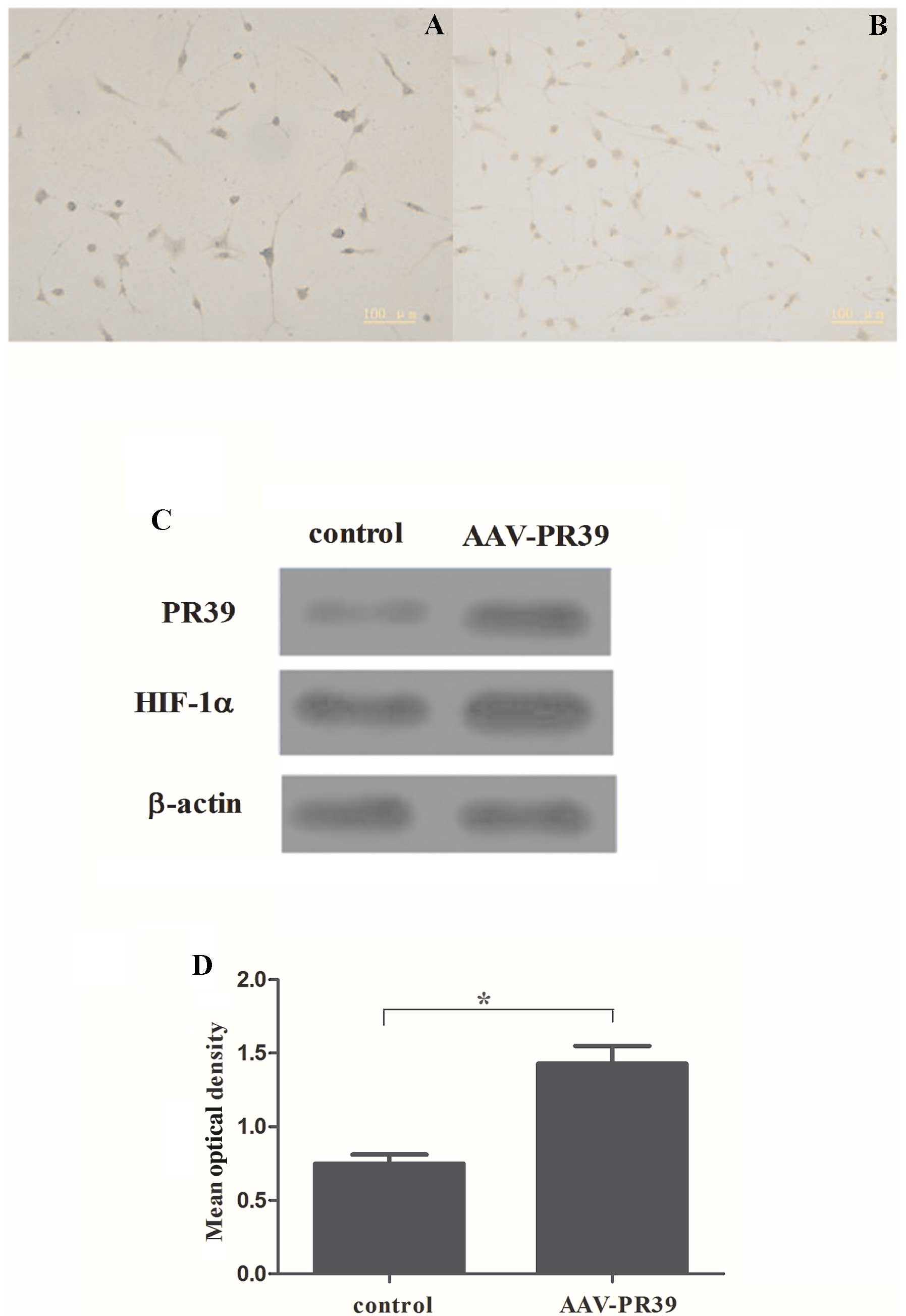
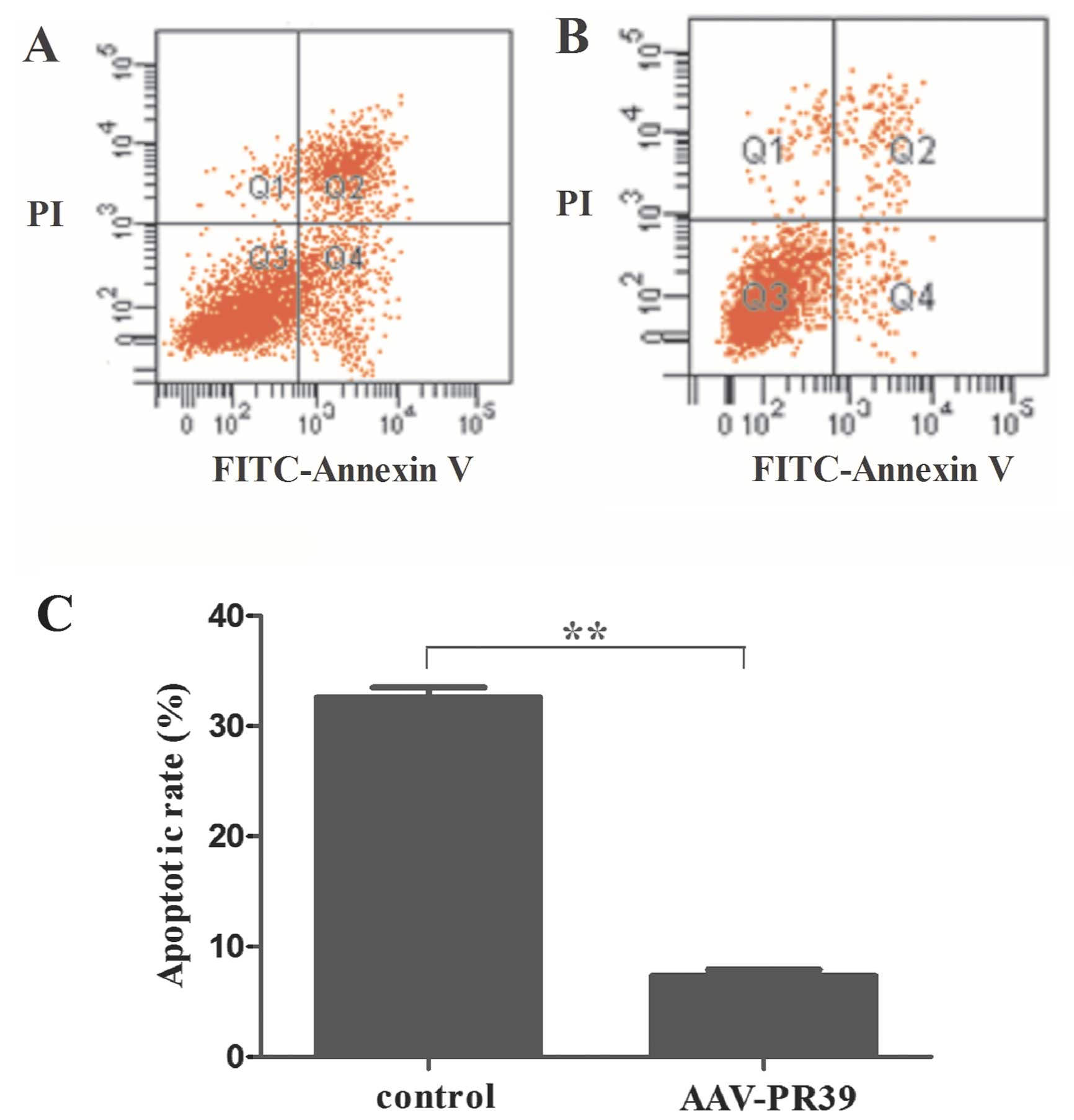
|
1
|
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons
ML, Chaitman BR and White HD: Third universal definition of
myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 60:1581–1598. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kanashiro-Takeuchi RM, Schulman IH and
Hare JM: Pharmacologic and genetic strategies to enhance cell
therapy for cardiac regeneration. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 51:619–625.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Potente M, Gerhardt H and Carmeliet P:
Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell. 146:873–887.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lykouras D, Flordellis C and Dougenis D:
Gene therapy targets and the role of pharmacogenomics in heart
failure. Targets in Gene Therapy. You Y: InTech; View Article : Google Scholar : 2011, Available at:
http://www.intechopen.com/books/targets-in-gene-therapy/gene-therapy-targets-and-the-role-of-pharmacogenomics-in-heart-failure.
|
|
6
|
Lee RJ, Springer ML, Blanco-Bose WE, Shaw
R, Ursell PC and Blau HM: VEGF gene delivery to myocardium:
deleterious effects of unregulated expression. Circulation.
