|
1
|
Wakabayashi S, Yamaguchi K, Kumakura S, et
al: Effects of anesthesia with sevoflurane and propofol on the
cytokine/chemokine production at the airway epithelium during
esophagectomy. Int J Mol Med. 34:137–144. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Signorelli SS, Fiore V and Malaponte G:
Inflammation and peripheral arterial disease: the value of
circulating biomarkers (Review). Int J Mol Med. 33:777–783.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Clavel G, Thiolat A and Boissier MC:
Interleukin newcomers creating new numbers in rheumatology: IL-34
to IL-38. Joint Bone Spine. 80:449–453. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lin H, Lee E, Hestir K, Leo C, et al:
Discovery of a cytokine and its receptor by functional screening of
the extracellular proteome. Science. 320:807–811. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
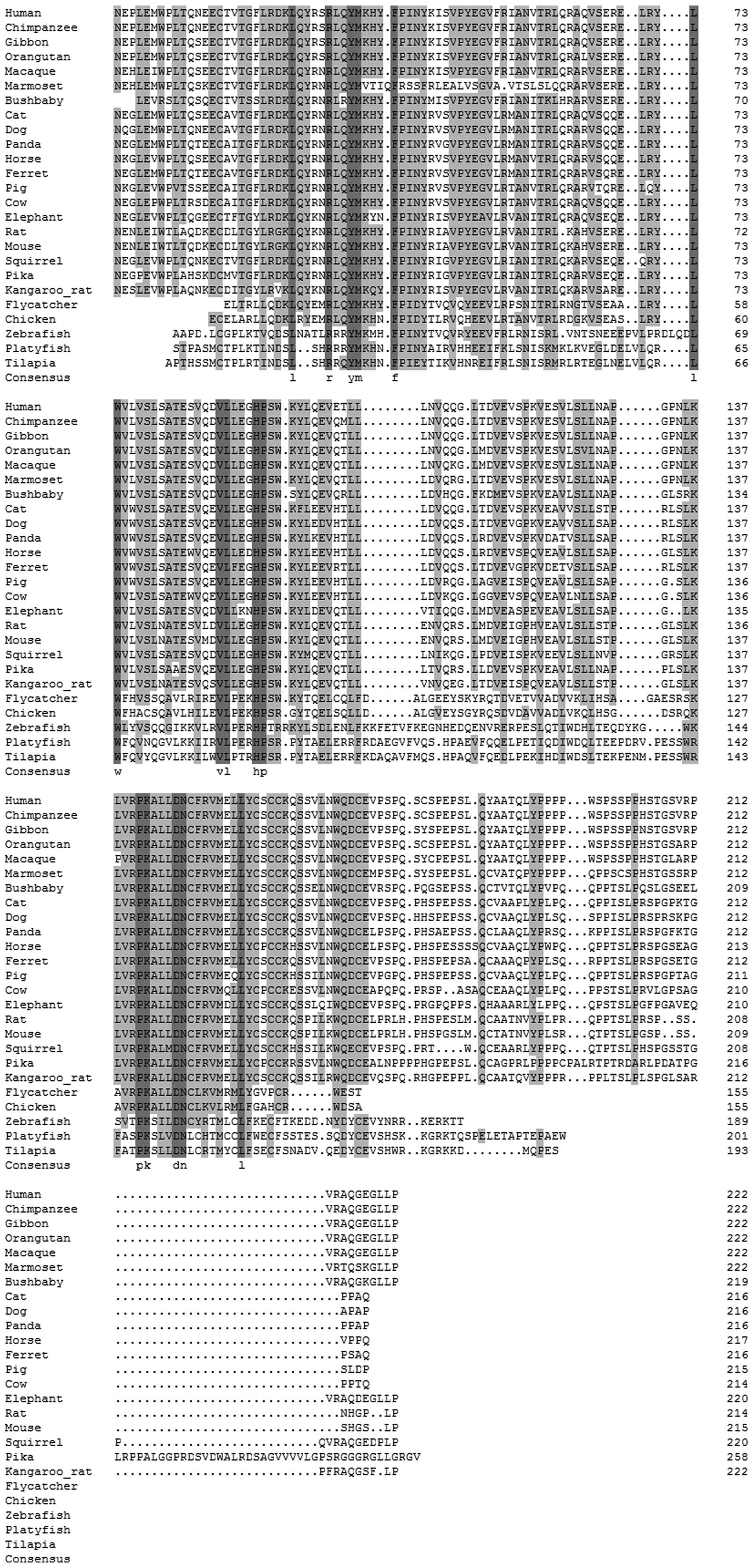
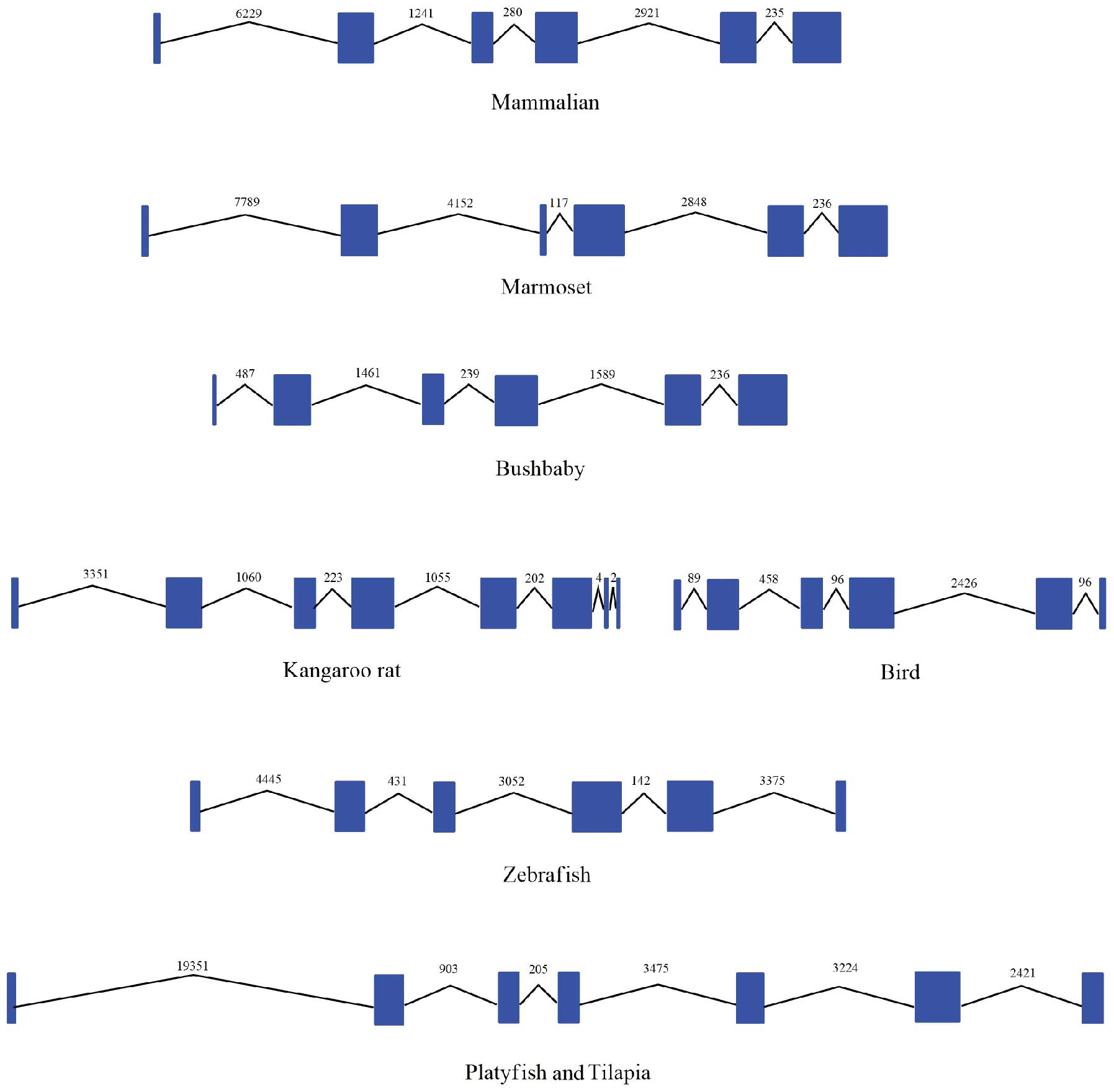
Boström EA and Lundberg P: The newly
discovered cytokine IL-34 is expressed in gingival fibroblasts,
shows enhanced expression by pro-inflammatory cytokines, and
stimulates osteoclast differentiation. PLoS One. 8:e816652013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moon SJ, Hong YS, Ju JH, Kwok SK, Park SH
and Min JK: Increased levels of interleukin 34 in serum and
synovial fluid are associated with rheumatoid factor and anticyclic
citrullinated peptide antibody titers in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. J Rheumatol. 40:1842–1849. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hwang SJ, Choi B, Kang SS, et al:
