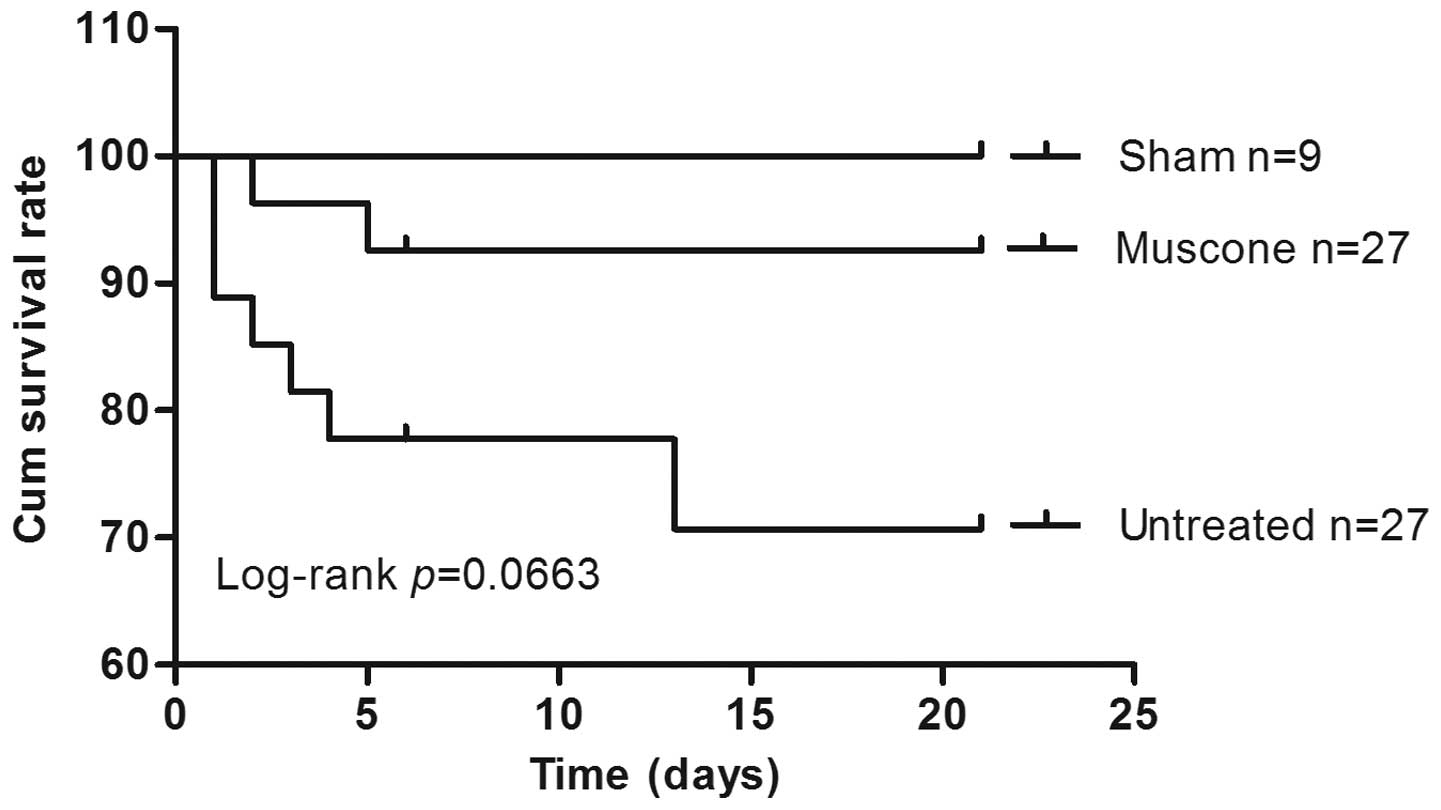
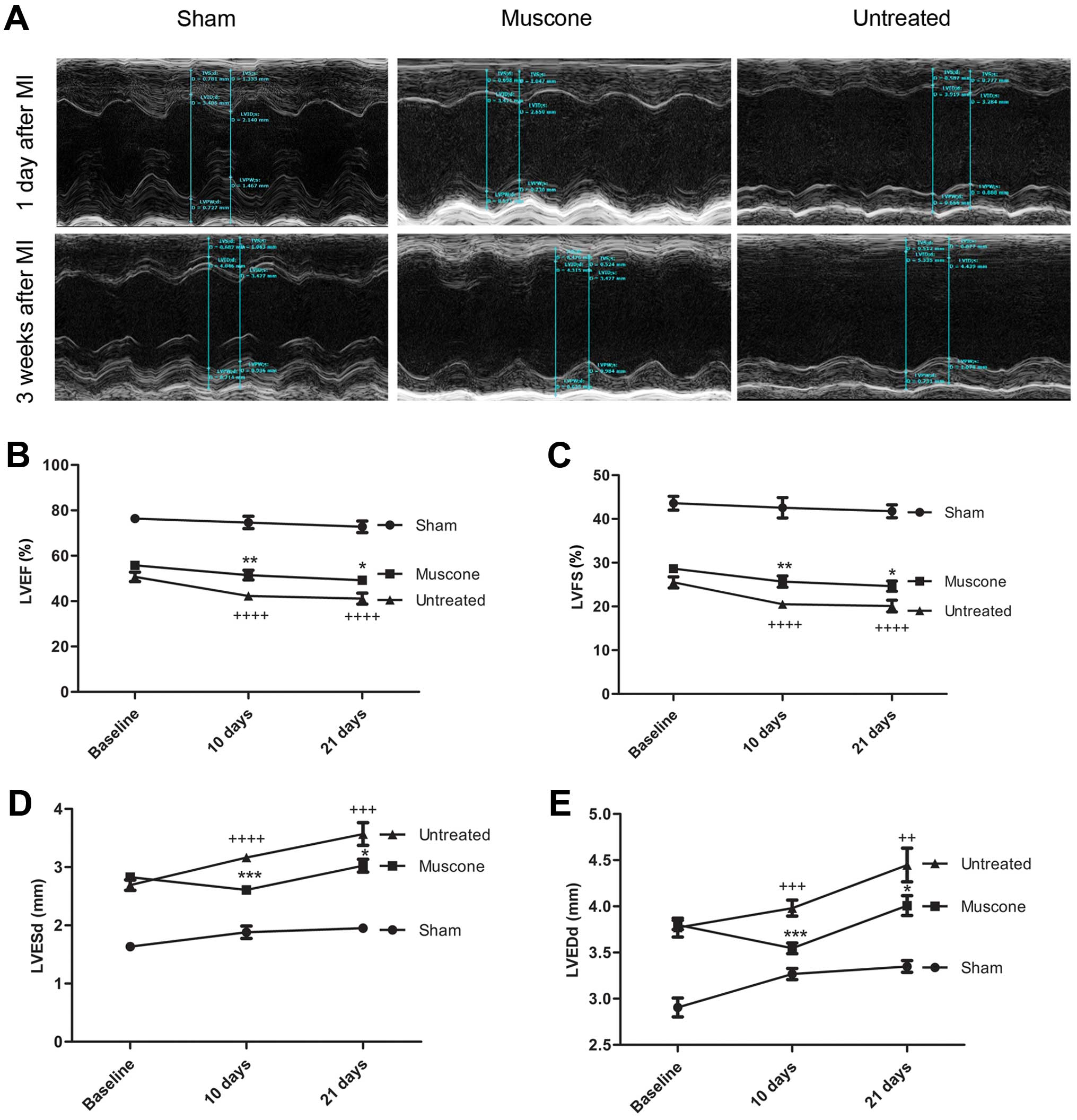
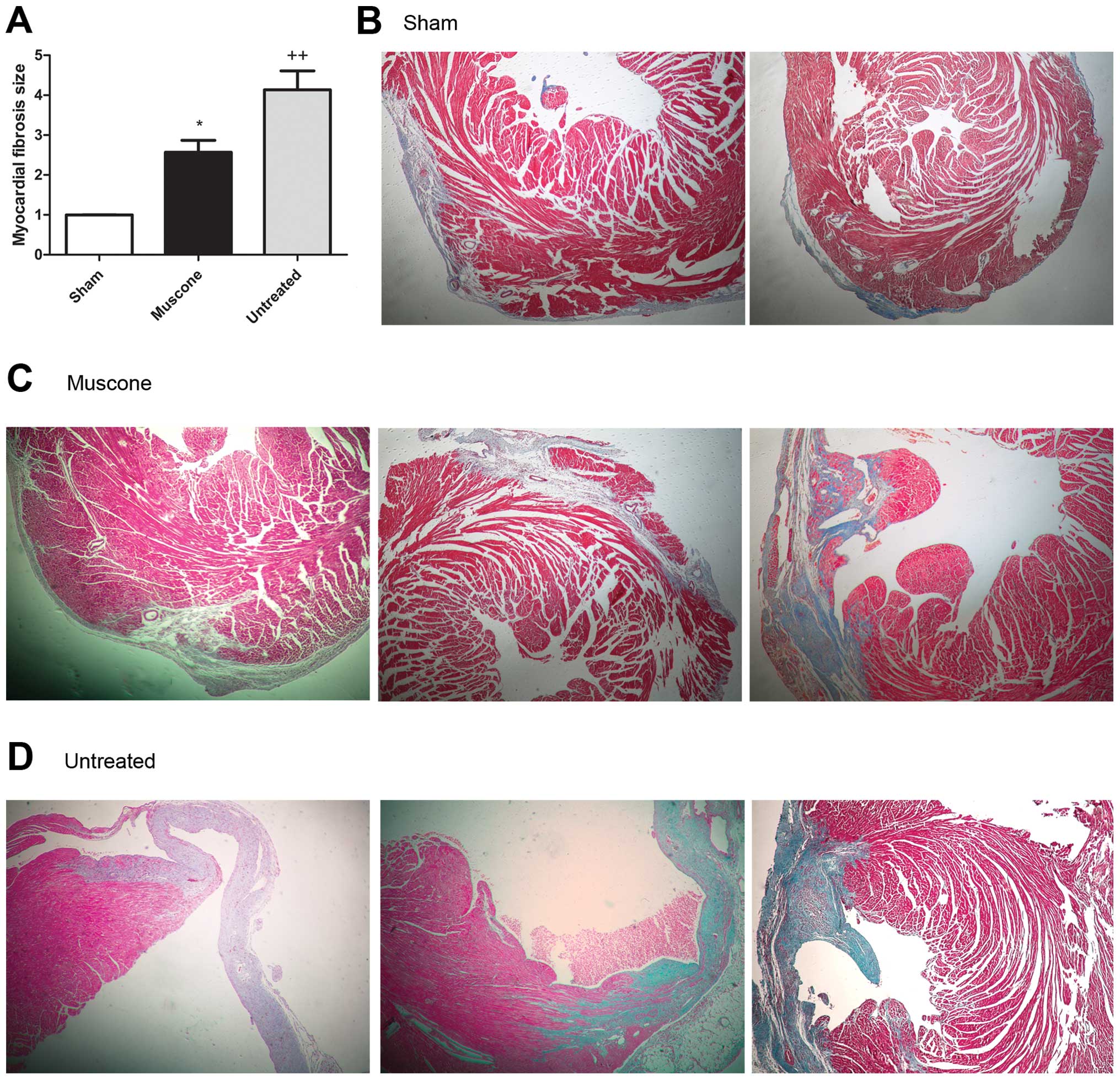
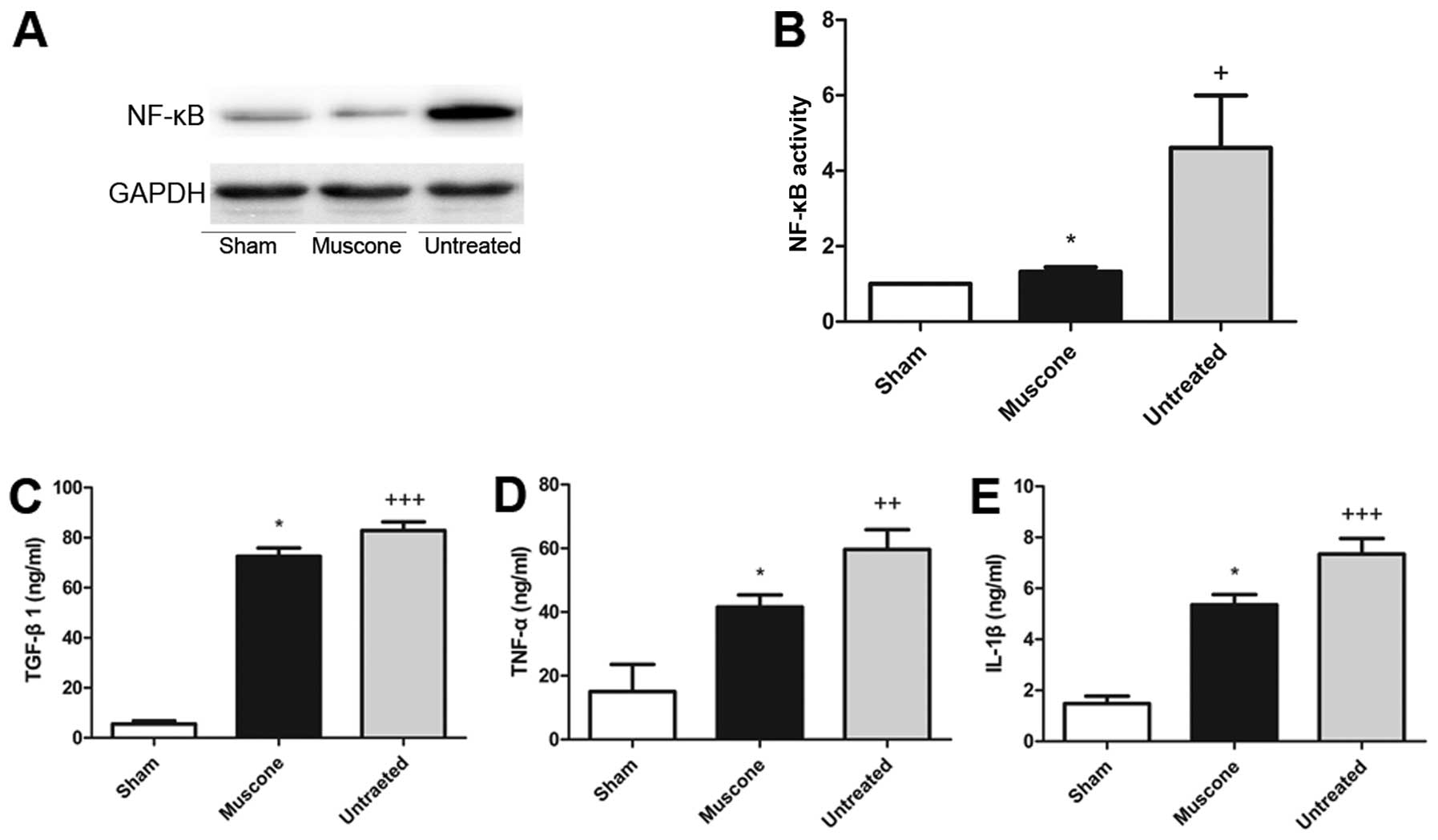
|
1
|
Lin DL, Chang HC and Huang SH:
Characterization of allegedly musk-containing medicinal products in
Taiwan. J Forensic Sci. 49:1187–1193. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco
S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ,
Huffman MD, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH,
Lisabeth LD, Magid D, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK,
