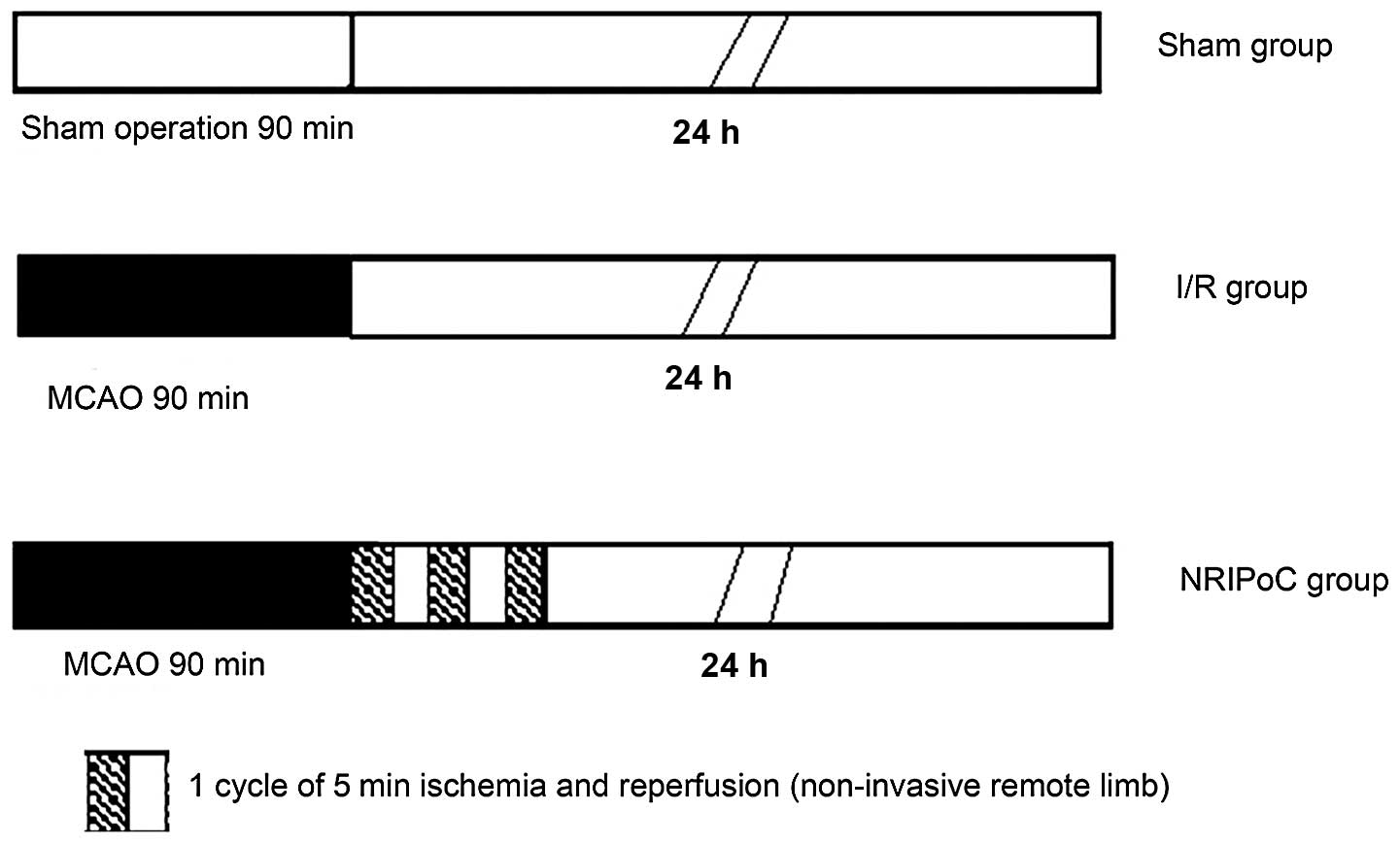
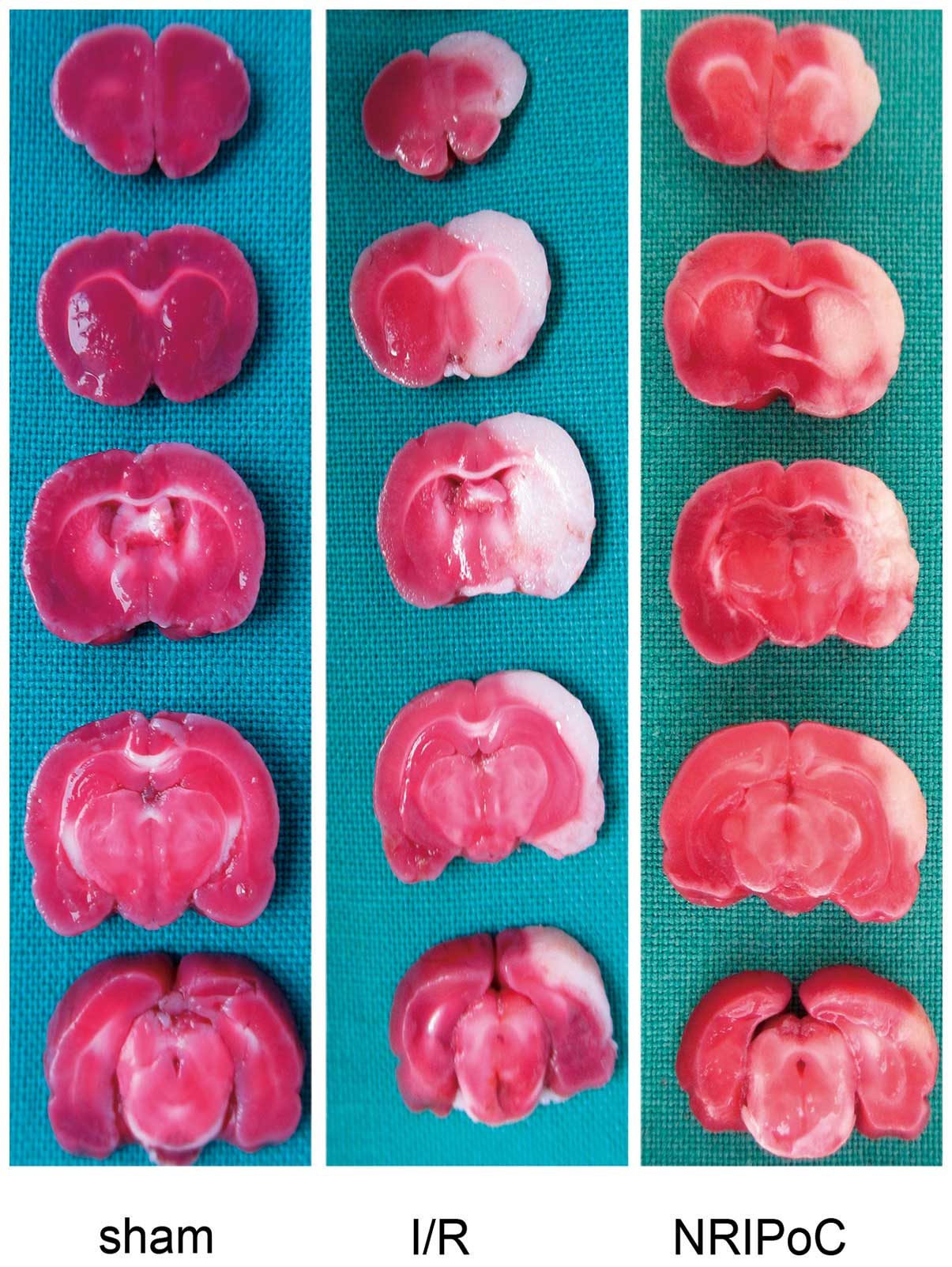
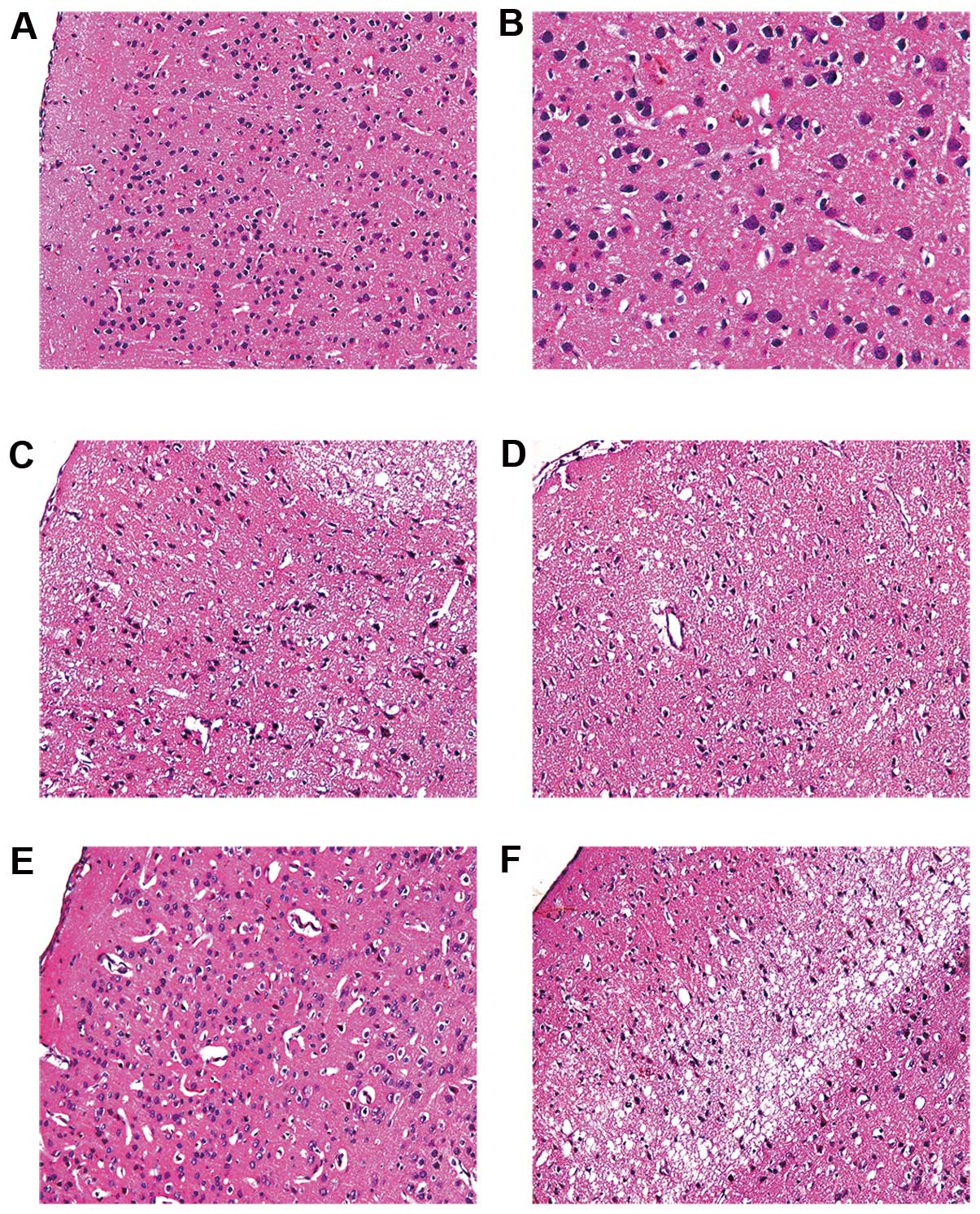
|
1
|
Bonita R: Epidemiology of stroke. Lancet.
339:342–344. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Murray CJ and Lopez AD: Mortality by cause
for eight regions of the world: Global Burden of Disease Study.
Lancet. 349:1269–1276. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gourdin MJ, Bree B and De Kock M: The
impact of ischaemia-reperfusion on the blood vessel. Eur J
Anaesthesiol. 26:537–547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Murry CE, Jennings RB and Reimer KA:
Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in
ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 74:1124–1136. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kitagawa K, Matsumoto M, Tagaya M, et al:
‘Ischemic tolerance’ phenomenon found in the brain. Brain Res.
528:21–24. 1990.
|
|
6
|
Zhao H, Sapolsky RM and Steinberg GK:
Interrupting reperfusion as a stroke therapy: ischemic
postconditioning reduces infarct size after focal ischemia in rats.
