and Rh3 protect scopolamine-induced
memory deficits in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 146:294–299. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Quan Q, Wang J, Li X and Wang Y:
Ginsenoside Rg1 decreases Aβ(1–42) level by upregulating PPARγ and
IDE expression in the hippocampus of a rat model of Alzheimer’s
disease. PloS One. 8:e591552013.
|
|
7
|
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR,
Toni N, Palmer TD and Gage FH: Functional neurogenesis in the adult
hippocampus. Nature. 415:1030–1034. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shors TJ, Miesegaes G, Beylin A, Zhao M,
Rydel T and Gould E: Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the
formation of trace memories. Nature. 410:372–376. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aimone JB, Wiles J and Gage FH: Potential
role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new
memories. Nat Neurosci. 9:723–727. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Johansson CB, Svensson M, Wallstedt L,
Janson AM and Frisén J: Neural stem cells in the adult human brain.
Exp Cell Res. 253:733–736. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Leuner B, Gould E and Shors TJ: Is there a
link between adult neurogenesis and learning? Hippocampus.
16:216–224. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Drapeau E, Montaron MF, Aguerre S and
Abrous DN: Learning-induced survival of new neurons depends on the
cognitive status of aged rats. J Neurosci. 27:6037–6044. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Olson AK, Eadie BD, Ernst C and Christie
BR: Environmental enrichment and voluntary exercise massively
increase neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus via dissociable
pathways. Hippocampus. 16:250–260. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Klempin F and Kempermann G: Adult
hippocampal neurogenesis and aging. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin
Neurosci. 257:271–280. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mirescu C and Gould E: Stress and adult
neurogenesis. Hippocampus. 16:233–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rinwa P and Kumar A: Piperine potentiates
the protective effects of curcumin against chronic unpredictable
stress-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative damage in mice.
Brain Res. 1488:38–50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Quadrato G, Benevento M, Alber S, et al:
Nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFATc4) is required for
BDNF-dependent survival of adult-born neurons and spatial memory
formation in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 109:E1499–E1508.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lai L, Hao H, Liu Y, et al:
Characterization of pharmacokinetic profiles and metabolic pathways
of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh1 in vivo and in vitro. Planta Med.
75:797–802. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Joh EH, Lee IA, Jung IH and Kim DH:
Ginsenoside Rb1 and its metabolite compound K inhibit IRAK-1
activation-the key step of inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol.
82:278–286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang L, Zhang J, Zheng K, Shen H and Chen
X: Long-term ginsenoside Rg1 supplementation improves age-related
cognitive decline by promoting synaptic plasticity associated
protein expression in C57BL/6J mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
July.5–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
21
|
Liu L, Hoang-Gia T, Wu H, et al:
Ginsenoside Rb1 improves spatial learning and memory by regulation
of cell genesis in the hippocampal subregions of rats. Brain Res.
1382:147–154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang YZ, Chen J, Chu SF, et al:
Improvement of memory in mice and increase of hippocampal
excitability in rats by ginsenoside Rg1’s metabolites ginsenoside
Rh1 and protopanaxatriol. J Pharmacol Sci. 109:504–510.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, et al:
Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects
of antidepressants. Science. 301:805–809. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Snyder JS, Hong NS, McDonald RJ and
Wojtowicz JM: A role for adult neurogenesis in spatial long-term
memory. Neuroscience. 130:843–852. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shors TJ, Mathew J, Sisti HM, Edgecomb C,
Beckoff S and Dalla C: Neurogenesis and helplessness are mediated
by controllability in males but not in females. Biol Psychiatry.
62:487–495. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wati H, Kudo K, Qiao C, Kuroki T and Kanba
S: A decreased survival of proliferated cells in the hippocampus is
associated with a decline in spatial memory in aged rats. Neurosci
Lett. 399:171–174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thoenen H: Neurotrophins and neuronal
plasticity. Science. 270:593–598. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bergami M, Rimondini R, Santi S, Blum R,
Götz M and Canossa M: Deletion of TrkB in adult progenitors alters
newborn neuron integration into hippocampal circuits and increases
anxiety-like behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:15570–15575.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Derecki NC, Cardani AN, Yang CH, et al:
Regulation of learning and memory by meningeal immunity: a key role
for IL-4. J Exp Med. 207:1067–1080. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schwabe L, Schächinger H, de Kloet ER and
Oitzl MS: Corticosteroids operate as a switch between memory
systems. J Cogn Neurosci. 22:1362–1372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zatorre RJ, Fields RD and Johansen-Berg H:
Plasticity in gray and white: neuroimaging changes in brain
structure during learning. Nat Neurosci. 15:528–536. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Benito E and Barco A: CREB’s control of
intrinsic and synaptic plasticity: implications for CREB-dependent
memory models. Trends Neurosci. 33:230–240. 2010.
|
|
33
|
Wang YH and Du GH: Ginsenoside Rg1
inhibits β-secretase activity in vitro and protects against
Abeta-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res.
11:604–612. 2009.
|