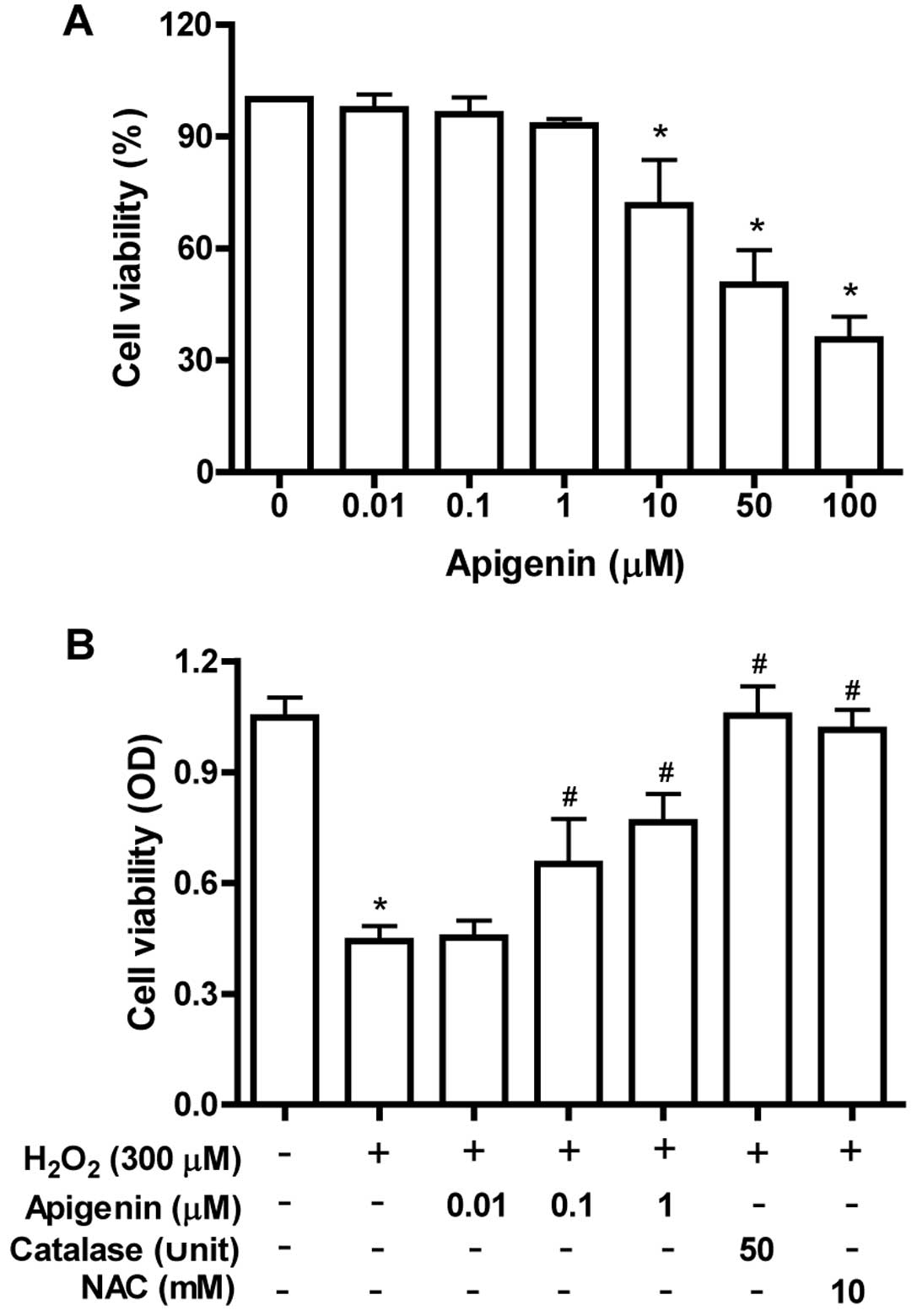
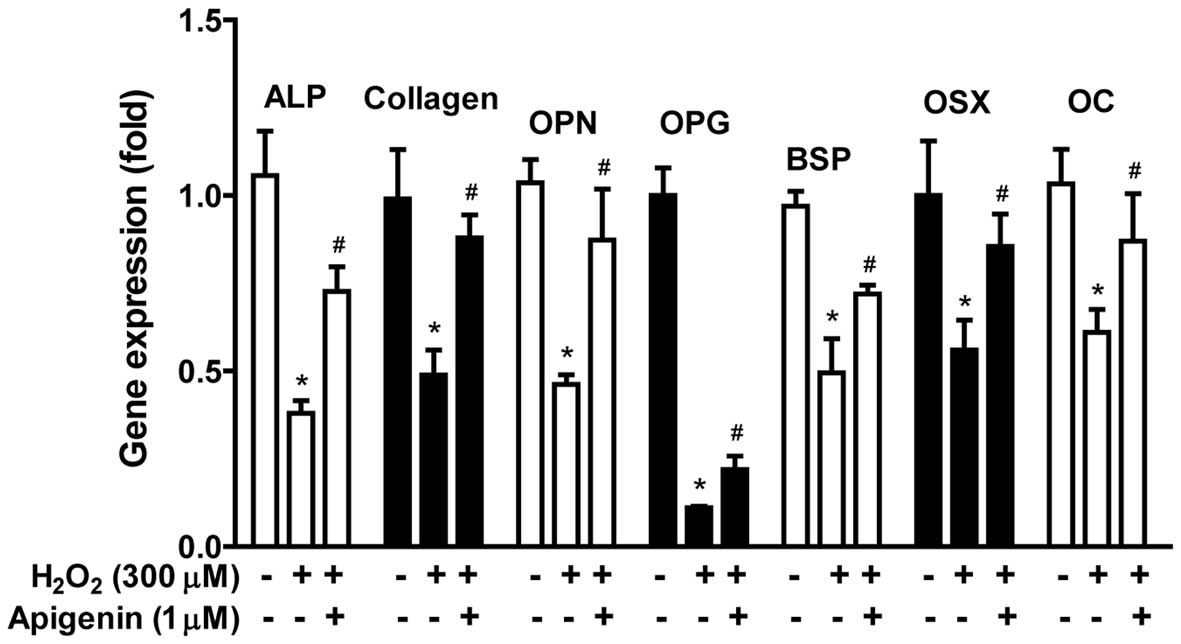
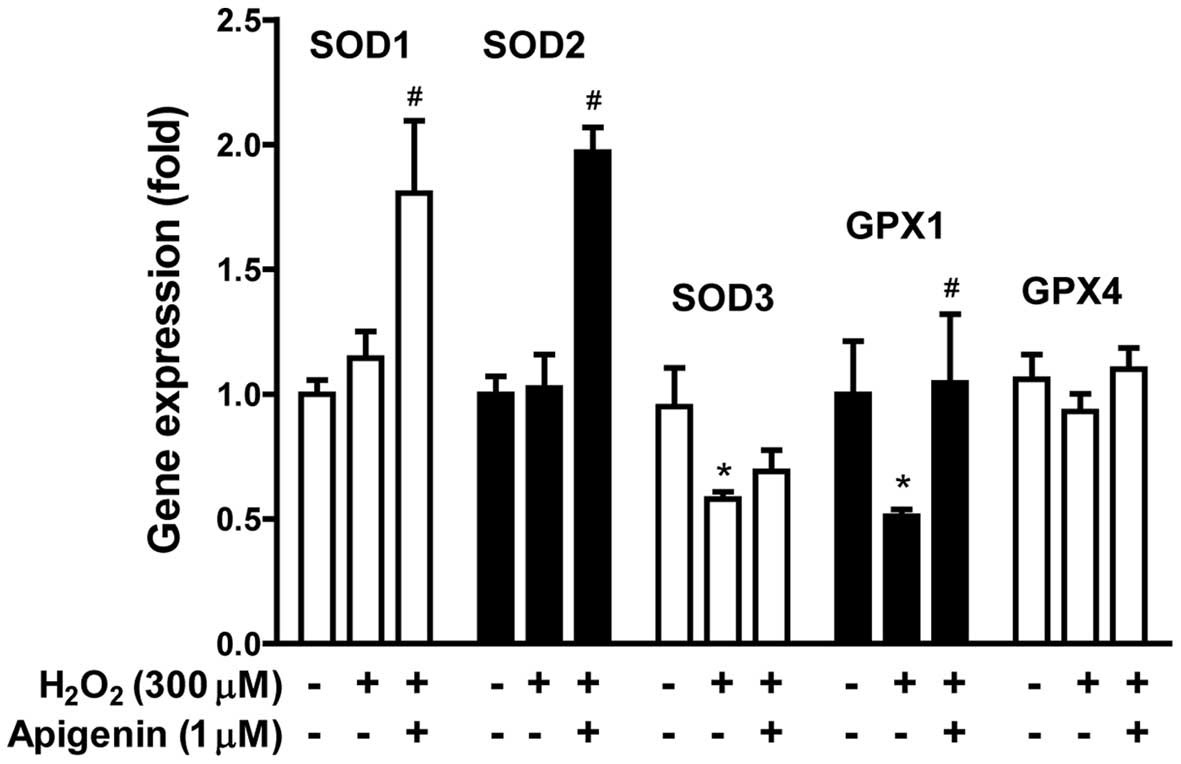
|
1
|
Da Silva FM, Marques A and Chaveiro A:
Reactive oxygen species: a double-edged sword in reproduction. Open
Vet Sci J. 4:127–133. 2010.
