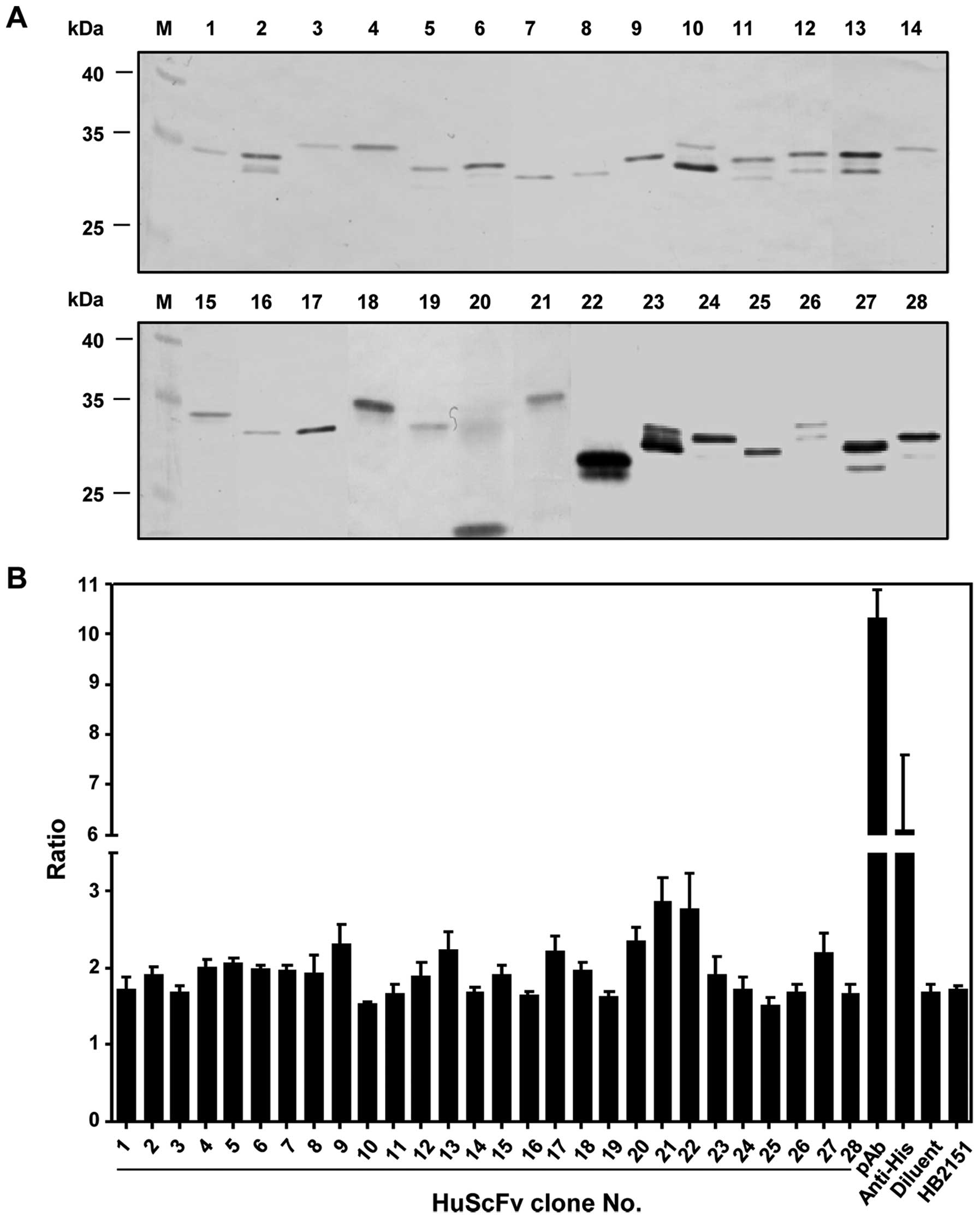
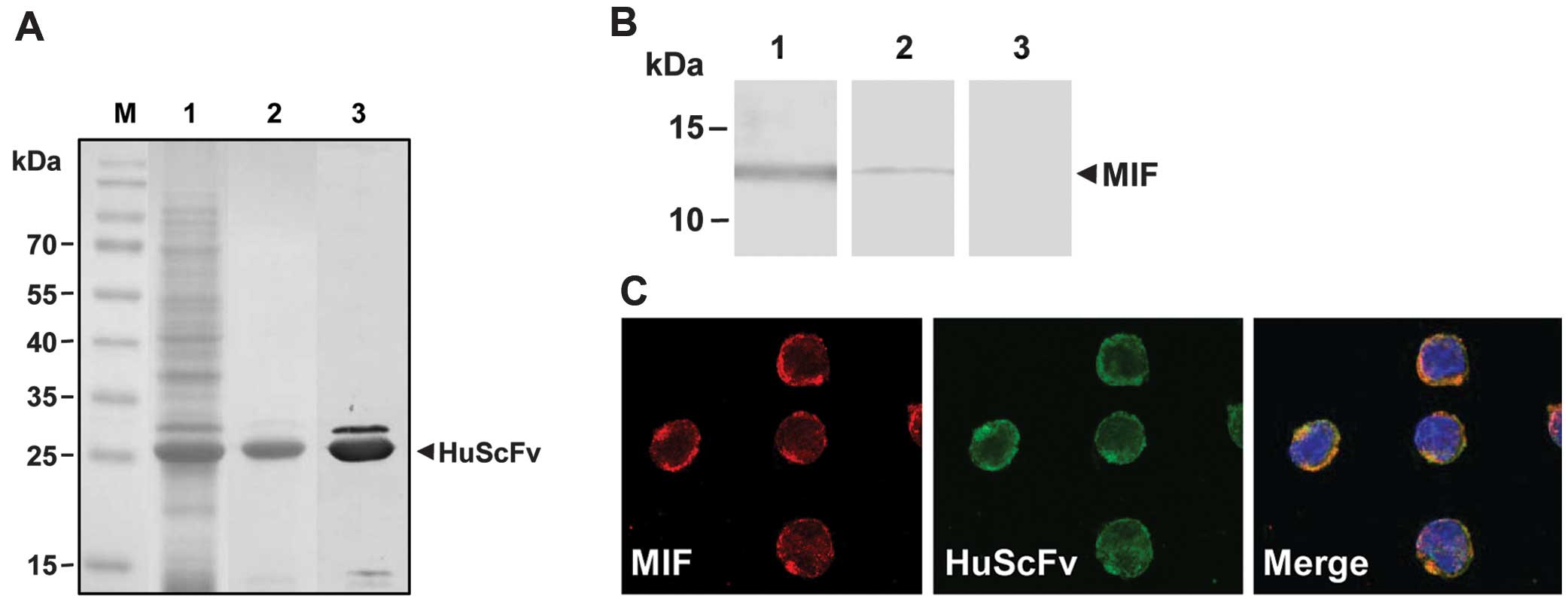
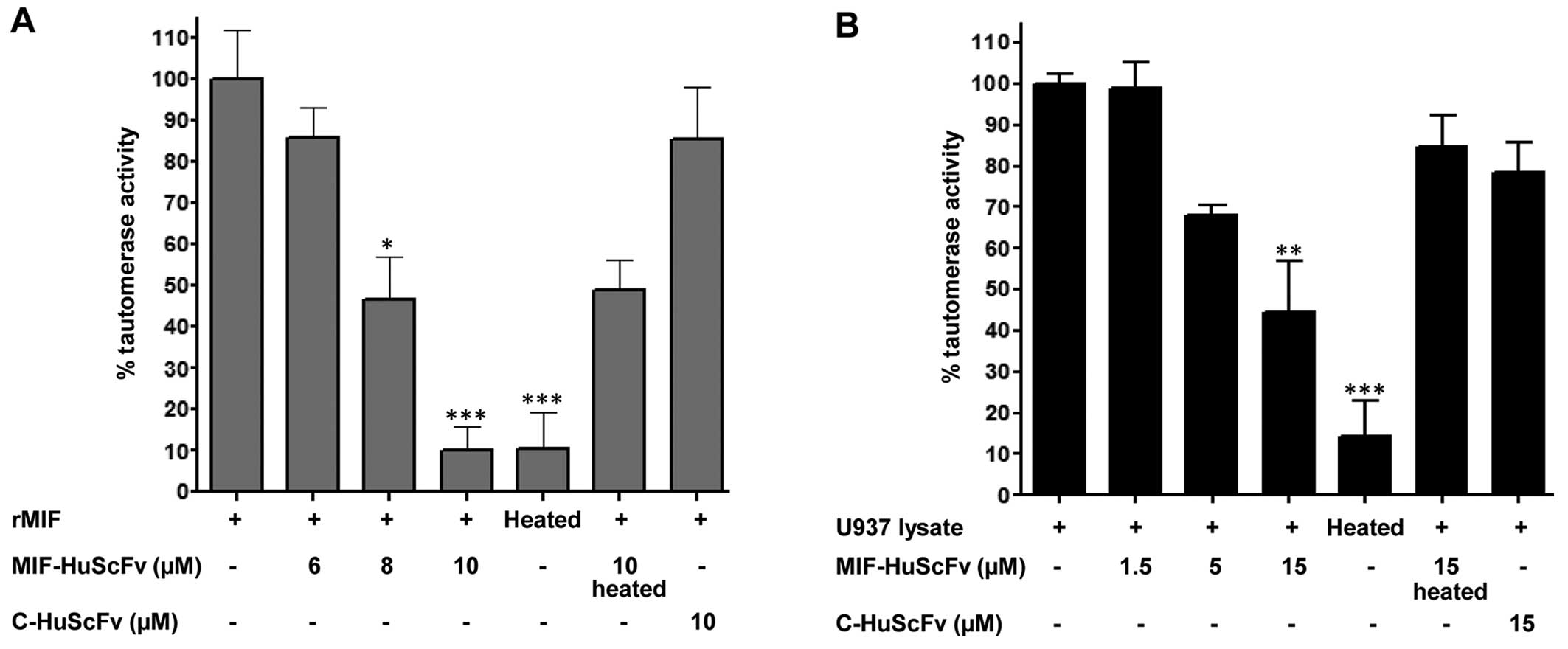
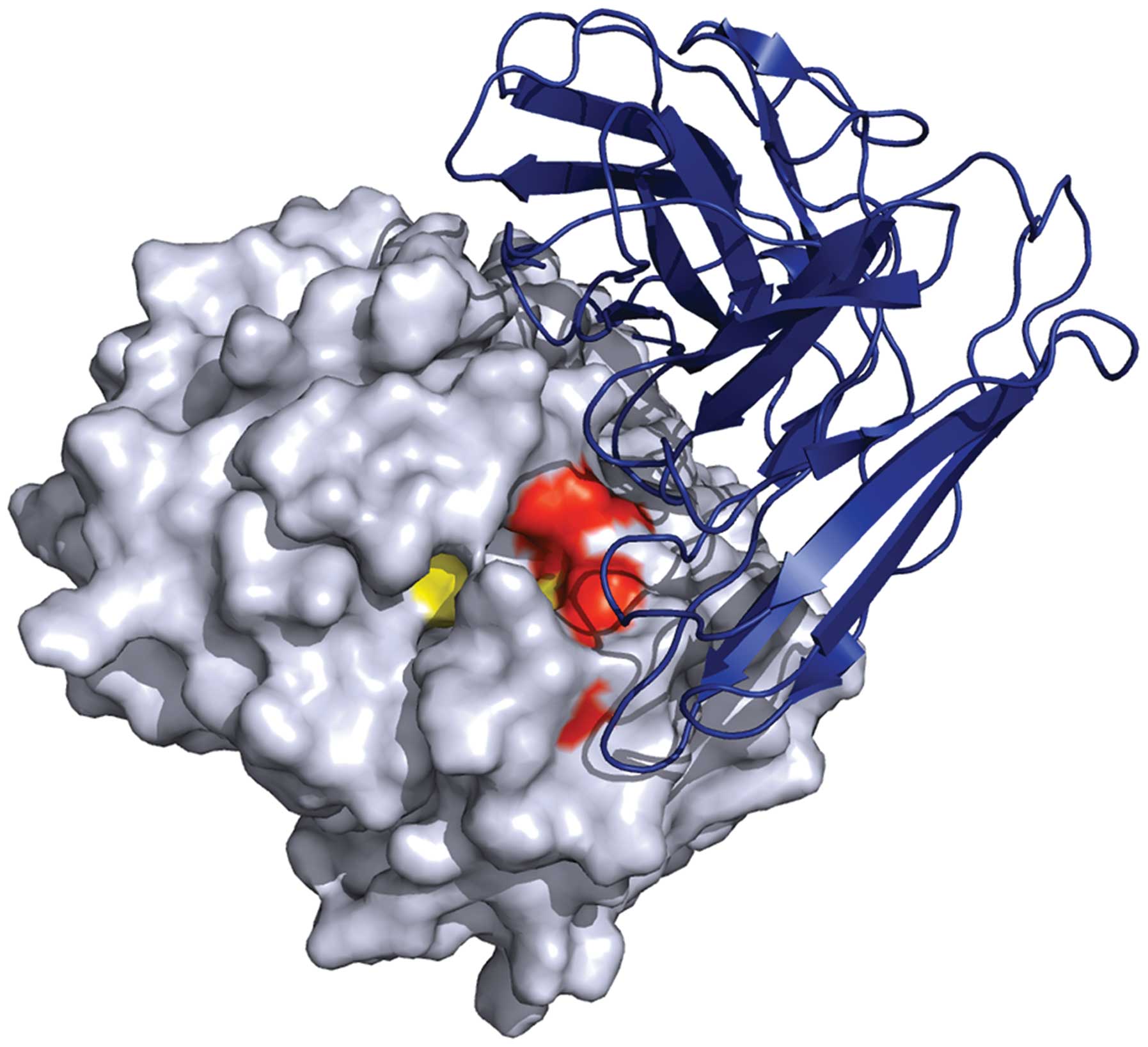
|
1
|
David JR: Delayed hypersensitivity in
vitro: its mediation by cell-free substances formed by lymphoid
cell-antigen interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 56:72–77. 1966.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Merk M, Zierow S, Leng L, et al: The
D-dopachrome tautomerase (DDT) gene product is a cytokine
and functional homolog of macrophage migration inhibitory factor
(MIF). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:E577–E585. 2011.
