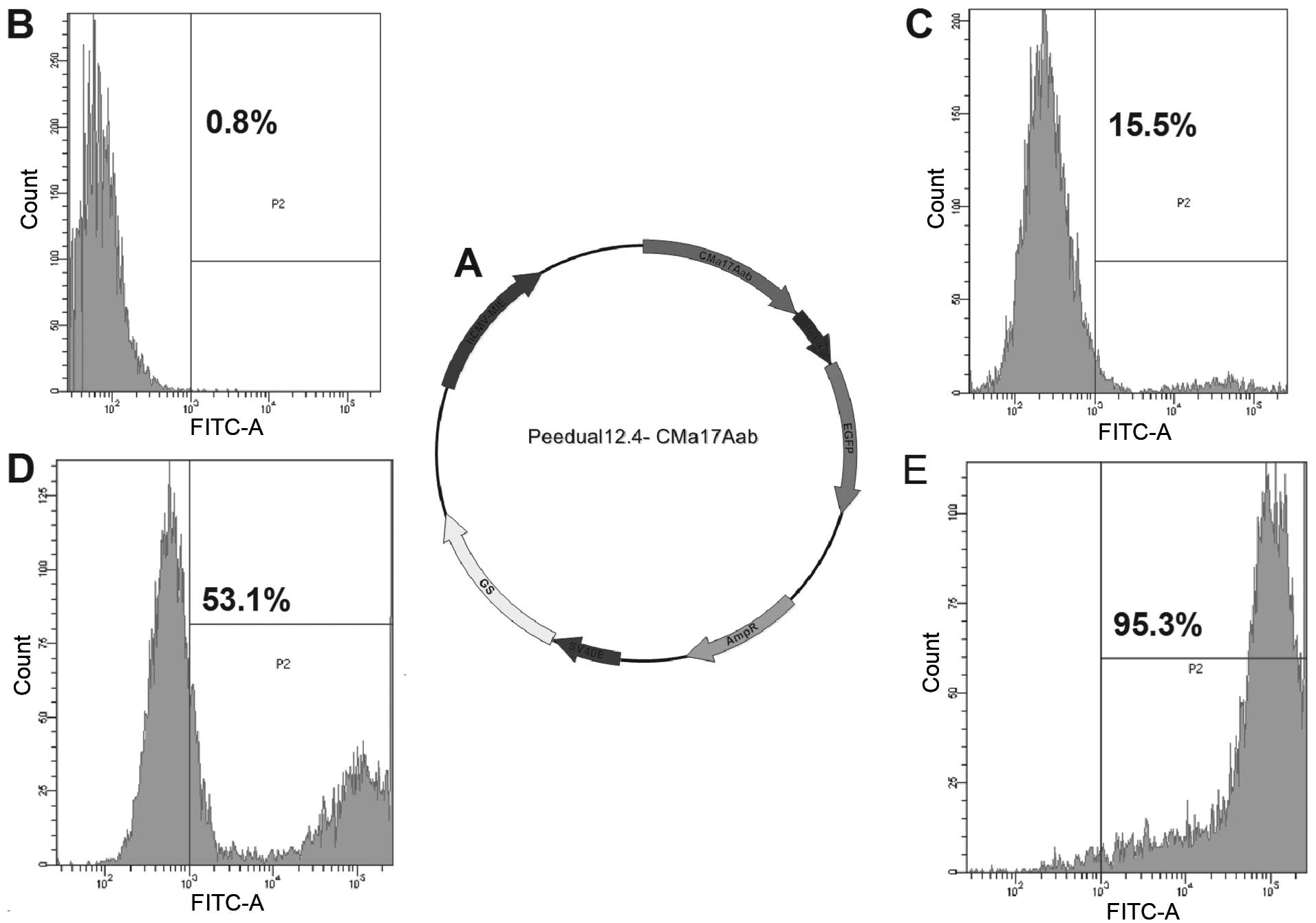
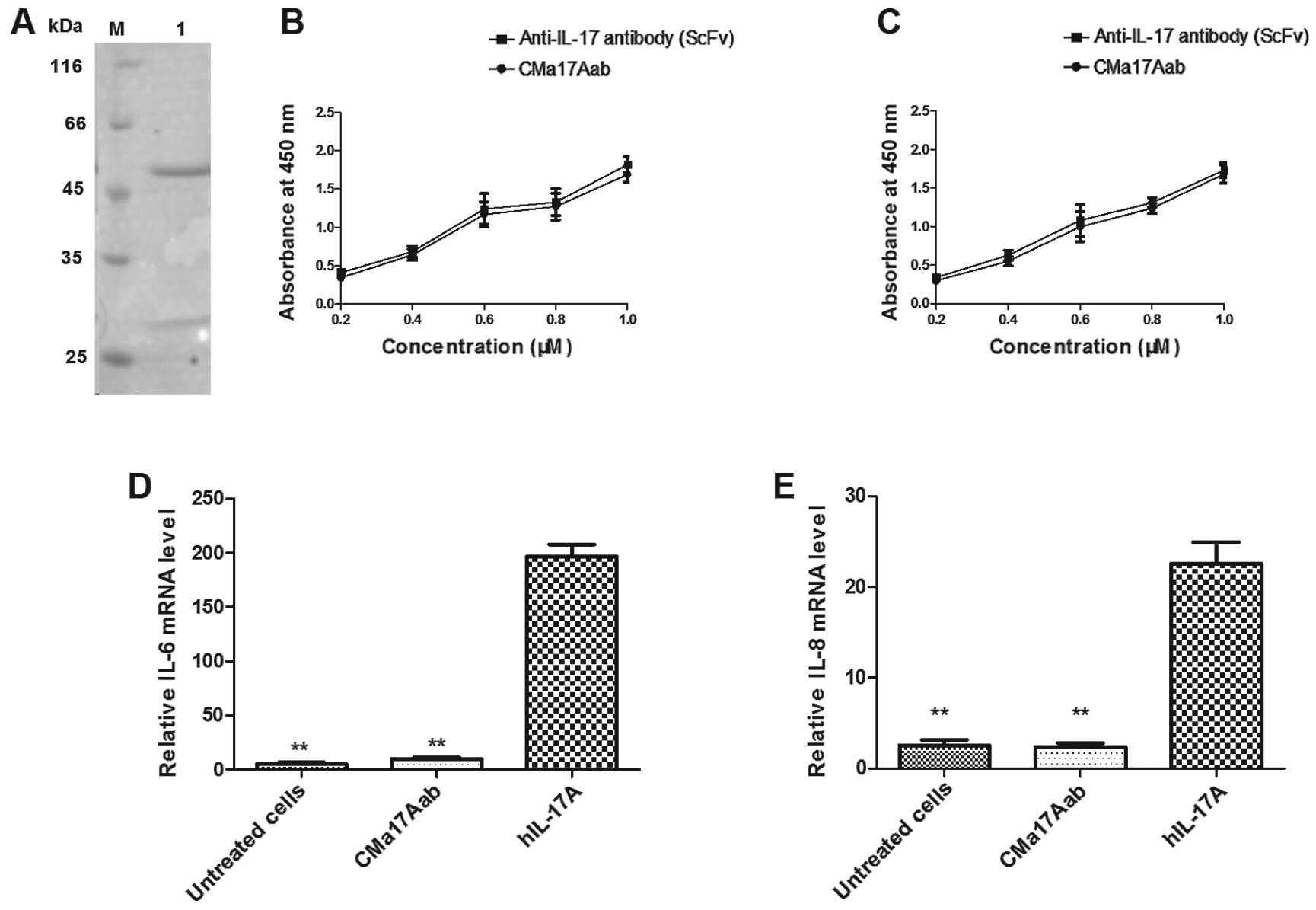
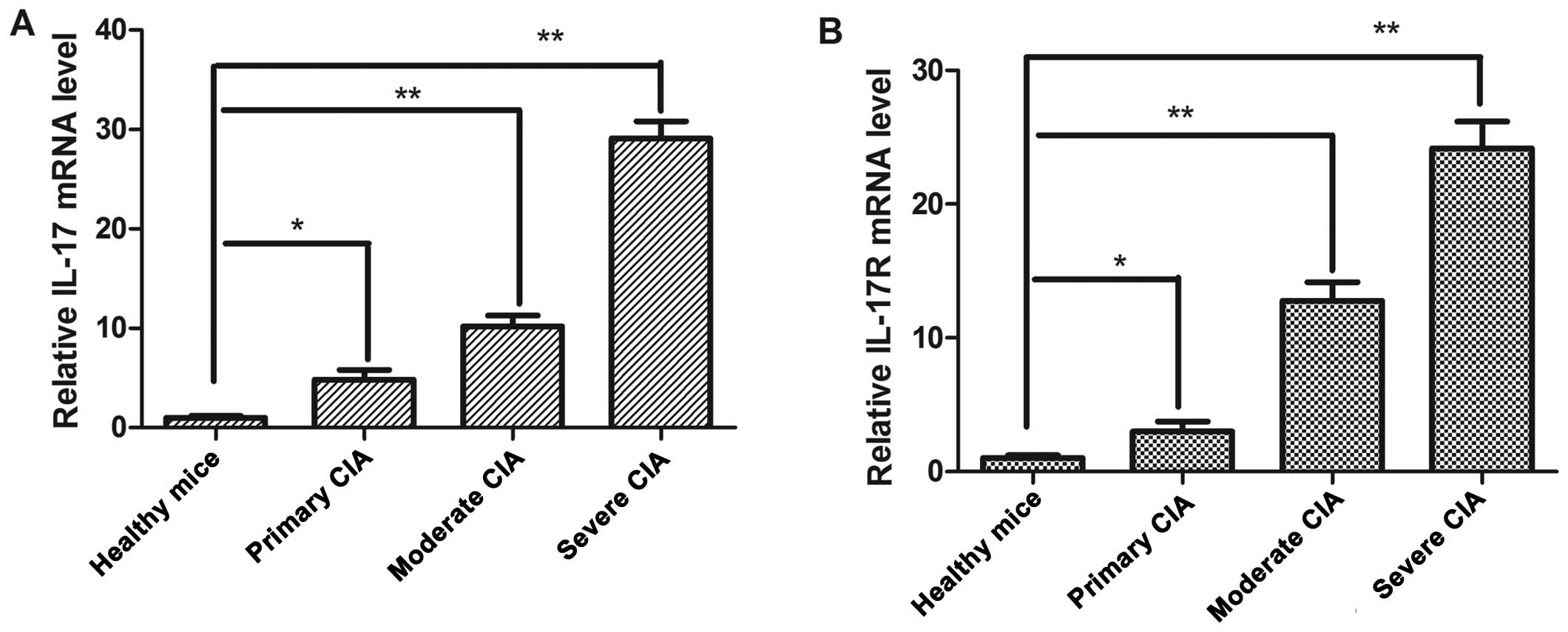
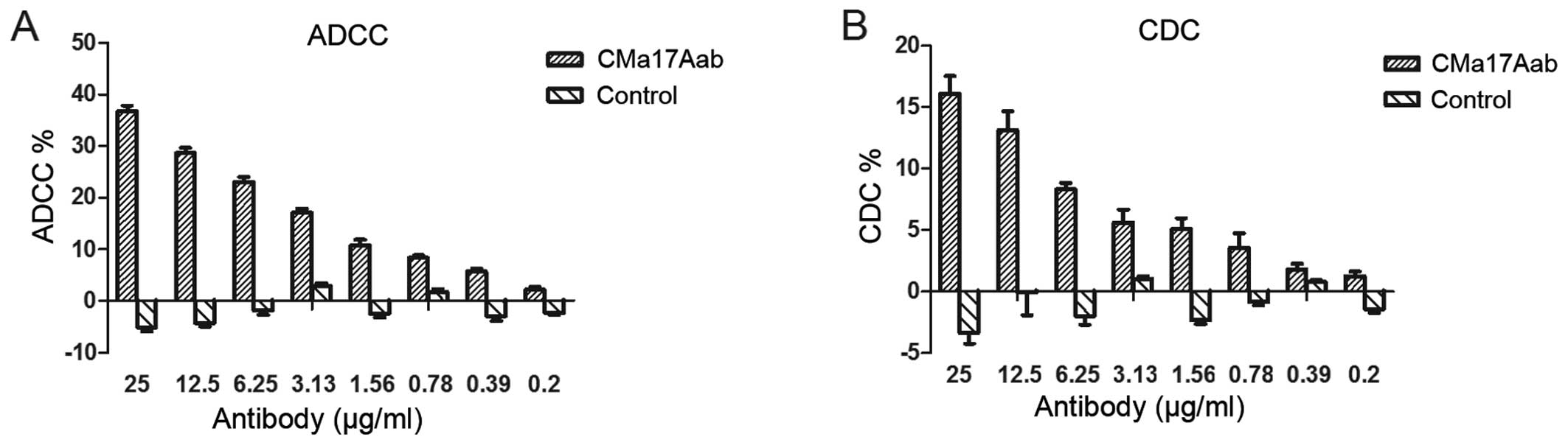
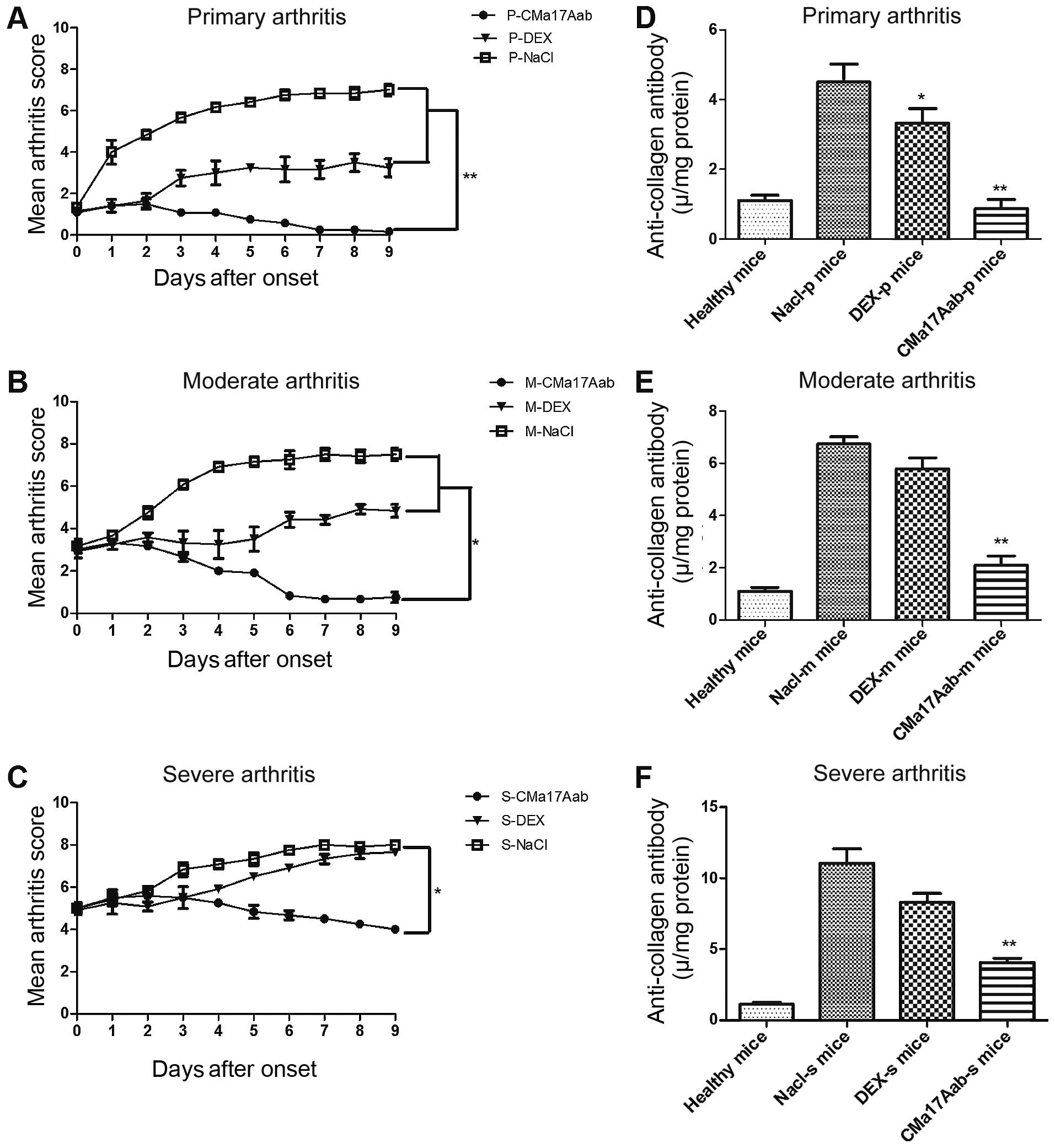
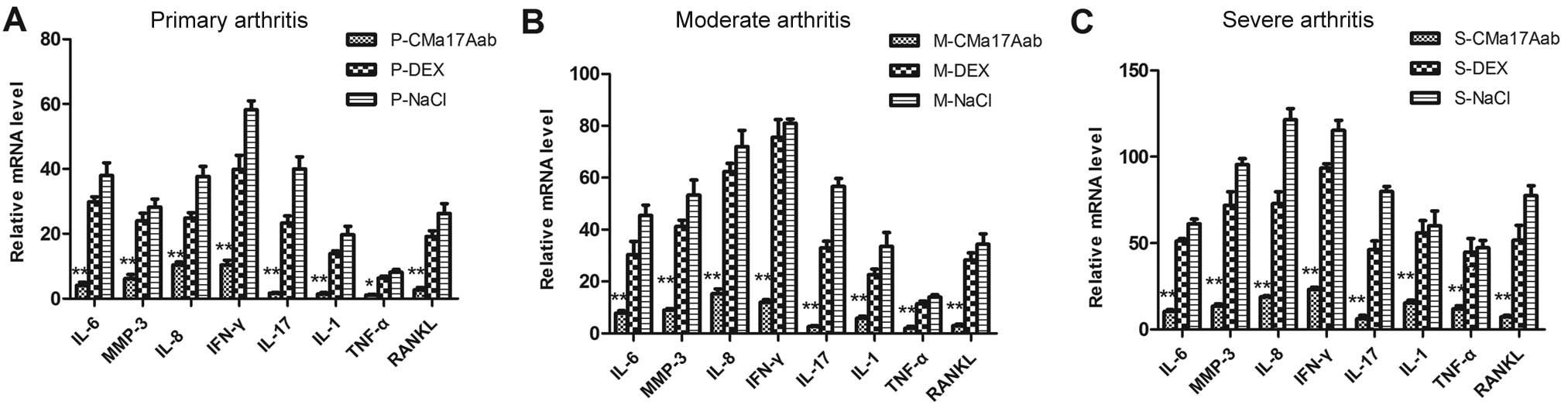
|
1
|
van den Berg WB and Miossec P: IL-17 as a
future therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 5:549–553. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Onishi RM and Gaffen SL: Interleukin-17
and its target genes: mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in
disease. Immunology. 129:311–321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leipe J, Grunke M, Dechant C, et al: Role
of Th17 cells in human autoimmune arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
62:2876–2885. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maione F, Paschalidis N, Mascolo N, Dufton
N, Perretti M and D’Acquisto F: Interleukin 17 sustains rather than
induces inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:878–887. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen H, Wang W, Xie H, et al: A pathogenic
role of IL- 17 at the early stage of corneal allograft rejection.