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 26:1114–1121. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang JY, Shen J, Gao Q, et al: Ischemic
postconditioning protects against global cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Stroke. 39:983–990.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu X, Chen H, Zhan B, et al: Attenuation
of reperfusion injury by renal ischemic postconditioning: the role
of NO. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 359:628–634. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yellon DM and Dana A: The preconditioning
phenomenon: A tool for the scientist or a clinical reality? Circ
Res. 87:543–550. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li CM, Zhang XH, Ma XJ and Luo M: Limb
ischemic postconditioning protects myocardium from
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Scand Cardiovasc J. 40:312–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hong DM, Jeon Y, Lee CS, et al: Effects of
remote ischemic preconditioning with postconditioning in patients
undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery - randomized
controlled trial. Circ J. 76:884–890. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vinten-Johansen J and Shi W: The science
and clinical translation of remote postconditioning. J Cardiovasc
Med (Hagerstown). 14:206–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ren C, Yan Z, Wei D, Gao X, Chen X and
Zhao H: Limb remote ischemic postconditioning protects against
focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 1288:88–94. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun J, Tong L, Luan Q, et al: Protective
effect of delayed remote limb ischemic postconditioning: role of
mitochondrial K(ATP) channels in a rat model of focal cerebral
ischemic reperfusion injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 32:851–859.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Q, Zhang X, Ding Q, et al: Limb
remote postconditioning alleviates cerebral reperfusion injury
through reactive oxygen species-mediated inhibition of delta
protein kinase C in rats. Anesth Analg. 113:1180–1187. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhou Y, Fathali N, Lekic T, et al: Remote
limb ischemic postconditioning protects against neonatal
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rat pups by the opioid
receptor/Akt pathway. Stroke. 42:439–444. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ren C, Gao X, Steinberg GK and Zhao H:
Limb remote-preconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats
and contradicts the dogma of therapeutic time windows for
preconditioning. Neuroscience. 151:1099–1103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qi ZF, Luo YM, Liu XR, et al:
AKT/GSK3beta-dependent autophagy contributes to the neuroprotection
of limb remote ischemic postconditioning in the transient cerebral
ischemic rat model. CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:965–973. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peng B, Guo QL, He ZJ, et al: Remote
ischemic postconditioning protects the brain from global cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury by up-regulating endothelial nitric
oxide synthase through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Brain Res.
1445:92–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Koch S, Katsnelson M, Dong C and
Perez-Pinzon M: Remote ischemic limb preconditioning after
subarachnoid hemorrhage: a phase Ib study of safety and
feasibility. Stroke. 42:1387–1391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Walsh SR, Nouraei SA, Tang TY, Sadat U,
Carpenter RH and Gaunt ME: Remote ischemic preconditioning for
cerebral and cardiac protection during carotid endarterectomy:
results from a pilot randomized clinical trial. Vasc Endovascular
Surg. 44:434–439. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hu S, Dong H, Zhang H, et al: Noninvasive
limb remote ischemic preconditioning contributes neuroprotective
effects via activation of adenosine A1 receptor and redox status
after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res.
1459:81–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhong H, Gao Z, Chen M, et al:
Cardioprotective effect of remote ischemic postconditioning on
children undergoing cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial.
Paediatr Anaesth. 23:726–733. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Sha O and Cho EY: Remote ischemic
postconditioning promotes the survival of retinal ganglion cells
after optic nerve injury. J Mol Neurosci. 51:639–646. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dave KR, Saul I, Prado R, Busto R and
Perez-Pinzon MA: Remote organ ischemic preconditioning protect
brain from ischemic damage following asphyxial cardiac arrest.
Neurosci Lett. 404:170–175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A and Hofer M:
Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches.
J Transl Med. 7:972009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Broughton BR, Reutens DC and Sobey CG:
Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 40:e331–e339.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
MacManus JP and Linnik MD: Gene expression
induced by cerebral ischemia: an apoptotic perspective. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 17:815–832. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Y, Powers C, Jiang N and Chopp M:
Intact, injured, necrotic and apoptotic cells after focal cerebral
ischemia in the rat. J Neurol Sci. 156:119–132. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Feuerstein GZ, Wang X and Barone FC:
Inflammatory gene expression in cerebral ischemia and trauma.
