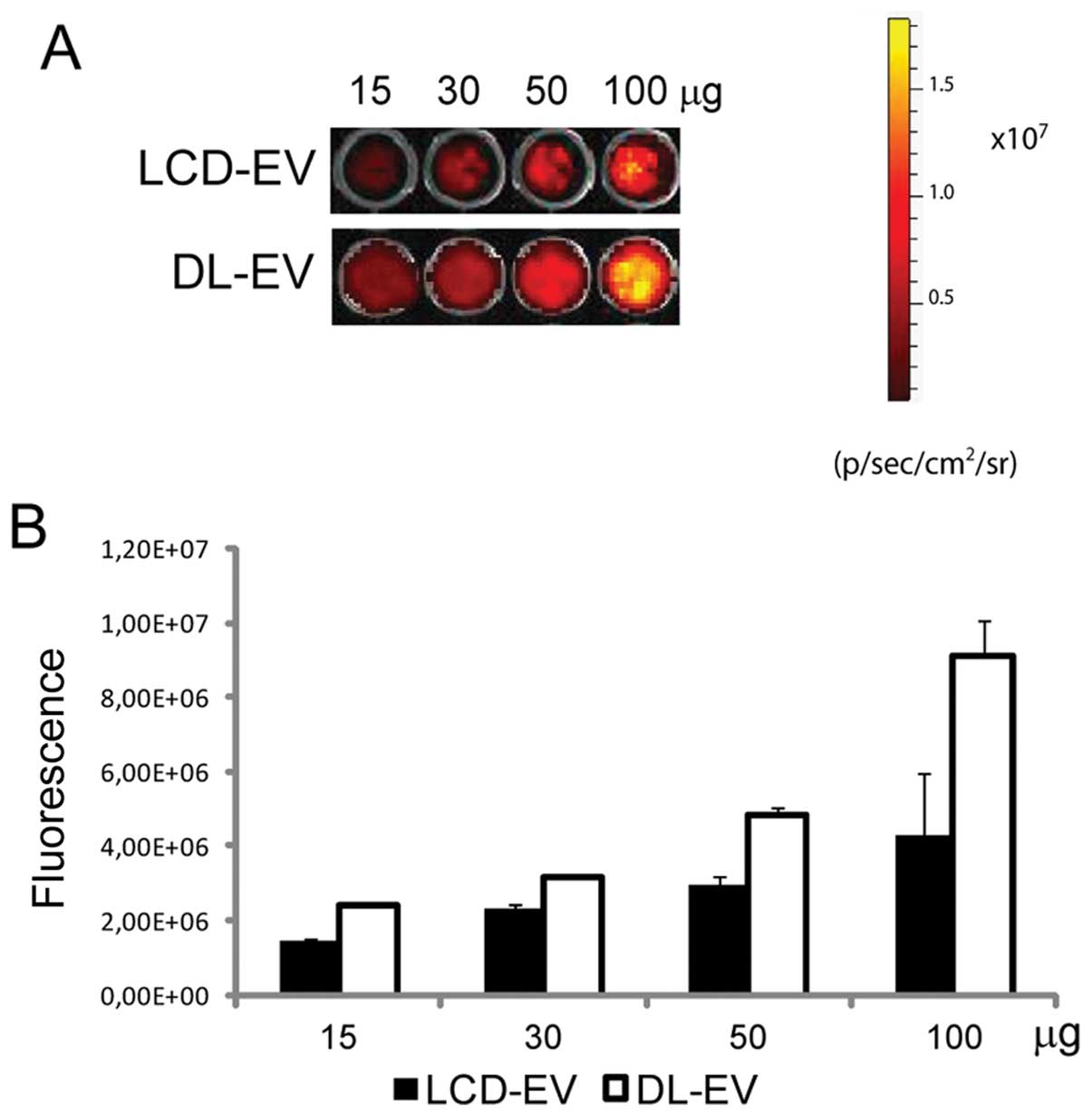
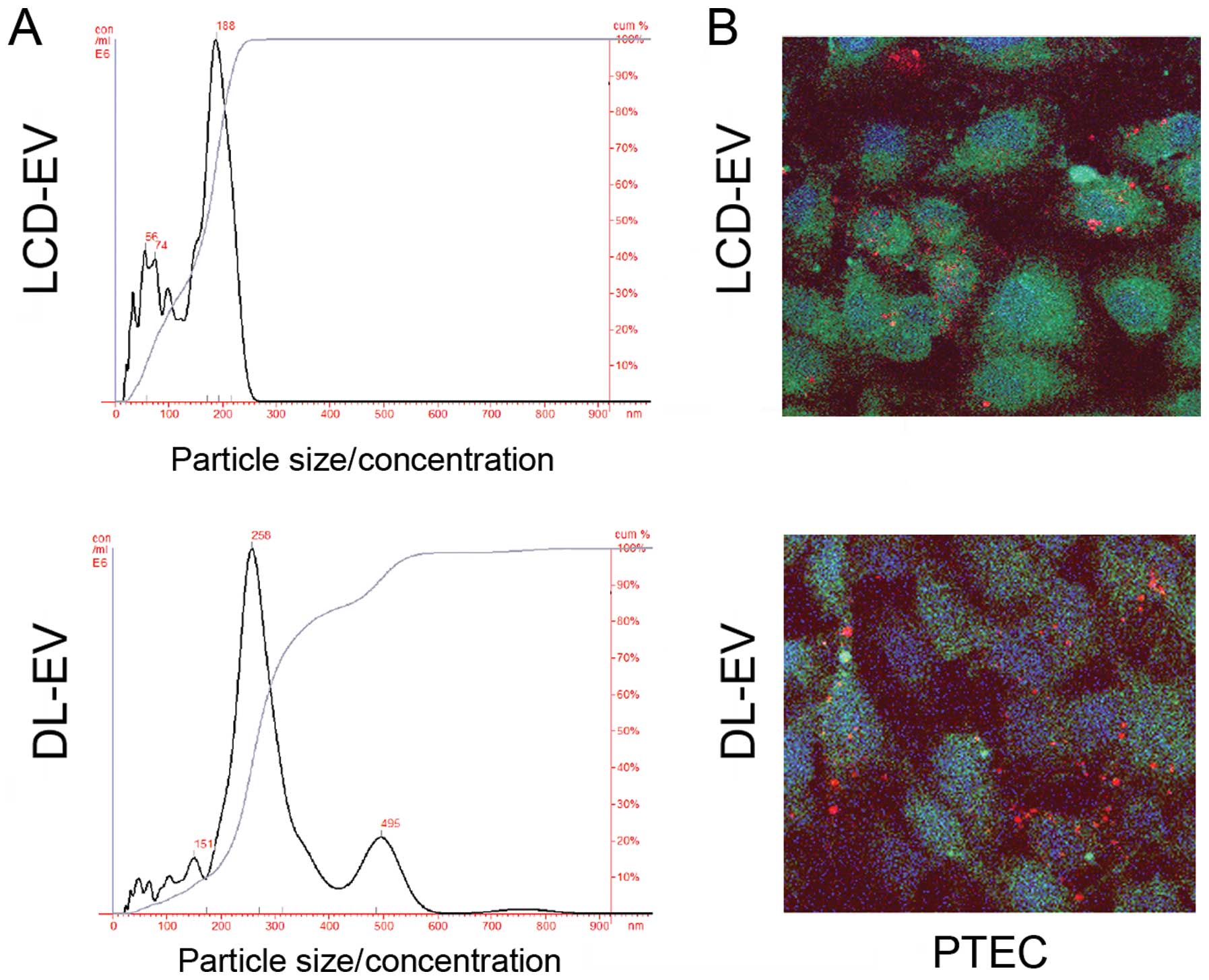
|
1
|
Aliotta JM, Pereira M, Johnson KW, et al:
Microvesicle entry into marrow cells mediates tissue-specific
changes in mRNA by direct delivery of mRNA and induction of
transcription. Exp Hematol. 38:233–245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ludwig AK and Giebel B: Exosomes: small
vesicles participating in intercellular communication. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 44:11–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van Dommelen SM, Vader P, Lakhal S,
Kooijmans SA, van Solinge WW, Wood MJ and Schiffelers RM:
Microvesicles and exosomes: opportunities for cell-derived membrane
vesicles in drug delivery. J Control Release. 161:635–644.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deregibus MC, Cantaluppi V, Calogero R, Lo
Iacono M, Tetta C, Biancone L, Bruno S, et al: Endothelial
progenitor cell-derived microvescicles activate an angiogenic
program in endothelial cells by a horizontal transfer of mRNA.
Blood. 110:2440–2448. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand
M, Lee JJ and Lötvall JO: Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and
microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:654–659. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aliotta JM, Sanchez-Guijo FM, Dooner GJ,
et al: Alteration of marrow cell gene expression, protein
production, and engraftment into lung by lung-derived
microvesicles: a novel mechanism for phenotype modulation. Stem
Cells. 25:2245–2256. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Collino F, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, et al:
Microvesicles derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue
specific mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs.
PLoS One. 5:e118032010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ratajczak J, Miekus K, Kucia M, Zhang J,
Reca R, Dvorak P and Ratajczak MZ: Embryonic stem cell-derived
microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: evidence for
horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia.
20:847–856. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin HJ, Bae YK, Kim M, et al: Comparative
analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose
tissue, and umbilical cord blood as sources of cell therapy. Int J
Mol Sci. 14:17986–8001. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Humphreys BD and Bonventre JV: Mesenchymal
stem cells in acute kidney injury. Annu Rev Med. 59:311–325. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bi B, Schmitt R, Israilova M, Nishio H and
Cantley LG: Stromal cells protect against acute tubular injury via
an endocrine effect. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:2486–2496. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Quesenberry PJ and Aliotta JM: Cellular
phenotype switching and microvesicles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
62:1141–1148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bruno S, Grange C, Deregibus MC, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute
tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1053–1067. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Camussi G, Deregibus MC and Cantaluppi V:
Role of stem-cell-derived microvesicles in the paracrine action of
stem cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 41:283–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Goldstein SL, Jaber BL, Faubel S and
Chawla LS; Acute Kidney Injury Advisory Group of American Society
of Nephrology. AKI transition of care: a potential opportunity to
detect and prevent CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 8:476–483. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Herrera MB, Bussolati B, Bruno S, et al:
Exogenous mesenchymal stem cells localize to the kidney by means of
CD44 following acute tubular injury. Kidney Int. 72:430–441. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Morigi M, Introna M, Imberti B, et al:
Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells accelerate recovery of
acute renal injury and prolong survival in mice. Stem Cells.
