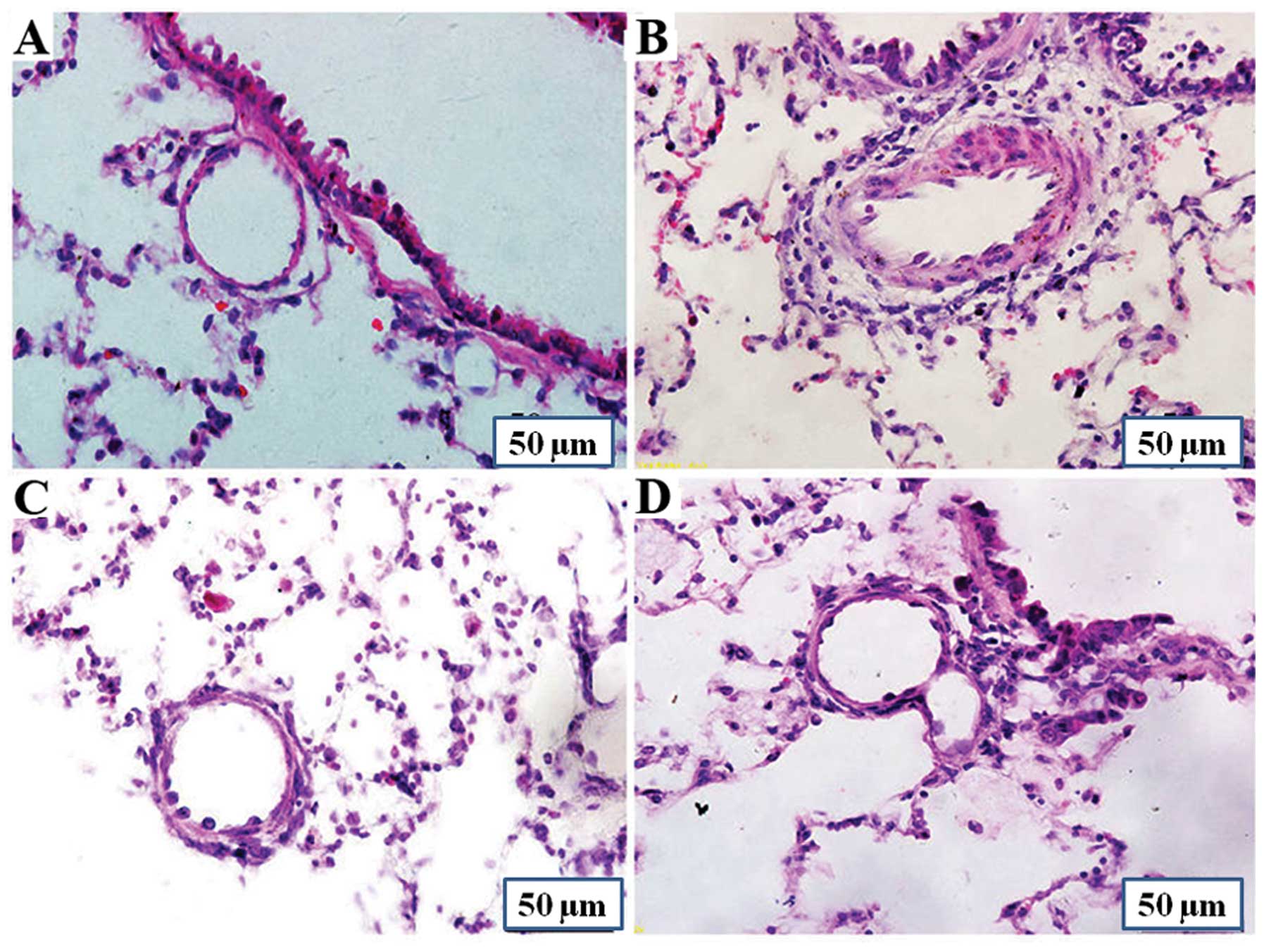
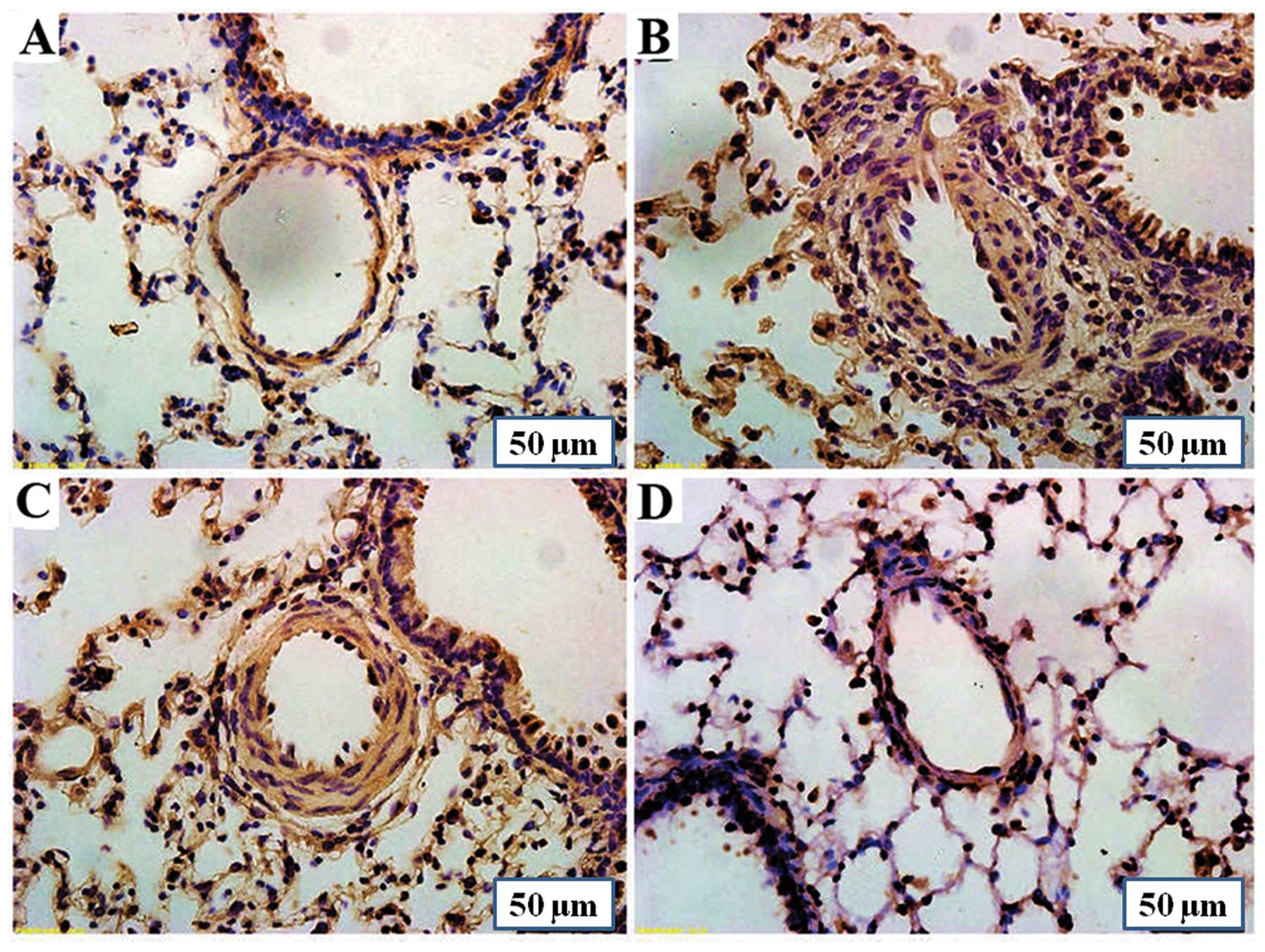
