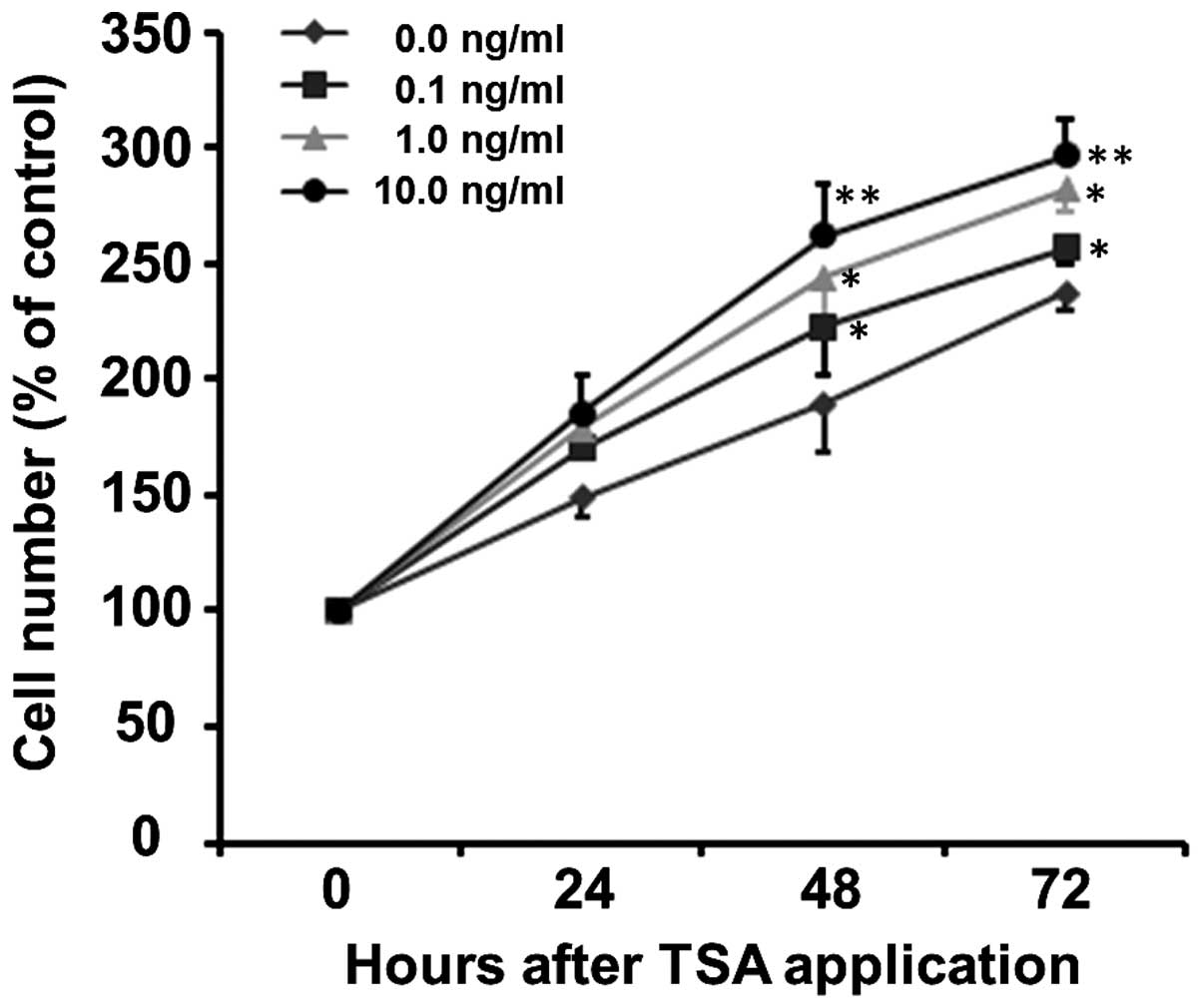
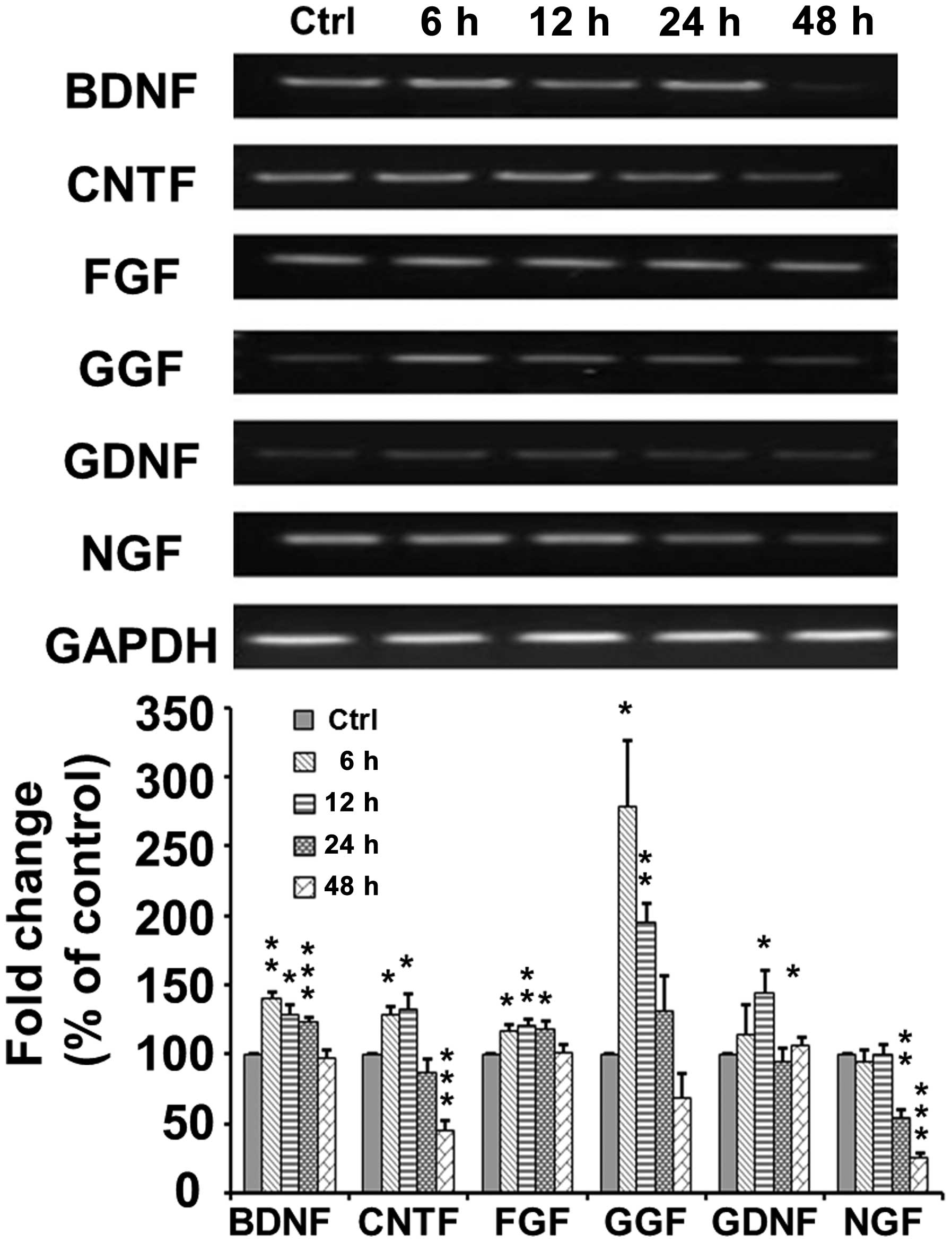
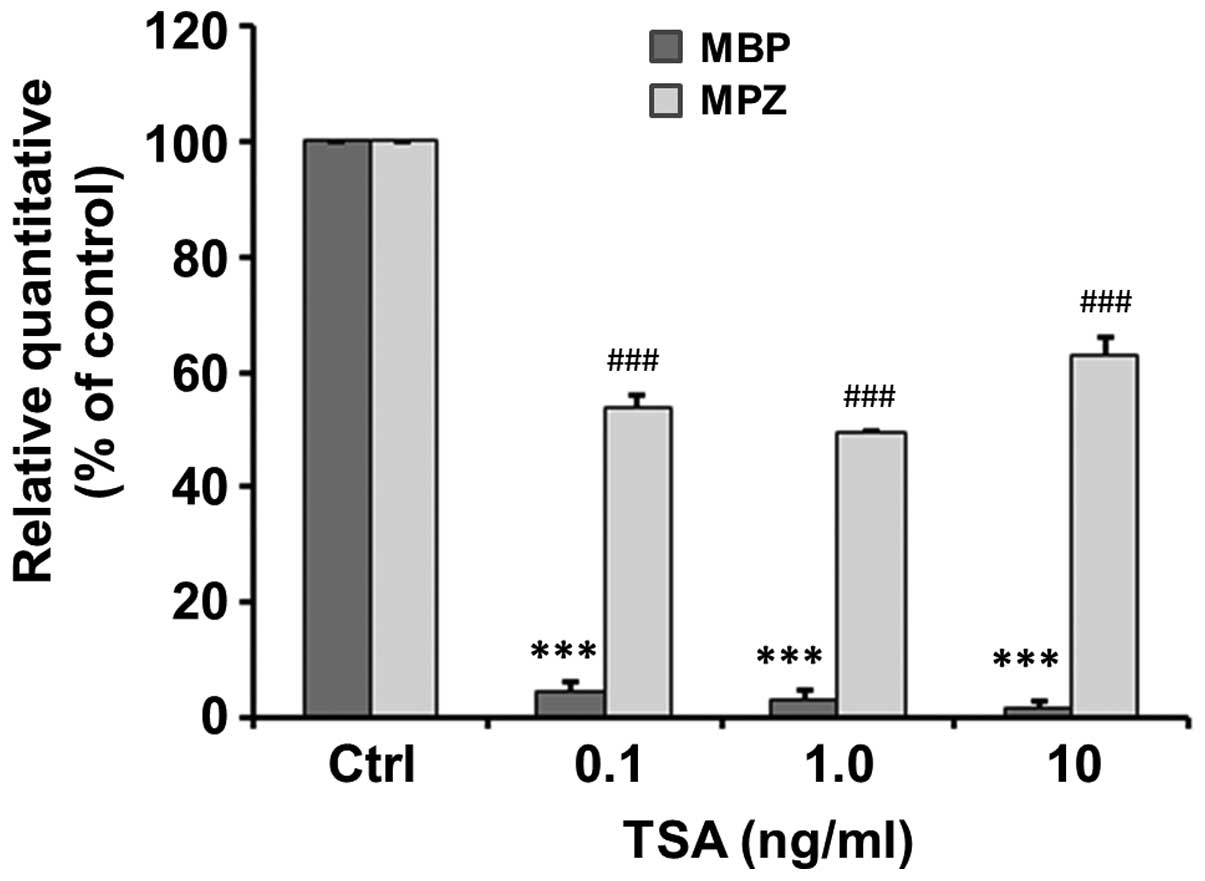
|
1
|
Sobani ZA, Quadr SA and Enam SA: Stem
cells for spinal cord regeneration: current status. Surg Neurol
Int. 1:932010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Garbossa D, Boido M, Fontanella M, et al:
Recent therapeutic strategies for spinal cord injury treatment:
possible role of stem cells. Neurosurg Rev. 35:293–311. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hill CE, Hurtado A, Blits B, et al: Early
necrosis and apoptosis of Schwann cells transplanted into the
injured rat spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci. 26:1433–1445. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lavdas AA, Papastefanaki F, Thomaidou D