|
|
3
|
Calandra T and Roger T: Macrophage
migration inhibitory factor: a regulator of innate immunity. Nat
Rev Immunol. 3:791–800. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bernhagen J, Mitchell RA, Calandra T,
Voelter W, Cerami A and Bucala R: Purification, bioactivity, and
secondary structure analysis of mouse and human macrophage
migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Biochemistry. 33:14144–14155.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mitchell RA, Metz CN, Peng T and Bucala R:
Sustained mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and cytoplasmic
phospholipase A2 activation by macrophage migration inhibitory
factor (MIF). Regulatory role in cell proliferation and
glucocorticoid action. J Biol Chem. 274:18100–18106. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mitchell RA, Liao H, Chesney J,
Fingerle-Rowson G, Baugh J, David J and Bucala R: Macrophage
migration inhibitory factor (MIF) sustains macrophage
proinflammatory function by inhibiting p53: regulatory role in the
innate immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:345–350. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sugimoto H, Taniguchi M, Nakagawa A,
Tanaka I, Suzuki M and Nishihira J: Crystal structure of human
D-dopachrome tautomerase, a homologue of macrophage
migration inhibitory factor, at 1.54 A resolution. Biochemistry.
38:3268–3279. 1999.
|
|
8
|
Rosengren E, Aman P, Thelin S, et al: The
macrophage migration inhibitory factor MIF is a phenylpyruvate
tautomerase. FEBS Lett. 417:85–88. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kleemann R, Kapurniotu A, Frank RW, et al:
Disulfide analysis reveals a role for macrophage migration
inhibitory factor (MIF) as thiol-protein oxidoreductase. J Mol
Biol. 280:85–102. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bozza FA, Gomes RN, Japiassu AM, Soares M,
Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Bozza PT and Bozza MT: Macrophage migration
inhibitory factor levels correlate with fatal outcome in sepsis.
Shock. 22:309–313. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen LC, Lei HY, Liu CC, et al:
Correlation of serum levels of macrophage migration inhibitory
factor with disease severity and clinical outcome in dengue
patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 74:142–147. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Assunção-Miranda I, Amaral FA, Bozza FA,
et al: Contribution of macrophage migration inhibitory factor to
the pathogenesis of dengue virus infection. FASEB J. 24:218–228.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hou XQ, Gao YW, Yang ST, Wang CY, Ma ZY
and Xia XZ: Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in
influenza H5N1 virus pneumonia. Acta Virol. 53:225–231. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim HR, Park MK, Cho ML, et al: Macrophage
migration inhibitory factor upregulates angiogenic factors and
correlates with clinical measures in rheumatoid arthritis. J
Rheumatol. 34:927–936. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Foote A, Briganti EM, Kipen Y, Santos L,
Leech M and Morand EF: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in
systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 31:268–273.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lan HY, Yang N, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, et
al: Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in human
glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 57:499–509. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Niino M, Ogata A, Kikuchi S, Tashiro K and
Nishihira J: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the
cerebrospinal fluid of patients with conventional and optic-spinal
forms of multiple sclerosis and neuro-Behçet’s disease. J Neurol
Sci. 179:127–131. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burger-Kentischer A, Goebel H, Seiler R,
et al: Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in
different stages of human atherosclerosis. Circulation.
105:1561–1566. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Herder C, Kolb H, Koenig W, et al:
Association of systemic concentrations of macrophage migration
inhibitory factor with impaired glucose tolerance and type 2
diabetes: results from the Cooperative Health Research in the
Region of Augsburg, Survey 4 (KORA S4). Diabetes Care. 29:368–371.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bucala R and Donnelly SC: Macrophage
migration inhibitory factor: a probable link between inflammation
and cancer. Immunity. 26:281–285. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Al-Abed Y, Dabideen D, Aljabari B, et al:
ISO-1 binding to the tautomerase active site of MIF inhibits its
pro-inflammatory activity and increases survival in severe sepsis.
