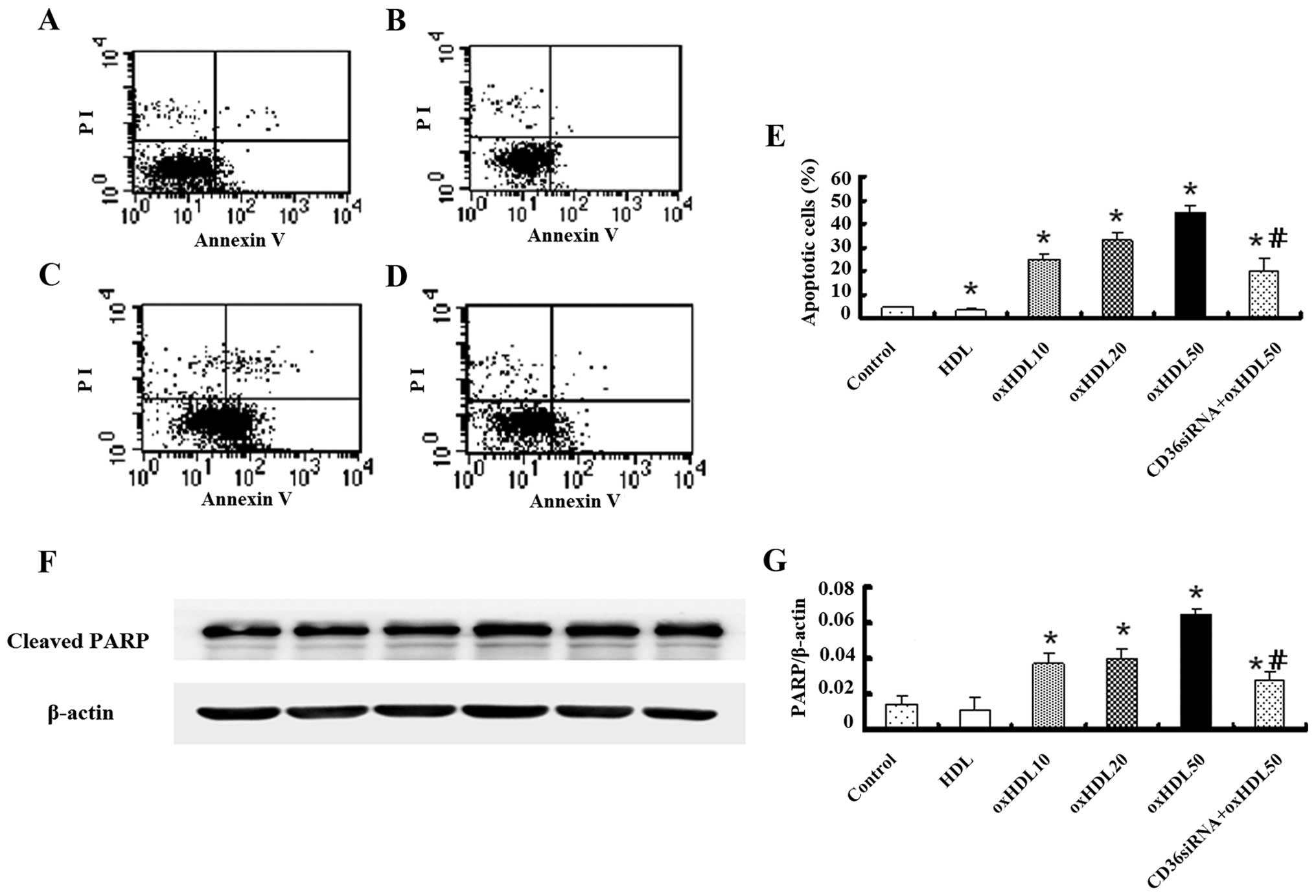
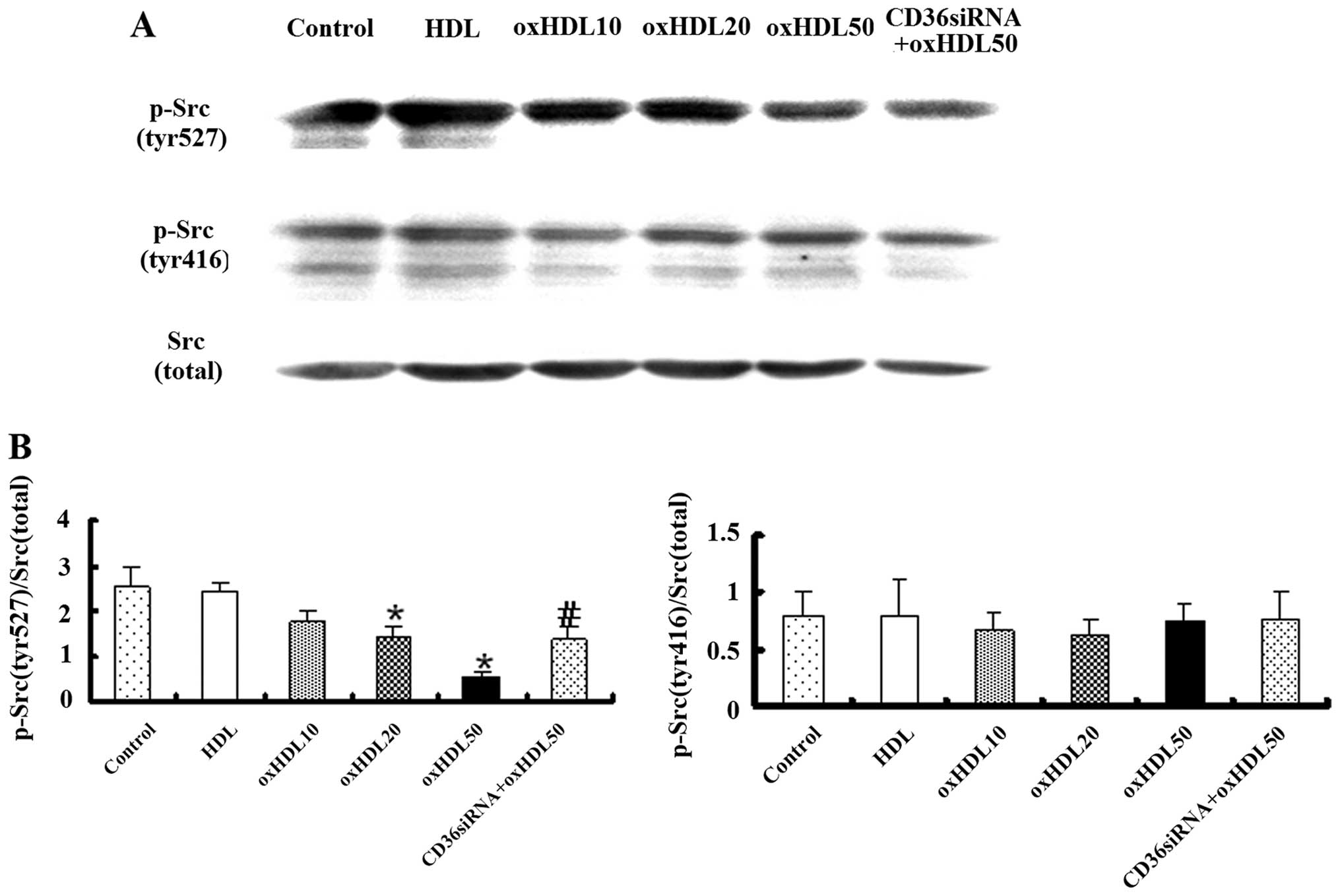
|
1
|
Risdon RA, Sloper JC and De Wardener HE:
Relationship between renal function and histological changes found
in renal-biopsy specimens from patients with persistent glomerular
nephritis. Lancet. 2:363–366. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rodriguez-Iturbe B and García García G:
The role of tubulointerstitial inflammation in the progression of
chronic renal failure. Nephron Clin Pract. 116:c81–c88. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gong R, Rifai A, Tolbert EM, Biswas P,
Centracchio JN and Dworkin LD: Hepatocyte growth factor ameliorates
renal interstitial inflammation in rat remnant kidney by modulating
tubular expression of macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 and
RANTES. J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:2868–2881. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Takase O, Minto AW, Puri TS, et al:
Inhibition of NF-kappaB-dependent Bcl-xL expression by clusterin
promotes albumin-induced tubular cell apoptosis. Kidney Int.
73:567–577. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bohle A, Wehrmann M, Bogenschütz O, et al:
The long-term prognosis of the primary glomerulonephritides. A
morphological and clinical analysis of 1747 cases. Pathol Res
Pract. 188:908–924. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davidson MH and Toth PP: High-density
lipoprotein metabolism: potential therapeutic targets. Am J
