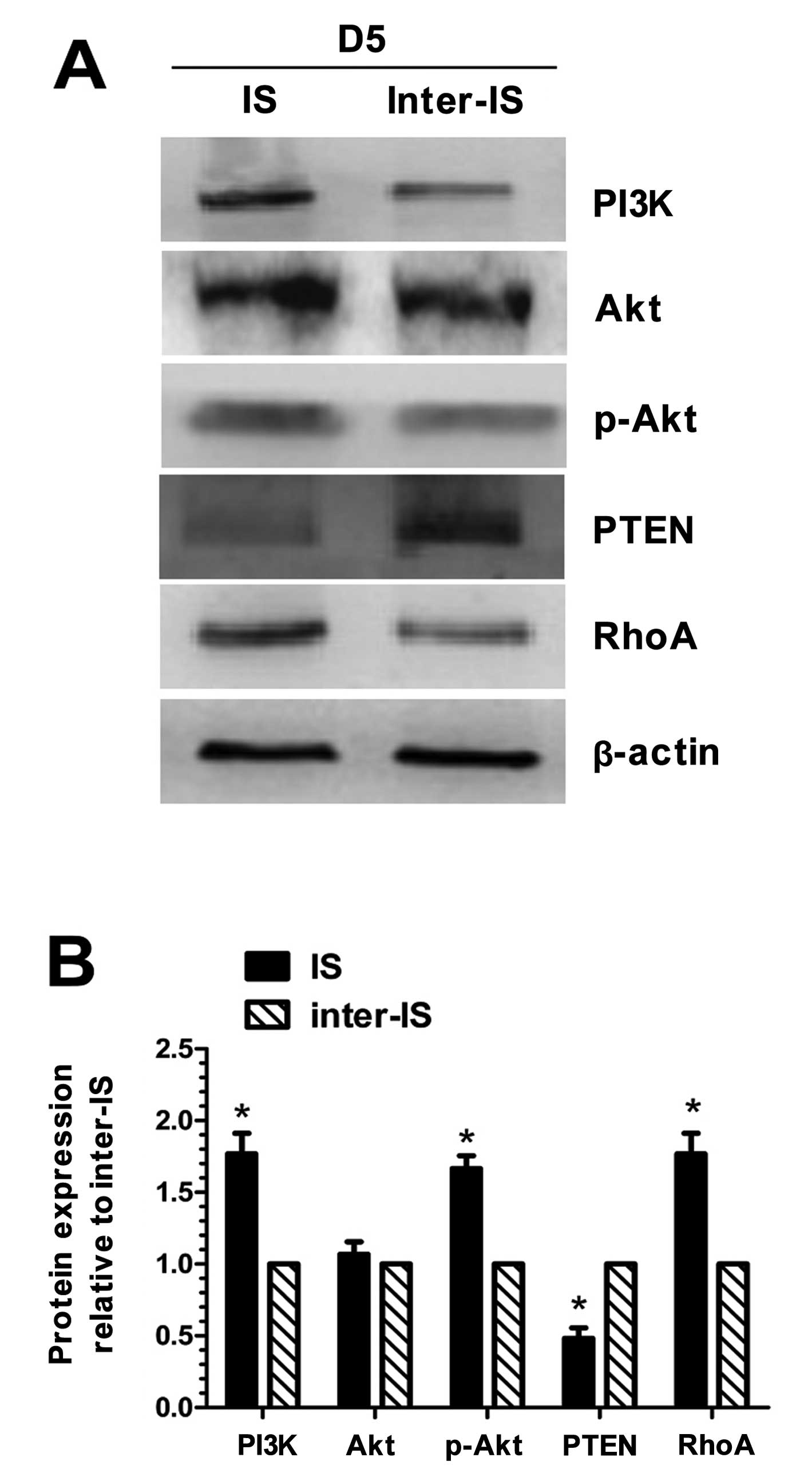
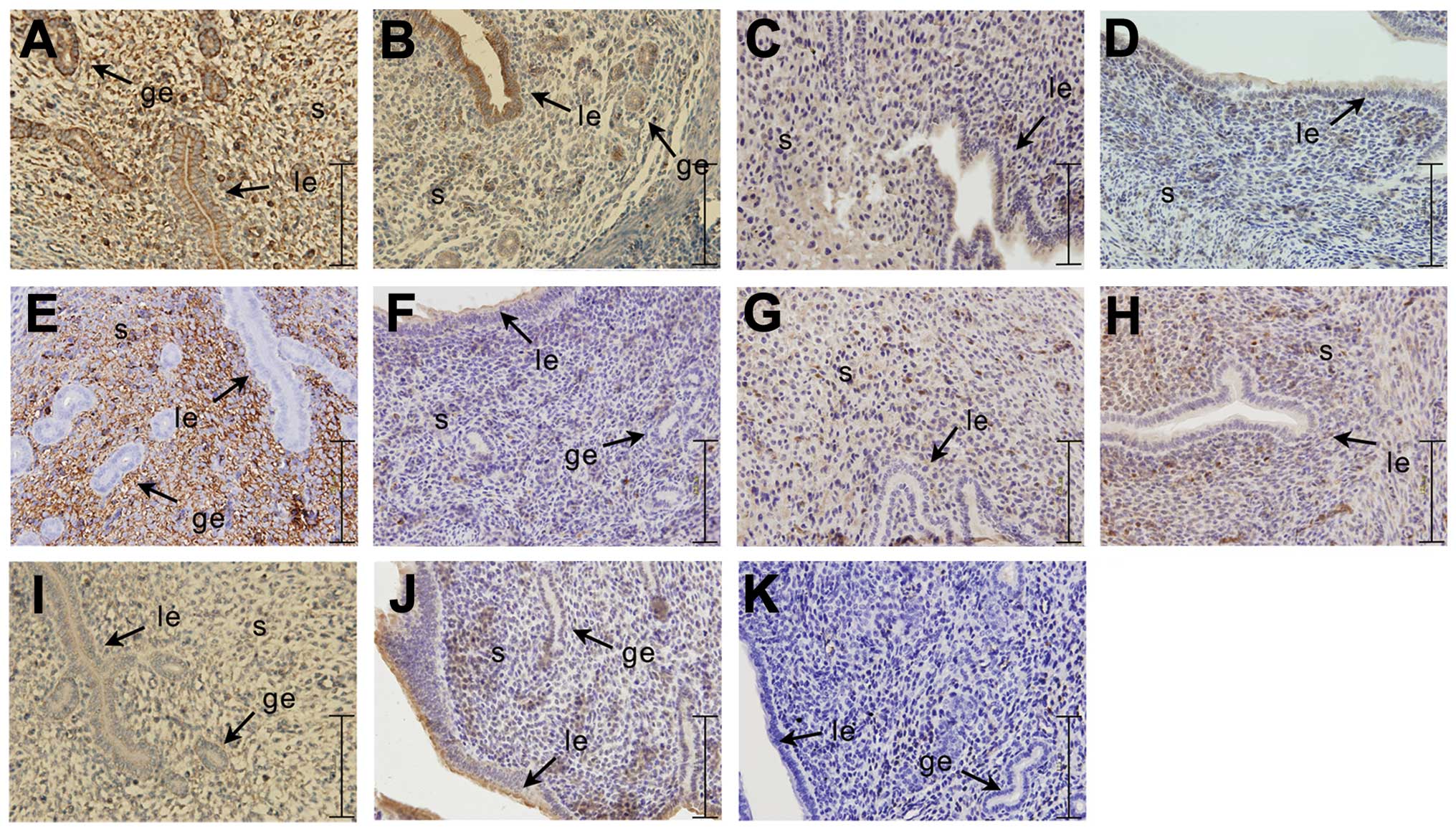
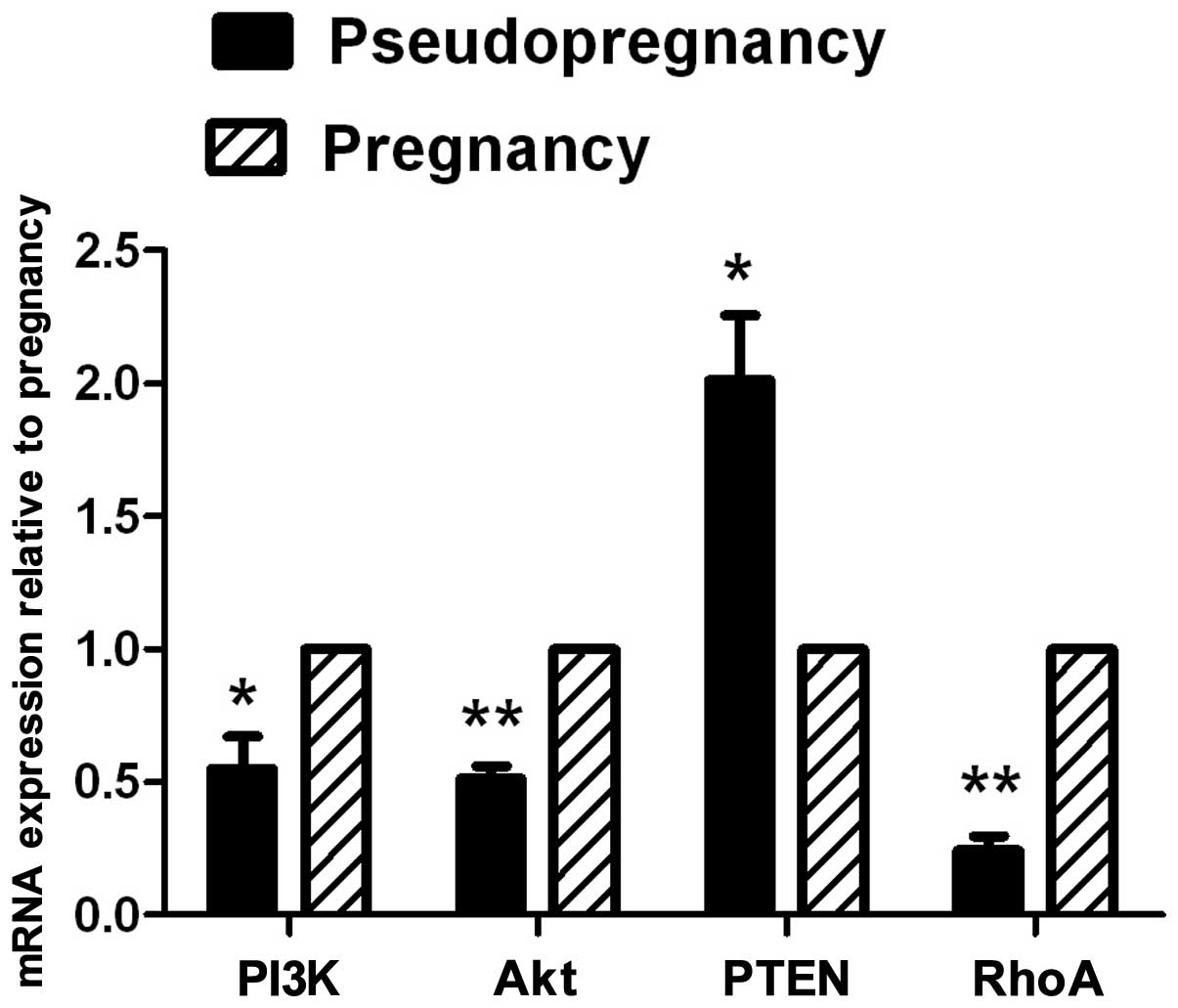
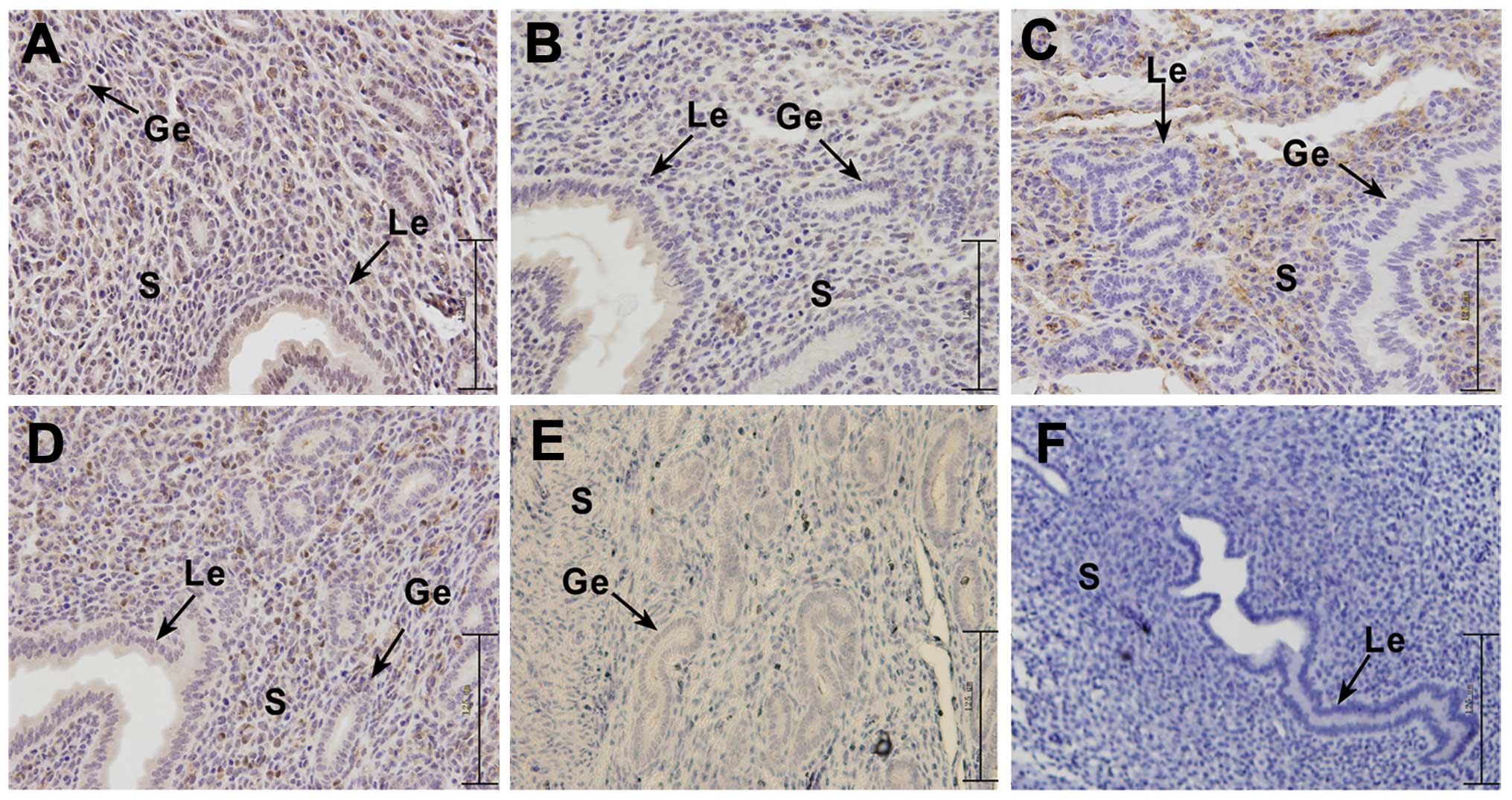
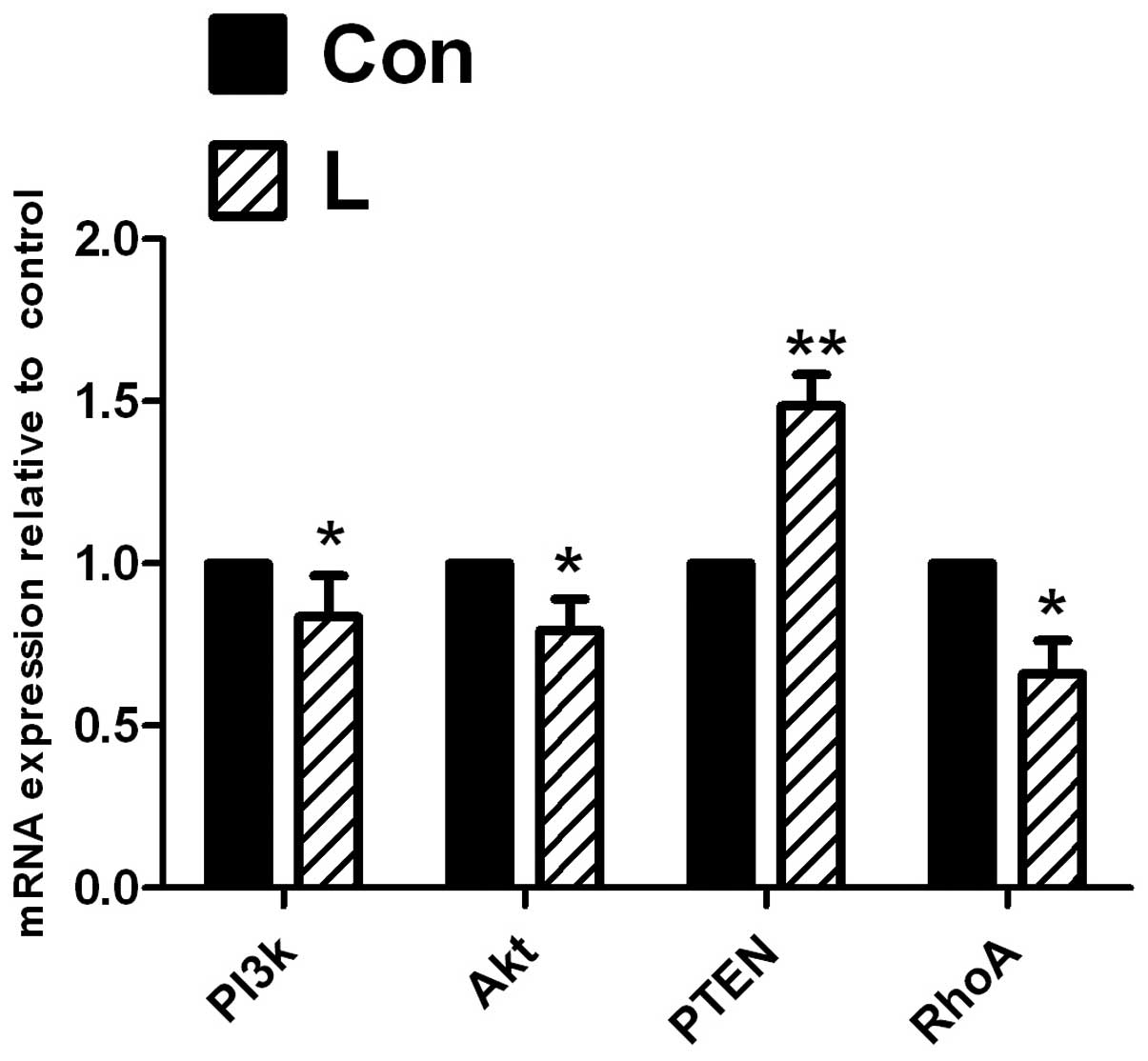
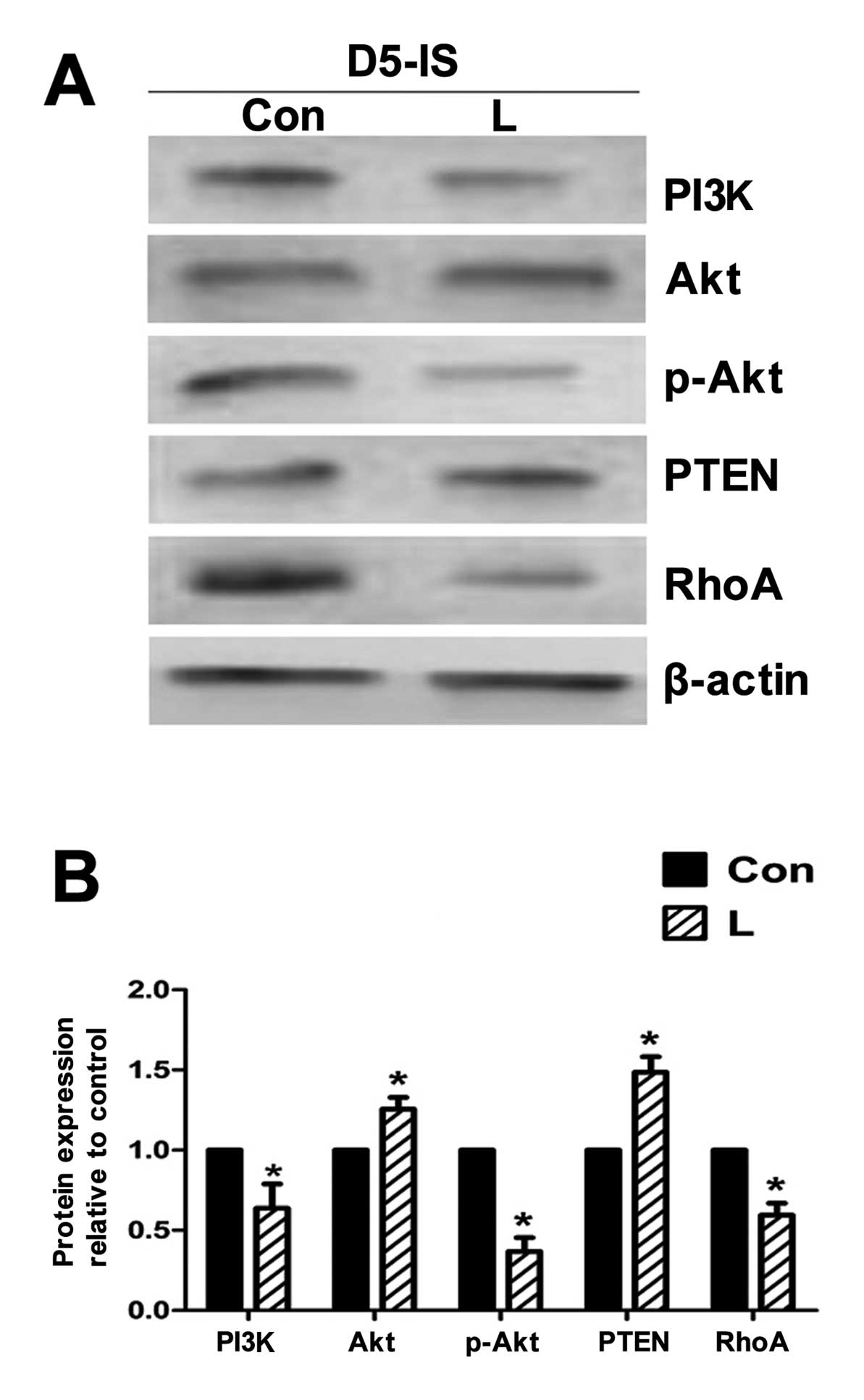
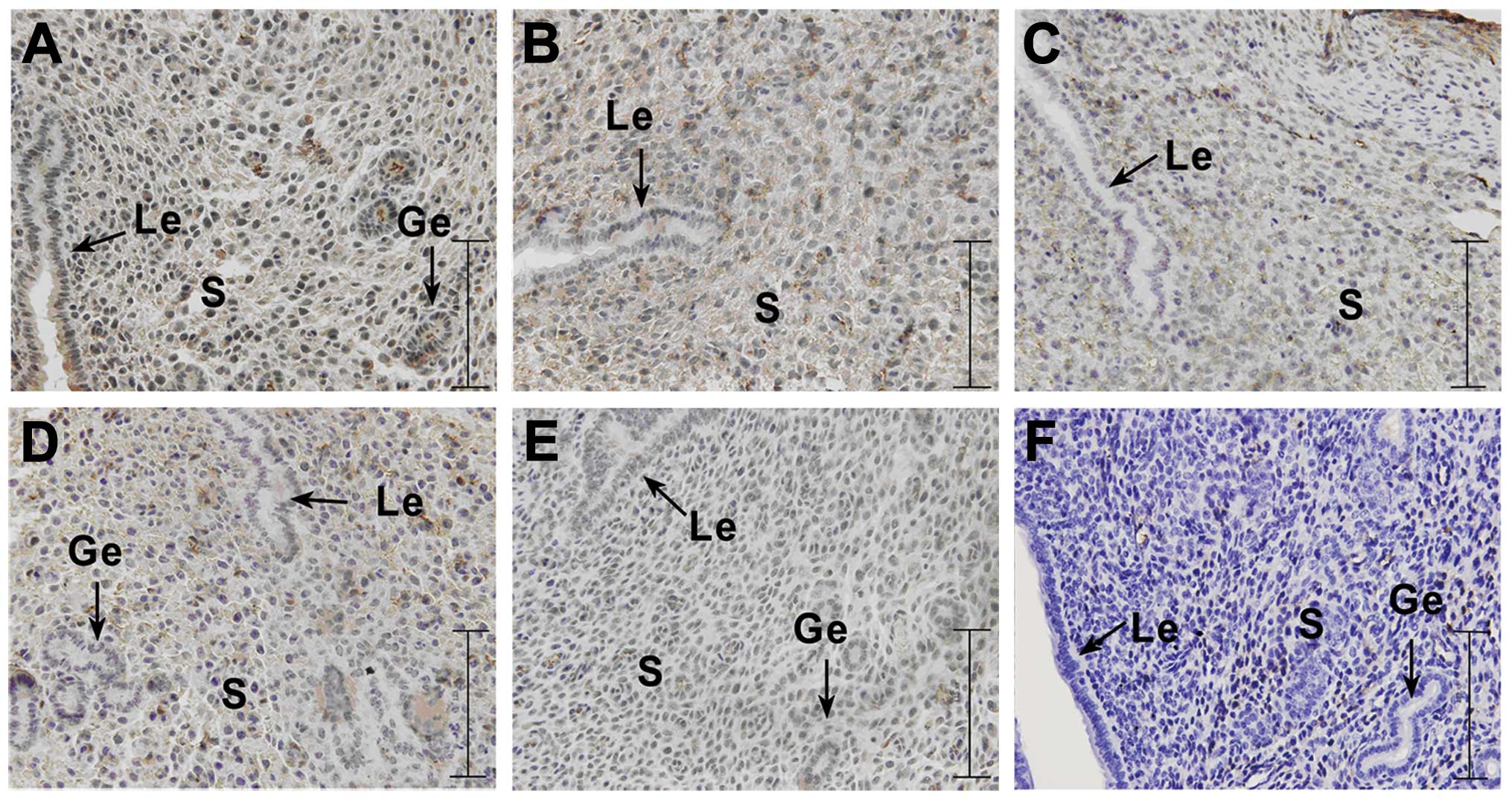
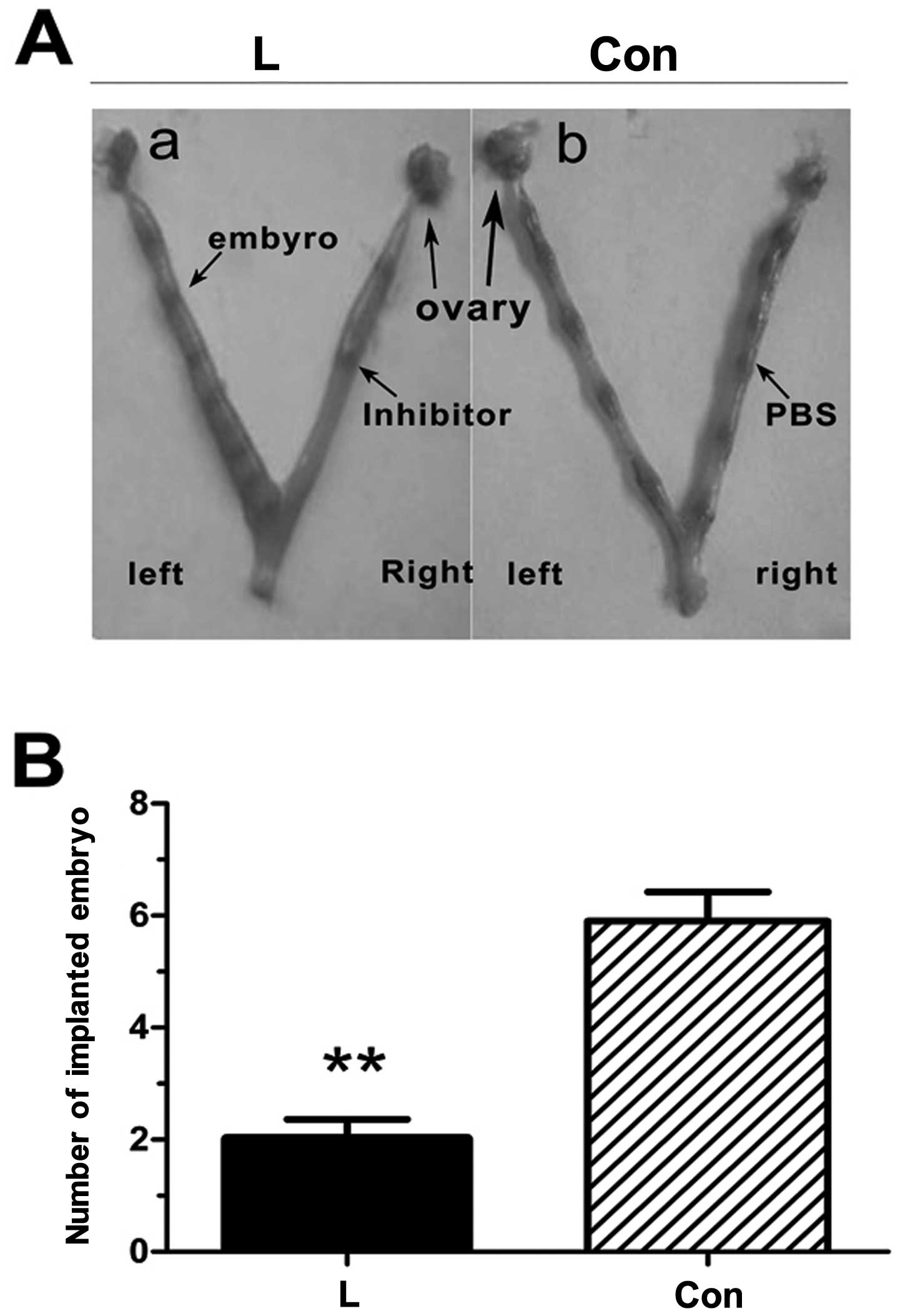
|
1
|
Banerjee P, Sapru K, Strakova Z and