Interleukin-34 produced by human fibroblast-like synovial cells in
rheumatoid arthritis supports osteoclastogenesis. Arthritis Res
Ther. 14:R142012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen Z, Buki K, Vääräniemi J, Gu G and
Väänänen HK: The critical role of IL-34 in osteoclastogenesis. PLoS
One. 6:e186892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
El-Gamal MI, Anbar HS, Yoo KH and Oh CH:
FMS kinase inhibitors: Current status and future prospects. Med Res
Rev. 33:599–636. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Burns CJ and Wilks AF: c-FMS inhibitors: a
patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 21:147–165. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baud’huin M, Renault R, Charrier C, et al:
Interleukin-34 is expressed by giant cell tumours of bone and plays
a key role in RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Pathol.
221:77–86. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Petráčková M, Staněk L, Mandys V, Dundr P
and Vonka V: Properties of bcr-abl-transformed mouse 12B1 cells
secreting interleukin-2 and granulocyte-macrophage colony
stimulating factor (GM-CSF): II. Adverse effects of GM-CSF. Int J
Oncol. 40:1915–1922. 2012.
|
|
13
|
Fournier P, Aigner M and Schirrmacher V:
Targeting of IL-2 and GM-CSF immunocytokines to a tumor vaccine
leads to increased anti-tumor activity. Int J Oncol. 38:1719–1729.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kitoh Y, Saio M, Gotoh N, et al: Combined
GM-CSF treatment and M-CSF inhibition of tumor-associated
