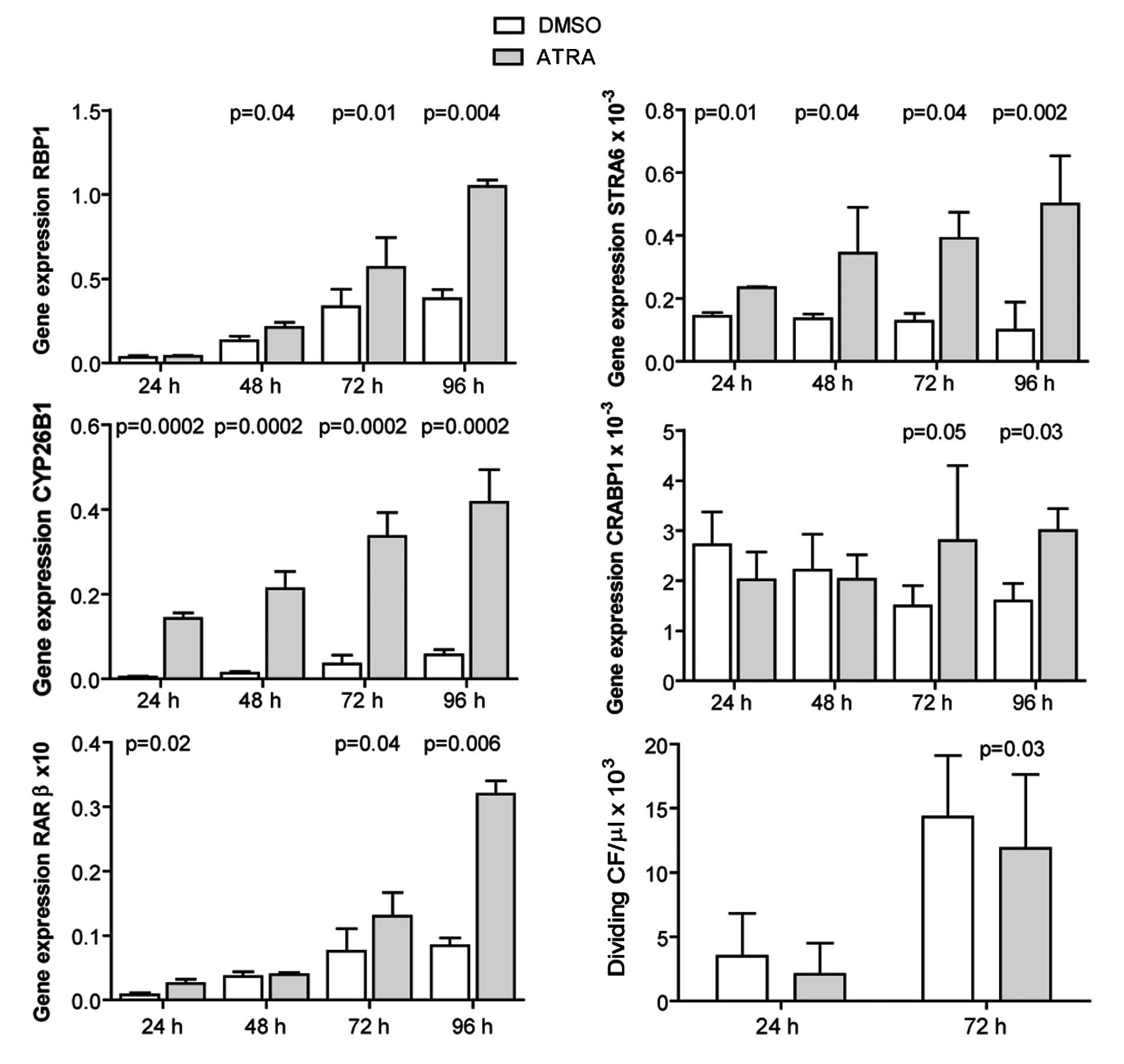
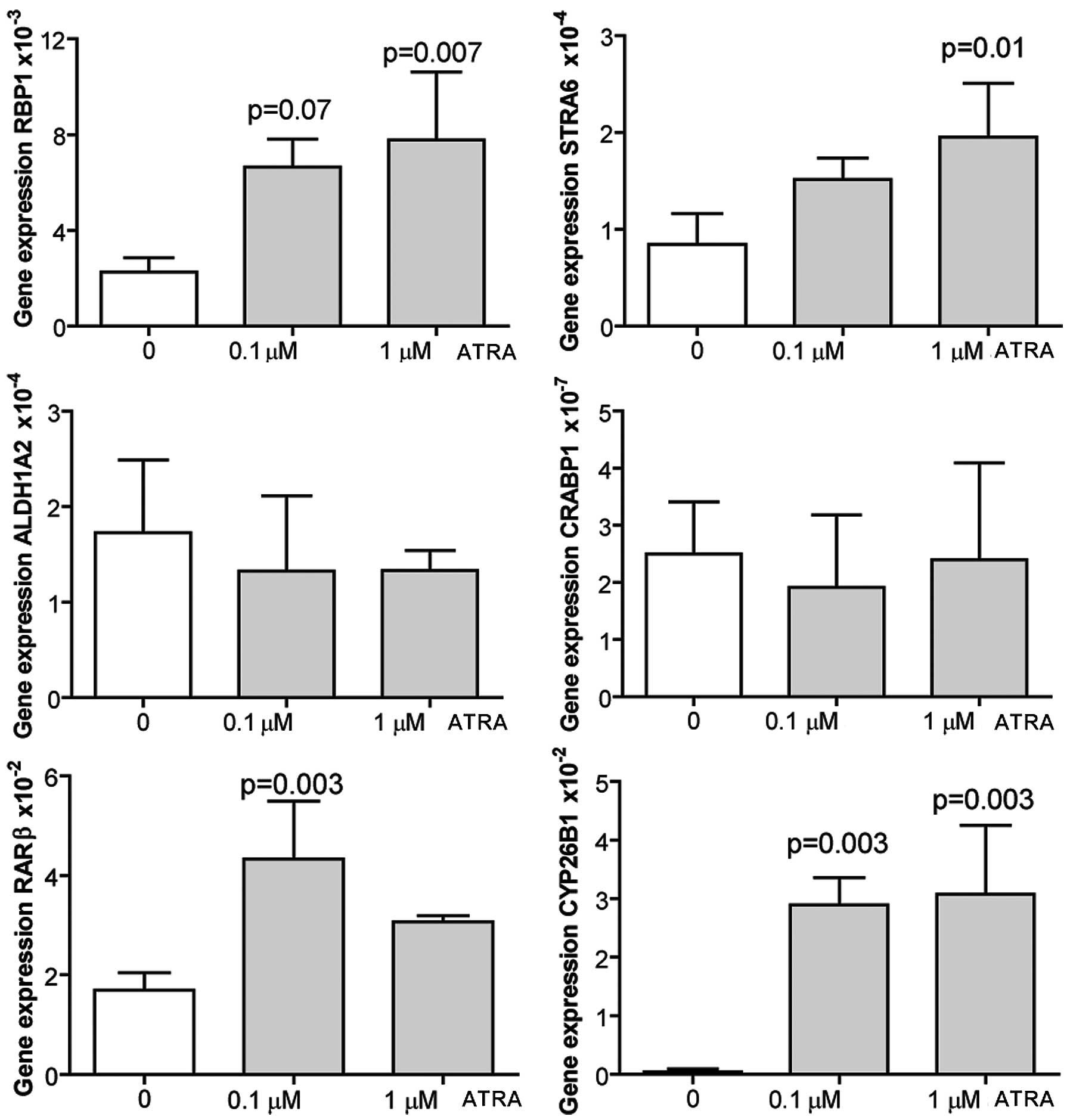
|
1
|
Hansson GK and Hermansson A: The immune
system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. 12:204–212. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tyagi SC, Meyer L, Schmaltz RA, Reddy HK
and Voelker DJ: Proteinases and restenosis in the human coronary
artery: extracellular matrix production exceeds the expression of
proteolytic activity. Atherosclerosis. 116:43–57. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fishbein MC: The vulnerable and unstable
atherosclerotic plaque. Cardiovasc Pathol. 19:6–11. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McKay RG, Pfeffer MA, Pasternak RC, Markis
JE, Come PC, Nakao S, et al: Left ventricular remodeling after
myocardial infarction: a corollary to infarct expansion.