|
|
2
|
Maggio D, Barabani M, Pierandrei M,
Polidori MC, Catani M, Mecocci P, Senin U, Pacifici R and Cherubini
A: Marked decrease in plasma antioxidants in aged osteoporotic
women: results of a cross-sectional study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
88:1523–1527. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Basu S, Michaëlsson K, Olofsson H,
Johansson S and Melhus H: Association between oxidative stress and
bone mineral density. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 288:275–279.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ozgocmen S, Kaya H, Fadillioglu E, Aydogan
R and Yilmaz Z: Role of antioxidant systems, lipid peroxidation,
and nitric oxide in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Mol Cell Biochem.
295:45–52. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Manolagas SC: De-fense! de-fense!
de-fense: scavenging H2O2 while making
cholesterol. Endocrinology. 149:3264–3266. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee DH, Lim BS, Lee YK and Yang HC:
Effects of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) on
alkaline phosphatase activity and matrix mineralization of
odontoblast and osteoblast cell lines. Cell Biol Toxicol. 22:39–46.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mody N, Parhami F, Sarafian TA and Demer
LL: Oxidative stress modulates osteoblastic differentiation of
vascular and bone cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 31:509–519. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mogi M, Kinpara K, Kondo A and Togari A:
Involvement of nitric oxide and biopterin in proinflammatory
cytokine-induced apoptotic cell death in mouse osteoblastic cell
line MC3T3-E1. Biochem Pharmacol. 58:649–654. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Choi EM, Kim GH and Lee YS: Protective
effects of dehydrocostus lactone against hydrogen peroxide-induced
dysfunction and oxidative stress in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells.
Toxicol In Vitro. 23:862–867. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao Y, Cui J, Shi Y and Le G:
Alpha-lipoic acid protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced
oxidative stress in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells. J Funct Foods.
4:642–649. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fatokun AA, Stone TW and Smith RA:
Hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in MC3T3-E1 cells: the
effects of glutamate and protection by purines. Bone. 39:542–551.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Parfitt AM and
Manolagas SC: Inhibition of osteoblastogenesis and promotion of
apoptosis of osteoblasts end osteocytes by glucocorticoids.
Potential mechanisms of their deleterious effects on bone. J Clin
Invest. 102:274–282. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Havsteen BH: The biochemistry and medical
significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol Ther. 96:67–202. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fernandez de Simon B, Perez-Ilzarbe J,
Hernandez T, Gomez-Cordoves C and Estrella I: Importance of
phenolic compounds for the characterization of fruit juices. J
Agric Food Chem. 40:1531–1535. 1992.
|
|
15
|
Chan LP, Chou TH, Ding HY, Chen PR, Chiang
FY, Kuo PL and Liang CH: Apigenin induces apoptosis via tumor
necrosis factor receptor and-Bcl-2-mediated pathway and enhances
susceptibility of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to
5-fluorouracil and cisplatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:1081–1091.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mafuvadze B, Liang Y, Besch-Williford C,
Zhang X and Hyder SM: Apigenin induces apoptosis and blocks growth
of medroxyprogesterone acetate-dependent BT-474 xenograft tumors.
