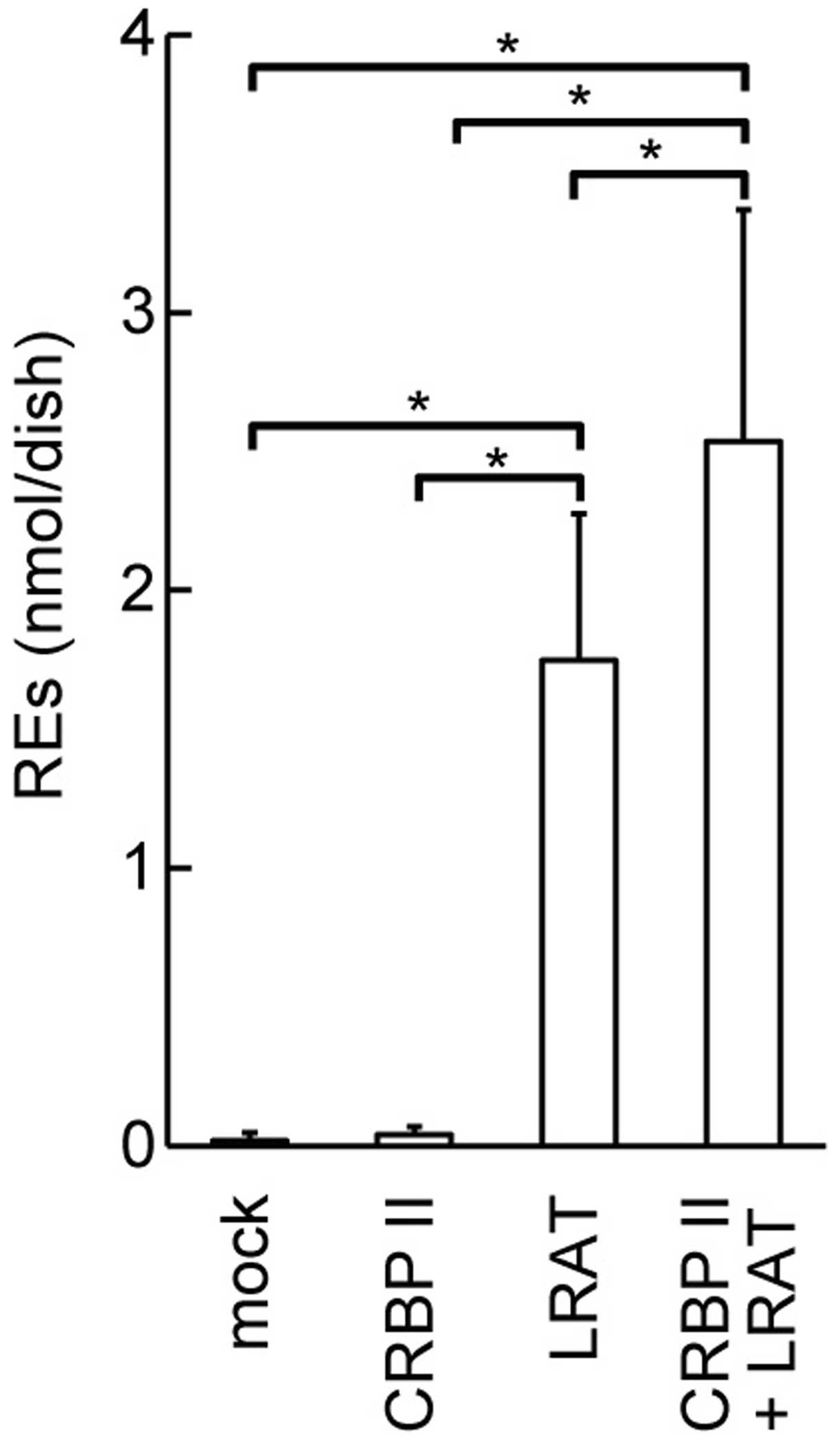
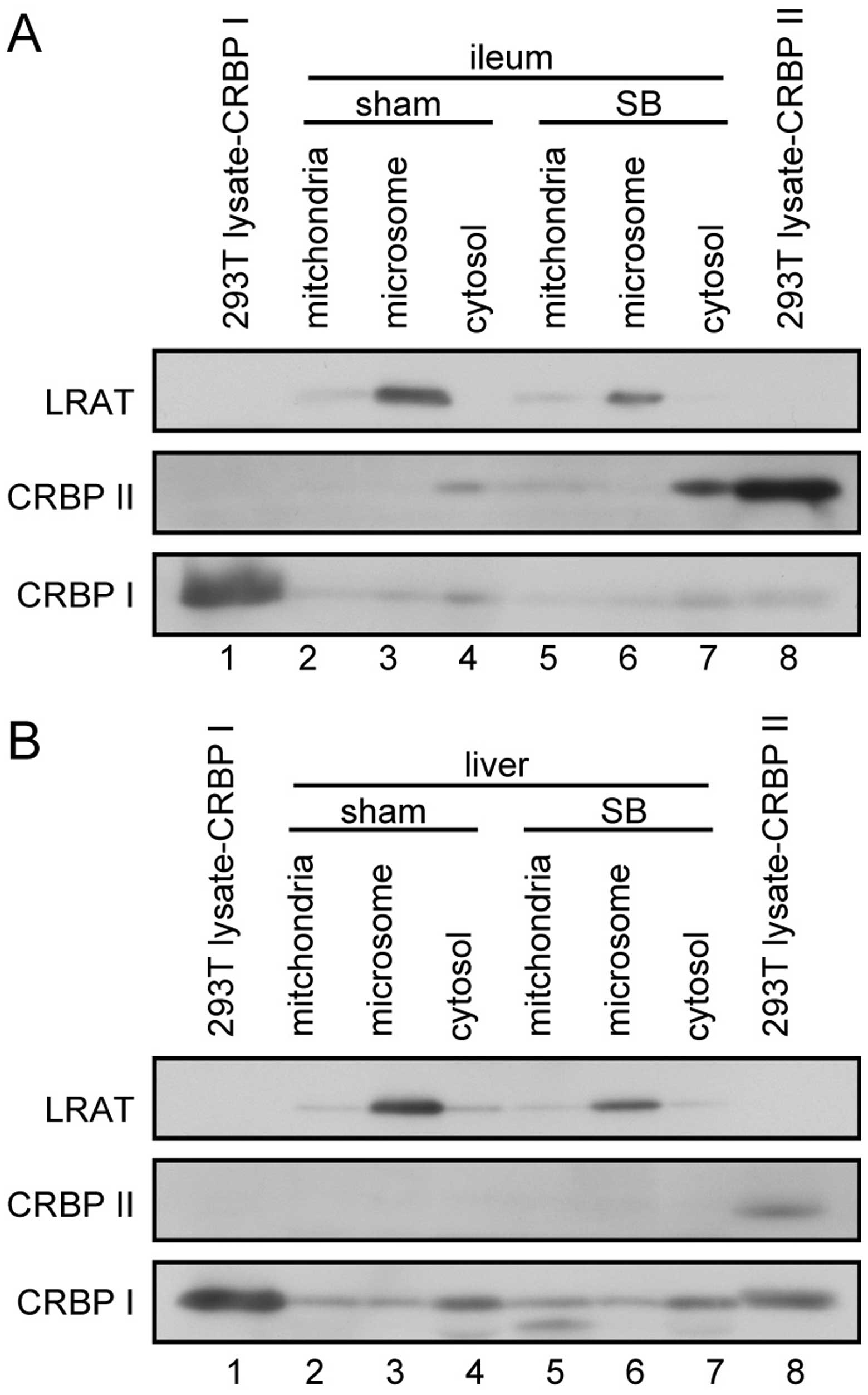
|
1
|
Duro D, Kamin D and Duggan C: Overview of
pediatric short bowel syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
47(Suppl 1): S33–S36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wall EA: An overview of short bowel
syndrome management: adherence, adaptation, and practical
recommendations. J Acad Nutr Diet. 113:1200–1208. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shaw D, Gohil K and Basson MD: Intestinal
mucosal atrophy and adaptation. World J Gastroenterol.