Transpl Immunol. 21:155–161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hot A, Zrioual S, Lenief V and Miossec P:
IL-17 and tumour necrosis factor α combination induces a
HIF-1α-dependent invasive phenotype in synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis.
71:1393–1401. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M and Kuchroo
VK: IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:485–517. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chabaud M, Durand JM, Buchs N, et al:
Human interleukin-17: A T cell-derived proinflammatory cytokine
produced by the rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 42:963–970.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, et al:
IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is
a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest.
103:1345–1352. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chabaud M, Fossiez F, Taupin JL and
Miossec P: Enhancing effect of IL-17 on IL-1-induced IL-6 and
leukemia inhibitory factor production by rheumatoid arthritis
synoviocytes and its regulation by Th2 cytokines. J Immunol.
161:409–414. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jovanovic DV, Di Battista JA,
Martel-Pelletier J, et al: IL-17 stimulates the production and
expression of proinflammatory cytokines, IL-beta and TNF-alpha, by
human macrophages. J Immunol. 160:3513–3521. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Katz Y, Nadiv O and Beer Y: Interleukin-17
enhances tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced synthesis of
interleukins 1,6, and 8 in skin and synovial fibroblasts: a
possible role as a ‘fine-tuning cytokine’ in inflammation
processes. Arthritis Rheum. 44:2176–2184. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kehlen A, Thiele K, Riemann D and Langner
J: Expression, modulation and signalling of IL-17 receptor in
fibroblast-like synoviocytes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Clin Exp Immunol. 127:539–546. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Numasaki M, Lotze MT and Sasaki H:
Interleukin-17 augments tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced
elaboration of proangiogenic factors from fibroblasts. Immunol
Lett. 93:39–43. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takahashi H, Numasaki M, Lotze MT and
Sasaki H: Interleukin-17 enhances bFGF-, HGF- and VEGF-induced
growth of vascular endothelial cells. Immunol Lett. 98:189–193.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miossec P: Interleukin-17 in rheumatoid
arthritis: if T cells were to contribute to inflammation and
destruction through synergy. Arthritis Rheum. 48:594–601. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Granet C, Maslinski W and Miossec P:
Increased AP-1 and NF-kappaB activation and recruitment with the
combination of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1beta, tumor
necrosis factor alpha and IL-17 in rheumatoid synoviocytes.
Arthritis Res Ther. 6:R190–R198. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chabaud M and Miossec P: The combination
of tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade with interleukin-1 and
interleukin-17 blockade is more effective for controlling synovial
inflammation and bone resorption in an ex vivo model. Arthritis
Rheum. 44:1293–1303. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chabaud M, Page G and Miossec P: Enhancing
effect of IL-1, IL-17, and TNF-alpha on macrophage inflammatory
protein-3alpha production in rheumatoid arthritis: regulation by
soluble receptors and Th2 cytokines. J Immunol. 167:6015–6020.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Granet C and Miossec P: Combination of the
pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1, TNF-alpha and IL-17 leads to
enhanced expression and additional recruitment of AP-1 family
members, Egr-1 and NF-kappaB in osteoblast-like cells. Cytokine.
