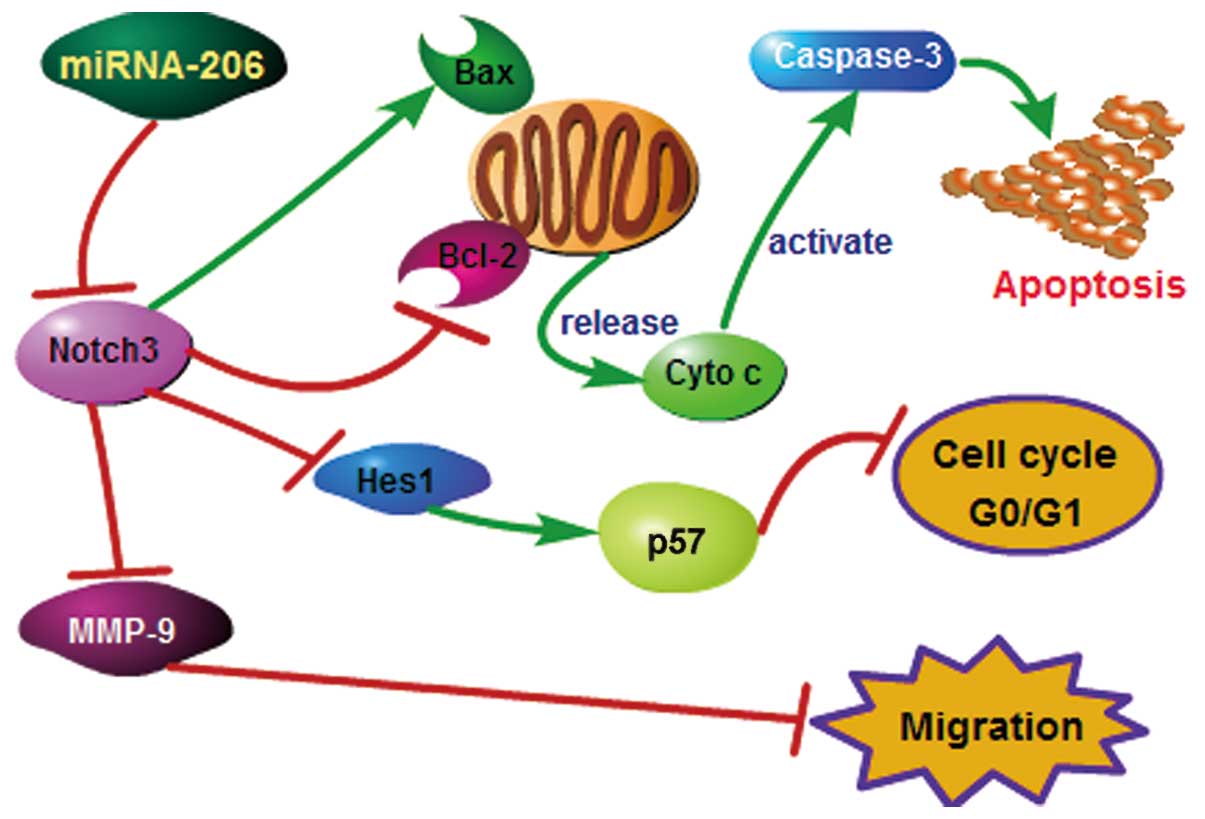
|
1
|
Jalali S, Ramanathan GK, Parthasarathy PT,
et al: Mir-206 regulates pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell
proliferation and differentiation. PLoS One. 7:e468082012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Subramaniam A, Shanmugam MK, Perumal E, et
al: Potential role of signal transducer and activator of
transcription (STAT)3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival,
proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1835.46–60. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
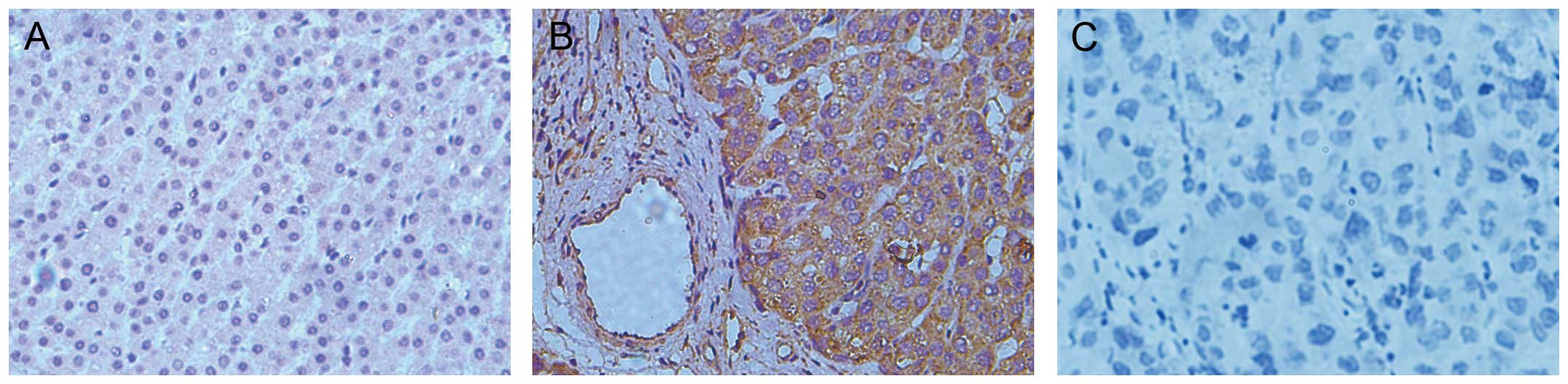
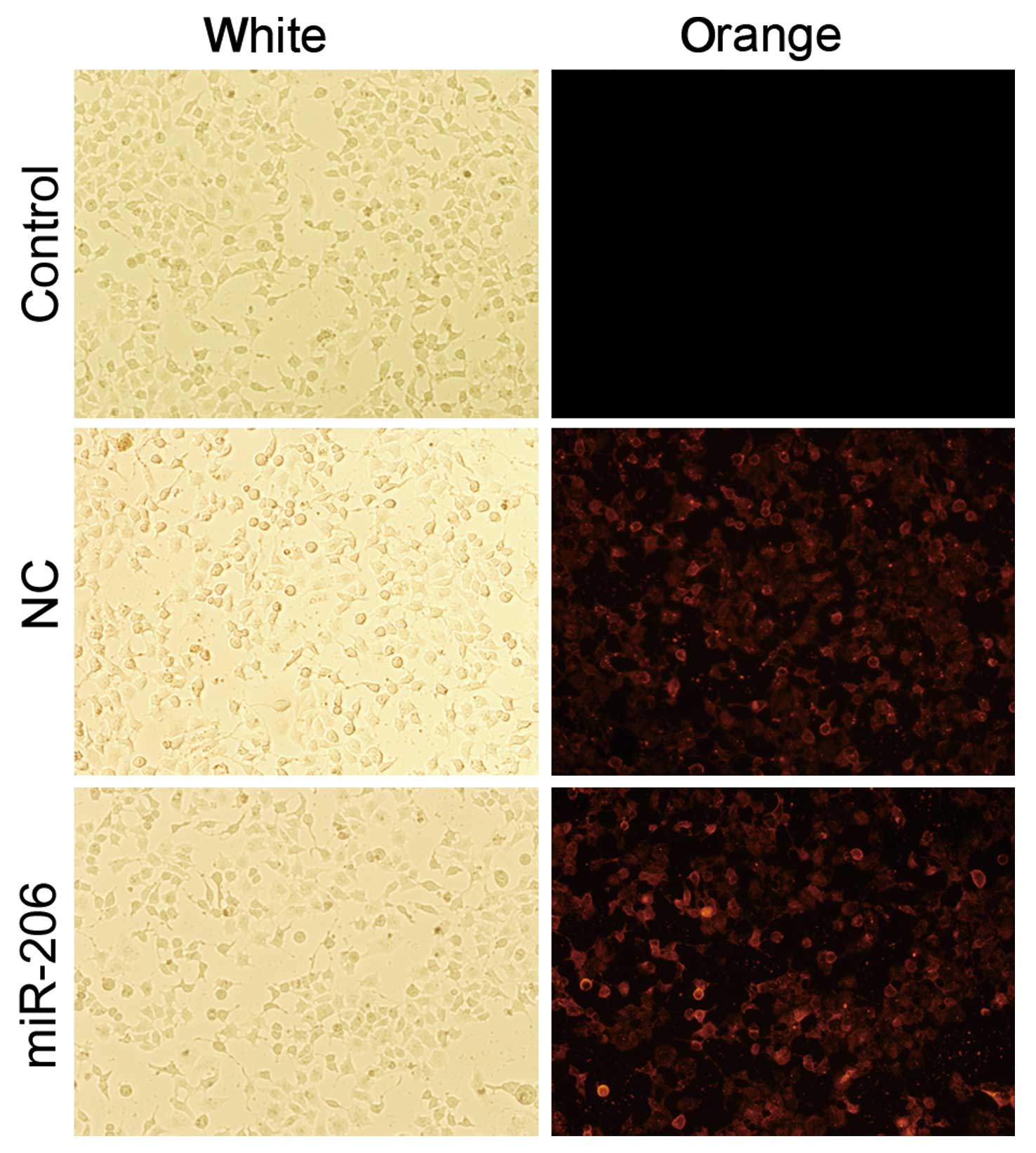
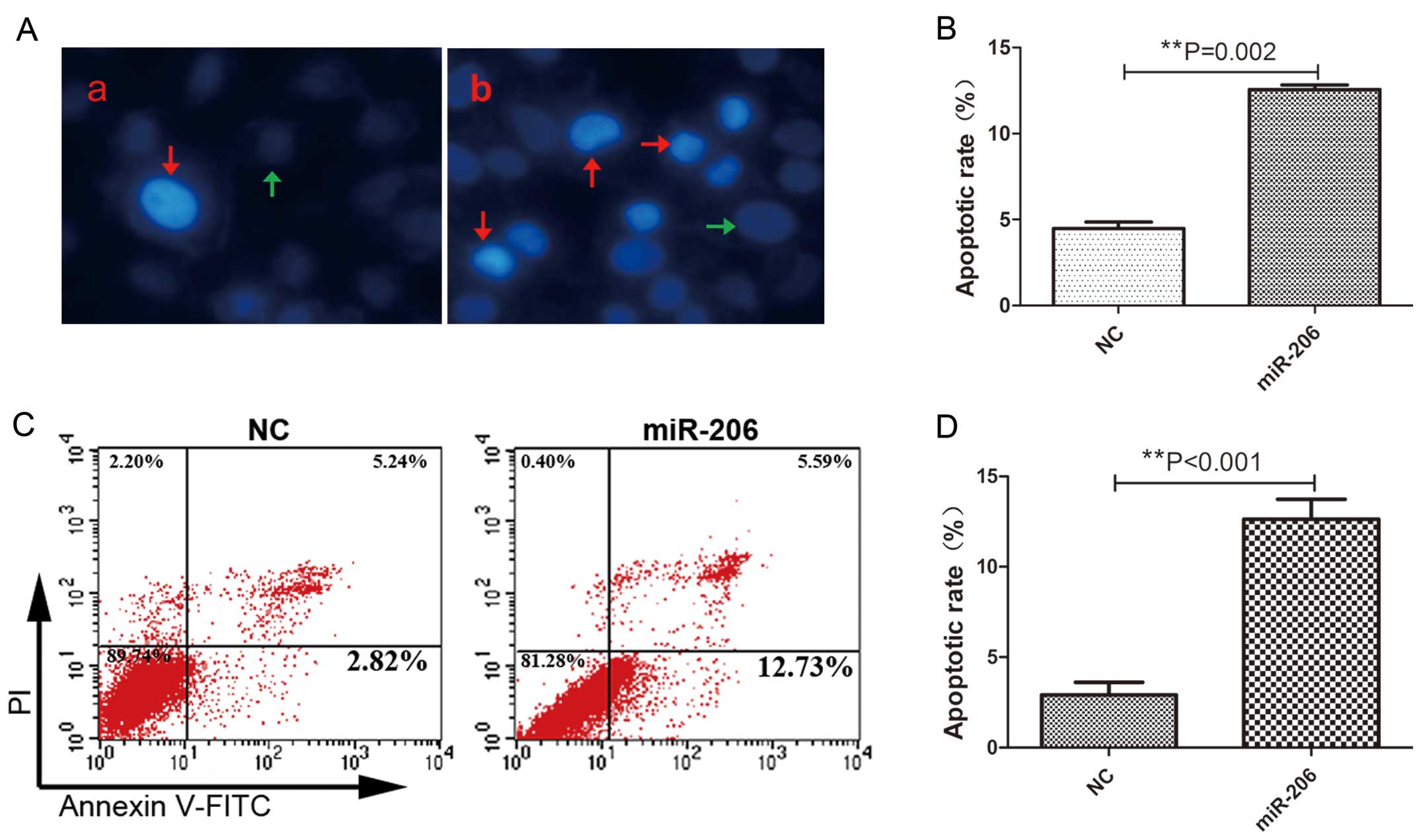
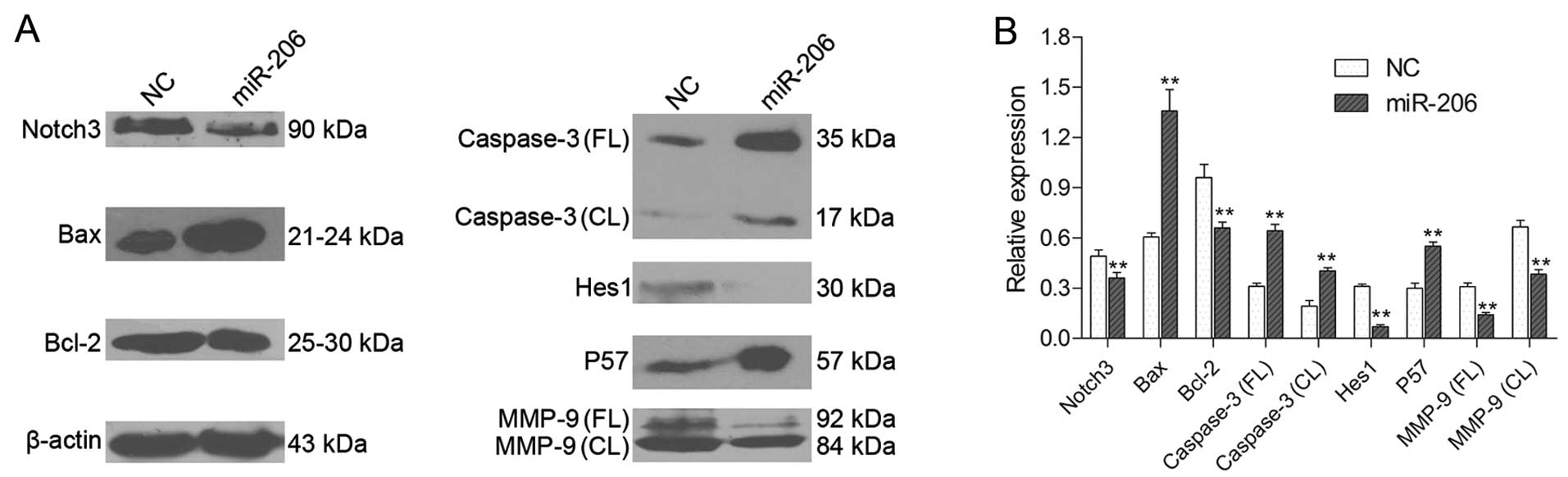
|
Sia D and Villanueva A: Signaling pathways
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 81(Suppl 1): S18–S23. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Qin LX and Tang ZY: Recent progress in
