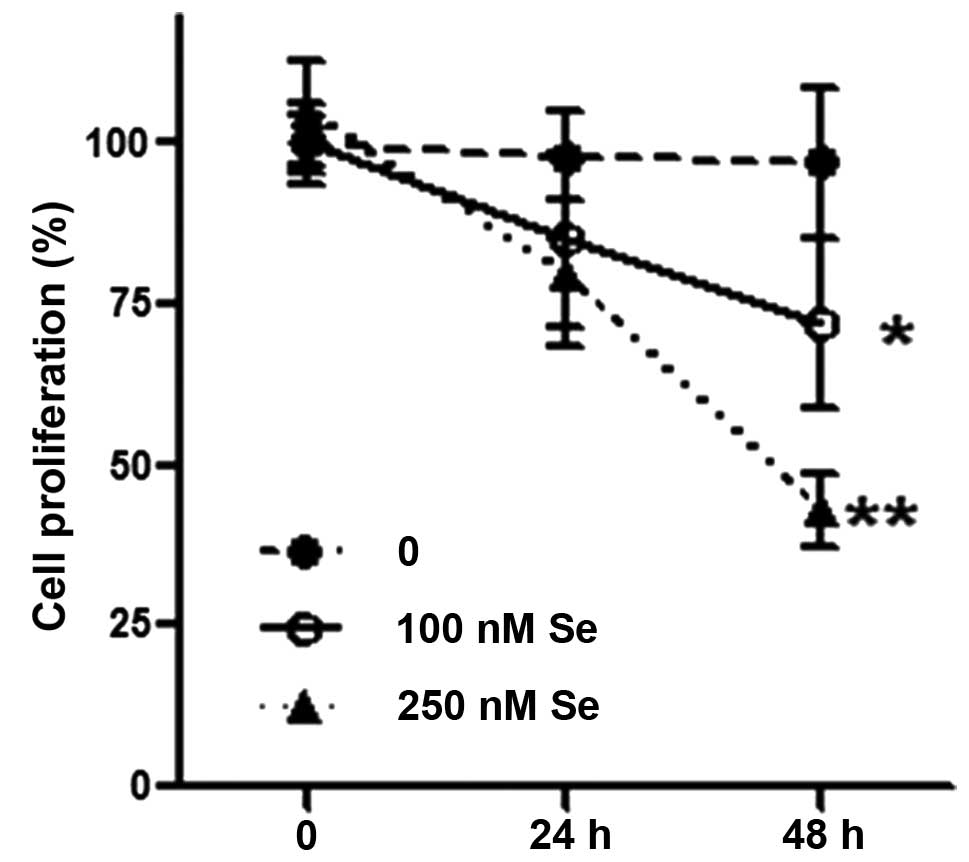
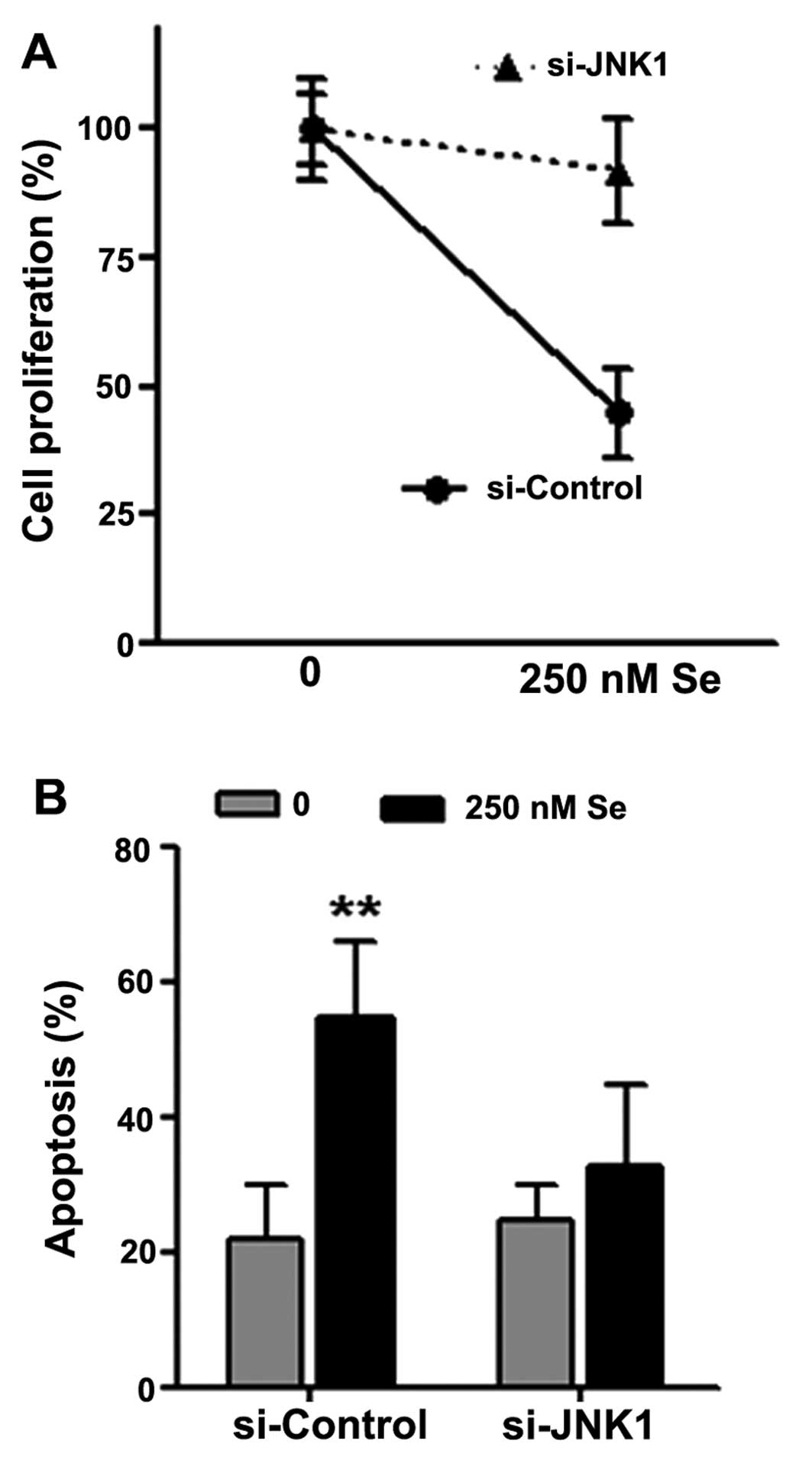
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Uğuz AC, Naziroğlu M, Espino J, Bejarano
I, Gonzalez D, Rodriguez AB and Pariente JA: Selenium modulates
oxidative stress-induced cell apoptosis in human myeloid HL-60
cells through regulation of calcium release and caspase-3 and -9
activities. J Membr Biol. 232:15–23. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Ip C: Lessons from basic research in
selenium and cancer prevention. J Nutr. 128:1845–1854.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Bonorden MJ, Li GX, Lee HJ, Hu H,
Zhang Y, Liao JD, Cleary MP and Lü J: Methyl-selenium compounds
inhibit prostate carcinogenesis in the transgenic adenocarcinoma of
mouse prostate model with survival benefit. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 2:484–495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Facompre N and El-Bayoumy K: Potential
stages for prostate cancer prevention with selenium: implications
for cancer survivors. Cancer Res. 69:2699–2703. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Clark LC, Combs GF Jr, Turnbull BW, Slate
EH, Chalker DK, Chow J, Davis LS, Glover RA, Graham GF, Gross EG,
et al: Effects of selenium supplementation for cancer prevention in
patients with carcinoma of the skin. A randomized controlled trial
Nutritional Prevention of Cancer Study Group. JAMA. 276:1957–1963.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Greenwald P, Anderson D, Nelson SA and
Taylor PR: Clinical trials of vitamin and mineral supplements for
cancer prevention. Am J Clin Nutr. 85:314S–317S. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hawk ET and Levin B: Colorectal cancer
prevention. J Clin Oncol. 23:378–391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Peters U and Takata Y: Selenium and the
prevention of prostate and colorectal cancer. Mol Nutr Food Res.