Mohler ER, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Nichol G, Paynter NP, Schreiner
PJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D and
Turner MB: Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013 update: a
report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
127:e6–e245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hung J, Teng TH, Finn J, Knuiman M, Briffa
T, Stewart S, Sanfilippo FM, Ridout S and Hobbs M: Trends from 1996
to 2007 in incidence and mortality outcomes of heart failure after
acute myocardial infarction: a population-based study of 20,812
patients with first acute myocardial infarction in Western
Australia. J Am Heart Assoc. 2:e0001722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun Y, Zhang JQ, Zhang J and Lamparter S:
Cardiac remodeling by fibrous tissue after infarction in rats. J
Lab Clin Med. 135:316–323. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
See F, Kompa A, Martin J, Lewis DA and
Krum H: Fibrosis as a therapeutic target post-myocardial
infarction. Curr Pharm Des. 11:477–487. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tucci PJ: Pathophysiological
characteristics of the post-myocardial infarction heart failure
model in rats. Arq Bras Cardiol. 96:420–424. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rohde LE, Ducharme A, Arroyo LH, Aikawa M,
Sukhova GH, Lopez-Anaya A, McClure KF, Mitchell PG, Libby P and Lee
RT: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition attenuates early left
ventricular enlargement after experimental myocardial infarction in
mice. Circulation. 99:3063–3070. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lindsey ML, Mann DL, Entman ML and Spinale
FG: Extracellular matrix remodeling following myocardial injury.