Circulation. 74:693–702. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Valen G: Innate immunity and remodelling.
Heart Fail Rev. 16:71–78. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wakino S, Kintscher U, Kim S, Jackson S,
Yin F, Nagpal S, Chandraratna RA, Hsueh WA and Law RE: Retinoids
inhibit proliferation of human coronary smooth muscle cells by
modulating cell cycle regulators. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
21:746–751. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He Y, Huang Y, Zhou L, Lu LM, Zhu YC and
Yao T: All-trans retinoic acid inhibited angiotensin
II-induced increase in cell growth and collagen secretion of
neonatal cardiac fibroblasts. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:423–429.
2006.
|
|
8
|
Gidlof AC, Ocaya P, Krivospitskaya O and
Sirsjo A: Vitamin A: a drug for prevention of
restenosis/reocclusion after percutaneous coronary intervention?
Clin Sci (Lond). 114:19–25. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miano JM, Kelly LA, Artacho CA, Nuckolls
TA, Piantedosi R and Blaner WS: All-trans-retinoic acid
reduces neointimal formation and promotes favorable geometric
remodeling of the rat carotid artery after balloon withdrawal
injury. Circulation. 98:1219–1227. 1998.
|
|
10
|
Lee CW, Park SJ, Park SW, Kim JJ, Hong MK
and Song JK: All-trans-retinoic acid attenuates neointima
formation with acceleration of reendothelialization in
balloon-injured rat aorta. J Korean Med Sci. 15:31–36. 2000.
|
|
11
|
Fujii H, Sato T, Kaneko S, Gotoh O,
Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Osawa K, Kato S and Hamada H: Metabolic
inactivation of retinoic acid by a novel P450 differentially
expressed in developing mouse embryos. EMBO J. 16:4163–4173. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dong D, Ruuska SE, Levinthal DJ and Noy N:
Distinct roles for cellular retinoic acid-binding proteins I and II
in regulating signaling by retinoic acid. J Biol Chem.
274:23695–23698. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Blomhoff R, Green MH, Berg T and Norum KR:
Transport and storage of vitamin A. Science. 250:399–404. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Czibik G, Wu Z, Berne GP, Tarkka M, Vaage
J, Laurikka J, Järvinen O and Valen G: Human adaptation to ischemia
by preconditioning or unstable angina: involvement of nuclear
factor kappa B, but not hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in the
heart. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 34:976–984. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Olofsson PS, Sheikine Y, Jatta K, Ghaderi
M, Samnegard A, Eriksson P and Sirsjö A: A functional interleukin-1
receptor antagonist polymorphism influences atherosclerosis
development. The interleukin-1beta:interleukin-1 receptor
antagonist balance in atherosclerosis. Circ J. 73:1531–1536. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Olofsson PS, Söderström LA, Jern C, Sirsjö
A, Ria M, Sundler E, de Faire U, Wiklund PG, Ohrvik J, Hedin U,
Paulsson-Berne G, Hamsten A, Eriksson P and Hansson GK: Genetic
variants of TNFSF4 and risk for carotid artery disease and stroke.
J Mol Med (Berl). 87:337–346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gundersen TE, Bastani NE and Blomhoff R:
Quantitative high-throughput determination of endogenous retinoids
in human plasma using triple-stage liquid chromatography/tandem
mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 21:1176–1186. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
O’Connell TD, Rodrigo MC and Simpson PC:
Isolation and culture of adult mouse cardiac myocytes. Methods Mol
Biol. 357:271–296. 2007.
|
|
19
|
Le Tallec LP, Korwin-Zmijowska C and
Adolphe M: Limitations of alginate gels as a culture model for the
study of the effects of UVA radiation on human dermal fibroblasts.