26:2075–2082. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qi S and Wu D: Bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells protect against cisplatin-induced acute
kidney injury in rats by inhibiting cell apoptosis. Int J Mol Med.
32:1262–1272. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bruno S, Grange C, Collino F, Deregibus MC
and Cantaluppi V: Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells
enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS
One. 7:e331152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gatti S, Bruno S, Deregibus MC, Sordi A,
Cantaluppi V, Tetta C and Camussi G: Microvesicles derived from
human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against
ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 26:1474–1483. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boddington S, Henning TD, Sutton EJ and
Daldrup-Link HE: Labeling stem cells with fluorescent dyes for
non-invasive detection with optical imaging. J Vis Exp.
14:pii6862008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tögel F, Yang Y, Zhang P, Hu Z and
Westenfelder C: Bioluminescence imaging to monitor the in vivo
distribution of administered mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney
injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 295:F315–F321. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sutton EJ, Henning TD, Boddington S, Demos
S, Krug C, Meier R, Kornak J, et al: In vivo magnetic resonance
imaging and optical imaging comparison of viable and nonviable
mesenchymal stem cells with a bifunctional label. Mol Imaging.
9:278–290. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garrovo C, Bergamin N, Bates D, et al: In
vivo tracking of murine adipose tissue-derived multipotent adult
stem cells and ex vivo cross-validation. Int J Mol Imaging.
2013:4269612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chatterjee DK, Gnanasammandhan MK and
Zhang Y: Small upconverting fluorescent nanoparticles for
biomedical applications. Small. 6:2781–2795. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rao J, Dragulescu-Andrasi A and Yao H:
Fluorescence imaging in vivo: recent advances. Curr Opin
Biotechnol. 18:17–25. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Boddington SE, Sutton EJ, Henning TD,
Nedopil AJ, Sennino B, Kim A and Daldrup-Link HE: Labeling human
mesenchymal stem cells with fluorescent contrast agents: the
biological impact. Mol Imaging Biol. 13:3–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hood JL, San RS and Wickline SA: Exosomes
released by melanoma cells prepare sentinel lymph nodes for tumor
metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:3792–3801. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ansa-Addo EA, Lange S, Stratton D, et al:
Human plasma membrane-derived vesicles halt proliferation and
induce differentiation of THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cells. J
Immunol. 185:5236–5246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grant R, Ansa-Addo E, Stratton D, et al: A
filtration-based protocol to isolate human plasma membrane-derived
vesicles and exosomes from blood plasma. J Immunol Methods.
371:143–151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sutton EJ, Boddington SE, Nedopil AJ,
Henning TD, Demos SG, Baehner R, Sennino B, et al: An optical
imaging method to monitor stem cell migration in a model of
immune-mediate arthritis. Opt Express. 17:24403–24413. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Herrera MB, Fonsato V, Bruno S, et al:
Human liver stem cells improve liver injury in a model of fulminant
liver failure. Hepatology. 57:311–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zou P, Xu S, Povoski SP, et al:
Near-infrared fluorescence labeled anti-TAG-72 monoclonal
antibodies for tumor imaging in colorectal cancer xenograft mice.
Mol Pharm. 6:428–440. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lai CP, Tannous BA and Breakefield XO:
Noninvasive in vivo monitoring of extracellular vesicles. Methods
Mol Biol. 1098:249–258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Suetsugu A, Honma K, Saji S, Moriwaki H,
Ochiya T and Hoffman RM: Imaging exosome transfer from breast
cancer cells to stroma at metastatic sites in orthotopic nude-mouse
models. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 65:383–390. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Takahashi Y, Nishikawa M, Shinotsuka H,
Matsui Y, Ohara S, Imai T and Takakura Y: Visualization and in vivo
tracking of the exosomes of murine melanoma B16-BL6 cells in mice
after intravenous injection. J Biotechnol. 165:77–84. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Raposo G and Stoorvogel W: Extracellular
vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol.
200:373–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S,
Cantaluppi V and Biancone L: Exosomes/microvesicles as a mechanism
of cell-to-cell communication. Kidney Int. 78:838–848. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kalchenko V, Shivtiel S, Malina V, Lapid
K, Haramati S, Lapidot T, Brill A and Harmelin A: Use of lipophilic
near-infrared dye in whole-body optical imaging of hematopoietic
cell homing. J Biomed Opt. 11:0505072006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|