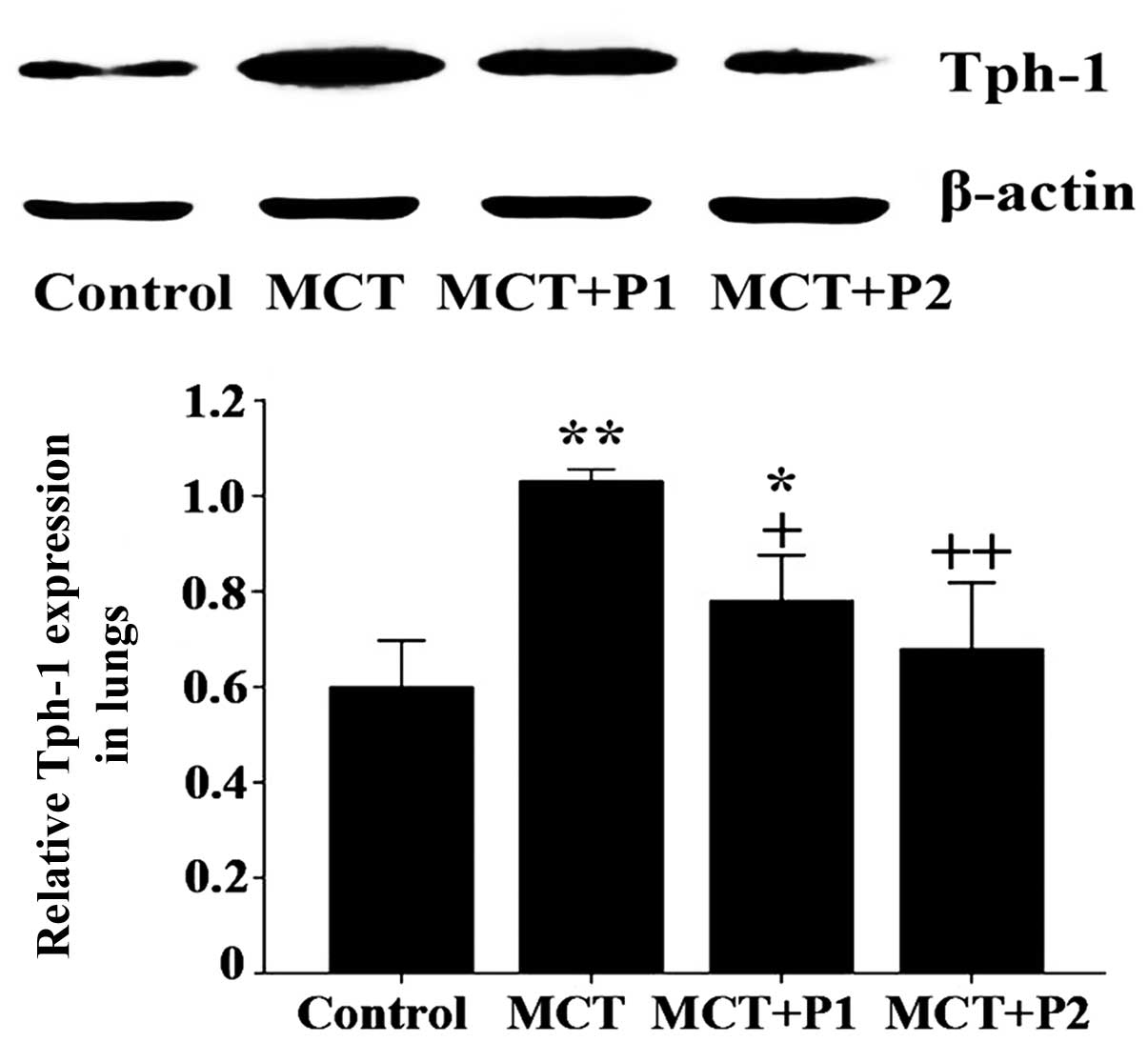
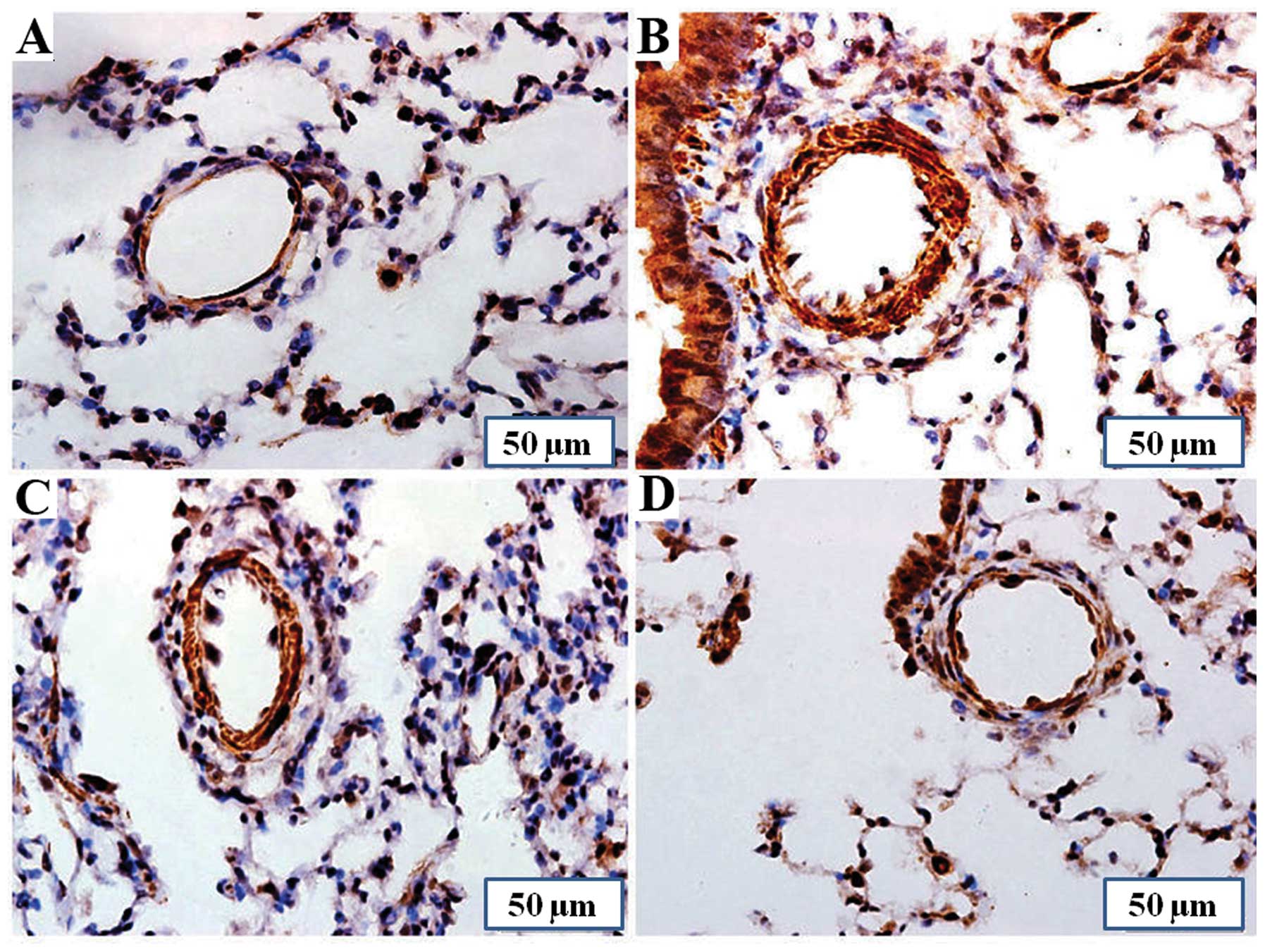
