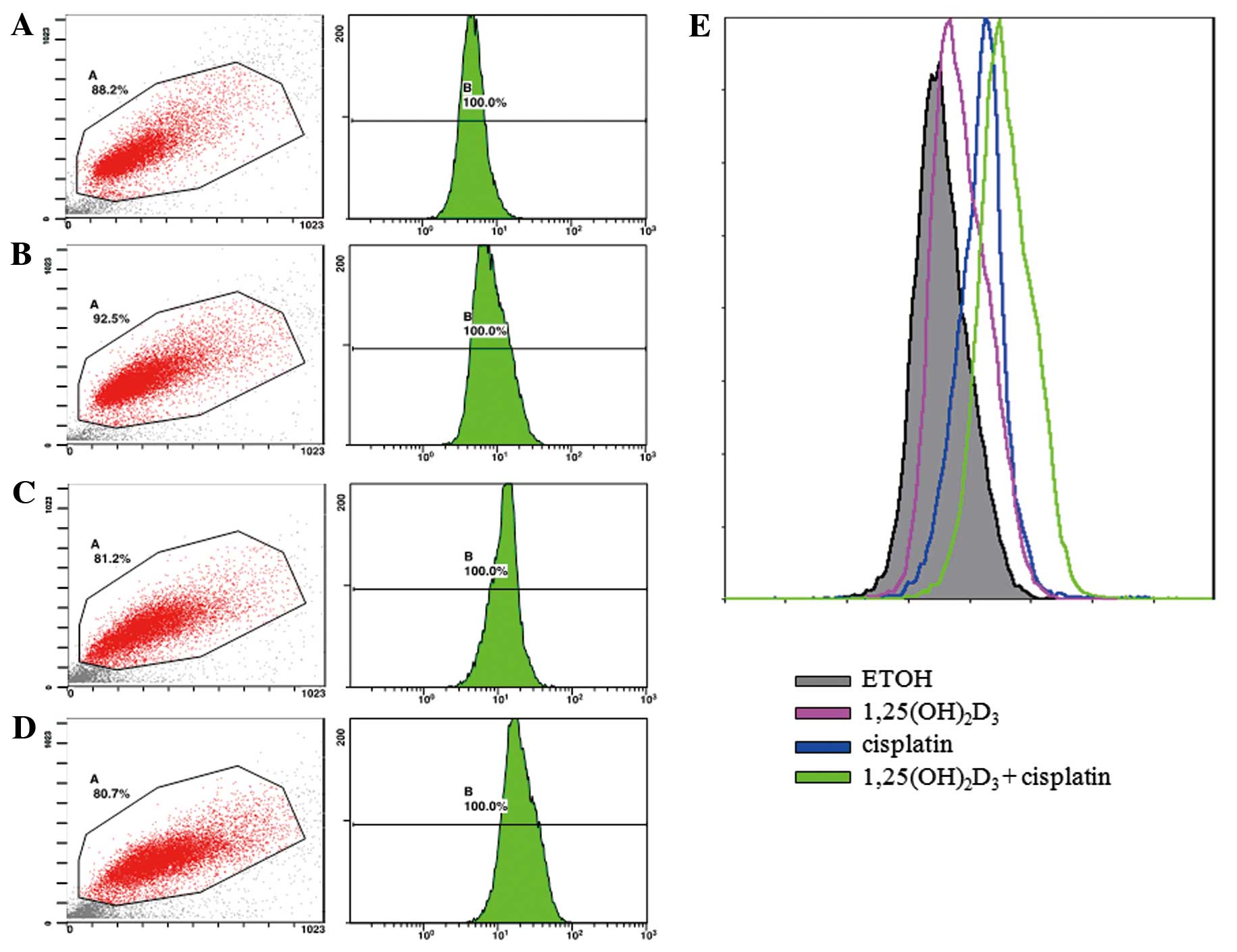
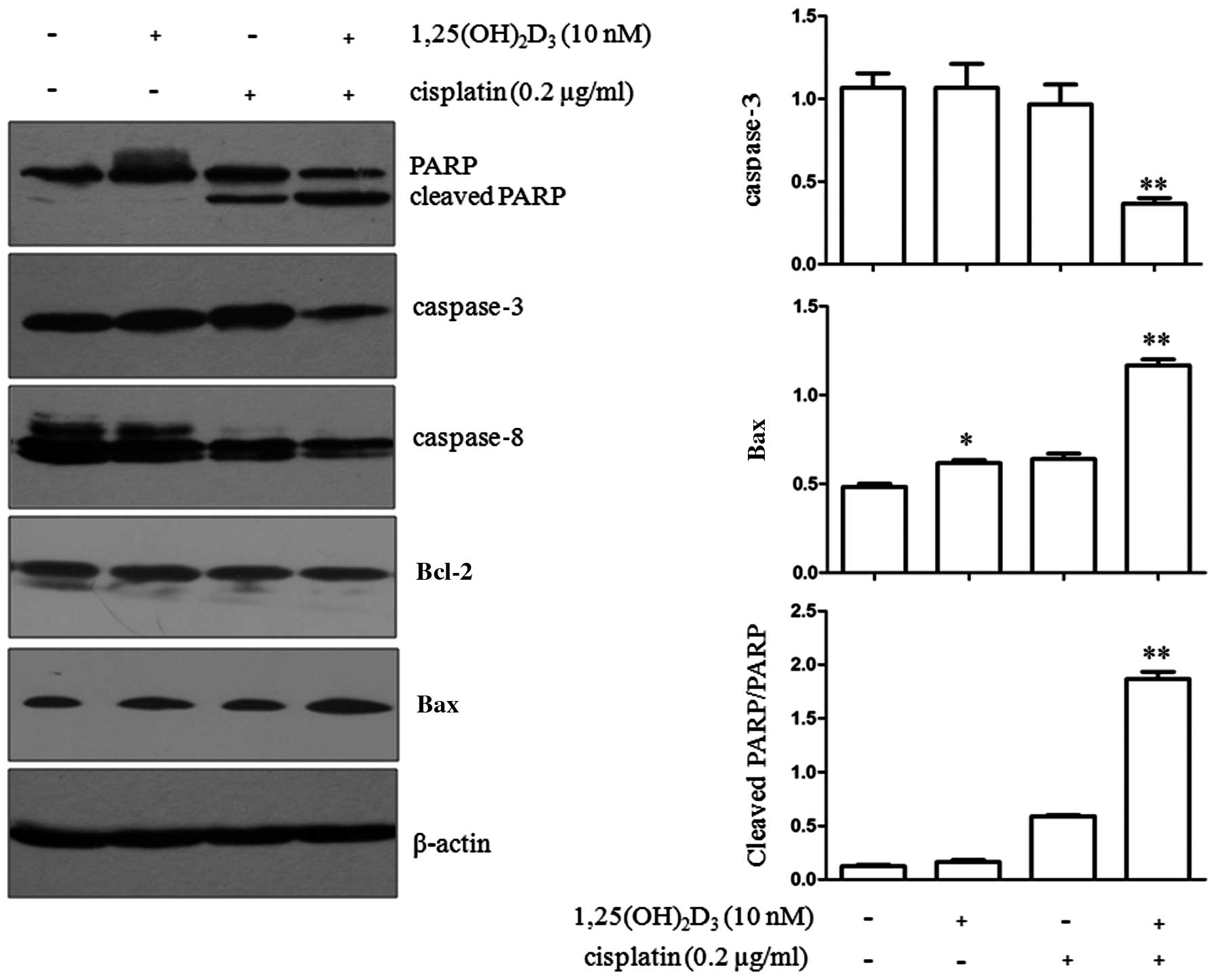
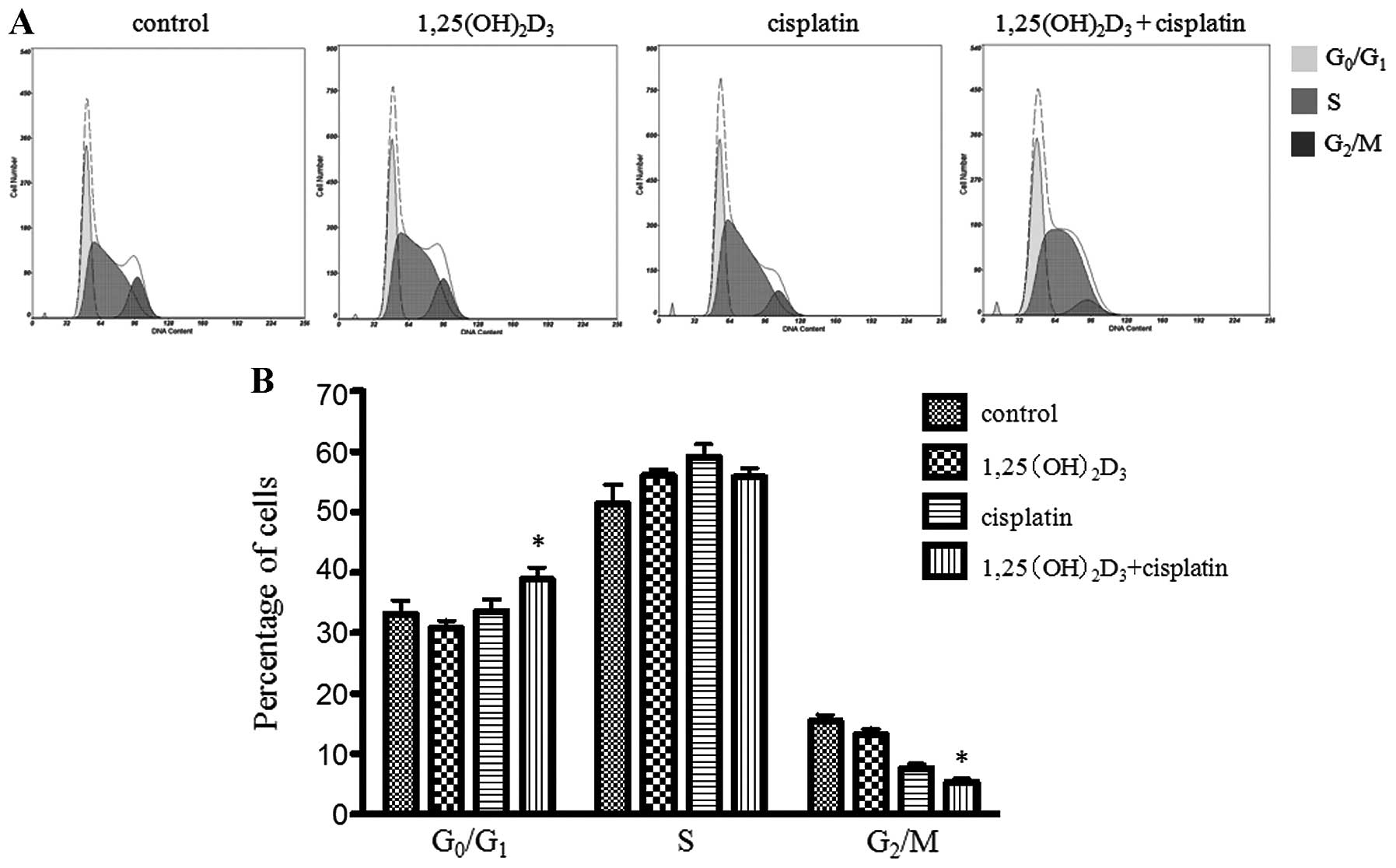
|
1
|
Deeb KK, Trump DL and Johnson CS: Vitamin
D signalling pathways in cancer: potential for anticancer
therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:684–700. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eelen G, Verlinden L, De Clercq P,
Vandewalle M, Bouillon R and Verstuyf A: Vitamin D analogs and
coactivators. Anticancer Res. 26:2717–2721. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wadhwa R, Song S, Lee JS, Yao Y, Wei Q and
Ajani JA: Gastric cancer-molecular and clinical dimensions. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 10:643–655. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abnet CC, Chen Y, Chow WH, et al:
Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of esophageal and gastric
cancer: Cohort Consortium Vitamin D Pooling Project of Rarer
Cancers. Am J Epidemiol. 172:94–106. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Fleet JC: Molecular actions of vitamin D
contributing to cancer prevention. Mol Aspects Med. 29:388–396.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feldman DR, Bosl GJ, Sheinfeld J and
Motzer RJ: Medical treatment of advanced testicular cancer. JAMA.