macrophages induces dendritic cell-like signaling in vitro. Int J
Oncol. 38:1409–1419. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tada F, Abe M, Hirooka M, et al: Phase
I/II study of immunotherapy using tumor antigen-pulsed dendritic
cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
41:1601–1609. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang L, Luo Y and Wei J: Integrative
genomic analyses on Ikaros and its expression related to solid
cancer prognosis. Oncol Rep. 24:571–577. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang L, Luo Y, Wei J and He S: Integrative
genomic analyses on IL28RA, the common receptor of interferon-λ1,
-λ2 and -λ3. Int J Mol Med. 25:807–812. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang L, Wei J and He S: Integrative
genomic analyses on interferon-λs and their roles in cancer
prediction. Int J Mol Med. 25:299–304. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu H, Yuan J, Xiao C and Qin Y:
Integrative genomic analyses of recepteur d’origine nantais and its
prognostic value in cancer. Int J Mol Med. 31:1248–1254.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang M, Wei X, Shi L, Chen B, Zhao G and
Yang H: Integrative genomic analyses of the histamine H1 receptor
and its role in cancer prediction. Int J Mol Med. 33:1019–1026.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang B, Chen K, Xu W, Chen D, Tang W and
Xia TS: Integrative genomic analyses of secreted protein acidic and
rich in cysteine and its role in cancer prediction. Mol Med Rep.
