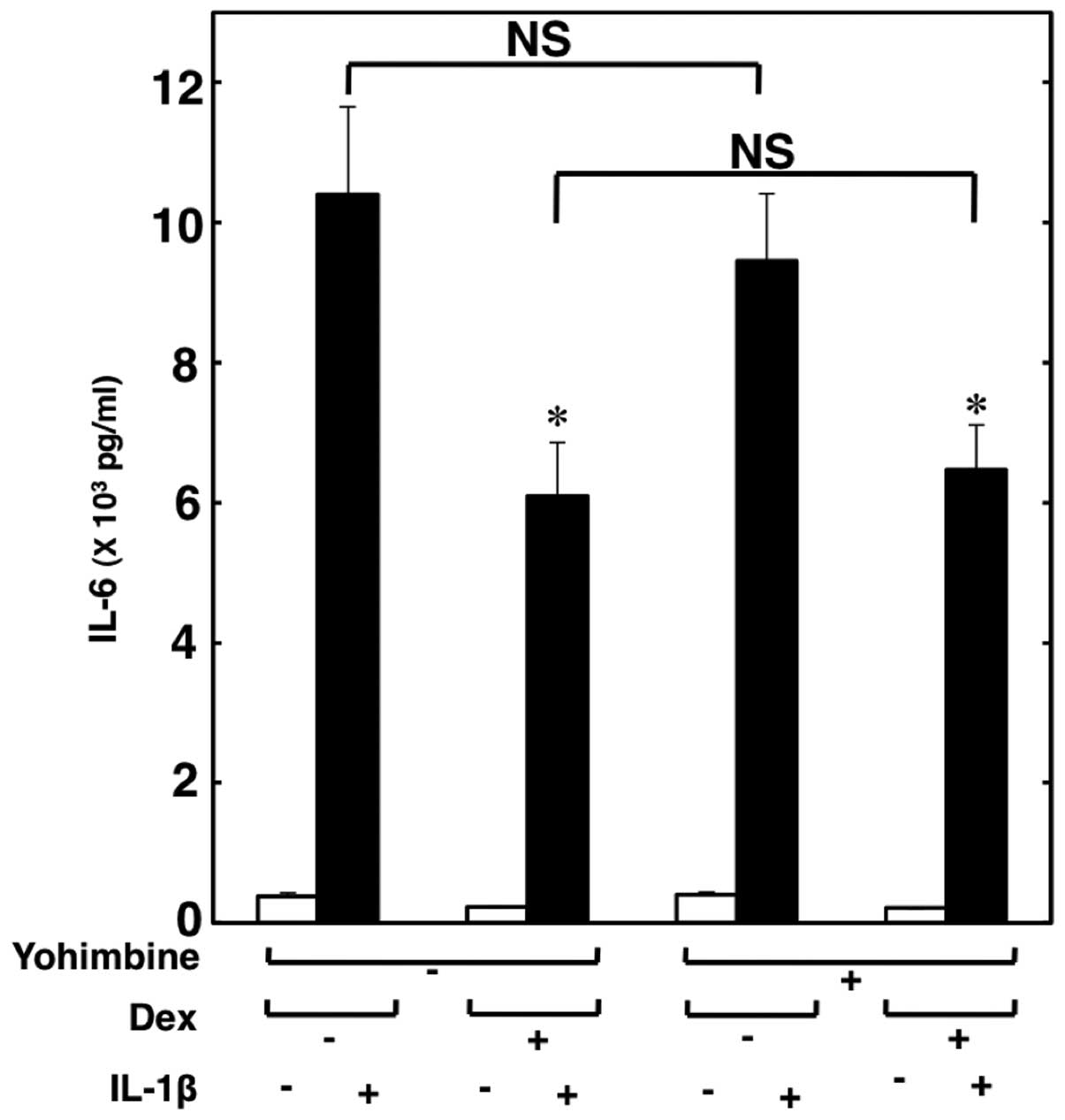
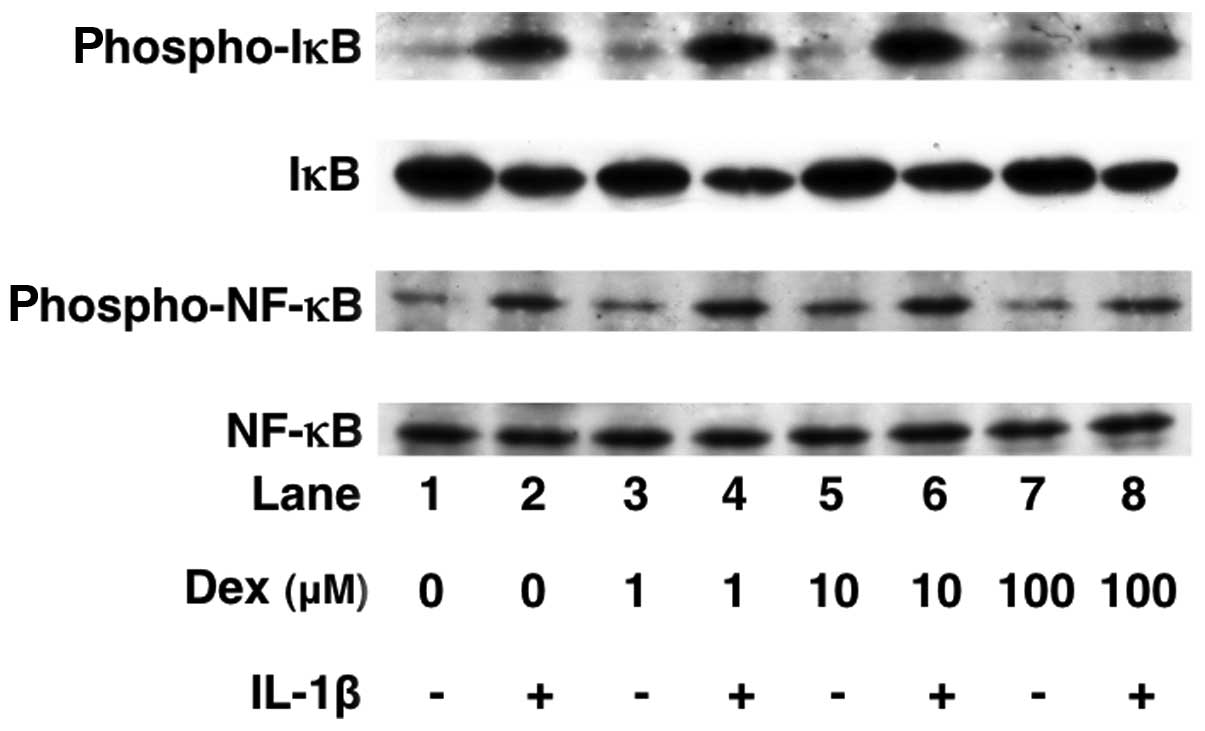
|
1
|
Ma D, Rajakumaraswamy N and Maze M:
α2-Adrenoceptor agonists: shedding light on
neuroprotection? Br Med Bull. 71:77–92. 2004.
|
|
2
|
Zhang Y and Kimelberg HK: Neuroprotection
by alpha 2 adrenergic agonists in cerebral ischemia. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 3:317–323. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sanders RD and Maze M:
α2-Adrenoceptor agonists. Curr Opin Invest. 8:25–33.
2007.
|
|
4
|
Benarroch EE: Neuron-astrocyte
interactions: partnership for normal function and disease in the
central nervous system. Mayo Clin Proc. 80:1326–1338. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Talke P and Bickler PE: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on hypoxia-evoked glutamate release and glutamate
receptor activity in hippocampal slices. Anesthesiology.
85:551–557. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan M, Dai H, Ding T, Dai A, Zhang F, Yu
L, Chen G and Chen Z: Effects of dexmedetomodine on the release of
glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor from rat astrocyte
cells. Neurochem Int. 58:549–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang F, Ding T, Yu L, Zhong Y, Dai H and
Yan M: Dexmedetomidine protects against oxygen-glucose
deprivation-induced injury through the I2 imidazoline
receptor-PI3K/AKT pathway in rat C6 glioma cells. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 64:120–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ and Rothwell NJ:
Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunnol. 5:629–640.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Simi A, Tsakiri N, Wang P and Rothwell NJ:
Interleukin-1 and inflammatory neurodegeneration. Biochem Soc
Trans. 35:1122–1126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Spooren A, Kolmus K, Laureys G, Clinckers
R, De Keyser J, Haegeman G and Gerlo S: Interleukin-6, a mental
cytokine. Brain Res Rev. 67:157–183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sanders RD, Hussell T and Maze M: Sedation
& immunomodulation. Anesthesiol Clin. 29:687–706. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Eser O, Fidan H, Sahin O, Cosar M, Yaman
M, Mollaoglu H, Songur A and Buyukbas S: The influence of
dexmedtomidine on ischemic rat hippocampus. Brain Res.