299:672–684. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Krishnan AV, Trump DL, Johnson CS and
Feldman D: The role of vitamin D in cancer prevention and
treatment. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 38:161–178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Krege S, Beyer J, Souchon R, et al:
European consensus conference on diagnosis and treatment of germ
cell cancer: a report of the second meeting of the European Germ
Cell Cancer Consensus group (EGCCCG): part I. Eur Urol. 53:478–496.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tanida S, Mizoshita T, Ozeki K, et al:
Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced apoptosis and of cisplatin
sensitivity: potential of BIN1 to act as a potent predictor of
cisplatin sensitivity in gastric cancer treatment. Int J Surg
Oncol. 2012:8628792012.
|
|
11
|
Moffatt KA, Johannes WU and Miller GJ:
1Alpha, 25dihydroxyvitamin D3 and platinum drugs act
synergistically to inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cell
lines. Clin Cancer Res. 5:695–703. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho YL, Christensen C, Saunders DE, et al:
Combined effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and
platinum drugs on the growth of MCF-7 cells. Cancer Res.
51:2848–2853. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma Y, Yu WD, Trump DL and Johnson CS:
1,25D3 enhances antitumor activity of gemcitabine and
cisplatin in human bladder cancer models. Cancer. 116:3294–3303.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Light BW, Yu WD, McElwain MC, Russell DM,
Trump DL and Johnson CS: Potentiation of cisplatin antitumor
activity using a vitamin D analogue in a murine squamous cell
carcinoma model system. Cancer Res. 57:3759–3764. 1997.
|
|
15
|
Almhanna K, Strosberg J and Malafa M:
Targeting AKT protein kinase in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res.
31:4387–4392. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yao J, Qian CJ, Ye B, Zhang X and Liang Y:
ERK inhibition enhances TSA-induced gastric cancer cell apoptosis
via NF-κB-dependent and Notch-independent mechanism. Life Sci.
91:186–193. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen S, Law CS and Gardner DG: Vitamin
D-dependent suppression of endothelin-induced vascular smooth
muscle cell proliferation through inhibition of CDK2 activity. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 118:135–141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bao A, Li Y, Tong Y, Zheng H, Wu W and Wei
C: Tumor-suppressive effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
in gastric cancer cells. Hepatogastroenterology. 60:943–948.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mitrea DM, Yoon MK, Ou L and Kriwacki RW:
Disorder-function relationships for the cell cycle regulatory
proteins p21 and p27. Biol Chem. 393:259–274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leung WK, Wu MS, Kakugawa Y, et al:
Screening for gastric cancer in Asia: current evidence and
practice. Lancet Oncol. 9:279–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Macdonald JS: Treatment of localized
gastric cancer. Semin Oncol. 31:566–573. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carrato A, Gallego-Plazas J and
Guillen-Ponce C: Adjuvant therapy of resected gastric cancer is
necessary. Semin Oncol. 32(Suppl 9): S105–S108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Topuz E, Basaran M, Saip P, et al:
Adjuvant intraperitoneal chemotherapy with cisplatinum,
mitoxantrone, 5-fluorouracil, and calcium folinate in patients with
gastric cancer: a phase II study. Am J Clin Oncol. 25:619–624.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cavanna L, Artioli F, Codignola C, et al:
Oxaliplatin in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and
leucovorin (LV) in patients with metastatic gastric cancer (MGC).