52:1261–1272. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fang W, Han A, Bi X, Xiong B and Yang W:
Tumor inhibition by sodium selenite is associated with activation
of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 and suppression of beta-catenin
signaling. Int J Cancer. 127:32–42. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Song Z, Tong C, Liang J, Dockendorff A,
Huang C, Augenlicht LH and Yang W: JNK1 is required for
sulindac-mediated inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of
apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 560:95–100. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tong C, Yin Z, Song Z, Dockendorff A,
Huang C, Mariadason J, Flavell RA, Davis RJ, Augenlicht LH and Yang
W: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 plays a critical role in intestinal
homeostasis and tumor suppression. Am J Pathol. 171:297–303. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Davis RJ: Signal transduction by the JNK
group of MAP kinases. Cell. 103:239–252. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu D, Fang W, Han A, Gallagher L, Davis
RJ, Xiong B and Yang W: c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 interacts with
and negatively regulates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling through
GSK3beta pathway. Carcinogenesis. 29:2317–2324. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang WC, Mathew J, Velcich A, Edelmann W,
Kucherlapati R, Lipkin M, Yang K and Augenlicht LH: Targeted
inactivation of the p21(WAF1/cip1) gene enhances Apc-initiated
tumor formation and the tumor-promoting activity of a Western-style
high-risk diet by altering cell maturation in the intestinal
mucosal. Cancer Res. 61:565–569. 2001.
|
|
17
|
van de Wetering M, Sancho E, Verweij C, de
Lau W, Oving I, Hurlstone A, van der Horn K, Batlle E, Coudreuse D,
Haramis AP, et al: The beta-catenin/TCF-4 complex imposes a crypt
progenitor phenotype on colorectal cancer cells. Cell. 111:241–250.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lü J and Jiang C: Selenium and cancer
chemoprevention: hypotheses integrating the actions of
selenoproteins and selenium metabolites in epithelial and
non-epithelial target cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:1715–1727.
2005.
|
|
20
|
Diwadkar-Navsariwala V and Diamond AM: The
link between selenium and chemoprevention: a case for
selenoproteins. J Nutr. 134:2899–2902. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Narayanan BA, Narayanan NK, Desai D,
Pittman B and Reddy BS: Effects of a combination of docosahexaenoic
acid and 1,4-phenylene bis(methylene) selenocyanate on
cyclooxygenase 2, inducible nitric oxide synthase and beta-catenin
pathways in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 25:2443–2449. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rao CV, Cooma I, Rodriguez JG, Simi B,
El-Bayoumy K and Reddy BS: Chemoprevention of familial adenomatous
polyposis development in the APC(min) mouse model by 1,4-phenylene
bis(methylene)selenocyanate. Carcinogenesis. 21:617–621. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu H, Jiang C, Ip C, Rustum YM and Lü J:
Methylseleninic acid potentiates apoptosis induced by
chemotherapeutic drugs in androgen-independent prostate cancer
cells. Clin Cancer Res. 11:2379–2388. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang C, Wang Z, Ganther H and Lu J:
Distinct effects of methylseleninic acid versus selenite on
apoptosis, cell cycle, and protein kinase pathways in DU145 human
prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 1:1059–1066.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bi X, Pohl N, Dong H and Yang W: Selenium
and sulindac are synergistic to inhibit intestinal tumorigenesis in
Apc/p21 mice. J Hematol Oncol. 6:82013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu D, Bi X, Fang W, Han A and Yang W:
GSK3beta is involved in JNK2-mediated beta-catenin inhibition. PLoS
One. 4:e66402009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bode AM and Dong Z: The functional
contrariety of JNK. Mol Carcinog. 46:591–598. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lippman SM, Klein EA, Goodman PJ, Lucia
MS, Thompson IM, Ford LG, Parnes HL, Minasian LM, Gaziano JM,
Hartline JA, et al: Effect of selenium and vitamin E on risk of
prostate cancer and other cancers: the Selenium and Vitamin E
Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT). JAMA. 301:39–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fang W, Goldberg ML, Pohl NM, Bi X, Tong
C, Xiong B, Koh TJ, Diamond AM and Yang W: Functional and physical
interaction between the selenium-binding protein 1 (SBP1) and the
glutathione peroxidase 1 selenoprotein. Carcinogenesis.
31:1360–1366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chu IM, Hengst L and Slingerland JM: The
Cdk inhibitor p27 in human cancer: prognostic potential and
relevance to anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:253–267. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|