Fazleabas AT: Chorionic gonadotropin regulates prostaglandin E
synthase via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-extracellular
regulatory kinase pathway in a human endometrial epithelial cell
line: implications for endometrial responses for embryo
implantation. Endocrinology. 150:4326–4337. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sales KJ, Grant V, Catalano RD and Jabbour
HN: Chorionic gonadotrophin regulates CXCR4 expression in human
endometrium via E-series prostanoid receptor 2 signalling to
PI3K-ERK1/2: implications for fetal-maternal crosstalk for embryo
implantation. Mol Hum Reprod. 17:22–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Singh M, Chaudhry P and Asselin E:
Bridging endometrial receptivity and implantation: network of
hormones, cytokines, and growth factors. J Endocrinol. 210:5–14.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Timpson P, McGhee EJ, Morton JP, et al:
Spatial regulation of RhoA activity during pancreatic cancer cell
invasion driven by mutant p53. Cancer Res. 71:747–757. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lazarini M, Traina F, Machado-Neto JA, et
al: ARHGAP21 is a RhoGAP for RhoA and RhoC with a role in
proliferation and migration of prostate adenocarcinoma cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832.365–374. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nalbant P, Chang YC, Birkenfeld J, Chang
ZF and Bokoch GM: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor-H1 regulates
cell migration via localized activation of RhoA at the leading
edge. Mol Biol Cell. 20:4070–4082. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bischof P and Campana A: A model for
implantation of the human blastocyst and early placentation. Hum
Reprod Update. 2:262–270. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shiokawa S, Sakai K, Akimoto Y, et al:
Function of the small guanosine triphosphate-binding protein RhoA
in the process of implantation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
85:4742–4749. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Melendez J, Stengel K, Zhou X, et al: RhoA
GTPase is dispensable for actomyosin regulation but is essential
for mitosis in primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts. J Biol Chem.