Am J Clin Oncol. 29:371–375. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Louvet C, Andre T, Tigaud JM, et al: Phase
II study of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinic acid in locally
advanced or metastatic gastric cancer patients. J Clin Oncol.
20:4543–4548. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mocellin S: Vitamin D and cancer:
deciphering the truth. Biochim Biophys Actas. 1816:172–178.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Picotto G, Liaudat AC, Bohl L and Tolosa
de Talamoni N: Molecular aspects of vitamin D anticancer activity.
Cancer Invest. 30:604–614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reichrath J, Friedrich M and Vogt T:
Vitamin D and its analogs in cancer prevention and therapy.
Anticancer Res. 32:209–210. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rahman N: Realizing the promise of cancer
predisposition genes. Nature. 505:302–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fingas CD, Altinbas A, Schlattjan M, et
al: Expression of apoptosis- and vitamin D pathway-related genes in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Digestion. 87:176–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang W, Zhao CH, Zhang N and Wang J:
Vitamin D analog EB1089 induces apoptosis in a subpopulation of
SGC-7901 gastric cancer cells through a mitochondrial-dependent
apoptotic pathway. Nutr Cancer. 65:1067–1075. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Narvaez CJ and Welsh J: Role of
mitochondria and caspases in vitamin D-mediated apoptosis of MCF-7
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 276:9101–9107. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Koshizuka K, Koike M, Kubota T, Said J,
Binderup L and Koeffler HP: Novel vitamin D3 analog
(CB1093) when combined with paclitaxel and cisplatin inhibit growth
of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in vivo. Int J Oncol.
13:421–428. 1998.
|
|
35
|
Wagner N, Wagner KD, Schley G, Badiali L,
Theres H and Scholz H: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced
apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells is associated with reciprocal
changes of Bcl-2 and bax. Exp Eye Res. 77:1–9. 2003.
|
|
36
|
Basu A and Krishnamurthy S: Cellular
responses to cisplatin-induced DNA damage. J Nucleic Acids.
2010:2013672010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang S, Li W, Xue Z, et al: Molecular
imaging of p53 signal pathway in lung cancer cell cycle arrest
induced by cisplatin. Mol Carcinog. 52:900–907. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ma Y, Yu WD, Kong RX, Trump DL and Johnson
CS: Role of nongenomic activation of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1/2 pathways in 1,25D3-mediated apoptosis in squamous cell
carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 66:8131–8138. 2006.
|
|
39
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiao H, Shi W, Liu S, et al:
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) prevents puromycin
aminonucleoside-induced apoptosis of glomerular podocytes by
activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-signaling pathway.
Am J Nephrol. 30:34–43. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shen XJ, Wang HB, Ma XQ and Chen JH:
β,β-Dimethylacrylshikonin induces mitochondria dependent apoptosis
through ERK pathway in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. PLoS
One. 7:e417732012.
|
|
43
|
Lee HJ, So JY, DeCastro A, et al: Gemini
vitamin D analog suppresses ErbB2-positive mammary tumor growth via
inhibition of ErbB2/AKT/ERK signaling. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
121:408–412. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu S, Lao XY, Sun TT, et al: Knockdown of
ZFX inhibits gastric cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo via
downregulating the ERK-MAPK pathway. Cancer Lett. 337:293–300.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Artaza JN, Sirad F, Ferrini MG and Norris
KC: 1,25(OH)2vitamin D3 inhibits cell
proliferation by promoting cell cycle arrest without inducing
apoptosis and modifies cell morphology of mesenchymal multipotent
cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 119:73–83. 2010.
|
|
46
|
Luo W, Chen Y, Liu M, et al: EB1089
induces Skp2-dependent p27 accumulation, leading to cell growth
inhibition and cell cycle G1 phase arrest in human hepatoma cells.
Cancer Invest. 27:29–37. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Banerjee P and Chatterjee M:
Antiproliferative role of vitamin D and its analogs - a brief
overview. Mol Cell Biochem. 253:247–254. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|