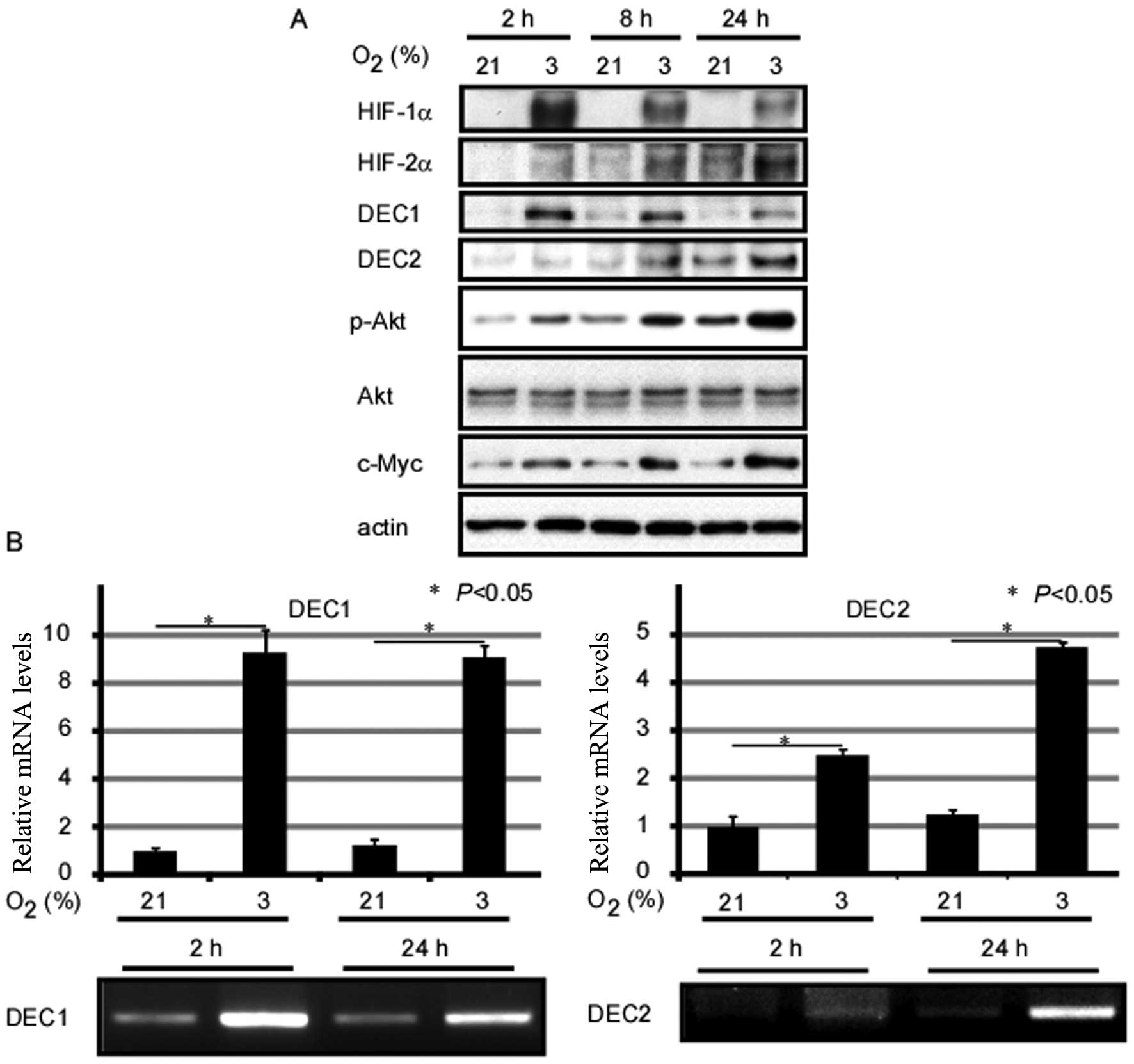
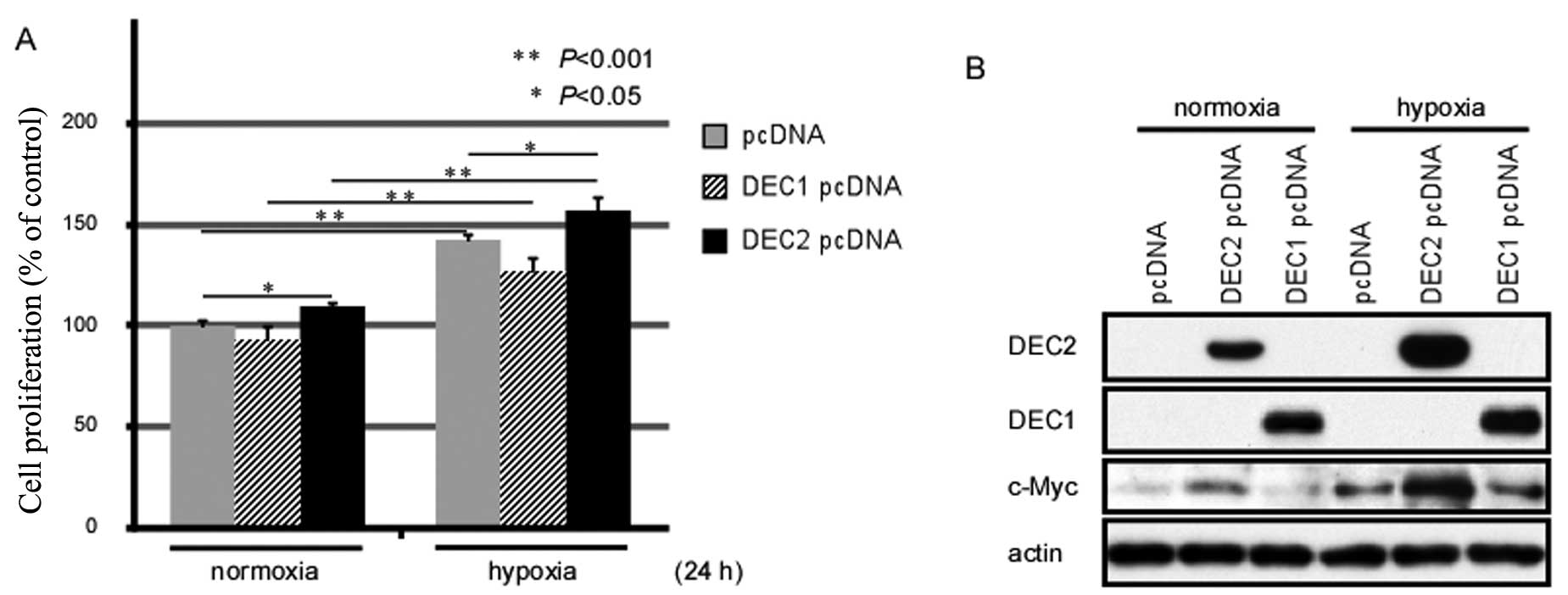
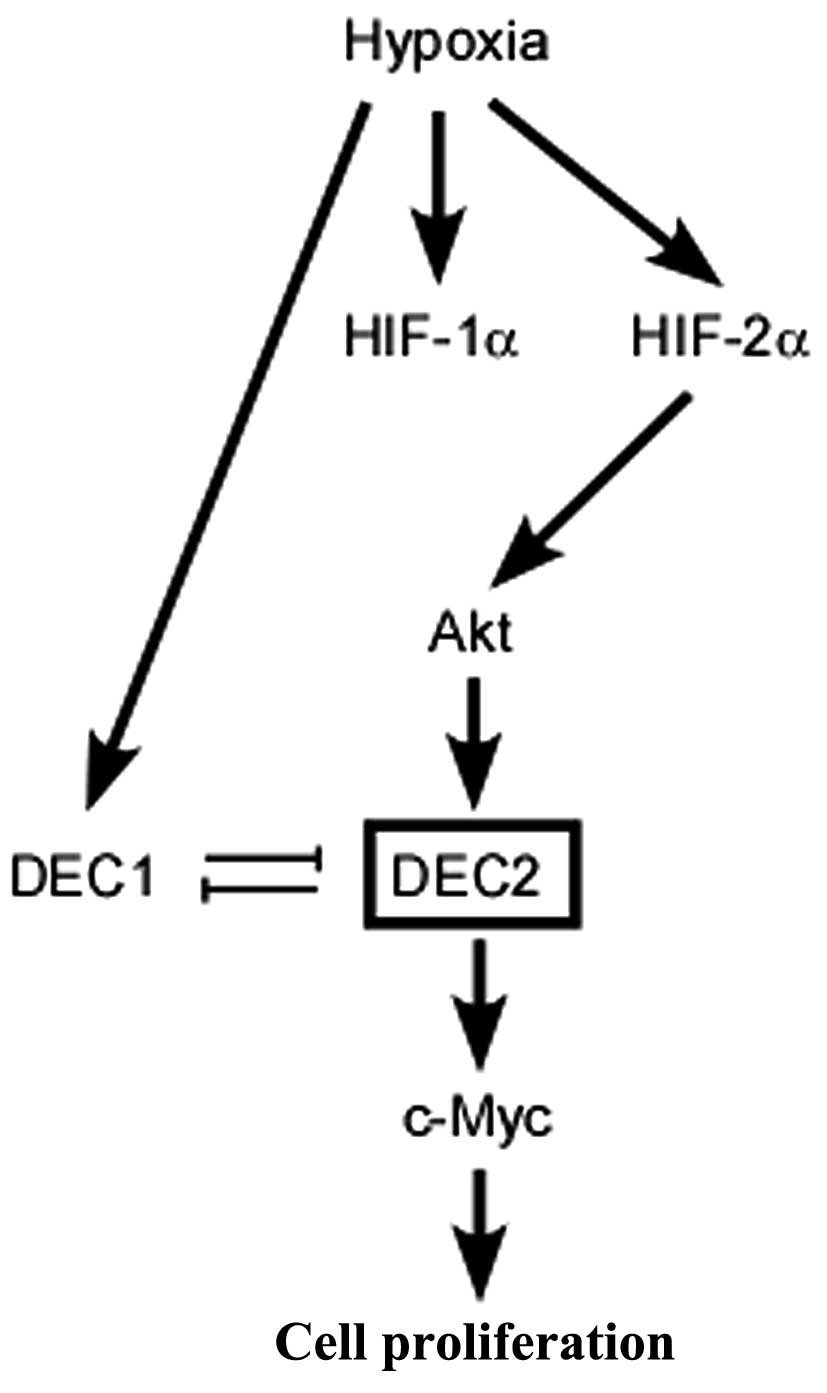
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Favaro E, Lord S, Harris AL and Buffa FM:
Gene expression and hypoxia in breast cancer. Genome Med. 3:552011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fyles A, Milosevic M, Hedley D, et al:
Tumor hypoxia has independent predictor impact only in patients
with node-negative cervix cancer. J Clin Oncol. 20:680–687. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hockel M, Schlenger K, Aral B, Mitze M,
Schaffer U and Vaupel P: Association between tumor hypoxia and
malignant progression in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix.
Cancer Res. 56:4509–4515. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jubb AM, Buffa FM and Harris AL:
Assessment of tumour hypoxia for prediction of response to therapy
