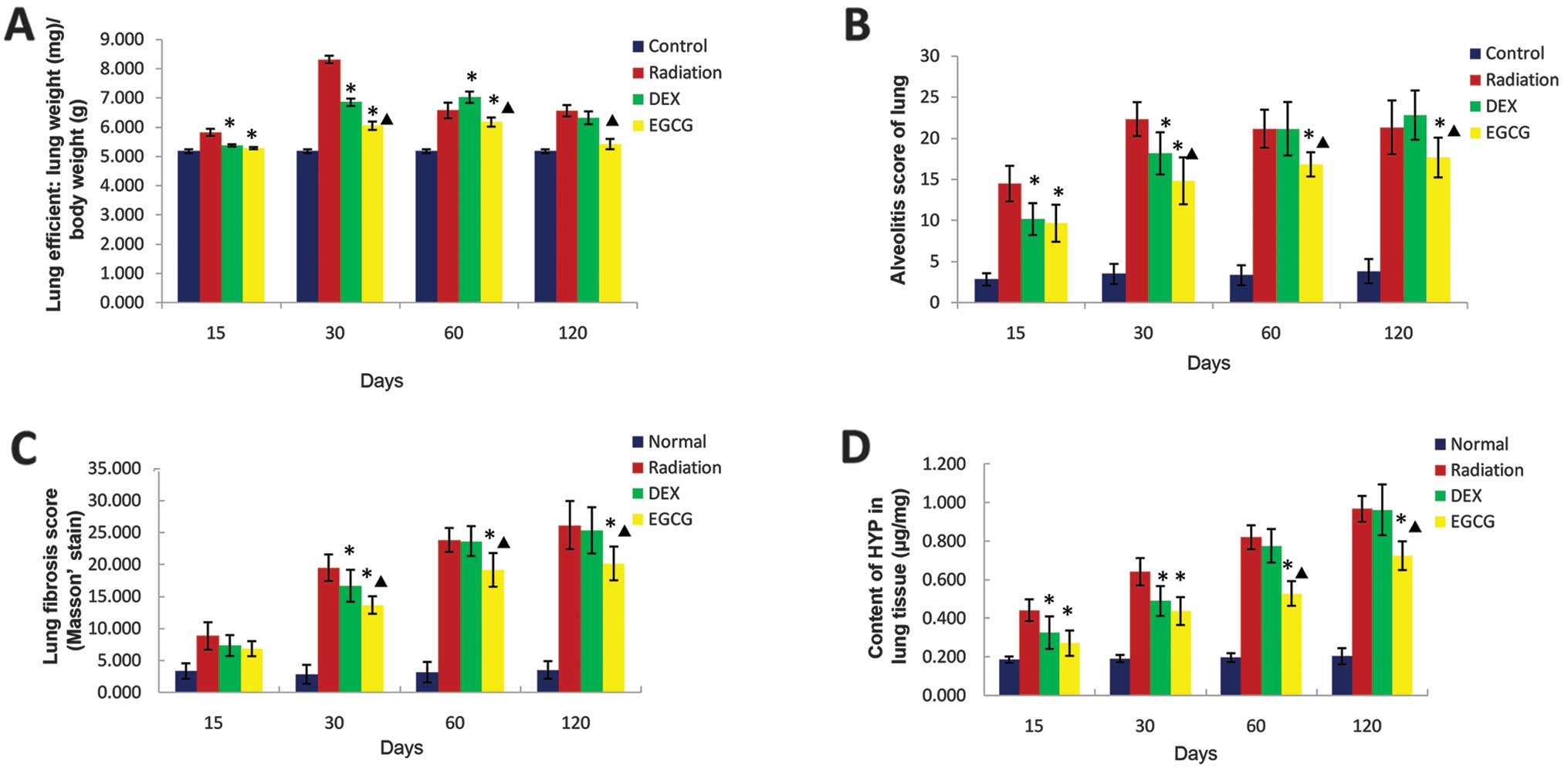
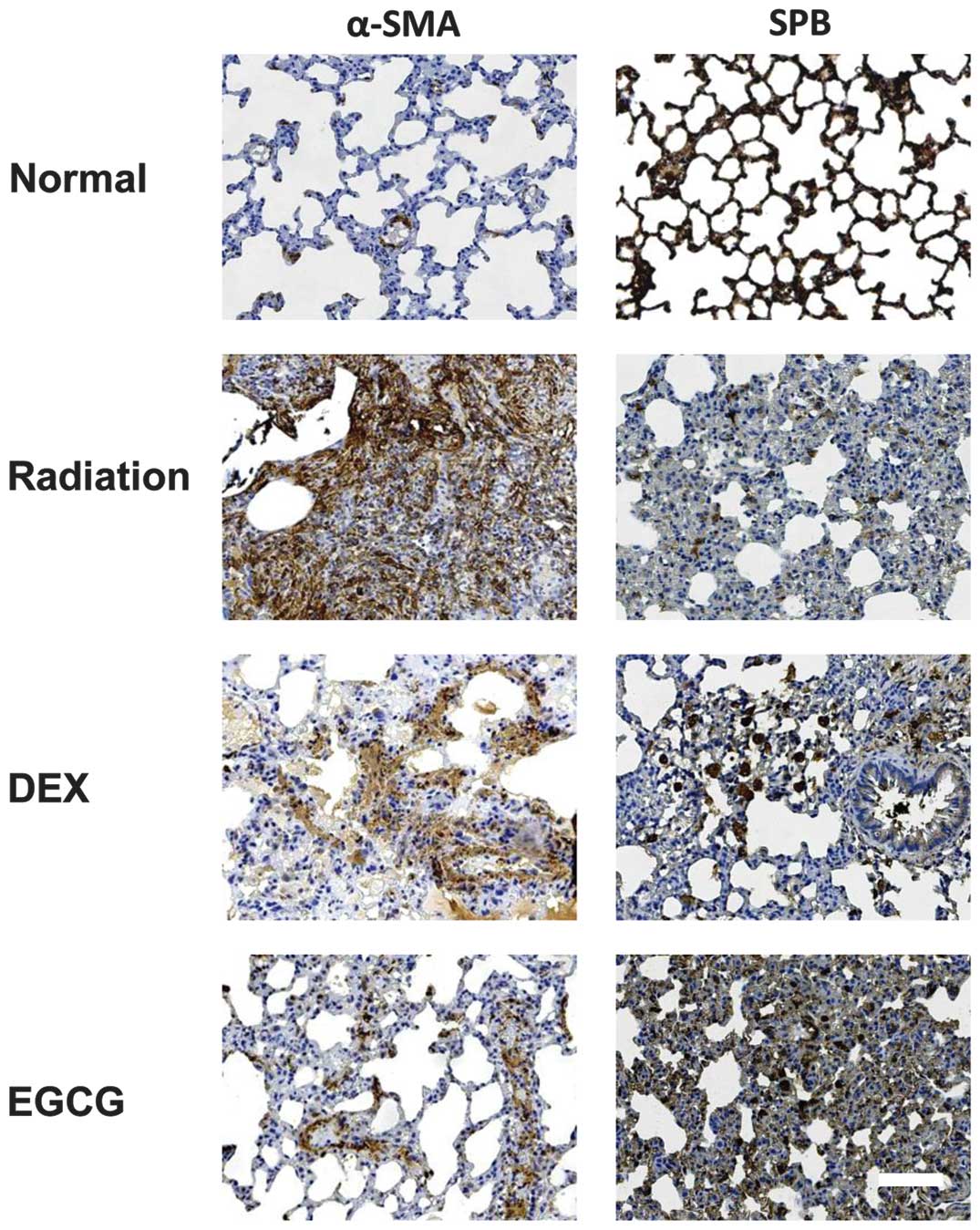
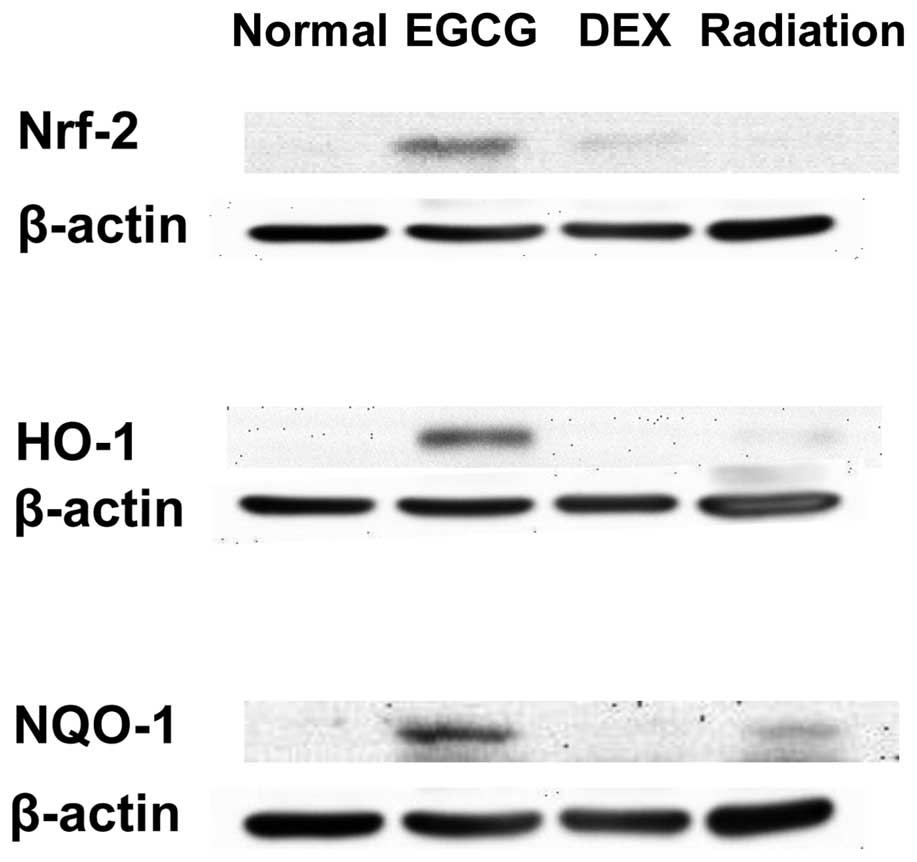
|
1
|
Almeida C, Nagarajan D, Tian J, et al: The
role of alveolar epithelium in radiation-induced lung injury. PLoS
One. 8:e536282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Epperly MW, Guo H, Gretton JE and
Greenberger JS: Bone marrow origin of myofibroblasts in irradiation
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 29:213–224. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matsuo Y, Shibuya K, Nakamura M, et al:
Dose-volume metrics associated with radiation pneumonitis after
stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung cancer. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 83:e545–e549. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Minor GI, Yashar CM, Spanos WJ Jr, et al:
The relationship of radiation pneumonitis to treated lung volume in
breast conservation therapy. Breast J. 12:48–52. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rosenzweig KE, Zauderer MG, Laser B, et
al: Pleural intensity-modulated radiotherapy for malignant pleural
mesothelioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 83:1278–1283. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu HW, Seftel MD, Rubinger M, et al:
Total body irradiation compared with BEAM: long-term outcomes of
peripheral blood autologous stem cell transplantation for