1218:250–256. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qiao H, Sanders RD, Ma D, Wu X and Maze M:
Sedation improves early outcome in severely septic Sprague Dawley
rats. Crit Care. 13:R1362009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Venn RM, Bryant A, Hall GM and Grounds RM:
Effects of dexmedetomidine on adrenocortical function, and the
cardiovascular, endocrine and inflammatory responses in
post-operative patients needing sedation in the intensive care
unit. Br J Anaesth. 86:650–656. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meniş D, Hekimoğlu S, Vatan İ, Yandım T,
Yüksel M and Süt N: Effects of midazolam and dexmedetomidine on
inflammatory responses and gastric intramucosal pH to sepsis, in
critically ill patients. Br J Anaesth. 98:550–552. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kawashima A, Harada T, Imada K, Yano T and
Mizuguchi K: Eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits interleukin-6
production in interleukin-1β-stimulated C6 glioma cells through
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Prostaglandins
Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 79:59–65. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanabe K, Kozawa O and Iida H: Midazolam
suppresses interleukin-1β-induced interleukin-6 release from rat
glial cells. J Neuroinflammation. 8:682011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zumwalt JW, Thunstrom BJ and Spangelo BL:
Interleukin-1β and catecholamines synergistically stimulate
interleukin-6 release from rat C6 glioma cells in vitro: a
potential role for lysophosphatidylcholine. Endocrinology.
140:888–896. 1999.
|
|
19
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morioka N, Sugimoto T, Tokuhara M, Dohi T
and Nakata Y: Noradrenaline induces clock gene Per1 mRNA expression
in C6 glioma cells through β2-adrenergic receptor
coupled with protein kinase A-cAMP response element binding protein
(PKA-CREB) and Src-tyrosine kinase-glycogen synthase kinase-3β
(Src-GSK-3β). J Pharmacol Sci. 113:234–245. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aantaa R, Marjamäki A and Scheinin M:
Molecular pharmacology of α2-adrenoceptor subtypes. Ann Med.
27:439–449. 1995.
|
|
22
|
Edwards LP, Brown-Bryan TA, McLean L and
Ernsberger P: Pharmacological properties of the central
antihypertensive agent, moxonidine. Cardiovasc Ther. 30:199–208.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nishizuka Y: Studies and perspectives of
protein kinase C. Science. 233:305–312. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Simonds WF: G protein regulation of
adenylate cyclase. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 20:66–73. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gallagher HC, Bacon CL, Odumeru OA,
Gallagher KF, Fitzpatrick T and Regan CM: Valproate activates
phosphodiesterase-mediated cAMP degradation: relevance to C6 glioma
G1 phase progression. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 26:73–81. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Adcock IM and Caramori G: Cross-talk
between pro-inflammatory transcription factors and glucocorticoids.
Immunol Cell Biol. 79:376–384. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iirola T, Ihmsen H, Laitio R, Kentala E,
Aantaa R, Kurvinen JP, Scheinin M, Schwilden H, Schüttler J and
Olkkola KT: Population pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine during
long-term sedation in intensive care patients. Br J Anaesth.
108:460–468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang R and Hertz L: Receptor subtype and
dose dependence of dexmedetomidine-induced accumulation of
[14C]glutamine in astrocytes suggests glial involvement
in its hypnotic-sedative and anesthetic-sparing effects. Brain Res.
873:297–301. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Y, Zhao Z, Code WE and Hertz L: A
correlation between dexmedetomidine-induced biphasic increases in
free cytosolic calcium concentration and energy metabolism in
astrocytes. Anesth Analg. 91:353–357. 2000.
|
|
30
|
Lambertsen KL, Biber K and Finsen B:
Inflammatory cytokines in experimental and human stroke. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 32:1677–1698. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bekker A, Haile M, Kline R, Didehvar S,
Babu R, Martiniuk F and Urban M: The effect of intraoperative
infusion of dexmedetomidine on the quality of recovery after major
surgery. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 25:16–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kang AH, Kim YS, Hong TH, Chae MS, Cho ML,
Her YM and Lee J: Effects of dexmedetomidine on inflammatory
responses in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Acta
Anaesthesiol Scand. 57:480–487. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saavedra A, Baltazar G and Duarte EP:
Driving GDNF expression: the green and the red traffic light. Prog
Neurobiol. 86:186–215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|