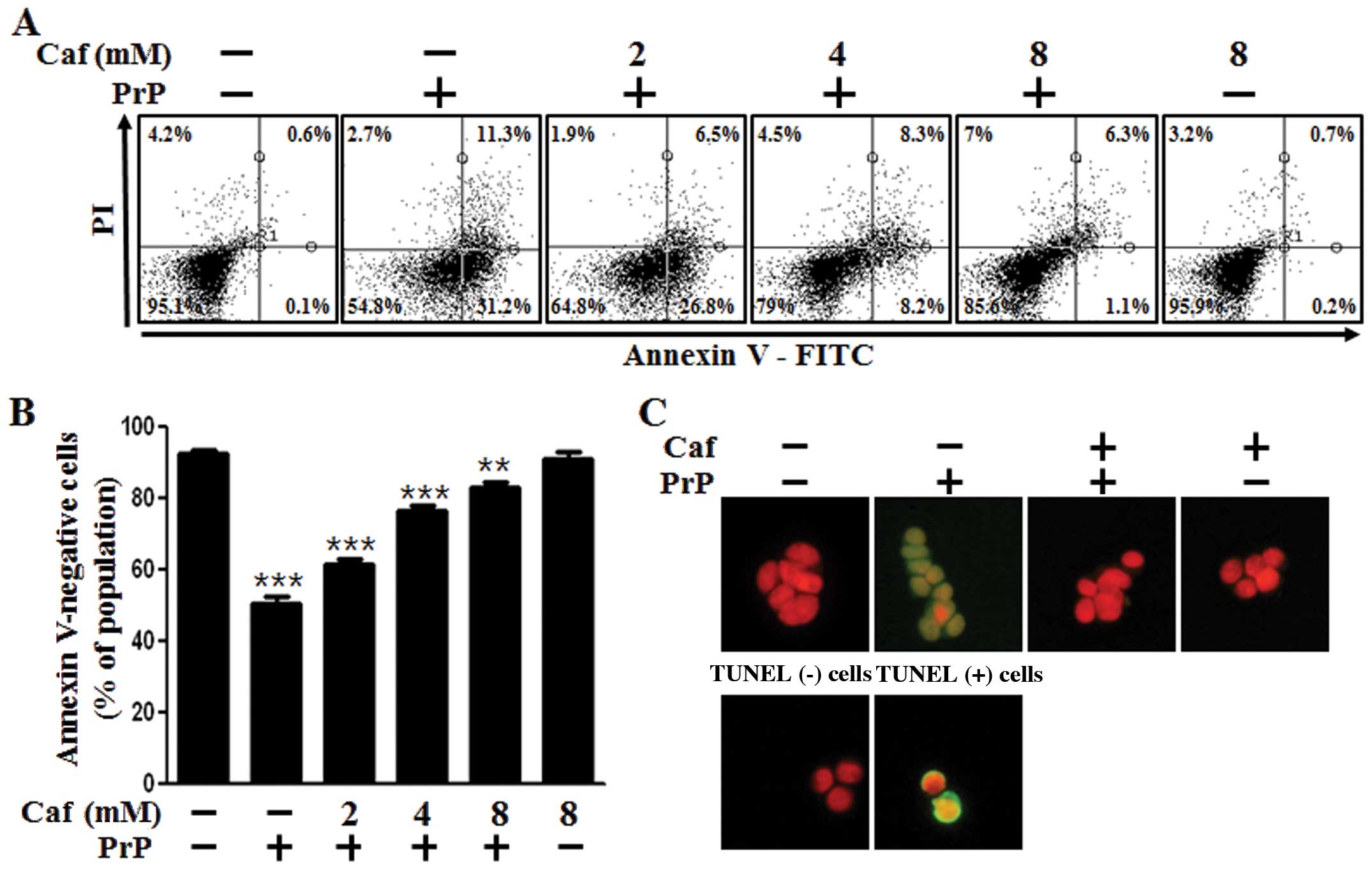
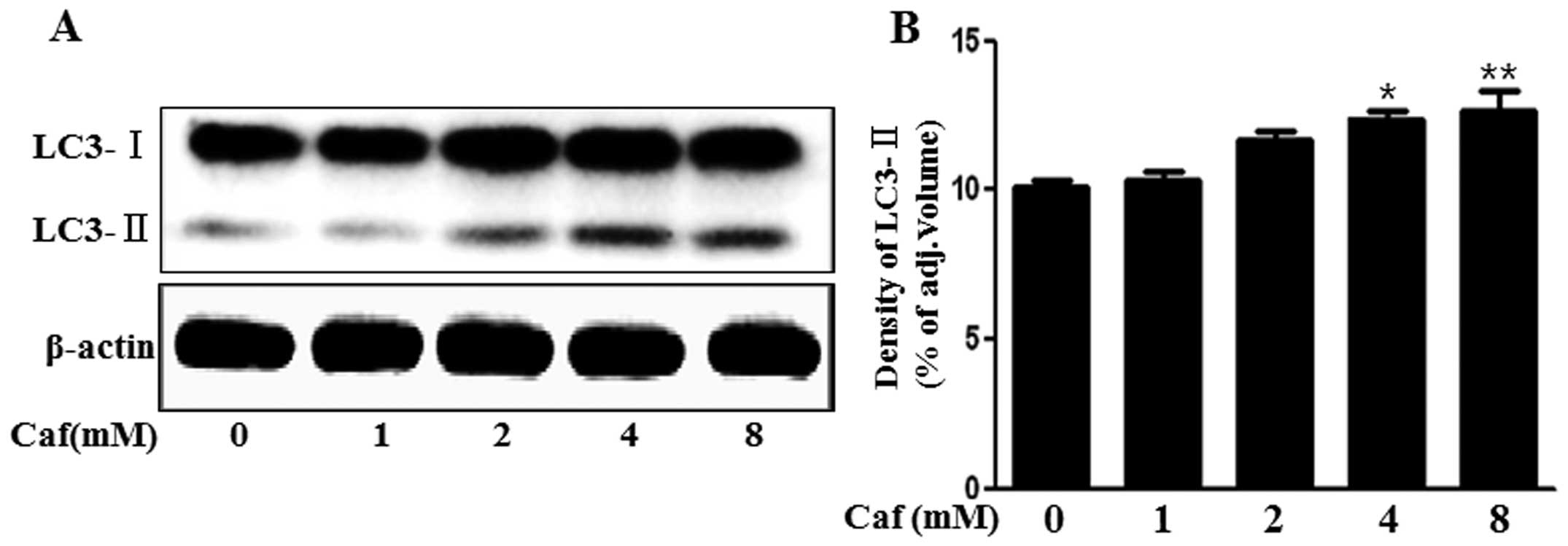
|
1
|
Costanzo M and Zurzolo C: The cell biology
of prion-like spread of protein aggregates: mechanisms and
implication in neurodegeneration. Biochem J. 452:1–17.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prusiner SB: Novel proteinaceous
infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 216:136–144. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Prusiner SB: Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:13363–13383. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aguzzi A: Staining, straining and
restraining prions. Nat Neurosci. 11:1239–1240. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Forloni G, Angeretti N, Chiesa R, et al:
Neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature. 362:543–546.