non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 78:513–520.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Rabbani ZN, Jackson IL
and Vujaskovic Z: Oxidative stress mediates radiation lung injury
by inducing apoptosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 83:740–748.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mak JC: Potential role of green tea
catechins in various disease therapies: progress and promise. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 39:265–273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li CP, Yao J, Tao ZF, Li XM, Jiang Q and
Yan B: Epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG) regulates autophagy in human
retinal pigment epithelial cells: a potential role for reducing UVB
light-induced retinal damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
438:739–745. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Donà M, Dell’Aica I, Calabrese F, et al:
Neutrophil restraint by green tea: inhibition of inflammation,
associated angiogenesis, and pulmonary fibrosis. J Immunol.
170:4335–4341. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sriram N, Kalayarasan S and Sudhandiran G:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate exhibits anti-fibrotic effect by
attenuating bleomycin-induced glycoconjugates, lysosomal hydrolases
and ultrastructural changes in rat model pulmonary fibrosis. Chem
Biol Interact. 180:271–280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sriram N, Kalayarasan S and Sudhandiran G:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate augments antioxidant activities and
inhibits inflammation during bleomycin-induced experimental
pulmonary fibrosis through Nrf2-Keap1 signaling. Pulm Pharmacol
Ther. 22:221–236. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sriram N, Kalayarasan S and Sudhandiran G:
Enhancement of antioxidant defense system by
epigallocatechin-3-gallate during bleomycin induced experimental
pulmonary fibrosis. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:1306–1311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tipoe GL, Leung TM, Liong EC, Lau TY, Fung
ML and Nanji AA: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces liver
inflammation, oxidative stress and fibrosis in carbon tetrachloride
(CCl4)-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicology. 273:45–52. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
de Vries HE, Witte M, Hondius D, et al:
Nrf2-induced antioxidant protection: a promising target to
counteract ROS-mediated damage in neurodegenerative disease? Free
Radic Biol Med. 45:1375–1383. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Dong XW, Wang JN, et al:
PEP-1-CAT-transduced mesenchymal stem cells acquire an enhanced
viability and promote ischemia-induced angiogenesis. PLoS One.