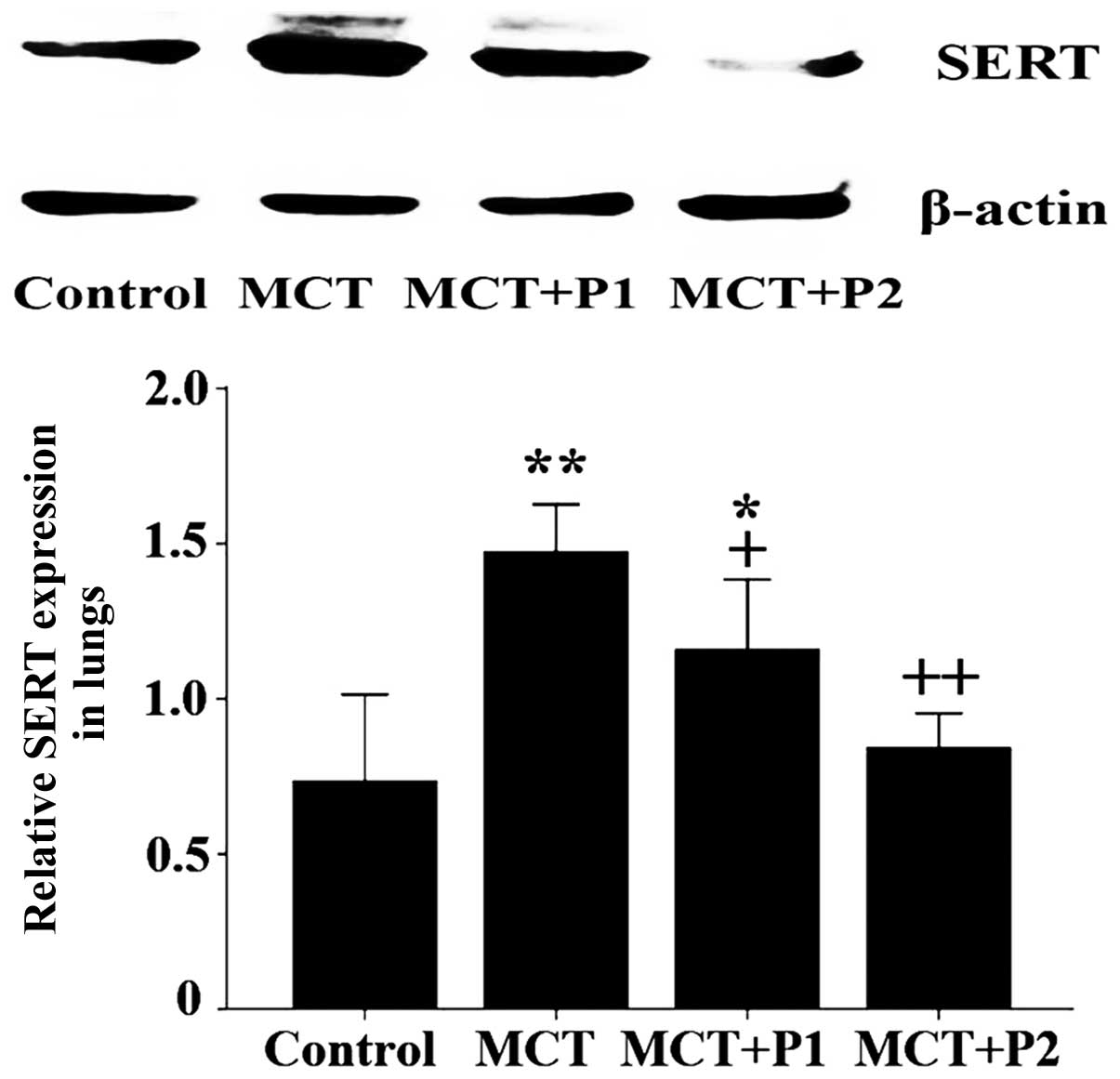