286:15132–15137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yuan TL, Wulf G, Burga L and Cantley LC:
Cell-to-cell variability in PI3K protein level regulates PI3K-AKT
pathway activity in cell populations. Curr Biol. 21:173–183. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fang J, Ding M, Yang L, Liu LZ and Jiang
BH: PI3K/PTEN/AKT signaling regulates prostate tumor angiogenesis.
Cell Signal. 19:2487–2497. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu LJ, Bagchi MK and Bagchi IC:
Attenuation of calcitonin gene expression in pregnant rat uterus
leads to a block in embryonic implantation. Endocrinology.
139:330–339. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song H, Han K and Lim H: Progesterone
supplementation extends uterine receptivity for blastocyst
implantation in mice. Reproduction. 133:487–493. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li S, Chen X, Ding Y, Liu X, Wang Y and He
J: Expression of translationally controlled tumor protein (TCTP) in
the uterus of mice of early pregnancy and its possible significance
during embryo implantation. Hum Reprod. 26:2972–2980. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nallasamy S, Li Q, Bagchi MK and Bagchi
IC: Msx homeobox genes critically regulate embryo implantation by
controlling paracrine signaling between uterine stroma and
epithelium. PLoS Genet. 8:e10025002012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Carson DD, Bagchi I, Dey SK, et al: Embryo
implantation. Dev Biol. 223:217–237. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dey SK, Lim H, Das SK, et al: Molecular
cues to implantation. Endocr Rev. 25:341–373. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ramathal CY, Bagchi IC, Taylor RN and
Bagchi MK: Endometrial decidualization: of mice and men. Semin
Reprod Med. 28:17–26. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gentilini D, Busacca M, Di Francesco S,
Vignali M, Viganò P and Di Blasio AM: PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2
signalling pathways are involved in endometrial cell migration
induced by 17beta- estradiol and growth factors. Mol Hum Reprod.
13:317–322. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Riley JK, Carayannopoulos MO, Wyman AH,
Chi M and Moley KH: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity is
critical for glucose metabolism and embryo survival in murine
blastocysts. J Biol Chem. 281:6010–6019. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Riley JK, Carayannopoulos MO, Wyman AH,
Chi M, Ratajczak CK and Moley KH: The PI3K/Akt pathway is present
and functional in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Dev Biol.
284:377–386. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Q, Zhang Y, Lu J, et al:
Embryo-uterine cross-talk during implantation: the role of Wnt
signaling. Mol Hum Reprod. 15:215–221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kawamura K, Kawamura N, Sato W, Fukuda J,
Kumagai J and Tanaka T: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes
implantation and subsequent placental development by stimulating
trophoblast cell growth and survival. Endocrinology. 150:3774–3782.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Vanhaesebroeck B, Ali K, Bilancio A,
Geering B and Foukas LC: Signalling by PI3K isoforms: insights from
gene-targeted mice. Trends Biochem Sci. 30:194–204. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Larue L and Bellacosa A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: role
of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene.
24:7443–7454. 2005.
|
|
27
|
Zuo T, Liu TM, Lan X, et al: Epigenetic
silencing mediated through activated PI3K/AKT signaling in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 71:1752–1762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu R, Hu TC, Rehemtulla A, Fearon ER and
Cho KR: Preclinical testing of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling inhibitors
in a mouse model of ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:7359–7372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fournier NM, Lee B, Banasr M, Elsayed M
and Duman RS: Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates adult
hippocampal cell proliferation through MEK/ERK- and
PI3K/Akt-dependent signaling. Neuropharmacology. 63:642–652. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hou TC, Lin JJ, Wen HC, Chen LC, Hsu SP
and Lee WS: Folic acid inhibits endothelial cell migration through
inhibiting the RhoA activity mediated by activating the folic acid
receptor/cSrc/p190RhoGAP-signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
85:376–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kato K, Yazawa T, Taki K, et al: The
inositol 5-phosphatase SHIP2 is an effector of RhoA and is involved
in cell polarity and migration. Mol Biol Cell. 23:2593–2604. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|