Horm Cancer. 3:160–171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nicholas C, Batra S, Vargo MA, Voss OH,
Gavrilin MA, Wewers MD, Guttridge DC, Grotewold E and Doseff AI:
Apigenin blocks lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality in vivo and
proinflammatory cytokines expression by inactivating NF-κB through
the suppression of p65 phosphorylation. J Immunol. 179:7121–7127.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Landolfi R, Mower RL and Steiner M:
Modification of platelet function and arachidonic acid metabolism
by bioflavonoids. Structure-activity relations. Biochem Pharmacol.
33:1525–1530. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Henkel KM, Frondorf K, Gonzalez-Mejia ME,
Doseff AL and Gomez-Cambronero J: IL-8-induced neutrophil
chemotaxis is mediated by Janus kinase 3 (JAK3). FEBS Lett.
585:159–166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choi EM: Apigenin increases osteoblastic
differentiation and inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α-induced
production of interleukin-6 and nitric oxide in osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells. Pharmazie. 62:216–220. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kanno S, Anuradha CD and Hirano S:
Localization of zinc after in vitro mineralization in osteoblastic
cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 83:39–47. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suh KS, Chon S, Oh S, Kim SW, Kim JW, Kim
YS and Woo JT: Prooxidative effects of green tea polyphenol
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the HIT-T15 pancreatic beta cell
line. Cell Biol Toxicol. 26:189–199. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Kim HS, Suh KS, Ko A, Sul D, Choi D, Lee
SK and Jung WW: The flavonoid glabridin attenuates
2-deoxy-D-ribose-induced oxidative damage and cellular dysfunction
in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:243–251.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szilágyi G, Simon L, Koska P, Telek G and
Nagy Z: Visualization of mitochondrial membrane potential and
reactive oxygen species via double staining. Neurosci Lett.
399:206–209. 2006.
|
|
25
|
Salido M, Gonzalez JL and Vilches J: Loss
of mitochondrial membrane potential is inhibited by bombesin in
etoposide-induced apoptosis in PC-3 prostate carcinoma cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 6:1292–1299. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sudo H, Kodama HA, Amagai Y, Yamamoto S
and Kasai S: In vitro differentiation and calcification in a new
clonal osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J
Cell Biol. 96:191–198. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bellows CG, Aubin JE and Heersche JN:
Initiation and progression of mineralization of bone nodules formed
in vitro: the role of alkaline phosphatase and organic phosphate.
Bone Miner. 14:27–40. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Domon S, Shimokawa H, Yamaguchi S and Soma
K: Temporal and spatial mRNA expression of bone sialoprotein and
type I collagen during rodent tooth movement. Eur J Orthod.
23:339–348. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang L, Takai H, Utsunomiya T, Li X, Li Z,
Wang Z, Wang S, Sasaki Y, Yamamoto H and Ogata Y: Kaempferol
stimulates bone sialoprotein gene transcription and new bone
formation. J Cell Biochem. 110:1342–1355. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Khosla S: Minireview: the OPG/RANKL/RANK
system. Endocrinology. 142:5050–5055. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wade-Gueye NM, Boudiffa M, Vanden-Bossche
A, Laroche N, Aubin JE, Vico L, Lafage-Proust MH and Malaval L:
Absence of bone sialoprotein (BSP) impairs primary bone formation
and resorption: the marrow ablation model under PTH challenge.
Bone. 50:1064–1073. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cao Y, Zhou Z, de Crombrugghe B, Nakashima
K, Guan H, Duan X, Jia SF and Kleinerman ES: Osterix, a
transcription factor for osteoblast differentiation, mediates
antitumor activity in murine osteosarcoma. Cancer Res.
65:1124–1128. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou X, Zhang Z, Feng JQ, Dusevich VM,
Sinha K, Zhang H, Darnay BG and de Crombrugghe B: Multiple
functions of Osterix are required for bone growth and homeostasis
in postnatal mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:12919–12924. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takuwa Y, Ohse C, Wang EA, Wozney JM and
Yamashita K: Bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates alkaline
phosphatase activity and collagen synthesis in cultured
osteoblastic cells, MC3T3-E1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
174:96–101. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nakase T, Takaoka K, Masuhara K, Shimizu
K, Yoshikawa H and Ochi T: Interleukin-1β enhances and tumor
necrosis factor-α inhibits bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced
alkaline phosphatase activity in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Bone.