and Matsas R: Schwann cell transplantation for CNS repair. Curr Med
Chem. 15:151–160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Takami T, Oudega M, Bates ML, et al:
Schwann cell but not olfactory ensheathing glia transplants improve
hindlimb locomotor performance in the moderately contused adult rat
thoracic spinal cord. J Neurosci. 22:6670–6681. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ide C, Nakai Y, Nakano N, et al: Bone
marrow stromal cell transplantation for treatment of sub-acute
spinal cord injury in the rat. Brain Res. 1332:32–47. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schaal SM, Kitay BM, Cho KS, et al:
Schwann cell transplantation improves reticulospinal axon growth
and forelimb strength after severe cervical spinal cord contusion.
Cell Transplant. 16:207–228. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kocsis JD and Waxman SG: Schwann cells and
their precursors for repair of central nervous system myelin.
Brain. 130:1978–1980. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Patel V, Joseph G, Patel A, et al:
Suspension matrices for improved Schwann-cell survival after
implantation into the injured rat spinal cord. J Neurotrauma.
27:789–801. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Redell JB, Moore AN, Ward NH III,
Hergenroeder GW and Dash PK: Human traumatic brain injury alters
plasma microRNA levels. J Neurotrauma. 27:2147–2156. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu IT, Park JY, Kim SH, et al: Valproic
acid promotes neuronal differentiation by induction of proneural
factors in association with H4 acetylation. Neuropharmacology.