Potential new therapeutic targets. Ann NY Acad Sci. 825:179–193.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Benjelloun N, Renolleau S, Represa A,
Ben-Ari Y and Charriaut-Marlangue C: Inflammatory responses in the
cerebral cortex after ischemia in the P7 neonatal Rat. Stroke.
30:1916–1924. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng L, Wang Y, Liu J, et al:
Pro-inflammatory cytokine network in peripheral inflammation
response to cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 548:4–9. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saito K, Suyama K, Nishida K, Sei Y and
Basile AS: Early increases in TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-1 beta levels
following transient cerebral ischemia in gerbil brain. Neurosci
Lett. 206:149–152. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maddahi A, Kruse LS, Chen QW and Edvinsson
L: The role of tumor necrosis factor-α and TNF-α receptors in
cerebral arteries following cerebral ischemia in rat. J
Neuroinflammation. 8:1072011.
|
|
35
|
Vakili A, Mojarrad S, Akhavan MM and
Rashidy-Pour A: Pentoxifylline attenuates TNF-α protein levels and
brain edema following temporary focal cerebral ischemia in rats.
Brain Res. 1377:119–125. 2011.
|
|
36
|
Latanich CA and Toledo-Pereyra LH:
Searching for NF-kappaB-based treatments of ischemia reperfusion
injury. J Invest Surg. 22:301–315. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ridder DA and Schwaninger M: NF-kappaB
signaling in cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 158:995–1006. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
MacDonald RL and Stoodley M:
Pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo).
38:1–11. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang S, Qi Y, Xu Y, et al: Protective
effect of flavonoid-rich extract from Rosa laevigata Michx
on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppression of
apoptosis and inflammation. Neurochem Int. 63:522–532.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang L, Dong LY, Li YJ, Hong Z and Wei
WS: The microRNA miR-181c controls microglia-mediated neuronal
apoptosis by suppressing tumor necrosis factor. J
Neuroinflammation. 9:2112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gu JH, Ge JB, Li M, Wu F, Zhang W and Qin
ZH: Inhibition of NF-κB activation is associated with
anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of Ginkgolide B in a
mouse model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharm
Sci. 47:652–660. 2012.
|
|
42
|
Justicia C, Gabriel C and Planas AM:
Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway following transient focal
cerebral ischemia: signaling through Jak1 and Stat3 in astrocytes.
Glia. 30:253–270. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Suzuki S, Tanaka K, Nogawa S, Dembo T,
Kosakai A and Fukuuchi Y: Phosphorylation of signal transducer and
activator of transcription-3 (Stat3) after focal cerebral ischemia
in rats. Exp Neurol. 170:63–71. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Satriotomo I, Bowen KK and Vemuganti R:
JAK2 and STAT3 activation contributes to neuronal damage following
transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem. 98:1353–1368. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xie HF, Xu RX, Wei JP, Jiang XD and Liu
ZH: P-JAK2 and P-STAT3 protein expression and cell apoptosis
following focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Nan
Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 27:208–211. 2182007.(In Chinese).
|
|
46
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang N, Guo QL, Ye Z, Xia PP, Wang E and
Yuan YJ: Preconditioning of intravenous parecoxib attenuates focal
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Chin Med J (Engl).
124:2004–2008. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wei L, Yu SP, Gottron F, Snider BJ, Zipfel
GJ and Choi DW: Potassium channel blockers attenuate hypoxia- and
ischemia-induced neuronal death in vitro and in vivo. Stroke.
34:1281–1286. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T:
Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. 2nd edition. Cold Spring
Harbor Laboratory Press; New York: 1989
|
|
50
|
Astrup J, Siesjö BK and Symon L:
Thresholds in cerebral ischemia - the ischemic penumbra. Stroke.
12:723–725. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Paciaroni M, Caso V and Agnelli G: The
concept of ischemic penumbra in acute stroke and therapeutic
opportunities. Eur Neurol. 61:321–330. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tajiri S, Oyadomari S, Yano S, et al:
Ischemia-induced neuronal cell death is mediated by the endoplasmic
reticulum stress pathway involving CHOP. Cell Death Differ.
11:403–415. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hu BR, Martone ME, Jones YZ and Liu CL:
Protein aggregation after transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci.