21:17–21. 1997.
|
|
36
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yao R and Cooper GM: Requirement for
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in the prevention of apoptosis by
nerve growth factor. Science. 267:2003–2006. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Franke TF, Kaplan DR and Cantley LC: PI3K:
downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell. 88:435–437. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Choi EM: Deoxyactein isolated from
cimicifuga racemosa protects osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells against
antimycin A-induced cytotoxicity. J Appl Toxicol. 33:488–494. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Choi EM and Lee YS: Protective effect of
apocynin on antimycin A-induced cell damage in osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells. J Appl Toxicol. 32:714–721. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Choi EM: Honokiol protects osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells against antimycin A-induced cytotoxicity. Inflamm
Res. 60:1005–1012. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kim HJ, Kim JH, Bae SC, Choi JY, Kim HJ
and Ryoo HM: The protein kinase C pathway plays a central role in
the fibroblast growth factor-stimulated expression and
transactivation activity of Runx2. J Biol Chem. 278:319–326. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Xiao G, Jiang D, Gopalakrishnan R and
Franceschi RT: Fibroblast growth factor 2 induction of the
osteocalcin gene requires MAPK activity and phosphorylation of the
osteoblast transcription factor, Cbfa1/Runx2. J Biol Chem.
277:36181–36187. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee YS and Choi EM: Effect of pollen from
Typha angustata on hydrogen peroxide induced toxicity in
osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. J Oral Pathol Med. 41:171–177.
2012.
|
|
45
|
Liang D, Yang M, Guo B, Cao J, Yang L, Guo
X, Li Y and Gao Z: Zinc inhibits H2O2-induced
MC3T3-E1 cells apoptosis via MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways. Biol Trace
Elem Res. 148:420–429. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bai XC, Lu D, Bai J, Zheng H, Ke ZY, Li XM
and Luo SQ: Oxidative stress inhibits osteoblastic differentiation
of bone cells by ERK and NF-κB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
314:197–207. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Schmidt KN, Amstad P, Cerutti P and
Baeuerle PA: Identification of hydrogen peroxide as the relevant
messenger in the activation pathway of transcription factor NF-κB.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 387:63–68. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li X, Han Y, Guan Y, Zhang L, Bai C and Li
Y: Aluminum induces osteoblast apoptosis through the oxidative
stress-mediated JNK signaling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res.
150:502–508. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zelko IN, Mariani TJ and Folz RJ:
Superoxide dismutase multigene family: a comparison of the CuZn-SOD
(SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures,
evolution, and expression. Free Radic Biol Med. 33:337–349. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Braun KF, Ehnert S, Freude T, Egaña JT,
Schenck TL, Buchholz A, Schmitt A, Siebenlist S, Schyschka L,
Neumaier M, Stöckle U and Nussler AK: Quercetin protects primary
human osteoblasts exposed to cigarette smoke through activation of
the antioxidative enzymes HO-1 and SOD-1. ScientificWorldJournal.
11:2348–2357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sun L, Zhang J, Lu X, Zhang L and Zhang Y:
Evaluation to the antioxidant activity of total flavonoids extract
from persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.) leaves. Food Chem
Toxicol. 49:2689–2696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nojiri H, Saita Y, Morikawa D, Kobayashi
K, Tsuda C, Miyazaki T, Saito M, Marumo K, Yonezawa I, Kaneko K,
Shirasawa T and Shimizu T: Cytoplasmic superoxide causes bone
fragility owing to low-turnover osteoporosis and impaired collagen
cross-linking. J Bone Miner Res. 26:2682–2694. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bao YY, Zhou SH, Fan J and Wang QY:
Anticancer mechanism of apigenin and the implications of GLUT-1
expression in head and neck cancers. Future Oncol. 9:1353–1364.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Maggioni D, Garavello W, Rigolio R,
Pignataro L, Gaini R and Nicolini G: Apigenin impairs oral squamous
cell carcinoma growth in vitro inducing cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 43:1675–1682. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|