|
1
|
Gorlin RJ and Goltz RW: Multiple nevoid
basal-cell epithelioma, jaw cysts and bifid rib: a syndrome. N Engl
J Med. 262:908–912. 1960. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gorlin RJ: Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma
syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore). 66:98–113. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gorlin RJ: Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma
syndrome. Dermatol Clin. 13:113–125. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lo Muzio L: Nevoid basal cell carcinoma
syndrome (Gorlin syndrome). Orphanet J Rare Dis. 3:322008.
|
|
5
|
Ortega García de Amezaga A, García Arregui
O, Zepeda Nuño S, Acha Sagredo A and Aguirre Urizar JM:
Gorlin-Goltz syndrome: clinicopathologic aspects. Med Oral Patol
Oral Cir Bucal. 13:E338–E343. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kiran NK, Tilak Raj TN, Mukunda KS and
Rajashekar Reddy V: Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
(Gorlin-Goltz syndrome). Contemp Clin Dent. 3:514–518. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barreto DC, Gomez RS, Bale AE, Boson WL
and De Marco L: PTCH gene mutations in odontogenic keratocysts. J
Dent Res. 79:1418–1422. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lindström E, Shimokawa T, Toftgård R and
Zaphiropoulos PG: PTCH mutations: distribution and analyses. Hum
Mutat. 27:215–219. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yuan JW, Li TJ, Zhong HH and Zhao HS: PTCH
gene mutations in odontogenic keratocysts. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi
Xue Za Zhi. 41:41–44. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Li TJ, Yuan JW, Gu XM, Sun LS and Zhao HS:
PTCH germline mutations in Chinese nevoid basal cell carcinoma
syndrome patients. Oral Dis. 14:174–179. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pan S, Xu LL, Sun LS and Li TJ:
Identification of known and novel PTCH mutations in both syndromic
and non-syndromic keratocystic odontogenic tumors. Int J Oral Sci.
1:34–38. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hahn H, Christiansen J, Wicking C, et al:
A mammalian patched homolog is expressed in target tissues of sonic
hedgehog and maps to a region associated with developmental
abnormalities. J Biol Chem. 271:12125–12128. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, et al:
Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus
syndrome. Science. 272:1668–1671. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wicking C, Shanley S, Smyth L, et al: Most
germ-line mutations in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
lead to a premature termination of the PATCHED protein, and no
genotype-phenotype correlations are evident. Am J Hum Genet.
60:21–26. 1997.
|
|
15
|
Stone DM, Hynes M, Armanini M, et al: The
tumour-suppressor gene patched encodes a candidate receptor for
Sonic hedgehog. Nature. 384:129–134. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jenkins D: Hedgehog signalling: emerging
evidence for non-canonical pathways. Cell Signal. 21:1023–1034.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo YY, Zhang JY, Li XF, Luo HY, Chen F
and Li TJ: PTCH1 gene mutations in keratocystic odontogenic tumors:
a study of 43 Chinese patients and a systematic review. PLoS ONE.
8:e773052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun LS, Li XF and Li TJ: PTCH1 and SMO
gene alterations in keratocystic odontogenic tumors. J Dent Res.
87:575–579. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan S, Dong Q, Sun LS and Li TJ:
Mechanisms of inactivation of PTCH1 gene in nevoid basal cell
carcinoma syndrome: modification of the two-hit hypothesis. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:442–450. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li TJ: Odontogenic keratocyst: A cyst, or
a cystic neoplasm? J Dent Res. 90:133–142. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kalderon D: Transducing the hedgehog
signal. Cell. 103:371–374. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Evangelista M, Tian H and de Sauvage FJ:
The hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
12:5924–5928. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nurse P: Universal control mechanism
regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 344:503–508. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ducommun B, Brambilla P, Félix MA, Franza
BR Jr, Karsenti E and Draetta G: cdc2 phosphorylation is required
for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 10:3311–3319.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Heitlinger E, Peter M, Häner M, Lustig A,
Aebi U and Nigg A: Expression of chickenlamin B2 in Escherichia
coli: characterization of its structure, assembly, and molecular
interactions. J Cell Biol. 113:485–495. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pines J and Hunter T: The differential
localization of human cyclins A and B is due to a cytoplasmic
retention signal in cyclin B. EMBO J. 13:3772–3781. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Meyer AN and Donoghue DJ:
Requirement for phosphorylation of cyclin B1 for Xenopus
oocyte maturation. Mol Biol Cell. 6:1111–1124. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Meyer AN and Donoghue DJ: Nuclear
localization of cyclin B1 mediates its biological activity and is
regulated by phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:502–507.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Borgne A, Ostvold AC, Flament S and Meijer
L: Intra-M phase-promoting factor phosphorylation of cyclin B at
the prophase/metaphase transition. J Biol Chem. 274:11977–11986.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hagting A, Jackman M, Simpson K and Pines
J: Translocation of cyclin B1 to the nucleus at prophase requires a
phosphorylation-dependent nuclear import signal. Curr Biol.
