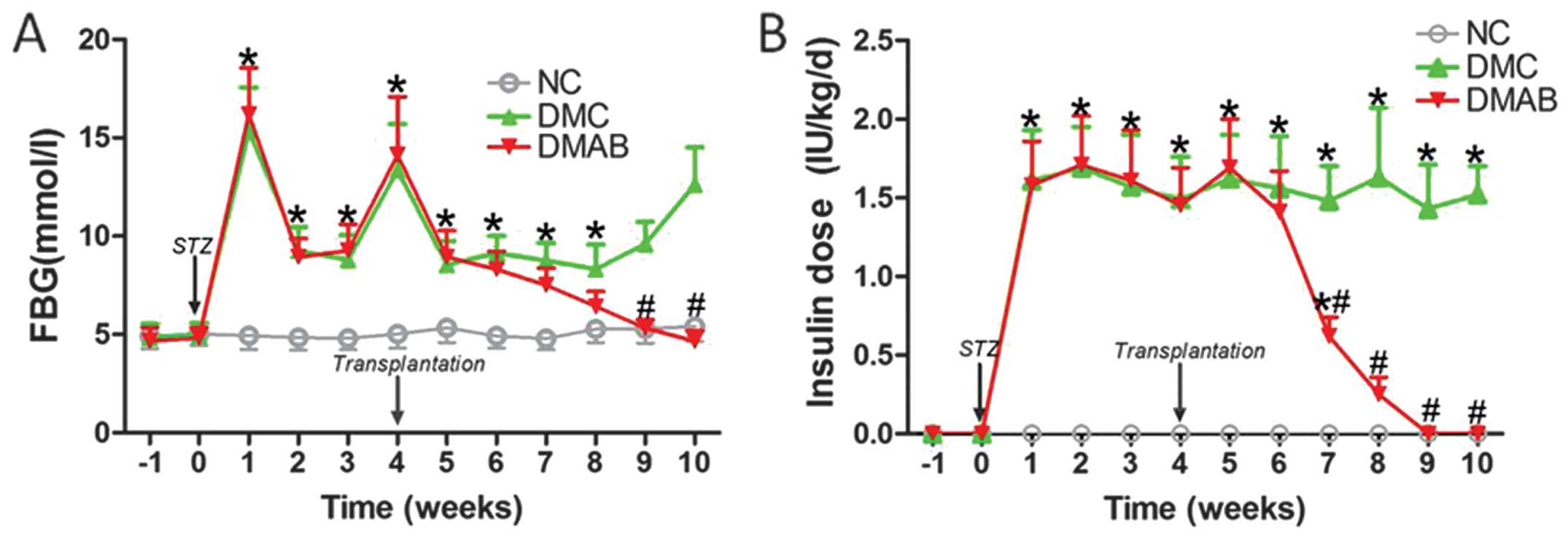
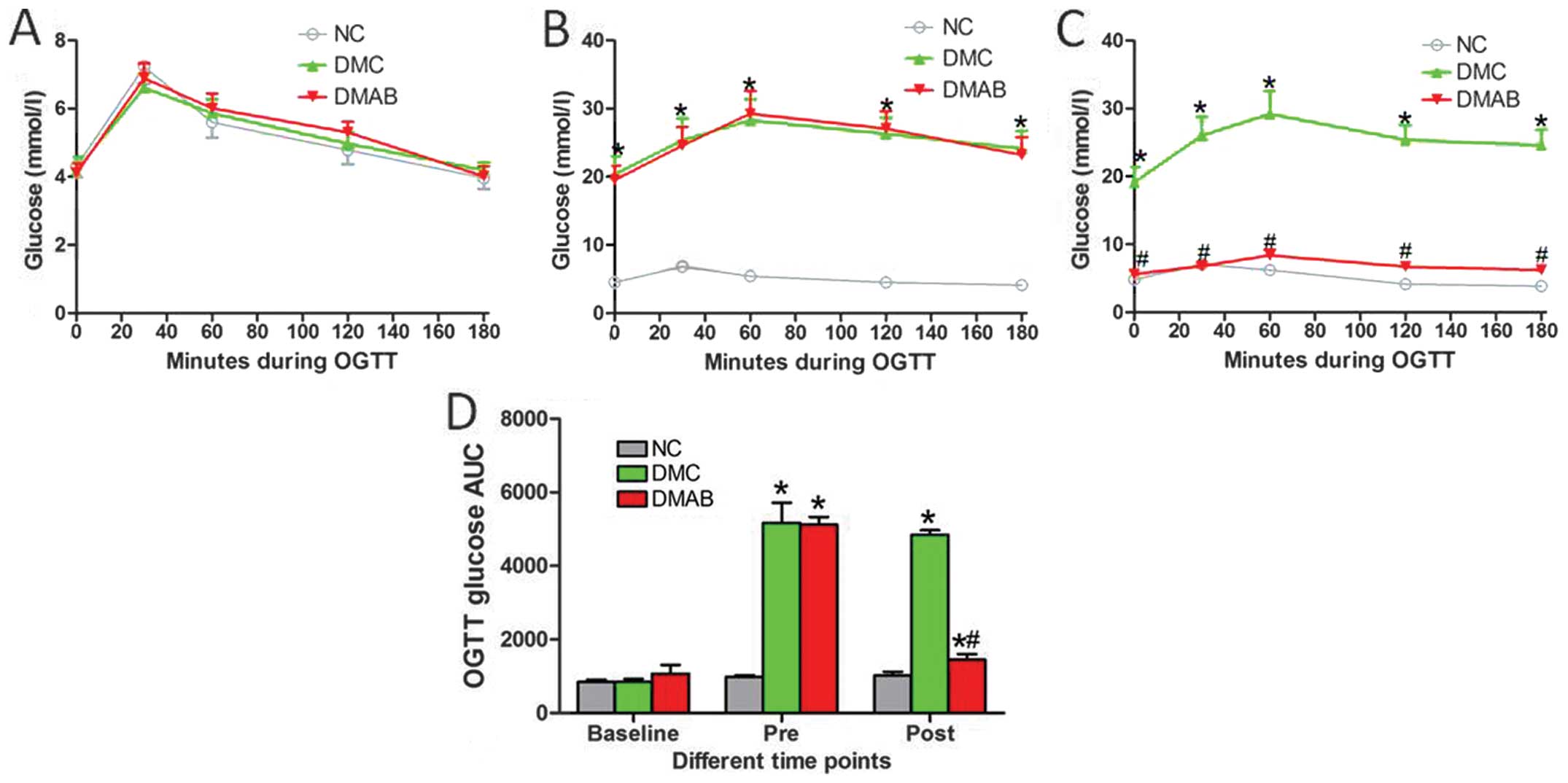
|
1
|
Haller MJ, Viener HL, Wasserfall C, Brusko
T, Atkinson MA and Schatz DA: Autologous umbilical cord blood
infusion for type 1 diabetes. Exp Hematol. 36:710–715. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Limbert C, Päth G, Jakob F and Seufert J:
Beta-cell replacement and regeneration: strategies of cell-based
therapy for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
79:389–399. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hussain MA and Theise ND: Stem-cell
therapy for diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 364:203–205. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jurewicz M, Yang S, Augello A, et al:
Congenic mesenchymal stem cell therapy reverses hyperglycemia in
experimental type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 59:3139–3147. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao Y, Jiang Z, Zhao T, et al: Reversal
of type 1 diabetes via islet β cell regeneration following immune
modulation by cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells. BMC Med.
10:32012.
|
|
6
|
Tang DQ, Cao LZ, Burkhardt BR, Xia CQ,
Litherland SA, Atkinson MA and Yang LJ: In vivo and in vitro
characterization of insulin-producing cells obtained from murine
bone marrow. Diabetes. 53:1721–1732. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ianus A, Holz GG, Theise ND and Hussain
MA: In vivo derivation of glucose-competent pancreatic endocrine
cells from bone marrow without evidence of cell fusion. J Clin
Invest. 111:843–850. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee RH, Seo MJ, Reger RL, Spees JL, Pulin
AA, Olson SD and Prockop DJ: Multipotent stromal cells from human
marrow home to and promote repair of pancreatic islets and renal
glomeruli in diabetic NOD/scid mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:17438–17443. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao X, Song L, Shen K, Wang H, Niu W and
Qin X: Transplantation of bone marrow derived cells promotes
pancreatic islet repair in diabetic mice. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 371:132–137. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hasegawa Y, Ogihara T, Yamada T, et al:
Bone marrow (BM) transplantation promotes beta-cell regeneration
after acute injury through BM cell mobilization. Endocrinology.