and cancer prognosis. J Cell Mol Med. 14:18–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nordsmark M, Bentzen SM, Rudat V, et al:
Prognostic value of tumor oxygenation in 397 head and neck tumors
after primary radiation therapy. An international multi-center
study. Radiother Oncol. 77:18–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vaupel P and Mayer A: Hypoxia in cancer:
significance and impact on clinical outcome. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:225–239. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu CJ, Sataur A, Wang L, Chen H and Simon
MC: The N-terminal transactivation domain confers target gene
specificity of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha.
Mol Biol Cell. 18:4528–4542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Keith B, Johnson RS and Simon MC: HIF1α
and HIF2α: sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and
progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:9–22. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Loboda A, Jozkowicz A and Dulak J: HIF-1
versus HIF-2–is one more important than the other? Vascul
Pharmacol. 56:245–251. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Packham G and Cleveland JL: c-Myc and
apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1242:11–28. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hoffman B and Liebermann DA: The
proto-oncogene c-myc and apoptosis. Oncogene. 17:3351–3357. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dang CV: c-Myc target genes involved in
cell growth, apoptosis, and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 19:1–11.
1999.
|
|
14
|
Dang CV, Resar LM, Emison E, et al:
Function of the c-Myc oncogenic transcription factor. Exp Cell Res.