J Biol Chem. 280:36541–36544. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cvetkovic I, Al-Abed Y, Miljkovic D, et
al: Critical role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor
activity in experimental autoimmune diabetes. Endocrinology.
146:2942–2951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nicoletti F, Créange A, Orlikowski D, et
al: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) seems crucially
involved in Guillain-Barré syndrome and experimental allergic
neuritis. J Neuroimmunol. 168:168–174. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Alam A, Haldar S, Thulasiram HV, et al:
Novel anti-inflammatory activity of epoxyazadiradione against
macrophage migration inhibitory factor: inhibition of tautomerase
and proinflammatory activities of macrophage migration inhibitory
factor. J Biol Chem. 287:24844–24861. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Calandra T, Echtenacher B, Roy DL, et al:
Protection from septic shock by neutralization of macrophage
migration inhibitory factor. Nat Med. 6:164–170. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bernhagen J, Bacher M, Calandra T, Metz
CN, Doty SB, Donnelly T and Bucala R: An essential role for
macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the tuberculin
delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. J Exp Med. 183:277–282.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mikulowska A, Metz CN, Bucala R and
Holmdahl R: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is involved in
the pathogenesis of collagen type II-induced arthritis in mice. J
Immunol. 158:5514–5517. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cvetkovic I and Stosic-Grujicic S:
Neutralization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor-novel
approach for the treatment of immunoinflammatory disorders. Int
Immunopharmacol. 6:1527–1534. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Greven D, Leng L and Bucala R: Autoimmune
diseases: MIF as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
14:253–264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kerschbaumer RJ, Rieger M, Völkel D, et
al: Neutralization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)
by fully human antibodies correlates with their specificity for the
β-sheet structure of MIF. J Biol Chem. 287:7446–7455.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kulkeaw K, Sakolvaree Y, Srimanote P, et
al: Human monoclonal ScFv neutralize lethal Thai cobra, Naja
kaouthia, neurotoxin. J Proteomics. 72:270–282. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Poungpair O, Pootong A, Maneewatch S, et
al: A human single chain transbody specific to matrix protein (M1)
interferes with the replication of influenza A virus. Bioconjug
Chem. 21:1134–1141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dios A, Mitchell RA, Aljabari B, et al:
Inhibition of MIF bioactivity by rational design of pharmacological
inhibitors of MIF tautomerase activity. J Med Chem. 45:2410–2416.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Thanongsaksrikul J, Srimanote P,
Maneewatch S, et al: A VHH that neutralizes the zinc
metalloproteinase activity of botulinum neurotoxin type A. J Biol
Chem. 285:9657–9666. 2010.
|
|
35
|
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS and
Thornton JM: PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical
quality of protein structures. J Appl Cryst. 26:283–291. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Grieb G, Merk M, Bernhagen J and Bucala R:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): a promising
biomarker. Drug News Perspect. 23:257–264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dagia NM, Kamath DV, Bhatt P, et al: A
fluorinated analog of ISO-1 blocks the recognition and biological
function of MIF and is orally efficacious in a murine model of
colitis. Eur J Pharmacol. 607:201–212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Thathaisong U, Maneewatch S, Kulkeaw K, et
al: Human monoclonal single chain antibodies (HuScFv) that bind to
the polymerase proteins of influenza A virus. Asian Pac J Allergy
Immunol. 26:23–35. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maneewatch S, Thanongsaksrikul J, Songserm
T, et al: Human single-chain antibodies that neutralize homologous
and heterologous stains and clades of influenza A virus subtype
H5N1. Antivir Ther. 14:221–230. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lubetsky JB, Dios A, Han J, et al: The
tautomerase active site of macrophage migration inhibitory factor
is a potential target for discovery of novel anti-inflammatory
agents. J Biol Chem. 277:24976–24982. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Al-Abed Y and Van Patten S: MIF as a
disease target: ISO-1 as a proof-of-concept therapeutic. Future Med
Chem. 3:45–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kithcart AP, Cox GM, Sielecki T, et al: A
small-molecule inhibitor of macrophage migration inhibitory factor
for the treatment of inflammatory disease. FASEB J. 24:4459–4466.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Y, Zeng X, Chen S, et al:
Characterization, epitope identification and mechanisms of the
anti-septic capacity of monoclonal antibodies against macrophage
migration inhibitory factor. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:1333–1340.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|