10:1461–1468. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
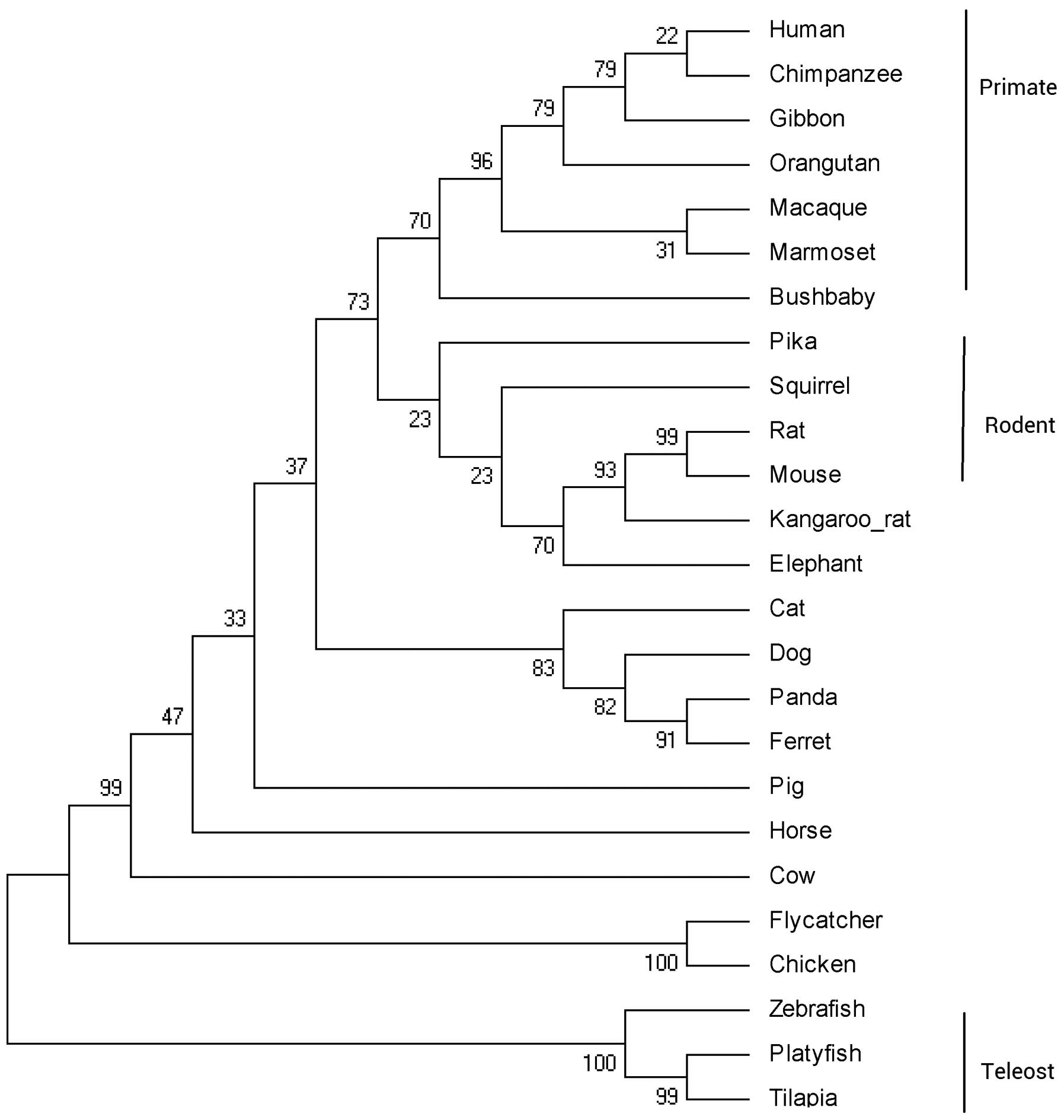
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J and Tamura K:
MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA
and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform. 9:299–306. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Z: PAML: a program package for
phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci.
13:555–556. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang Z, Nielsen R, Goldman N and Pedersen
AM: Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure
at amino acid sites. Genetics. 155:431–449. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Forbes SA, Bindal N, Bamford S, et al:
COSMIC: mining complete cancer genomes in the Catalogue of Somatic
Mutations in Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D945–D950. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: Integrative genomic
analyses on GLI1: positive regulation of GLI1 by Hedgehog-GLI,
TGFβ-Smads, and RTK-PI3K-AKT signals, and negative regulation of
GLI1 by Notch-CSL-HES/HEY, and GPCR-Gs-PKA signals. Int J Oncol.