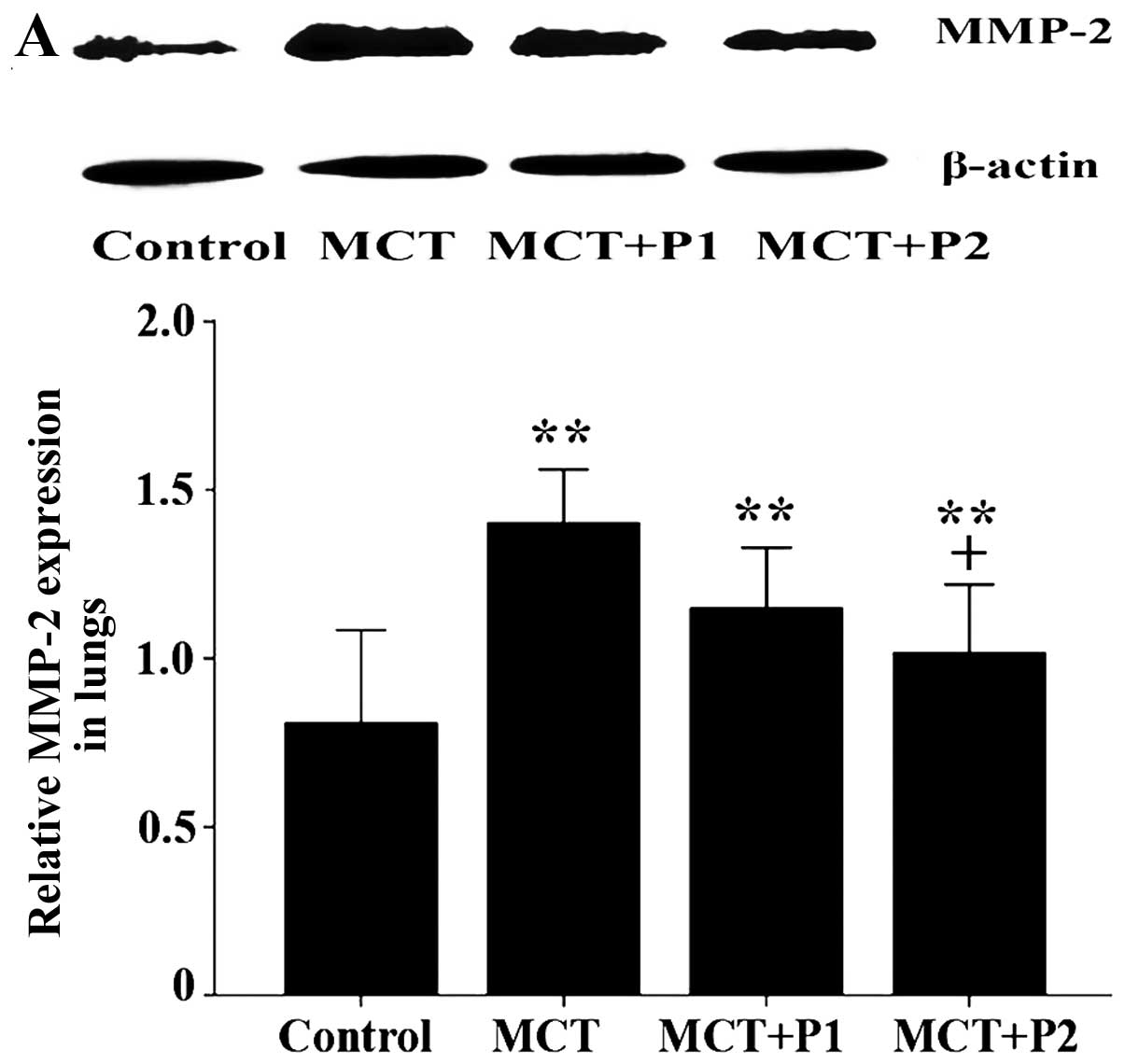
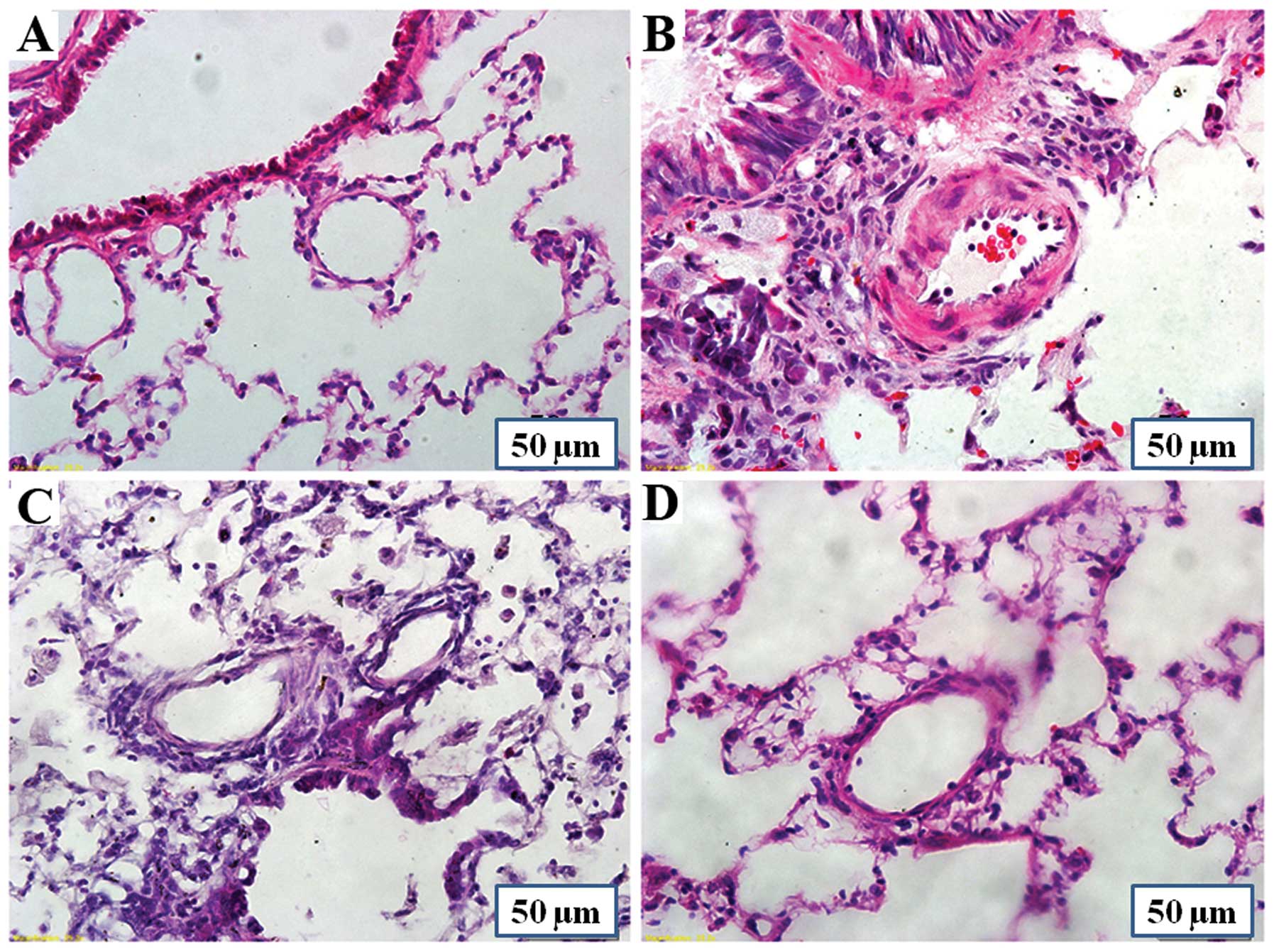