Ann Med. 35:316–326. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan SK, Zhang WD, Liu RH and Zhan YC:
Chemical fingerprinting of Shexiang Baoxin Pill and simultaneous
determination of its major constituents by HPLC with evaporative
light scattering detection and electrospray mass spectrometric
detection. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 54:1058–1062. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shen W, Fan WH and Shi HM: Effects of
shexiang baoxin pill on angiogenesis in atherosclerosis plaque and
ischemic myocardium. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
30:1284–1287. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Fan X, Shi M, Wang Y, Liang Q and Luo G:
Transcriptional profiling analysis of HMP-treated rats with
experimentally induced myocardial infarction. J Ethnopharmacol.
137:199–204. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu DJ, Hong HS and Jiang Q: Effect of
shexiang baoxin pill in alleviating myocardial fibrosis in
spontaneous hypertensive rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
25:350–353. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Cai YM, He Y, Qiu T, Zou J, Sun DP, Peng
QH, Jia RX and Zhao HR: Research on frequency of application with
modern Chinese herbal medicine. Chin J Integr Med. 17:64–70. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang LJ, Luo XP and Wang Y: Evaluation on
tolerability and safety of long-term administration with shexiang
baoxin pill in patients with coronary heart disease of stable
angina pectoris. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 28:399–401.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Wang S, Zheng Z, Weng Y, Yu Y, Zhang D,
Fan W, Dai R and Hu Z: Angiogenesis and anti-angiogenesis activity
of Chinese medicinal herbal extracts. Life Sci. 74:2467–2478. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiang L, Jiang P, Zhan C, Chen Z, Liu X,
Huang X, Wang S, Hu Y, Zhang W and Liu R: The serum metabolomic
study of intervention effects of the traditional Chinese medicine
Shexiang Baoxin Pill and a multi-component medicine polypill in the
treatment of myocardial infarction in rats. Mol Biosyst.
8:2434–2442. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sun R, Zhang ZP, Huang W, Lv LP and Ren
HY: Protective effects of muskone on rats with complete cerebral
ischemia. Trad Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol. 20:197–200. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Wei G, Chen DF, Lai XP, Liu DH, Deng RD,
Zhou JH, Zhang SX, Li YW, Li H and Zhang QD: Muscone exerts
neuroprotection in an experimental model of stroke via inhibition
of the fas pathway. Nat Prod Commun. 7:1069–1074. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tanaka E, Funae Y, Imaoka S and Misawa S:
Characterization of liver microsomal cytochrome P450 from rats
treated with muscone (3-methylcyclopentadecanone). Biochem
Pharmacol. 41:472–473. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu Q, Li H, Wu Y, Shen W, Zeng L, Cheng H
and He L: Protective effects of muscone on ischemia-reperfusion
injury in cardiac myocytes. J Ethnopharmacol. 138:34–39. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hori M and Nishida K: Oxidative stress and
left ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction.
Cardiovasc Res. 81:457–464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vilahur G, Juan-Babot O, Pena E, Onate B,
Casani L and Badimon L: Molecular and cellular mechanisms involved
in cardiac remodeling after acute myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 50:522–533. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang C, Talukder MA, Varadharaj S,
Velayutham M and Zweier JL: Early ischaemic preconditioning
requires Akt- and PKA-mediated activation of eNOS via serine1176
phosphorylation. Cardiovasc Res. 97:33–43. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen LL, Zhu TB, Yin H, Huang J, Wang LS,
Cao KJ and Yang ZJ: Inhibition of MAPK signaling by eNOS gene
transfer improves ventricular remodeling after myocardial
infarction through reduction of inflammation. Mol Biol Rep.
37:3067–3072. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu JX, Liang C and Ren YS: Effects of
shexiang baoxin pill on function and nitric oxide secretion of
endothelial progenitor cells. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
29:511–513. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Salto-Tellez M, Yung Lim S, El-Oakley RM,
Tang TP, Za AL and Lim SK: Myocardial infarction in the C57BL/6J
mouse: a quantifiable and highly reproducible experimental model.