26:169–177. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chevrel G, Page G, Granet C,
Streichenberger N, Varennes A and Miossec P: Interleukin-17
increases the effects of IL-1 beta on muscle cells: arguments for
the role of T cells in the pathogenesis of myositis. J
Neuroimmunol. 137:125–133. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kirkham BW, Lassere MN, Edmonds JP, et al:
Synovial membrane cytokine expression is predictive of joint damage
progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a two-year prospective study
(the DAMAGE study cohort). Arthritis Rheum. 54:1122–1131.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yao Z, Spriggs MK, Derry JM, et al:
Molecular characterization of the human interleukin (IL)-17
receptor. Cytokine. 9:794–800. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tachihara A, Jin E, Matsuoka T, et al:
Critical roles of capillary endothelial cells for alveolar
remodeling in nonspecific and usual interstitial pneumonias. J
Nippon Med Sch. 73:203–213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian E, Sawyer JR, Largaespada DA, Jenkins
NA, Copeland NG and Shaughnessy JD Jr: Evi27 encodes a novel
membrane protein with homology to the IL17 receptor. Oncogene.
19:2098–2109. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shi Y, Ullrich SJ, Zhang J, et al: A novel
cytokine receptor-ligand pair. Identification, molecular
characterization, and in vivo immunomodulatory activity. J Biol
Chem. 275:19167–19176. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee J, Ho WH, Maruoka M, et al: IL-17E, a
novel proinflammatory ligand for the IL-17 receptor homolog
IL-17Rh1. J Biol Chem. 276:1660–1664. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zrioual S, Toh ML, Tournadre A, et al:
IL-17RA and IL-17RC receptors are essential for IL-17A-induced
ELR+ CXC chemokine expression in synoviocytes and are
overexpressed in rheumatoid blood. J Immunol. 180:655–663. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miljkovic D, Cvetkovic I, Vuckovic O,
Stosic-Grujicic S, Mostarica Stojkovic M and Trajkovic V: The role
of interleukin-17 in inducible nitric oxide synthase-mediated
nitric oxide production in endothelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci.
60:518–525. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lubberts E, Koenders MI, Oppers-Walgreen
B, et al: Treatment with a neutralizing anti-murine interleukin-17
antibody after the onset of collagen-induced arthritis reduces
joint inflammation, cartilage destruction, and bone erosion.
Arthritis Rheum. 50:650–659. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Genovese MC, Van den Bosch F, Roberson SA,
et al: LY2439821, a humanized anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal
antibody, in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A
phase I randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
proof-of-concept study. Arthritis Rheum. 62:929–939. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nardelli DT, Burchill MA, England DM,
Torrealba J, Callister SM and Schell RF: Association of
CD4+ CD25+ T cells with prevention of severe
destructive arthritis in Borrelia burgdorferi-vaccinated and
challenged gamma interferon-deficient mice treated with
anti-interleukin-17 antibody. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 11:1075–1084.
2004.
|
|
33
|
Nakajima H, Takamori H, Hiyama Y and
Tsukada W: The effect of treatment with interferon-gamma on type II
collagen-induced arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 81:441–445. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stuart JM, Townes AS and Kang AH: Type II
collagen-induced arthritis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 460:355–362. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Toy D, Kugler D, Wolfson M, et al: Cutting
edge: interleukin 17 signals through a heteromeric receptor
complex. J Immunol. 177:36–39. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fan Y, Weifeng W, Yuluan Y, Qing K, Yu P
and Yanlan H: Treatment with a neutralizing anti-murine
interleukin-17 antibody after the onset of coxsackievirus
b3-induced viral myocarditis reduces myocardium inflammation. Virol
J. 8:172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ziolkowska M, Koc A, Luszczykiewicz G,
Ksiezopolska-Pietrzak K, Klimczak E, Chwalinska-Sadowska H and
Maslinski W: High levels of IL-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients:
IL-15 triggers in vitro IL-17 production via cyclosporin
A-sensitive mechanism. J Immunol. 164:2832–2838. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bas DB, Su J, Sandor K, et al: Collagen
antibody-induced arthritis evokes persistent pain with spinal glial
involvement and transient prostaglandin dependency. Arthritis
Rheum. 64:3886–3896. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nandakumar KS and Holmdahl R: Collagen
antibody induced arthritis. Methods Mol Med. 136:215–223. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yao Z, Painter SL, Fanslow WC, et al:
Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J Immunol.