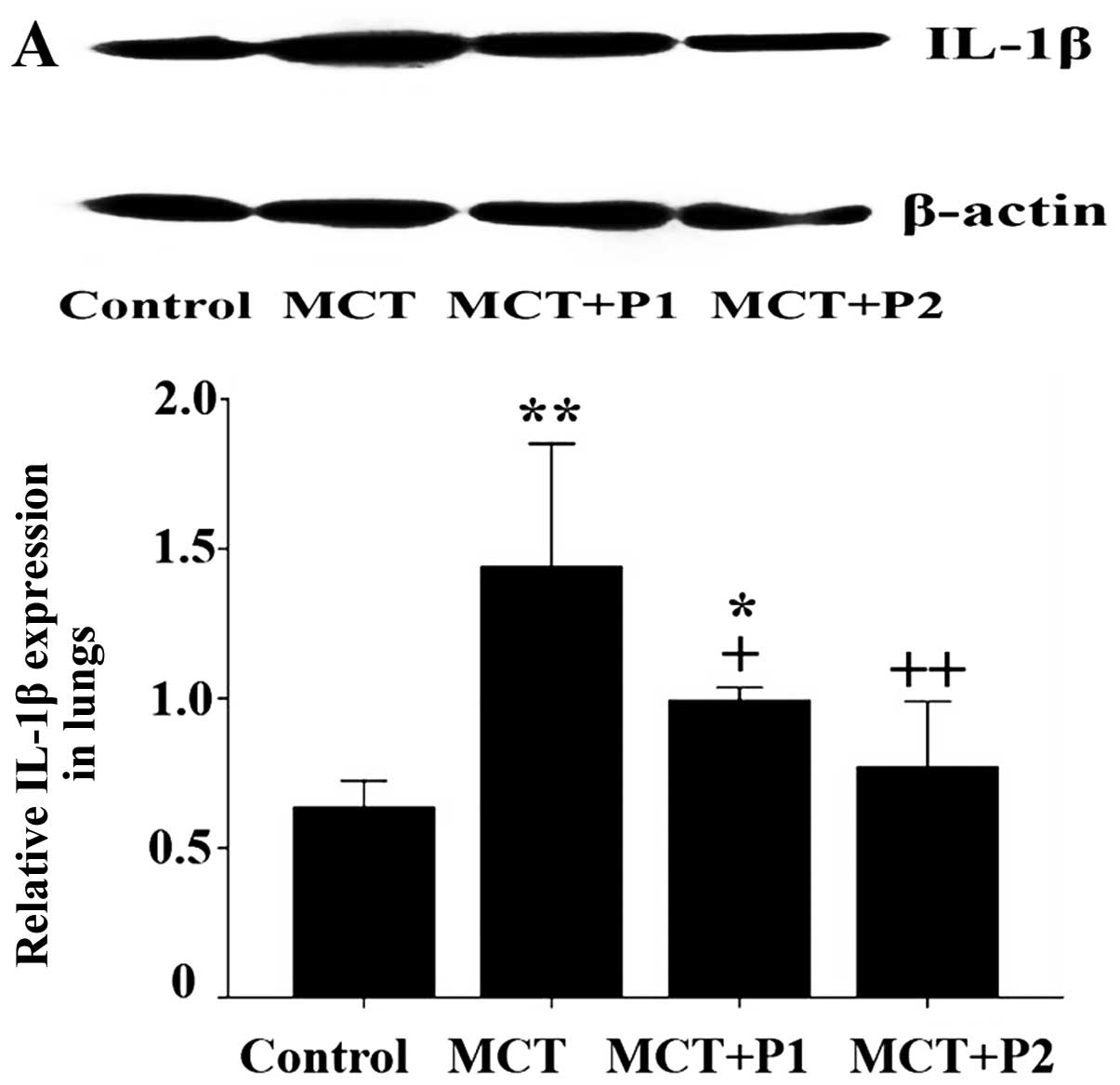
|
1
|
MacLean MR: Pulmonary hypertension and the
serotonin hypothesis: where are we now? Int J Clin Pract Suppl.