20:3191–3199. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xing B, Chen H, Zhang M, et al: Ischemic
postconditioning inhibits apoptosis after focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. Stroke. 39:2362–2369. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu Y, Sercombe R, Xie D, Liu K and Chen
L: Inhibition of caspase-9 activation and apoptosis is involved in
ischemic preconditioning-induced neuroprotection in rat brain.
Neurol Res. 29:855–861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Prasad SS, Russell M and Nowakowska M:
Neuroprotection induced in vitro by ischemic preconditioning and
postconditioning: modulation of apoptosis and PI3K-Akt pathways. J
Mol Neurosci. 43:428–442. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xia DY, Li W, Qian HR, Yao S, Liu JG and
Qi XK: Ischemia preconditioning is neuroprotective in a rat
cerebral ischemic injury model through autophagy activation and
apoptosis inhibition. Braz J Med Biol Res. 46:580–588. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kroemer G: Mitochondrial control of
apoptosis: an introduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
304:433–435. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lim ML, Lum MG, Hansen TM, Roucou X and
Nagley P: On the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
during cell death signaling. J Biomed Sci. 9:488–506. 2002.
|
|
60
|
Kuwana T, Mackey MR, Perkins G, et al:
Bid, Bax, and lipids cooperate to form supramolecular openings in
the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cell. 111:331–342. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Love S: Apoptosis and brain ischaemia.
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 27:267–282. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Planas AM, Gorina R and Chamorro A:
Signalling pathways mediating inflammatory responses in brain
ischaemia. Biochem Soc Trans. 34:1267–1270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Planas AM, Soriano MA, Berruezo M, et al:
Induction of Stat3, a signal transducer and transcription factor,
in reactive microglia following transient focal cerebral ischaemia.
Eur J Neurosci. 8:2612–2618. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yamaguchi K, Itoh Y, Yokomizo C, et al:
Blockade of interleukin-6 signaling enhances hepatic steatosis but
improves liver injury in methionine choline-deficient diet-fed
mice. Lab Invest. 90:1169–1178. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wen TC, Peng H, Hata R, Desaki J and
Sakanaka M: Induction of phosphorylated-Stat3 following focal
cerebral ischemia in mice. Neurosci Lett. 303:153–156. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Nielsen M, Kaestel CG, Eriksen KW, et al:
Inhibition of constitutively activated Stat3 correlates with
altered Bcl-2/Bax expression and induction of apoptosis in mycosis
fungoides tumor cells. Leukemia. 13:735–738. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Dinasarapu AR, Gupta S, Ram Maurya M, et
al: A combined omics study on activated macrophages - enhanced role
of STATs in apoptosis, immunity and lipid metabolism.
Bioinformatics. 29:2735–2743. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Spehlmann ME, Manthey CF, Dann SM, et al:
Trp53 deficiency protects against acute intestinal inflammation. J
Immunol. 191:837–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lee TL, Yeh J, Friedman J, et al: A signal
network involving coactivated NF-kappaB and STAT3 and altered p53
modulates BAX/BCL-XL expression and promotes cell survival of head
and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 122:1987–1998.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Chiang MF, et al:
Secretoneurin promotes neuroprotection and neuronal plasticity via
the Jak2/Stat3 pathway in murine models of stroke. J Clin Invest.
118:133–148. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jung JE, Kim GS and Chan PH:
Neuroprotection by interleukin-6 is mediated by signal transducer
and activator of transcription 3 and antioxidative signaling in
ischemic stroke. Stroke. 42:3574–3579. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Allen CL and Bayraktutan U: Oxidative
stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int J
Stroke. 4:461–470. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Blackwell TS and Christman JW: The role of
nuclear factor-kappa B in cytokine gene regulation. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 17:3–9. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ginis I, Jaiswal R, Klimanis D, Liu J,
Greenspon J and Hallenbeck JM: TNF-alpha-induced tolerance to
ischemic injury involves differential control of NF-kappaB
transactivation: the role of NF-kappaB association with p300
adaptor. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 22:142–152. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Jurewicz A, Matysiak M, Tybor K, Kilianek
L, Raine CS and Selmaj K: Tumour necrosis factor-induced death of
adult human oligodendrocytes is mediated by apoptosis inducing
factor. Brain. 128:2675–2688. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|