102:898–901. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muinck E, Nagy N, Tirziu D, Murakami M,
Gurusamy N, Goswami SK, Ghatpande S, Engelman RM, Simons M and Das
DK: Protection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by
the angiogenic Masterswitch protein PR 39 gene therapy: the roles
of HIF1alpha stabilization and FGFR1 signaling. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 9:437–445. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li J, Post M, Volk R, Gao Y, Li M, Metais
C, Sato K, Tsai J, Aird W and Rosenberg RD: PR39, a peptide
regulator of angiogenesis. Nat Med. 6:49–55. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cavadas MA, Nguyen LK and Cheong A:
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) network: insights from mathematical
models. Cell Commun Signal. 11:42–56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee PH, Ohtake T, Zaiou M, Murakami M,
Rudisill JA, Lin KH and Gallo RL: Expression of an additional
cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide protects against bacterial skin
infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:3750–3755. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen F, Fan Y, Su H, Zhu Y, Chen Y, Liu W,
Young WL and Yang GY: Adeno-associated viral vector-mediated
hypoxia-regulated VEGF gene transfer promotes angiogenesis
following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Gene Ther. 15:30–39.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bao J, Sato K, Li M, Gao Y, Abid R, Aird
W, Simons M and Post MJ: PR-39 and PR-11 peptides inhibit
ischemia-reperfusion injury by blocking proteasome-mediated IκBα
degradation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 281:H2612–H2618.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Korthuis RJ, Gute DC, Blecha F and Ross
CR: PR-39, a proline/arginine-rich antimicrobial peptide, prevents
postischemic microvascular dysfunction. Am J Physiol.
277:H1007–H1013. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Qiu S, Song L, Yan Q and Yang G:
Secretory expression of p53 (N15)-Ant following lentivirus-mediated
gene transfer induces cell death in human cancer cells. Cancer
Invest. 26:28–34. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Garrett DJ, Cohen JC and Larson JE: Long
term physiologic modification using rAAV in utero gene-therapy.
Genet Vaccines Ther. 2:42004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zaiss AK, Liu Q, Bowen GP, Wong NC,
Bartlett JS and Muruve DA: Differential activation of innate immune
responses by adenovirus and adeno-associated virus vectors. J
Virol. 76:4580–4590. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, Fukumura
D, Brusselmans K, Dewerchin M, Neeman M, Bono F, Abramovitch R,
Maxwell P, Koch CJ, Ratcliffe P, Moons L, Jain RK, Collen D and
Keshert E: Role of HIF-1alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell
proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature. 394:485–490. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gerber HP, Condorelli F, Park J and
Ferrara N: Differential transcriptional regulation of the two
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor genes Flt-1, but not
Flk-1/KDR, is up-regulated by hypoxia. J Biol Chem.
272:23659–23667. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wu J, Parungo C, Wu G, Kang PM, Laham RJ,
Sellke FW, Simons M and Li J: PR39 inhibits apoptosis in hypoxic
endothelial cells. Circulation. 109:1660–1667. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brevoord D, Kranke P, Kuijpers M, Weber N,
Hollmann M and Preckel B: Remote ischemic conditioning to protect
against ischemia-reperfusion injury: a systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e421792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Masci PG, Francone M, Desmet W, Ganame J,
Todiere G, Donato R, Siciliano V, Carbone I, Mangia M and Strata E:
Right ventricular ischemic injury in patients with acute ST-segment
elevation myocardial infarction clinical perspective
characterization with cardiovascular magnetic resonance.
Circulation. 122:1405–1412. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Post MJ, Sato K, Murakami M, Bao J, Tirziu
D, Pearlman JD and Simons M: Adenoviral PR39 improves blood flow
and myocardial function in a pig model of chronic myocardial
ischemia by enhancing collateral formation. Am J Physiol Regul
Integr Comp Physiol. 290:R494–R500. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|