253:63–77. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Elend M and Eilers M: Cell growth:
downstream of Myc - to grow or to cycle? Curr Biol. 9:R936–R938.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Prendergast GC: Mechanisms of apoptosis by
c-Myc. Oncogene. 18:2967–2987. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu Y, Sato F, Bhawal UK, et al: Basic
helix-loop-helix transcription factors DEC1 and DEC2 regulate the
paclitaxel-induced apoptotic pathway of MCF-7 human breast cancer
cells. Int J Mol Med. 27:491–495. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Sato F, Kawamoto T, et al:
Anti-apoptotic effect of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)
transcription factor DEC2 in human breast cancer cells. Genes
Cells. 15:315–325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang J, Zubovitz J, Petrocelli T, et al:
PKB/Akt phosphorylates p27, impairs nuclear import of p27 and
opposes p27-mediated G1 arrest. Nat Med. 8:1153–1160. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gordan JD, Thompson CB and Simon MC: HIF
and c-Myc: sibling rivals for control of cancer cell metabolism and
proliferation. Cancer Cell. 12:108–113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bhawal UK, Sato F, Arakawa Y, et al: Basic
helix-loop-helix transcription factor DEC1 negatively regulates
cyclin D1. J Pathol. 224:420–429. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hamaguchi H, Fujimoto K, Kawamoto T, et
al: Expression of the gene for Dec2, a basic helix-loop-helix
transcription factor, is regulated by a molecular clock system.
Biochem J. 382:43–50. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fujimoto K, Hamaguchi H, Hashiba T, et al:
Transcriptional repression by the basic helix-loop-helix protein
Dec2: multiple mechanisms through E-box elements. Int J Mol Med.
19:925–932. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nakashima A, Kawamoto T, Honda KK, et al:
DEC1 modulates the circadian phase of clock gene expression. Mol
Cell Biol. 28:4080–4092. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang L and Li QQ: Embryo-chondrocyte
expressed gene 1, downregulating hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha,
is another marker of lung tumor hypoxia. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
28:549–558. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zawel L, Yu J, Torrance CJ, et al: DEC1 is
a downstream target of TGF-beta with sequence-specific
transcriptional repressor activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:2848–2853. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ivanova AV, Ivanov SV, Zhang X, Ivanov VN,
Timofeeva OA and Lerman MI: STRA13 interacts with STAT3 and
modulates transcription of STAT3-dependent targets. J Mol Biol.
340:641–653. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boudjelal M, Taneja R, Matsubara S,
Bouillet P, Dolle P and Chambon P: Overexpression of Stra13, a
novel retinoic acid-inducible gene of the basic helix-loop-helix
family, inhibits mesodermal and promotes neuronal differentiation
of P19 cells. Genes Dev. 11:2052–2065. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamada K, Kawata H, Shou Z, Mizutani T,
Noguchi T and Miyamoto K: Insulin induces the expression of the
SHARP-2/Stra13/DEC1 gene via a phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. J
Biol Chem. 278:30719–30724. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Honma S, Kawamoto T, Takagi Y, et al: Dec1
and Dec2 are regulators of the mammalian molecular clock. Nature.
419:841–844. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamada K and Miyamoto K: Basic
helix-loop-helix transcription factors, BHLHB2 and BHLHB3; their
gene expressions are regulated by multiple extracellular stimuli.
Front Biosci. 10:3151–3171. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Loboda A, Jozkowicz A and Dulak J: HIF-1
and HIF-2 transcription factors - similar but not identical. Mol
Cells. 29:435–442. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koh MY and Powis G: Passing the baton: the
HIF switch. Trends Biochem Sci. 37:364–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bishop JM: Retroviruses and cancer genes.
Adv Cancer Res. 37:1–32. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liao DJ and Dickson RB: c-Myc in breast
cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 7:143–164. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Weng W, Yang Q, Huang M, et al: c-Myc
inhibits TP53INP1 expression via promoter methylation in esophageal
carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 405:278–284. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dang CV, O’Donnell KA, Zeller KI, Nguyen
T, Osthus RC and Li F: The c-Myc target gene network. Semin Cancer
Biol. 16:253–264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Adhikary S and Eilers M: Transcriptional
regulation and transformation by Myc proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 6:635–645. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang H, Gao P, Fukuda R, et al: HIF-1
inhibits mitochondrial biogenesis and cellular respiration in
VHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma by repression of C-MYC activity.
Cancer Cell. 11:407–420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Corn PG, Ricci MS, Scata KA, et al: Mxi1
is induced by hypoxia in a HIF-1-dependent manner and protects
cells from c-Myc-induced apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:1285–1294.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu Y, Sato F, Yamada T, et al: The BHLH
transcription factor DEC1 plays an important role in the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer. Int J
Oncol. 41:1337–1346. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|