Cardiovasc Pathol. 13:91–97. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liang H and Luo BY: The study of muscone
on attenuating excitotoxicity during acute cerebral ischemia. Zhong
Yao Yao Li Yu Lin Chuang. 21:12–13. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Vivar R, Humeres C, Ayala P, Olmedo I,
Catalan M, Garcia L, Lavandero S and Diaz-Araya G: TGF-beta1
prevents simulated ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac fibroblast
apoptosis by activation of both canonical and non-canonical
signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832.754–762.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gu Q, Yang XP, Bonde P, DiPaula A,
Fox-Talbot K and Becker LC: Inhibition of TNF-alpha reduces
myocardial injury and proinflammatory pathways following
ischemia-reperfusion in the dog. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
48:320–328. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Siwik DA, Chang DL and Colucci WS:
Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha decrease collagen
synthesis and increase matrix metalloproteinase activity in cardiac
fibroblasts in vitro. Circ Res. 86:1259–1265. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Stephenson D, Yin T, Smalstig EB, Hsu MA,
Panetta J, Little S and Clemens J: Transcription factor nuclear
factor-kappa B is activated in neurons after focal cerebral
ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 20:592–603. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ogawa K, Chen F, Kuang C and Chen Y:
Suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 transcription by
transforming growth factor-beta is mediated by a nuclear
factor-kappaB site. Biochem J. 381:413–422. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hirotani S, Otsu K, Nishida K, Higuchi Y,
Morita T, Nakayama H, Yamaguchi O, Mano T, Matsumura Y, Ueno H,
Tada M and Hori M: Involvement of nuclear factor-kappaB and
apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in G-protein-coupled receptor
agonist-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circulation.
105:509–515. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Morishita R, Sugimoto T, Aoki M, Kida I,
Tomita N, Moriguchi A, Maeda K, Sawa Y, Kaneda Y, Higaki J and
Ogihara T: In vivo transfection of cis element ‘decoy’ against
nuclear factor-kappaB binding site prevents myocardial infarction.
Nat Med. 3:894–899. 1997.
|
|
35
|
Elsasser A, Vogt AM, Nef H, Kostin S,
Mollmann H, Skwara W, Bode C, Hamm C and Schaper J: Human
hibernating myocardium is jeopardized by apoptotic and autophagic
cell death. J Am Coll Cardiol. 43:2191–2199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Crow MT, Mani K, Nam YJ and Kitsis RN: The
mitochondrial death pathway and cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circ
Res. 95:957–970. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Grimm S, Bauer MK, Baeuerle PA and
Schulze-Osthoff K: Bcl-2 down-regulates the activity of
transcription factor NF-kappaB induced upon apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
134:13–23. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Syed FM, Hahn HS, Odley A, Guo Y, Vallejo
JG, Lynch RA, Mann DL, Bolli R and Dorn GW: Proapoptotic effects of
caspase-1/interleukin-converting enzyme dominate in myocardial
ischemia. Circ Res. 96:1103–1109. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sharma S, Singh M and Sharma PL: Mechanism
of hyperhomocysteinemia-induced vascular endothelium dysfunction -
possible dysregulation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase and its
downstream phosphoinositide dependent kinase and protein kinase B.
Eur J Pharmacol. 721:365–372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yasuda S, Kobayashi H, Iwasa M, Kawamura
I, Sumi S, Narentuoya B, Yamaki T, Ushikoshi H, Nishigaki K,
Nagashima K, Takemura G, Fujiwara T, Fujiwara H and Minatoguchi S:
Antidiabetic drug pioglitazone protects the heart via activation of
PPAR-gamma receptors, PI3-kinase, Akt, and eNOS pathway in a rabbit
model of myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
296:H1558–H1565. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fulton D, Gratton JP, McCabe TJ, Fontana
J, Fujio Y, Walsh K, Franke TF, Papapetropoulos A and Sessa WC:
Regulation of endothelium-derived nitric oxide production by the
protein kinase Akt. Nature. 399:597–601. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bell RM and Yellon DM: Bradykinin limits
infarction when administered as an adjunct to reperfusion in mouse
heart: the role of PI3K, Akt and eNOS. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
35:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tsutsumi YM, Tsutsumi R, Mawatari K,
Nakaya Y, Kinoshita M, Tanaka K and Oshita S: Compound K, a
metabolite of ginsenosides, induces cardiac protection mediated
nitric oxide via Akt/PI3K pathway. Life Sci. 88:725–729. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Balakumar P, Kathuria S, Taneja G, Kalra S
and Mahadevan N: Is targeting eNOS a key mechanistic insight of
cardiovascular defensive potentials of statins? J Mol Cell Cardiol.
52:83–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao X, Lu X and Feng Q: Deficiency in
endothelial nitric oxide synthase impairs myocardial angiogenesis.
American journal of physiology Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
283:H2371–H2378. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|