27–31. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dewachter L, Adnot S, Fadel E, et al:
Angiopoietin/Tie2 pathway influences smooth muscle hyperplasia in
idiopathic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
174:1025–1033. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li XQ, Wang HM, Yang CG, Zhang XH, Han DD
and Wang HL: Fluoxetine inhibited extracellular matrix of pulmonary
artery and inflammation of lungs in monocrotaline-treated rats.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:217–222. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crapo PM, Medberry CJ, Reing JE, Tottey S,
Van der Merwe Y, Jones KE and Badylak SF: Biologic scaffolds
composed of central nervous system extracellular matrix.
Biomaterials. 33:3539–3547. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, Han DD, Wang HM, Liu M, Zhang XH
and Wang HL: Downregulation of osteopontin is associated with
fluoxetine amelioration of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary
inflammation and vascular remodelling. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
38:365–372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giantin M, Aresu L, Benali S, et al:
Expression of matrix metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases and vascular endothelial growth factor in canine
mast cell tumours. J Comp Pathol. 147:419–429. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Umesh A, Paudel O, Cao YN, Myers AC and
Sham JS: Alteration of pulmonary artery integrin levels in chronic
hypoxia and monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. J Vasc
Res. 48:525–537. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Price LC, Wort SJ, Perros F, et al:
Inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest.
141:210–221. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tuder RM, Groves B, Badesch DB and Voelkel
NF: Exuberant endothelial cell growth and element of inflammation
are present in plexiform lesions of pulmonary hypertension. Am J
Pathol. 144:275–285. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bauer EM, Zheng H, Comhair S, Erzurum S,
Billiar TR and Bauer PM: Complement C3 deficiency attenuates
chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. PLoS One.
6:e285782011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rashid M, Fahim M and Kotwani A: Efficacy
of tadalafil in chronic hypobaric hypoxia-induced pulmonary
hypertension: possible mechanisms. Fundam Clin Pharmacol.
27:271–278. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li M, Riddle SR, Frid MG, et al: Emergence
of fibroblasts with a proinflammatory epigenetically altered
phenotype in severe hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. J Immunol.
187:2711–2722. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guignabert C, Raffestin B, Benferhat R, et
al: Serotonin transporter inhibition prevents and reverses
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Circulation.
111:2812–2819. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fanburg BL and Lee SL: A new role for an
old molecule: serotonin as a mitogen. Am J Physiol. 272:L795–L806.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marcos E, Fadel E, Sanchez O, et al:
Serotonin-induced smooth muscle hyperplasia in various forms of
human pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res. 94:1263–1270. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eddahibi S, Guignabert C, Barlier-Mur AM,
et al: Cross talk between endothelial and smooth muscle cells in
pulmonary hypertension: critical role for serotonin-induced smooth
muscle hyperplasia. Circulation. 113:1857–1864. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morrell NW, Adnot S, Archer SL, et al:
Cellular and molecular basis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 54(Suppl 1): S20–S31. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rothman RB, Cadet JL, Dersch CM, et al:
Altered gene expression in pulmonary tissue of tryptophan
hydroxylase-1 knockout mice: implications for pulmonary arterial
hypertension. PLoS One. 6:e177352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Izikki M, Hanoun N, Marcos E, et al:
Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 knockout and tryptophan hydroxylase 2
polymorphism: effects on hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in mice. Am
J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L1045–L1052. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Margolis KG and Pothoulakis C: Serotonin
has a critical role in the pathogenesis of experimental colitis.
Gastroenterology. 137:1562–1566. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tucker A, Bryant SE, Frost HH and Miqally
N: Chemical sympathectomy and serotonin inhibition reduce
monocrotaline-induced right ventricular hypertrophy in rats. Can J
Physiol Pharmacol. 61:356–362. 1983. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu M, Wang Y, Wang HM, Bai Y, Zhang XH,
Sun YX and Wang HL: Fluoxetine attenuates chronic
methamphetamine-induced pulmonary arterial remodeling: possible
involvement of serotonin transporter and serotonin 1B receptor.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 112:77–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Agard C, Rolli-Derkinderen M,
Dumas-de-La-Roque E, et al: Protective role of the antidiabetic
drug metformin against chronic experimental pulmonary hypertension.