18:6357–6375. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Tang Y, Rubin DC and Levin MS:
Chronically administered retinoic acid has trophic effects in the
rat small intestine and promotes adaptation in a resection model of
short bowel syndrome. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
292:G1559–G1569. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Harrison EH: Mechanisms of digestion and
absorption of dietary vitamin A. Annu Rev Nutr. 25:87–103. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Blomhoff R and Blomhoff HK: Overview of
retinoid metabolism and function. J Neurobiol. 66:606–630. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wake K: ‘Sternzellen’ in the liver:
perisinusoidal cells with special reference to storage of vitamin
A. Am J Anat. 132:429–462. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Senoo H: Structure and function of hepatic
stellate cells. Med Electron Microsc. 37:3–15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Newcomer ME: Retinoid-binding proteins:
structural determinants important for function. FASEB J. 9:229–239.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Flower DR, North AC and Sansom CE: The
lipocalin protein family: structural and sequence overview. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1482:9–24. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sherman DR, Lloyd RS and Chytil F: Rat
cellular retinol-binding protein: cDNA sequence and rapid
retinol-dependent accumulation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
84:3209–3213. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Colantuoni V, Cortese R, Nilsson M,
Lundvall J, Bavik CO, Eriksson U, Peterson PA and Sundelin J:
Cloning and sequencing of a full length cDNA corresponding to human
cellular retinol-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
130:431–439. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li E, Demmer LA, Sweetser DA, Ong DE and
Gordon JI: Rat cellular retinol-binding protein II: use of a cloned
cDNA to define its primary structure, tissue-specific expression,
and developmental regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:5779–5783.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
E X, Zhang L, Lu J, Tso P, Blaner WS,
Levin MS and Li E: Increased neonatal mortality in mice lacking
cellular retinol-binding protein II. J Biol Chem. 277:36617–36623.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takase S, Goda T and Shinohara H: Adaptive
changes of intestinal cellular retinol-binding protein, type II
following jejunum-bypass operation in the rat. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1156:223–231. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dodson BD, Wang JL, Swietlicki EA, Rubin
DC and Levin MS: Analysis of cloned cDNAs differentially expressed
in adapting remnant small intestine after partial resection. Am J
Physiol. 271:G347–G356. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang JL, Swartz-Basile DA, Rubin DC and
Levin MS: Retinoic acid stimulates early cellular proliferation in
the adapting remnant rat small intestine after partial resection. J
Nutr. 127:1297–1303. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ong DE, Kakkad B and MacDonald PN:
Acyl-CoA-independent esterification of retinol bound to cellular
retinol-binding protein (type II) by microsomes from rat small
intestine. J Biol Chem. 262:2729–2736. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yost RW, Harrison EH and Ross AC:
Esterification by rat liver microsomes of retinol bound to cellular
retinol-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 263:18693–18701.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rubin DC, Swietlicki EA, Wang JL, Dodson
BD and Levin MS: Enterocytic gene expression in intestinal
adaptation: evidence for a specific cellular response. Am J
Physiol. 270:G143–G152. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Green PH, Glickman RM, Riley JW and Quinet
E: Human apolipoprotein A-IV Intestinal origin and distribution in
plasma. J Clin Invest. 65:911–919. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Goodman DW, Huang HS and Shiratori T:
Tissue distribution and metabolism of newly absorbed vitamin A in
the rat. J Lipid Res. 6:390–396. 1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ruiz A, Winston A, Lim YH, Gilbert BA,
Rando RR and Bok D: Molecular and biochemical characterization of
lecithin retinol acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 274:3834–3841. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ong DE and Chytil F: Cellular
retinol-binding protein from rat liver Purification and
characterization. J Biol Chem. 253:828–832. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Napoli JL: Interactions of retinoid
binding proteins and enzymes in retinoid metabolism. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1440:139–162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bok D, Ruiz A, Yaron O, Jahng WJ, Ray A,
Xue L and Rando RR: Purification and characterization of a
transmembrane domain-deleted form of lecithin retinol
acyltransferase. Biochemistry. 42:6090–6098. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moise AR, Golczak M, Imanishi Y and
Palczewski K: Topology and membrane association of lecithin:retinol
acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 282:2081–2090. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Senoo H, Mezaki Y, Morii M, Hebiguchi T,
Miura M and Imai K: Uptake and storage of vitamin A as lipid
droplets in the cytoplasm of cells in the lamina propria mucosae of
the rat intestine. Cell Biol Int. 37:1171–1180. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wakabayashi Y, Yamada E, Yoshida T and
Takahashi H: Arginine becomes an essential amino acid after massive
resection of rat small intestine. J Biol Chem. 269:32667–32671.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hebiguchi T, Kato T, Yoshino H, Mizuno M,
Wakui H, Komatsuda A and Imai H: Extremely short small bowel
induces focal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol
Nutr. 32:586–592. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Taguchi S, Masumoto K, Yamanouchi T and
Suita S: Decrease in hepatic circulation induces hepatic fibrosis
in a neonatal piglet model with short bowel syndrome. J Pediatr
Surg. 40:1592–1597. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Senoo H and Wake K: Suppression of
experimental hepatic fibrosis by administration of vitamin A. Lab
Invest. 52:182–194. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|