Cardiol. 100:n32–n40. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ansell BJ, Navab M, Hama S, et al:
Inflammatory/antiinflammatory properties of high-density
lipoprotein distinguish patients from control subjects better than
high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and are favorably
affected by simvastatin treatment. Circulation. 108:2751–2756.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Briel M, Ferreira-Gonzalez I, You JJ, et
al: Association between change in high density lipoprotein
cholesterol and cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality:
systematic review and meta-regression analysis. BMJ. 338:b922009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ferretti G, Bacchetti T, Nègre-Salvayre A,
Salvayre R, Dousset N and Curatola G: Structural modifications of
HDL and functional consequences. Atherosclerosis. 184:1–7. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu R, Yekta B, Vakili L, et al:
Proatherogenic high-density lipoprotein, vascular inflammation, and
mimetic peptides. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 10:171–176. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Valiyaveettil M, Kar N, Ashraf MZ, Byzova
TV, Febbraio M and Podrez EA: Oxidized high-density lipoprotein
inhibits platelet activation and aggregation via scavenger receptor
BI. Blood. 111:1962–1971. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsumura M, Kinouchi T, Ono S, Nakajima T
and Komoda T: Serum lipid metabolism abnormalities and change in
lipoprotein contents in patients with advanced-stage renal disease.