Cell Biol Toxicol. 13:95–102. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vinet L, Rouet-Benzineb P, Marniquet X,
Pellegrin N, Mangin L, Louedec L, Samuel JL and Mercadier JJ:
Chronic doxycycline exposure accelerates left ventricular
hypertrophy and progression to heart failure in mice after thoracic
aorta constriction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H352–H360.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Brattelid T, Winer LH, Levy FO, Liestol K,
Sejersted OM and Andersson KB: Reference gene alternatives to Gapdh
in rodent and human heart failure gene expression studies. BMC Mol
Biol. 11:222010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Seeland U, Selejan S, Engelhardt S, Muller
P, Lohse MJ and Böhm M: Interstitial remodeling in beta1-adrenergic
receptor transgenic mice. Basic Res Cardiol. 102:183–193. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun H and Kawaguchi R: The membrane
receptor for plasma retinol-binding protein, a new type of
cell-surface receptor. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 288:1–41. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wolf G: Identification of a membrane
receptor for retinol-binding protein functioning in the cellular
uptake of retinol. Nutr Rev. 65:385–388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Blomhoff R and Blomhoff HK: Overview of
retinoid metabolism and function. J Neurobiol. 66:606–630. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bilbija D, Haugen F, Sagave J, Baysa A,
Bastani N, Levy FO, Sirsjö A, Blomhoff R and Valen G: Retinoic acid
signalling is activated in the postischemic heart and may influence
remodelling. PloS One. 7:e447402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Palace VP, Hill MF, Khaper N and Singal
PK: Metabolism of vitamin A in the heart increases after a
myocardial infarction. Free Radic Biol Med. 26:1501–1507. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Azevedo PS, Minicucci MF, Chiuso-Minicucci
F, Justulin LA Jr, Matsubara LS, Matsubara BB, Novelli E, Seiva F,
Ebaid G, Campana AO, Zornoff LA and Paiva SA: Ventricular
remodeling induced by tissue vitamin A deficiency in rats. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 26:395–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oliveira LC, Azevedo PS, Minicucci ME,
Rafacho BP, Duarte DR, Matsubara LS, Matsubara BB, Paiva SA and
Zornoff LA: Retinoic acid prevents ventricular remodelling induced
by tobacco smoke exposure in rats. Acta Cardiol. 66:3–7.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Paiva SA, Matsubara LS, Matsubara BB,
Minicucci MF, Azevedo PS, Campana AO and Zornoff LA: Retinoic acid
supplementation attenuates ventricular remodeling after myocardial
infarction in rats. J Nutr. 135:2326–2328. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Krivospitskaya O, Elmabsout AA, Sundman E,
Söderström LA, Ovchinnikova O, Gidlöf AC, Scherbak N, Norata GD,
Samnegård A, Törmä H, Abdel-Halim SM, Jansson JH, Eriksson P,
Sirsjö A and Olofsson PS: A CYP26B1 polymorphism enhances retinoic
acid catabolism which may aggravate atherosclerosis. Mol Med.
18:712–718. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ocaya PA, Elmabsout AA, Olofsson PS, Torma
H, Gidlof AC and Sirsjo A: CYP26B1 plays a major role in the
regulation of all-trans-retinoic acid metabolism and
signaling in human aortic smooth muscle cells. J Vasc Res.
48:23–30. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saito A, Sugawara A, Uruno A, Kudo M,
Kagechika H, Sato Y, Owada Y, Kondo H, Sato M, Kurabayashi M,
Imaizumi M, Tsuchiya S and Ito S: all-trans retinoic acid
induces in vitro angiogenesis via retinoic acid receptor: possible
involvement of paracrine effects of endogenous vascular endothelial
growth factor signaling. Endocrinology. 148:1412–1423. 2007.
|
|
34
|
Lee CW, Park SJ, Park SW, Kim JJ, Hong MK
and Song JK: All-trans-retinoic acid attenuates neointima
formation with acceleration of reendothelialization in
balloon-injured rat aorta. J Korean Med Sci. 15:31–36. 2000.
|