148:2006–2015. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Urbán VS, Kiss J, Kovács J, Gócza E, Vas
V, Monostori E and Uher F: Mesenchymal stem cells cooperate with
bone marrow cells in therapy of diabetes. Stem Cells. 26:244–253.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Couri CE and Voltarelli JC: Autologous
stem cell transplantation for early type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Autoimmunity. 41:666–672. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Larsen MO, Wilken M, Gotfredsen CF, Carr
RD, Svendsen O and Rolin B: Mild streptozotocin diabetes in the
Göttingen minipig. A novel model of moderate insulin deficiency and
diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 282:E1342–E1351. 2002.
|
|
14
|
Larsen MO, Rolin B, Wilken M, Carr RD and
Gotfredsen CF: Measurements of insulin secretory capacity and
glucose tolerance to predict pancreatic beta-cell mass in vivo in
the nicotinamide/streptozotocin Göttingen minipig, a model of
moderate insulin deficiency and diabetes. Diabetes. 52:118–123.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hara H, Lin YJ, Zhu X, et al: Safe
induction of diabetes by high-dose streptozotocin in pigs.
Pancreas. 36:31–38. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wen Y, Ouyang J, Yang R, Chen J, Liu Y,
Zhou X and Burt RK: Reversal of new-onset type 1 diabetes in mice
by syngeneic bone marrow transplantation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 374:282–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ezquer FE, Ezquer ME, Parrau DB, Carpio D,
Yañez AJ and Conget PA: Systemic administration of multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells reverts hyperglycemia and prevents
nephropathy in type 1 diabetic mice. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant.
14:631–640. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang C, Niu D, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Li F and
Gong F: Mesenchymal stroma cells improve hyperglycemia and insulin
deficiency in the diabetic porcine pancreatic microenvironment.
Cytotherapy. 10:796–805. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Olmos PR and Borzone G: Autologous
nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in newly
diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 302:624author reply
624–625. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Couri CE, Oliveira MC, Stracieri AB, et
al: C-peptide levels and insulin independence following autologous
nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in newly
diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 301:1573–1579. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Scolding N, Marks D and Rice C: Autologous
mesenchymal bone marrow stem cells: practical considerations. J
Neurol Sci. 265:111–115. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamout B, Hourani R, Salti H, et al: Bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with
multiple sclerosis: a pilot study. J Neuroimmunol. 227:185–189.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jirák D1, Kríz J, Herynek V, et al: MRI of
transplanted pancreatic islets. Magn Reson Med. 52:1228–1233.
2004.
|
|
24
|
Neri M, Maderna C, Cavazzin C, et al:
Efficient in vitro labeling of human neural precursor cells with
superparamagnetic iron oxide particles: relevance for in vivo cell
tracking. Stem Cells. 26:505–516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Amsalem Y, Mardor Y, Feinberg MS, et al:
Iron-oxide labeling and outcome of transplanted mesenchymal stem
cells in the infarcted myocardium. Circulation. 116(Suppl 11):
I38–I45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Murray HE, Paget MB, Bailey CJ and Downing
R: Sustained insulin secretory response in human islets co-cultured
with pancreatic duct-derived epithelial cells within a rotational
cell culture system. Diabetologia. 52:477–485. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lipsett M, Aikin R, Castellarin M, Hanley
S, Jamal AM, Laganiere S and Rosenberg L: Islet neogenesis: a
potential therapeutic tool in type 1 diabetes. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 38:498–503. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jeong JO, Kim MO, Kim H, et al: Dual
angiogenic and neurotrophic effects of bone marrow-derived
endothelial progenitor cells on diabetic neuropathy. Circulation.
119:699–708. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shibata T, Naruse K, Kamiya H, et al:
Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
improves diabetic polyneuropathy in rats. Diabetes. 57:3099–3107.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kin T, Korbutt GS, Kobayashi T, Dufour JM
and Rajotte RV: Reversal of diabetes in pancreatectomized pigs
after transplantation of neonatal porcine islets. Diabetes.
54:1032–1039. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tang KX, Yan JH, Shen YF, et al: Tracing
type 1 diabetic Tibet miniature pig’s bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells in vitro by magnetic resonance imaging. J Diabetes.
6:123–131. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Layton DS, Strom AD, O’Neil TE, et al:
Development of an anti-porcine CD34 monoclonal antibody that
identifies hematopoietic stem cells. Exp Hematol. 35:171–178. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nir T, Melton DA and Dor Y: Recovery from
diabetes in mice by beta cell regeneration. J Clin Invest.
117:2553–2561. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alvarez SS, Jimenez LM, Murillo AZ, et al:
A new approach for bone marrow-derived stem cells intrapancreatic
autotransplantation in diabetic rats. Microsurgery. 26:539–542.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Frank JA, Miller BR, Arbab AS, et al:
Clinically applicable labeling of mammalian and stem cells by
combining superparamagnetic iron oxides and transfection agents.
Radiology. 228:480–487. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Barnett BP, Arepally A, Karmarkar PV, et
al: Magnetic resonance-guided, real-time targeted delivery and
imaging of magnetocapsules immunoprotecting pancreatic islet cells.
Nat Med. 13:986–991. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|