Clin Chim Acta. 314:27–37. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vaziri ND, Moradi H, Pahl MV, Fogelman AM
and Navab M: In vitro stimulation of HDL anti-inflammatory activity
and inhibition of LDL pro-inflammatory activity in the plasma of
patients with end-stage renal disease by an apoA-1 mimetic peptide.
Kidney Int. 76:437–444. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Norata GD, Banfi C, Pirillo A, et al:
Oxidised-HDL3 induces the expression of PAI-1 in human endothelial
cells. Role of p38MAPK activation and mRNA stabilization. Br J
Haematol. 127:97–104. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu HT, Li WM, Xu G, et al: Chitosan
oligosaccharides attenuate hydrogen peroxide-induced stress injury
in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Pharmacol Res.
59:167–175. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cirillo P, Gersch MS, Mu W, et al:
Ketohexokinase-dependent metabolism of fructose induces
proinflammatory mediators in proximal tubular cells. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 20:545–553. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao X, Huang L, Grosjean F, et al:
Low-protein diet supplemented with ketoacids reduces the severity
of renal disease in 5/6 nephrectomized rats: a role for KLF15.
Kidney Int. 79:987–996. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Matsunaga T, Hokari S, Koyama I, Harada T
and Komoda T: NF-kappa B activation in endothelial cells treated
with oxidized high-density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
303:313–319. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhuang S, Kinsey GR, Rasbach K and
Schnellmann RG: Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor and Src
family kinases in proliferation of renal epithelial cells. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 294:F459–F468. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feistritzer C, Mosheimer BA, Tancevski I,
et al: Src tyrosine kinase-dependent migratory effects of
antithrombin in leukocytes. Exp Cell Res. 305:214–220. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leung JC, Tang SC, Chan LY, Chan WL and
Lai KN: Synthesis of TNF-alpha by mesangial cells cultured with
polymeric anionic IgA - role of MAPK and NF-kappaB. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 23:72–81. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bouma HR, Ploeg RJ and Schuurs TA: Signal
transduction pathways involved in brain death-induced renal injury.
Am J Transplant. 9:989–997. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sabatel H, Pirlot C, Piette J and Habraken
Y: Importance of PIKKs in NF-κB activation by genotoxic stress.
Biochem Pharmacol. 82:1371–1383. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moradi H, Pahl MV, Elahimehr R and Vaziri
ND: Impaired antioxidant activity of high-density lipoprotein in
chronic kidney disease. Transl Res. 153:77–85. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vaziri ND: Dyslipidemia of chronic renal
failure: the nature, mechanisms, and potential consequences. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 290:F262–F272. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ansell BJ, Fonarow GC and Fogelman AM: The
paradox of dysfunctional high-density lipoprotein. Curr Opin
Lipidol. 18:427–434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou W, Guan Q, Kwan CC, et al: Loss of
clusterin expression worsens renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 298:F568–F578. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moore KJ and Freeman MW: Scavenger
receptors in atherosclerosis: beyond lipid uptake. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:1702–1711. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Febbraio M, Hajjar DP and Silverstein RL:
CD36: a class B scavenger receptor involved in angiogenesis,
atherosclerosis, inflammation, and lipid metabolism. J Clin Invest.
108:785–791. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Okamura DM, Lopez-Guisa JM, Koelsch K,
Collins S and Eddy AA: Atherogenic scavenger receptor modulation in
the tubulointerstitium in response to chronic renal injury. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 293:F575–F585. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Iwao Y, Nakajou K, Nagai R, et al: CD36 is
one of important receptors promoting renal tubular injury by
advanced oxidation protein products. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
295:F1871–F1880. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Okamura DM, Pennathur S, Pasichnyk K, et
al: CD36 regulates oxidative stress and inflammation in
hypercholesterolemic CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:495–505. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Thorne RF, Mhaidat NM, Ralston KJ and
Burns GF: CD36 is a receptor for oxidized high density lipoprotein:
implications for the development of atherosclerosis. FEBS Lett.
581:1227–1232. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Amin MA, Haas CS, Zhu K, et al: Migration
inhibitory factor upregulates vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 via Src, PI3 kinase, and
NFkappaB. Blood. 107:2252–2261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xing J, Zhang Z, Mao H, Schnellmann RG and
Zhuang S: Src regulates cell cycle protein expression and renal
epithelial cell proliferation via PI3K/Akt signaling-dependent and
-independent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 295:F145–F152.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|