1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Selvaggini C, De Gioia L, Cantu L, et al:
Molecular characteristics of a protease-resistant, amyloidogenic
and neurotoxic peptide homologous to residues 106-126 of the prion
protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 194:1380–1386. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Deter RL and De Duve C: Influence of
glucagon, an inducer of cellular autophagy, on some physical
properties of rat liver lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 33:437–449. 1967.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rubinsztein DC, Marino G and Kroemer G:
Autophagy and aging. Cell. 146:682–695. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Filomeni G, Graziani I, De Zio D, et al:
Neuroprotection of kaempferol by autophagy in models of
rotenone-mediated acute toxicity: possible implications for
Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 33:767–785. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Garcia JJ, Pinol-Ripoll G,
Martinez-Ballarin E, et al: Melatonin reduces membrane rigidity and
oxidative damage in the brain of SAMP8 mice. Neurobiol Aging.
32:2045–2054. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nakagaki T, Satoh K, Ishibashi D, et al:
FK506 reduces abnormal prion protein through the activation of
autolysosomal degradation and prolongs survival in prion-infected
mice. Autophagy. 9:2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu K, Xu YH, Chen JF and Schwarzschild MA:
Neuroprotection by caffeine: time course and role of its
metabolites in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience.
167:475–481. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rubinsztein DC, Cuervo AM, Ravikumar B, et
al: In search of an “autophagomometer”. Autophagy. 5:585–589.
2009.
|
|
17
|
Park JH, Lee JE, Lee SJ, et al: Potential
autophagy enhancers protect against fipronil-induced apoptosis in
SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol Lett. 223:25–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xia DY, Li W, Qian HR, Yao S, Liu JG and
Qi XK: Ischemia preconditioning is neuroprotective in a rat
cerebral ischemic injury model through autophagy activation and
apoptosis inhibition. Braz J Med Biol Res. 46:580–588. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim J, Kim TY, Cho KS, Kim HN and Koh JY:
Autophagy activation and neuroprotection by progesterone in the
G93A-SOD1 transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Neurobiol Dis. 59:80–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakaso K, Ito S and Nakashima K: Caffeine
activates the PI3K/Akt pathway and prevents apoptotic cell death in
a Parkinson’s disease model of SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Lett.
432:146–150. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carimalo J, Cronier S, Petit G, et al:
Activation of the JNK-c-Jun pathway during the early phase of
neuronal apoptosis induced by PrP106-126 and prion infection. Eur J
Neurosci. 21:2311–2319. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aoyama K, Matsumura N, Watabe M, Wang F,
Kikuchi-Utsumi K and Nakaki T: Caffeine and uric acid mediate
glutathione synthesis for neuroprotection. Neuroscience.
181:206–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen X, Ghribi O and Geiger JD: Caffeine
protects against disruptions of the blood-brain barrier in animal
models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. J Alzheimers Dis.
20(Suppl 1): S127–S141. 2010.
|
|
24
|
Winter G, Hazan R, Bakalinsky AT and
Abeliovich H: Caffeine induces macroautophagy and confers a
cytocidal effect on food spoilage yeast in combination with benzoic
acid. Autophagy. 4:28–36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saiki S, Sasazawa Y, Imamichi Y, et al:
Caffeine induces apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via
PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K inhibition. Autophagy. 7:176–187. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
White E and DiPaola RS: The double-edged
sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5308–5316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wei K, Wang P and Miao CY: A double-edged
sword with therapeutic potential: an updated role of autophagy in
ischemic cerebral injury. CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:879–886. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Foukas LC, Daniele N, Ktori C, Anderson
KE, Jensen J and Shepherd PR: Direct effects of caffeine and
theophylline on p110 delta and other phosphoinositide 3-kinases.
Differential effects on lipid kinase and protein kinase activities.
J Biol Chem. 277:37124–37130. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sarkaria JN, Busby EC, Tibbetts RS, et al:
Inhibition of ATM and ATR kinase activities by the radiosensitizing
agent, caffeine. Cancer Res. 59:4375–4382. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Davis RJ: Signal transduction by the JNK
group of MAP kinases. Cell. 103:239–252. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|