predictive biomarkers for metastatic recurrence of human
hepatocellular carcinoma: a review of the literature. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 130:497–513. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maluccio M and Covey A: Recent progress in
understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma.
CA Cancer J Clin. 62:394–399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giacomin A, Sergio A, Vanin V, Gazzola A,
Cazzagon N and Farinati F: Molecular targeted therapy in
hepatocellular carcinoma: present achievements and future
challenges. Dig Dis. 30:284–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ortiz R, Melguizo C, Prados J, et al: New
gene therapy strategies for cancer treatment: a review of recent
patents. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 7:297–312. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Psyrri A, Arkadopoulos N, Vassilakopoulou
M, Smyrniotis V and Dimitriadis G: Pathways and targets in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 12:1347–1357.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McCarthy JJ: MicroRNA-206: the skeletal
muscle-specific myomiR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1779:682–691. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Missiaglia E, Shepherd CJ, Patel S, et al:
MicroRNA-206 expression levels correlate with clinical behaviour of
rhabdomyosarcomas. Br J Cancer. 102:1769–1777. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Di Leva G, Gasparini P, Piovan C, et al:
MicroRNA cluster 221–222 and estrogen receptor alpha interactions
in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 102:706–721. 2010.
|
|
12
|
Liu H, Cao YD, Ye WX and Sun YY: Effect of
microRNA-206 on cytoskeleton remodelling by downregulating Cdc42 in
MDA-MB-231 cells. Tumori. 96:751–755. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen X, Yan Q, Li S, et al: Expression of
the tumor suppressor miR-206 is associated with cellular
proliferative inhibition and impairs invasion in ERα-positive
endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 314:41–53.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Ling C, Bai Y and Zhao J:
MicroRNA-206 is associated with invasion and metastasis of lung
cancer. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 294:88–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song G, Zhang Y and Wang L: MicroRNA-206
targets notch3, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell
migration and focus formation. J Biol Chem. 284:31921–31927. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bellavia D, Campese AF, Vacca A, Gulino A
and Screpanti I: Notch3, another Notch in T cell development. Semin
Immunol. 15:107–112. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hansson EM, Lendahl U and Chapman G: Notch
signaling in development and disease. Semin Cancer Biol.