9:680–689. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Barnes EA, Kong M, Ollendorff V and
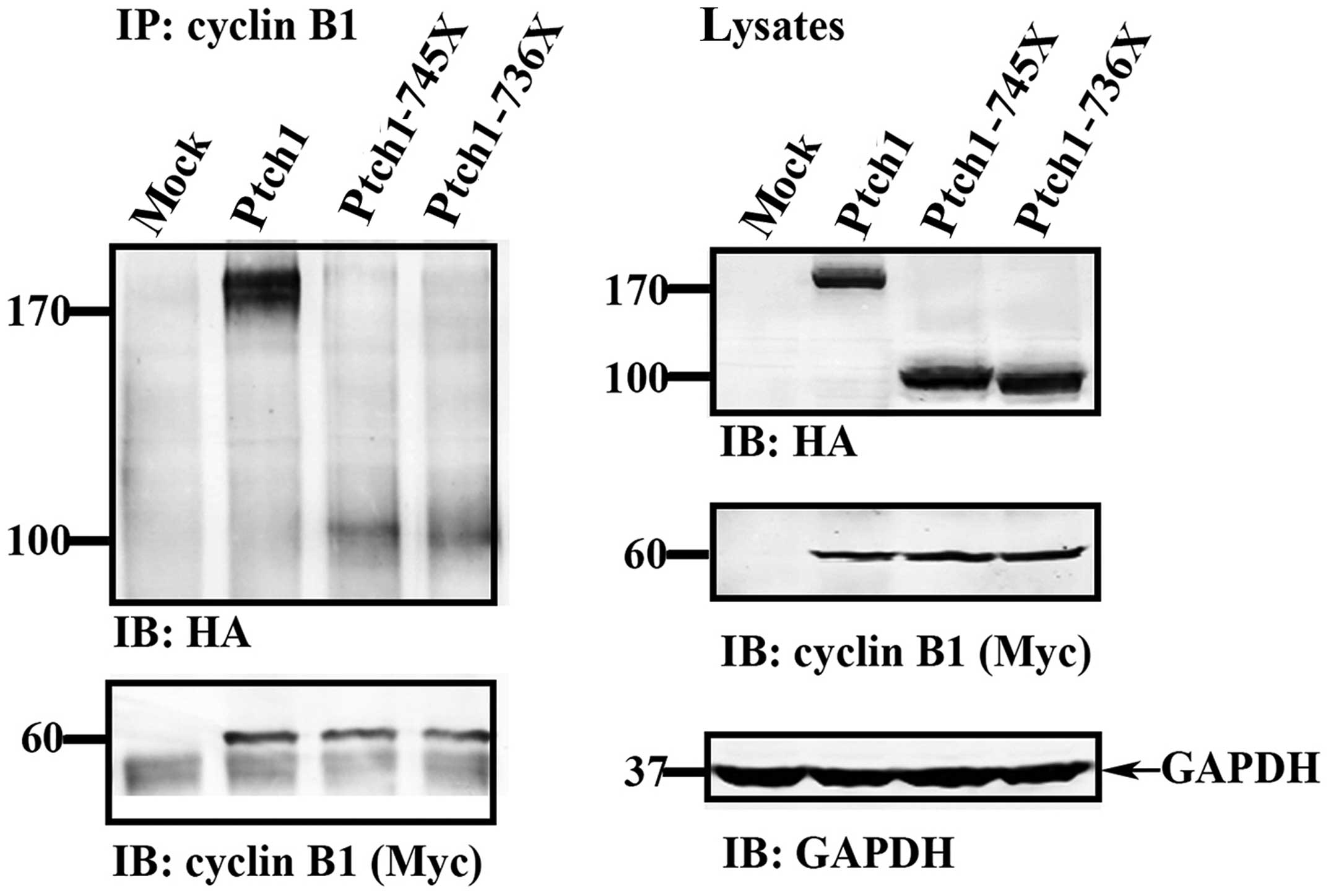
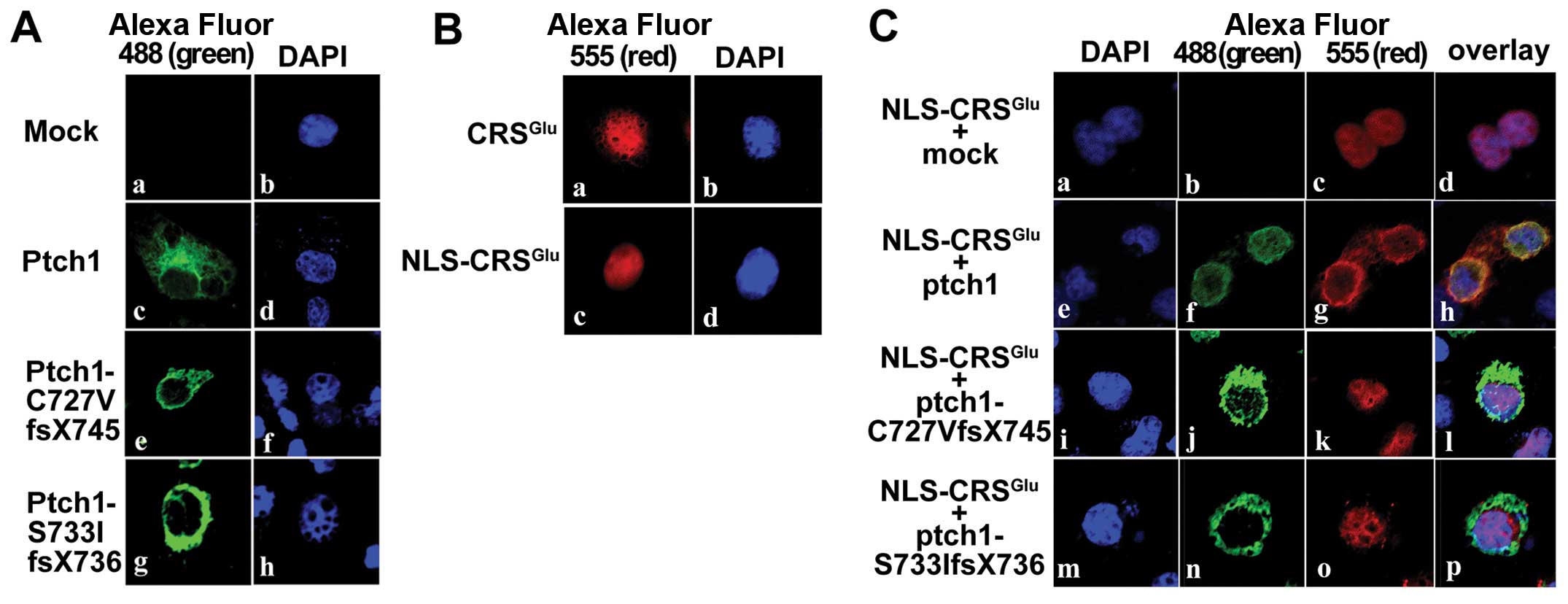
Donoghue DJ: Patched1 interacts with cyclin B1 to regulate cell
cycle progression. EMBO J. 20:2214–2223. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Barnes EA, Heidtman KJ and Donoghue DJ:
Constitutive activation of the shh-ptc1 pathway by a patched1
mutation identified in BCC. Oncogene. 24:902–915. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wicking C and McGlinn E: The role of
hedgehog signalling in tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 173:1–7. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Agaram NP, Collins BM, Barnes L, et al:
Molecular analysis to demonstrate that odontogenic keratocysts are
neoplastic. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 128:313–317. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Manfredi M, Vescovi P, Bonanini M and
Porter S: Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome: a review of the
literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 33:117–124. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ingham PW and McMahon AP: Hedgehog
signaling in animal development: paradigmsand principles. Genes
Dev. 15:3059–3087. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Robbins DJ, Fei DL and Riobo NA: The
Hedgehog signal transduction network. Sci Signal.
5:re62012.PubMed/NCBI
|