7:e525372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang YE, Fu SZ, Li XQ, et al: PEP-1-SOD1
protects brain from ischemic insult following asphyxial cardiac
arrest in rats. Resuscitation. 82:1081–1086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Williams JP, Johnston CJ and Finkelstein
JN: Treatment for radiation-induced pulmonary late effects: spoiled
for choice or looking in the wrong direction? Curr Drug Targets.
11:1386–1394. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rizvi M, Pathak D, Freedman JE and
Chakrabarti S: CD40-CD40 ligand interactions in oxidative stress,
inflammation and vascular disease. Trends Mol Med. 14:530–538.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mikkelsen RB and Wardman P: Biological
chemistry of reactive oxygen and nitrogen and radiation-induced
signal transduction mechanisms. Oncogene. 22:5734–5754. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hügel HM and Jackson N: Redox chemistry of
green tea polyphenols: therapeutic benefits in neurodegenerative
diseases. Mini Rev Med Chem. 12:380–387. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Del Rio D, Stewart AJ and Pellegrini N: A
review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and
biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.
15:316–328. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lefaix JL, Delanian S, Leplat JJ, et al:
Successful treatment of radiation-induced fibrosis using Cu/Zn-SOD
and Mn-SOD: an experimental study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
35:305–312. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vujaskovic Z, Batinic-Haberle I, Rabbani
ZN, et al: A small molecular weight catalytic metalloporphyrin
antioxidant with superoxide dismutase (SOD) mimetic properties
protects lungs from radiation-induced injury. Free Radic Biol Med.
33:857–863. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schaue D, Kachikwu EL and McBride WH:
Cytokines in radiobiological responses: a review. Radiat Res.
178:505–523. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martin M, Lefaix J and Delanian S:
TGF-beta1 and radiation fibrosis: a master switch and a specific
therapeutic target? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 47:277–290. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang J, Qiao XY, Lu FH, et al: TGF-beta1
in serum and induced sputum for predicting radiation pneumonitis in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer after radiotherapy. Chin J
Cancer. 29:325–329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dong XR, Wang JN, Liu L, et al: Modulation
of radiation-induced tumour necrosis factor-α and transforming
growth factor β1 expression in the lung tissue by Shengqi Fuzheng
injection. Mol Med Rep. 3:621–627. 2010.
|
|
30
|
Wynn TA: Integrating mechanisms of
pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp Med. 208:1339–1350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Denis M: Interleukin-6 in mouse
hypersensitivity pneumonitis: changes in lung free cells following
depletion of endogenous IL-6 or direct administration of IL-6. J
Leukoc Biol. 52:197–201. 1992.
|
|
32
|
Zdanov A: Structural features of the
interleukin-10 family of cytokines. Curr Pharm Des. 10:3873–3884.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alhamad EH, Cal JG, Shakoor Z, Almogren A
and Alboukai AA: Cytokine gene polymorphisms and serum cytokine
levels in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Med
Genet. 14:662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Barbarin V, Xing Z, Delos M, Lison D and
Huaux F: Pulmonary overexpression of IL-10 augments lung fibrosis
and Th2 responses induced by silica particles. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 288:L841–L848. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bae HB, Li M, Kim JP, et al: The effect of
epigallocatechin gallate on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury in a murine model. Inflammation. 33:82–91. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun Q, Zheng Y, Zhang X, et al: Novel
immunoregulatory properties of EGCG on reducing inflammation in
EAE. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 18:332–342. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sahin K, Tuzcu M, Gencoglu H, et al:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate activates Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in
cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Life Sci. 87:240–245.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|