14:320–328. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Konishi J, Yi F, Chen X, Vo H, Carbone DP
and Dang TP: Notch3 cooperates with the EGFR pathway to modulate
apoptosis through the induction of bim. Oncogene. 29:589–596. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Giovannini C, Lacchini M, Gramantieri L,
Chieco P and Bolondi L: Notch3 intracellular domain accumulates in
HepG2 cell line. Anticancer Res. 26:2123–2127. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jonusiene V, Sasnauskiene A, Lachej N, et
al: Down-regulated expression of Notch signaling molecules in human
endometrial cancer. Med Oncol. 30:4382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Samadi AK, Roby KF, Timmermann B
and Cohen MS: Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptosis
in ovarian carcinoma cell lines CaOV3 and SKOV3 by natural
withanolide Withaferin A. Gynecol Oncol. 124:606–612. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mizugaki H, Sakakibara-Konishi J, Ikezawa
Y, et al: γ-Secretase inhibitor enhances antitumour effect of
radiation in Notch-expressing lung cancer. Br J Cancer.
106:1953–1959. 2012.
|
|
23
|
Zhou M, Jin WY, Fan ZW and Han RC:
Analysis of the expression of the Notch3 receptor protein in adult
lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 5:499–504. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Ye YZ, Zhang ZH, Fan XY, Xu XL, Chen ML,
Chang BW and Zhang YB: Notch3 overexpression associates with poor
prognosis in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Med Oncol.
30:5952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Konishi J, Kawaguchi KS, Vo H, Haruki N,
Gonzalez A, Carbone DP and Dang TP: Gamma-secretase inhibitor
prevents Notch3 activation and reduces proliferation in human lung
cancers. Cancer Res. 67:8051–8057. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhou L, Zhang N, Song W, et al: The
significance of Notch1 compared with Notch3 in high metastasis and
poor overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e573822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Giovannini C, Gramantieri L, Minguzzi M,
Fornari F, Chieco P, Grazi GL and Bolondi L: CDKN1C/p57 is
regulated by the Notch target gene Hes1 and induces senescence in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 181:413–422. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fabregat I: Dysregulation of apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol. 15:513–520.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gramantieri L, Giovannini C, Lanzi A, et
al: Aberrant Notch3 and Notch4 expression in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Liver Int. 27:997–1007. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhong D, Huang G, Zhang Y, et al:
MicroRNA-1 and microRNA-206 suppress LXRα-induced lipogenesis in
hepatocytes. Cell Signal. 25:1429–1437. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maciotta S, Meregalli M, Cassinelli L, et
al: Hmgb3 is regulated by MicroRNA-206 during muscle regeneration.
PLoS One. 7:e434642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yan D, da Dong XE, Chen X, et al:
MicroRNA-1/206 targets c-Met and inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma
development. J Biol Chem. 284:29596–29604. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang W, Prince CZ, Mou Y and Pollman MJ:
Notch3 signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells induces c-FLIP
expression via ERK/MAPK activation. Resistance to Fas
ligand-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 277:21723–21729. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang DH, Hu JR, Wang LY, et al: The
apoptotic function analysis of p53, Apaf1, Caspase3 and Caspase7
during the spermatogenesis of the Chinese fire-bellied newt
Cynops orientalis. PLoS One. 7:e39920,2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen L, Zheng J, Zhang Y, et al:
Tumor-specific expression of microRNA-26a suppresses human
hepatocellular carcinoma growth via cyclin-dependent and
-independent pathways. Mol Ther. 19:1521–1528. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen RX, Xia YH, Xue TC, Zhang H and Ye
SL: Down-regulation of osteopontin inhibits metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via a mechanism involving MMP-2 and
uPA. Oncol Rep. 25:803–808. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yeh CB, Hsieh MJ, Hsieh YS, Chien MH, Lin
PY, Chiou HL and Yang SF: Terminalia catappa exerts
antimetastatic effects on hepatocellular carcinoma through
transcriptional inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 by
modulating NF-κB and AP-1 activity. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2012:5952922012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li J, Lau G, Chen L, et al: Interleukin 23
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via NF-kappa B induced
matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression. PLoS One. 7:e462642012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang S and He X: The role of microRNAs in
liver cancer progression. Br J Cancer. 104:235–240. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li Y, Hong F and Yu Z: Decreased
expression of microRNA-206 in breast cancer and its association
with disease characteristics and patient survival. J Int Med Res.
41:596–602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang Q, Zhang C, Huang B, Li H, Zhang R,
Huang Y and Wang J: Downregulation of microRNA-206 is a potent
prognostic marker for patients with gastric cancer. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:953–957. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|