Br J of Pharmacol. 158:1285–1294. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang XH, Chen L, Wang HL and Gao J:
Methodological study of determination of rat pulmonary artery
pressure. J Chin Med Univ. 33:388–389. 2004.(in Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Wang HM, Wang Y, Liu M, Bai Y, Zhang XH
and Wang HL: Fluoxetine inhibits monocrotaline-induced pulmonary
arterial remodeling involved in inhibition of RhoA-Rho kinase and
Akt signalling pathways in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
90:1506–1515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Herve P, Launay JM, Scrobohaci ML, et al:
Increased plasma serotonin in primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J
Med. 99:249–254. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hironaka E, Hongo M, Sakai A, et al:
Serotonin receptor antagonist inhibits monocrotaline-induced
pulmonary hypertension and prolongs survival in rats. Cardiovasc
Res. 60:692–699. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morecroft I, White K, Caruso P, et al:
Gene therapy by targeted adenovirus-mediated knockdown of pulmonary
endothelial Tph1 attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension.
Mol Ther. 20:1516–1528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fligny C, Fromes Y, Bonnin P, et al:
Maternal serotonin influences cardiac function in adult offspring.
FASEB J. 22:2340–2349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
MacLean MR and Dempsie Y: Serotonin and
pulmonary hypertension-from bench to bedside? Curr Opin Pharmacol.
9:281–286. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Walther DJ, Peter JU, Bashammakh S,
Hortnaql H, Voits M, Fink H and Bader M: Synthesis of serotonin by
a second tryptophan hydroxylase isoform. Science. 299:762003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Valzelli L, Bernasconi S and Dalessandro
M: Time-courses of p-CPA-induced depletion of brain serotonin and
muricidal aggression in the rat. Pharmacol Res Commun. 15:387–395.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ghia JE, Li N, Wang H, et al: Serotonin
has a key role in pathogenesis of experimental colitis.
Gastroenterology. 137:1649–1660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moreau AW, Amar M, Callebert J and Fossier
P: Serotonergic modulation of LTP at excitatory and inhibitory
synapses in the developing rat visual cortex. Neuroscience.
238:148–158. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nakadate K, Imamura K and Watanabe Y:
C-fos activity mapping reveals differential effects of
noradrenaline and serotonin depletion on the regulation of ocular
dominance plasticity in rats. Neuroscience. 235:1–9. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Song D, Wang HL, Wang S and Zhang XH:
5-Hydroxytryptamine-induced proliferation of pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cells are extracellular signal-regulated kinase
pathway dependent. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 26:563–567. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhai FG, Zhang XH and Wang HL: Fluoxetine
protects against monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial
hypertension: potential roles of induction of apoptosis and
upregulation of kv1.5 channels in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
36:850–856. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Rattray M, Baldessari S, Gobbi M, Mennini
T, Samanin R and Bendotti C: p-Chlorophenylalanine changes
serotonin transporter mRNA levels and expression of the gene
product. J Neurochem. 67:463–472. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chelladurai P, Seeger W and Pullamsetti
SS: Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in pulmonary
hypertension. Eur Respir J. 40:766–782. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Okada M, Kikuzuki R, Harada T, Hori Y,
Yamawaki H and Hara Y: Captopril attenuates matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and −9 in monocrotaline-induced right
ventricular hypertrophy in rats. J Pharmacol Sci. 108:487–494.
2008.
|
|
41
|
Karthikeyan VJ, Lane DA, Beevers DG, Lip
GY and Blann AD: Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue
inhibitors in hypertension-related pregnancy complications. J Hum
Hypertens. 27:72–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang HL: The serotonin receptor and
transporter are potential therapeutic targets for pulmonary
hypertension. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 5:963–966. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shum JK, Melendez JA and Jeffrey JJ:
Serotonin-induced MMP-13 production is mediated via phospholipase
C, protein kinase C, and ERK1/2 in rat uterine smooth muscle cells.
J Biol Chem. 277:42830–42840. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Witzenrath M, Ahrens B, Kube SM, et al:
Allergic lung inflammation induces pulmonary vascular
hyperresponsiveness. Eur Respir J. 28:370–377. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hassoun PM, Mouthon L, Barbera JA, et al:
Inflammation, growth factors, and pulmonary vascular remodeling. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 54(Suppl 1): S10–S19. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mikulski Z, Zaslona Z, Cakarova L, et al:
Serotonin activates murine alveolar macrophages through 5-HT2C
receptors. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 299:L272–L280. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lima C, Souza VM, Soares AL, Macedo MS,
Tavares-de-Lima W and Vargaftig BB: Interference of methysergide, a
specific 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor antagonist, with airway
chronic allergic inflammation and remodeling in a murine model of
asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 37:723–734. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kushnir-Sukhov NM, Gilfillan AM, Coleman
JW, Brown JM, Bruening S, Toth M and Metcalfe DD:
5-hydroxytryptamine induces mast cell adhesion and migration. J
Immunol. 177:6422–6432. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lawrie A, Waterman E, Southwood M, et al:
Evidence of a role for osteoprotegerin in the pathogenesis of
pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Pathol. 172:256–264. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wilkins MR: Pulmonary hypertension: the
science behind the disease spectrum. Eur Respir Rev. 21:19–26.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|