155:5483–5486. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Miyamoto M, Prause O, Sjostrand M, Laan M,
Lötvall J and Lindén A: Endogenous IL-17 as a mediator of
neutrophil recruitment caused by endotoxin exposure in mouse
airways. J Immunol. 170:4665–4672. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kennedy J, Rossi DL, Zurawski SM, et al:
Mouse IL-17: a cytokine preferentially expressed by alpha beta TCR
+ CD4-CD8-T cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 16:611–617. 1996.
|
|
43
|
Zhang R, Qian J, Guo J, Yuan YF and Xue K:
Suppression of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis by Anti-IL-17
antibody. Curr Eye Res. 34:297–303. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang Y, Ren G, Guo M, et al: Synergistic
effects of interleukin-1beta and interleukin-17A antibodies on
collagen-induced arthritis mouse model. Int Immunopharmacol.
15:199–205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Miossec P: IL-17 and Th17 cells in human
inflammatory diseases. Microbes Infect. 11:625–630. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bazzani C, Filippini M, Caporali R, et al:
Anti-TNFalpha therapy in a cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients:
clinical outcomes. Autoimmun Rev. 8:260–265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gandjbakhch F, Conaghan PG, Ejbjerg B, et
al: Synovitis and osteitis are very frequent in rheumatoid
arthritis clinical remission: results from an MRI study of 294
patients in clinical remission or low disease activity state. J
Rheumatol. 38:2039–2044. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Emery P, McInnes IB, van Vollenhoven R and
Kraan MC: Clinical identification and treatment of a rapidly
progressing disease state in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:392–398. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hornung N, Ellingsen T, Attermann J,
Stengaard-Pedersen K and Poulsen JH: Patients with rheumatoid
arthritis treated with methotrexate (MTX): concentrations of
steady-state erythrocyte MTX correlate to plasma concentrations and
clinical efficacy. J Rheumatol. 35:1709–1715. 2008.
|
|
50
|
Liu Y, Mei J, Gonzales L, et al: IL-17A
and TNF-alpha exert synergistic effects on expression of CXCL5 by
alveolar type II cells in vivo and in vitro. J Immunol.
186:3197–3205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Leung S, Liu X, Fang L, Chen X, Guo T and
Zhang J: The cytokine milieu in the interplay of pathogenic
Th1/Th17 cells and regulatory T cells in autoimmune disease. Cell
Mol Immunol. 7:182–189. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Myers LK, Rosloniec EF, Cremer MA and Kang
AH: Collagen-induced arthritis, an animal model of autoimmunity.
Life Sci. 61:1861–1878. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Griffiths MM, Nabozny GH, Hanson J, et al:
Collagen-induced arthritis and TCRs in SWR and B10. Q mice
expressing an Ek alpha transgene. J Immunol. 153:2758–2768.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Durie FH, Fava RA and Noelle RJ:
Collagen-induced arthritis as a model of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin
Immunol Immunopathol. 73:11–18. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nabozny GH, Bull MJ, Hanson J, Griffiths
MM, Luthra HS and David CS: Collagen-induced arthritis in T cell
receptor V beta congenic B10. Q mice J Exp Med. 180:517–524. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kadowaki KM, Matsuno H, Tsuji H and Tunru
I: CD4+ T cells from collagen-induced arthritic mice are
essential to transfer arthritis into severe combined
immunodeficient mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 97:212–218. 1994.
|