56:473–480. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feng HL, Leng Y, Ma CH, et al: Combined
lithium and valproate treatment delays disease onset, reduces
neurological deficits and prolongs survival in an amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis mouse model. Neuroscience. 155:567–572. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tsai LK, Tsai MS, Ting CH, Wang SH and Li
H: Restoring Bcl-x(L) levels benefits a mouse model of spinal
muscular atrophy. Neurobiol Dis. 31:361–367. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ferrante RJ, Kubilus JK, Lee J, et al:
Histone deacetylase inhibition by sodium butyrate chemotherapy
ameliorates the neurodegenerative phenotype in Huntington,’s
disease mice. J Neurosci. 23:9418–9427. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Langley B, D’Annibale MA, Suh K, et al:
Pulse inhibition of histone deacetylases induces complete
resistance to oxidative death in cortical neurons without toxicity
and reveals a role for cytoplasmic p21 (waf1/cip1) in cell
cycle-independent neuroprotection. J Neurosci. 28:163–176. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chuang DM, Leng Y, Marinova Z, Kim HJ and
Chiu CT: Multiple roles of HDAC inhibition in neurodegenerative
conditions. Trends Neurosci. 32:591–601. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Z, Zang C, Cui K, et al: Genome-wide
mapping of HATs and HDACs reveals distinct functions in active and
inactive genes. Cell. 138:1019–1031. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu H, Wu H, Wang Y, et al: Inhibition of
class II histone deacetylase blocks proliferation and promotes
neuronal differentiation of the embryonic rat neural progenitor
cells. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 72:365–376. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morrissey TK, Kleitman N and Bunge RP:
Isolation and functional characterization of Schwann cells derived
from adult peripheral nerve. J Neurosci. 11:2433–2442.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu XM, Guénard V, Kleitman N, Aebischer P
and Bunge MB: A combination of BDNF and NT-3 promotes supraspinal
axonal regeneration into Schwann cell grafts in adult rat thoracic
spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 134:261–272. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xu XM, Guénard VV, Kleitman N and Bunge
MB: Axonal regeneration into Schwann cell-seeded guidance channels
grafted into transected adult rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol.
351:145–160. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Fu S, Wang Y, et al:
Interleukin-1beta mediates proliferation and differentiation of
multipotent neural precursor cells through the activation of
SAPK/JNK pathway. Mol Cell Neurosci. 36:343–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jeong MR, Hashimoto R, Senatorov VV, et
al: Valproic acid, a mood stabilizer and anticonvulsant, protects
rat cerebral cortical neurons from spontaneous cell death: a role
of histone deacetylase inhibition. FEBS Lett. 542:74–78. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Forgione N and Tropepe V: Histone
deacetylase inhibition promotes Caspase-independent cell death of
ventral midbrain neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 48:117–128. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mi S, Lee X, Shao Z, et al: LINGO-1 is a
component of the Nogo-66 receptor/p75 signaling complex. Nat
Neurosci. 7:221–228. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Di Daniel E, Mudge AW and Maycox PR:
Comparative analysis of the effects of four mood stabilizers in
SH-SY5Y cells and in primary neurons. Bipolar Disord. 7:33–41.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hao Y, Creson T, Zhang L, et al: Mood
stabilizer valproate promotes ERK pathway-dependent cortical
neuronal growth and neurogenesis. J Neurosci. 24:6590–6599. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Michaelis M, Suhan T, Michaelis UR, et al:
Valproic acid induces extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
activation and inhibits apoptosis in endothelial cells. Cell Death
Differ. 13:446–453. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen PS, Peng GS, Li G, et al: Valproate
protects dopaminergic neurons in midbrain neuron/glia cultures by
stimulating the release of neurotrophic factors from astrocytes.
Mol Psychiatry. 11:1116–1125. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Castro LM, Gallant M and Niles LP: Novel
targets for valproic acid: up-regulation of melatonin receptors and
neurotrophic factors in C6 glioma cells. J Neurochem. 95:1227–1236.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Otsuka S, Adamson C, Sankar V, et al:
Delayed intrathecal delivery of RhoA siRNA to the contused spinal
cord inhibits allodynia, preserves white matter, and increases
serotonergic fiber growth. J Neurotrauma. 28:1063–1076. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ananthakrishnan R and Ehrlicher A: The
forces behind cell movement. Int J Biol Sci. 3:303–317. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heermann S and Schwab MH: Molecular
control of Schwann cell migration along peripheral axons: keep
moving! Cell Adh Migr. 7:18–22. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ishida-Yamamoto A, Yamauchi T, Tanaka H,
et al: Electron microscopic in situ DNA nick end-labeling in
combination with immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem.
47:711–717. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cornejo M, Nambi D, Walheim C, et al:
Effect of NRG1, GDNF, EGF and NGF in the migration of a Schwann
cell precursor line. Neurochem Res. 35:1643–1651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Heermann S, Spittau B, Zajzon K, Schwab MH
and Krieglstein K: Schwann cells migrate along axons in the absence
of GDNF signaling. BMC Neurosci. 13:922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jacob C, Christen CN, Pereira JA, et al:
HDAC1 and HDAC2 control the transcriptional program of myelination
and the survival of Schwann cells. Nat Neurosci. 14:429–436. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|