35:187–192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Integrative genomic
analyses of WNT11: transcriptional mechanisms based on canonical
WNT signals and GATA transcription factors signaling. Int J Mol
Med. 24:247–251. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Transcriptional
mechanisms of WNT5A based on NF-κB, Hedgehog, TGFβ, and Notch
signaling cascades. Int J Mol Med. 23:763–769. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Integrative genomic
analyses of ZEB2: Transcriptional regulation of ZEB2 based on
SMADs, ETS1, HIF1α, POU/OCT, and NF-κB. Int J Oncol. 34:1737–1742.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chalifa-Caspi V, Yanai I, Ophir R, et al:
GeneAnnot: comprehensive two-way linking between oligonucleotide
array probesets and GeneCards genes. Bioinformatics. 20:1457–1458.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Parkinson H, Sarkans U, Shojatalab M, et
al: ArrayExpress - a public repository for microarray gene
expression data at the EBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:D553–D555. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mizuno H, Kitada K, Nakai K and Sarai A:
PrognoScan: a new database for meta-analysis of the prognostic
value of genes. BMC Med Genomics. 2:182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang T, Kono T, Monte MM, et al:
Identification of IL-34 in teleost fish: differential expression of
rainbow trout IL-34, MCSF1 and MCSF2, ligands of the MCSF receptor.
Mol Immunol. 53:398–409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bouafia A, Corre S, Gilot D, Mouchet N,
Prince S and Galibert MD: p53 requires the stress sensor USF1 to
direct appropriate cell fate decision. PLoS Genet. 10:e10043092014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ikeda R, Nishizawa Y, Tajitsu Y, et al:
Regulation of major vault protein expression by upstream
stimulating factor 1 in SW620 human colon cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
31:197–201. 2014.
|
|
36
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: Comparative genomics
on Vangl1 and Vangl2 genes. Int J Oncol. 26:1435–1440.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Feng C, Zhang Y, Yin J, Li J, Abounader R
and Zuo Z: Regulatory factor X1 is a new tumor suppressive
transcription factor that acts via direct downregulation of CD44 in
glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 16:1078–1085. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu F, Zhu X, Han T, et al: The oncoprotein
hepatitis B X-interacting protein promotes the migration of ovarian
cancer cells through the upregulation of S-phase kinase-associated
protein 2 by Sp1. Int J Oncol. 45:255–263. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liang X, Li ZL, Jiang LL, Guo QQ, Liu MJ
and Nan KJ: Suppression of lung cancer cell invasion by LKB1 is due
to the downregulation of tissue factor and vascular endothelial
growth factor, partly dependent on SP1. Int J Oncol. 44:1989–1997.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chae JI, Cho JH, Lee KA, et al: Role of
transcription factor Sp1 in the quercetin-mediated inhibitory
effect on human malignant pleural mesothelioma. Int J Mol Med.
30:835–841. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee KA, Lee YJ, Ban JO, et al: The
flavonoid resveratrol suppresses growth of human malignant pleural
mesothelioma cells through direct inhibition of specificity protein
1. Int J Mol Med. 30:21–27. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moritsugu R, Tamai K, Nakano H, et al:
Functional analysis of the nuclear localization signal of the POU
transcription factor Skn-1a in epidermal keratinocytes. Int J Mol
Med. 34:539–544. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Human FOX gene family
(Review). Int J Oncol. 25:1495–1500. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Transcriptional
regulation of WNT2B based on the balance of Hedgehog, Notch, BMP
and WNT signals. Int J Oncol. 34:1411–1415. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Metzeler KH, Hummel M, Bloomfield CD, et
al: An 86-probe-set gene-expression signature predicts survival in
cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
112:4193–4201. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Freije WA, Castro-Vargas FE, Fang Z, et
al: Gene expression profiling of gliomas strongly predicts
survival. Cancer Res. 64:6503–6510. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Smith JJ, Deane NG, Wu F, et al:
Experimentally derived metastasis gene expression profile predicts
recurrence and death in patients with colon cancer.
Gastroenterology. 138:958–968. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Okayama H, Kohno T, Ishii Y, et al:
Identification of genes upregulated in ALK-positive and
EGFR/KRAS/ALK-negative lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res.
72:100–111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lee ES, Son DS, Kim SH, et al: Prediction
of recurrence-free survival in postoperative non-small cell lung
cancer patients by using an integrated model of clinical
information and gene expression. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7397–7404.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|