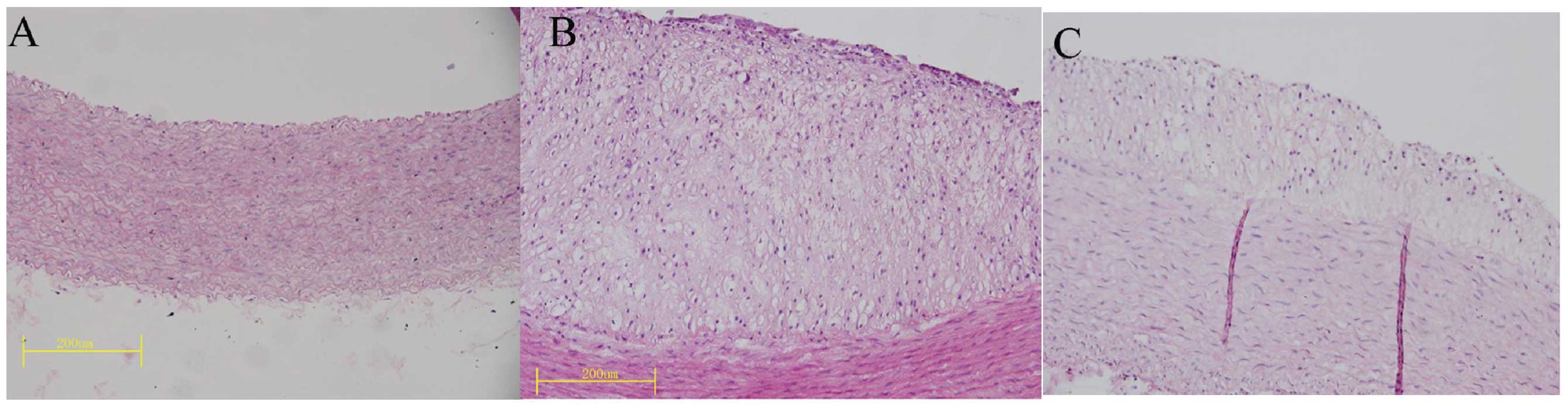
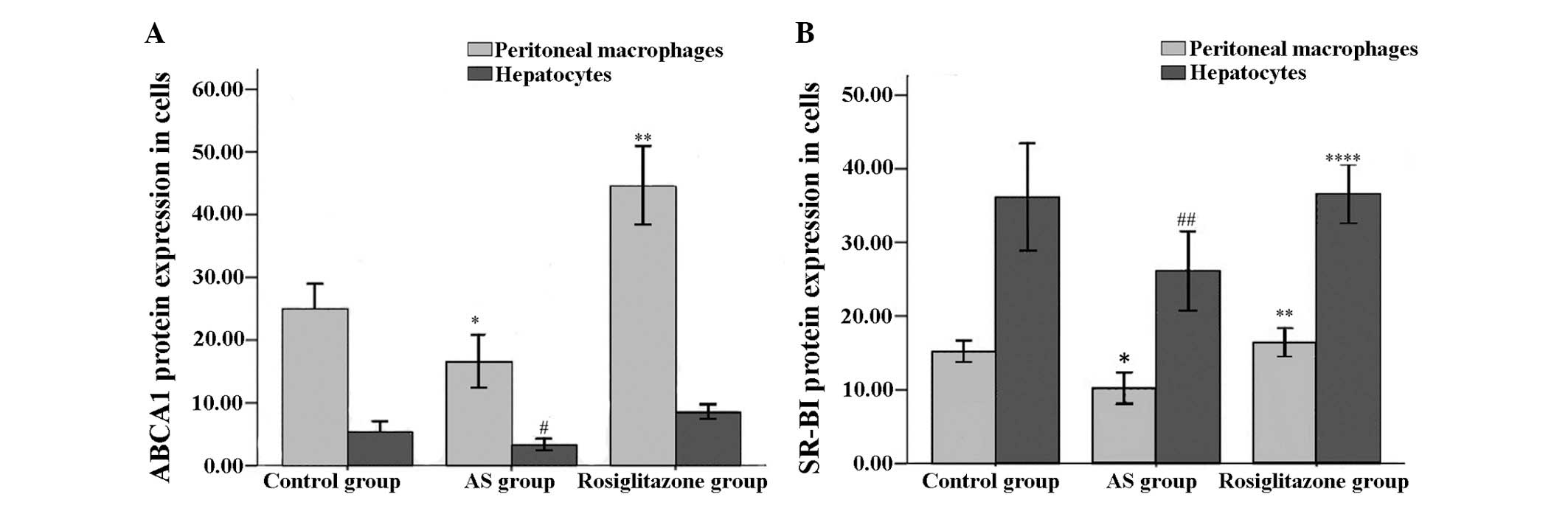
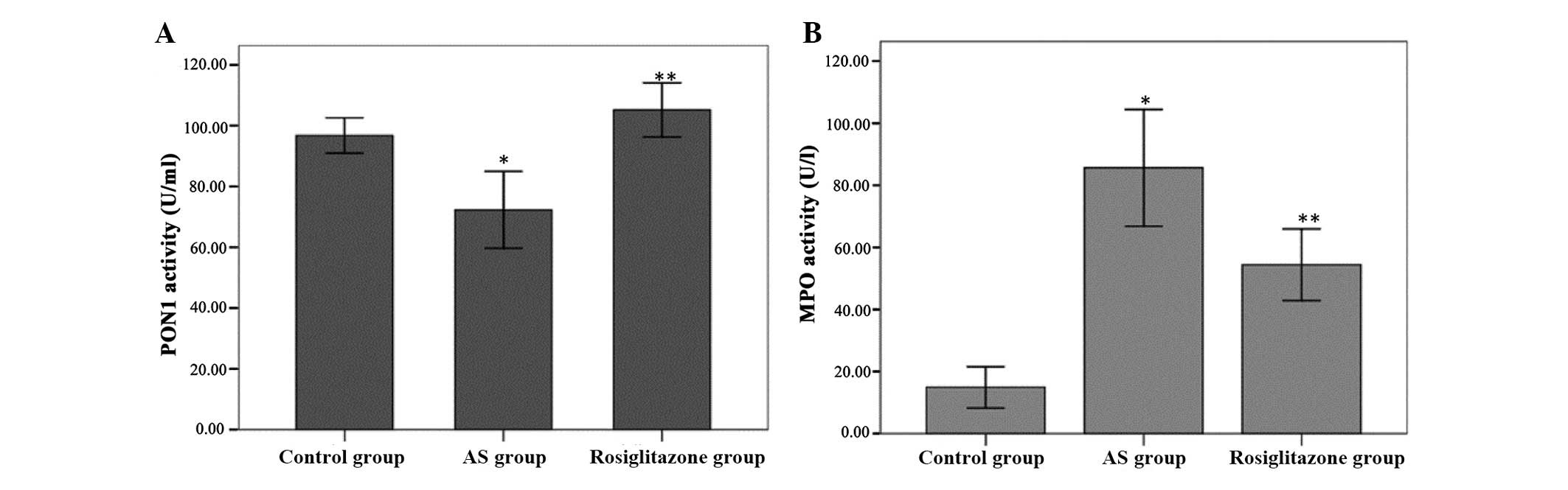
|
1
|
Rader DJ: Molecular regulation of HDL
metabolism and function: implications for novel therapies. J Clin
Invest. 116:3090–3100. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Frikke-Schmidt R, Nordestgaard BG, Stene
MC, et al: Association of loss-of-function mutations in the ABCA1
gene with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and risk of
ischemic heart disease. JAMA. 299:2524–2532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roberts CK, Ng C, Hama S, Eliseo AJ and
Barnard RJ: Effect of a short-term diet and exercise intervention
on inflammatory/anti-inflammatory properties of HDL in
overweight/obese men with cardiovascular risk factors. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 101:1727–1732. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dodani S, Grice DG and Joshi S: Is HDL
function as important as HDL quantity in the coronary artery
disease risk assessment? J Clin Lipidol. 3:70–77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Assmann G and Gotto AM Jr: HDL cholesterol
and protective factors in atherosclerosis. Circulation.
109:III8–III14. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Singh IM, Shishehbor MH and Ansell BJ:
High-density lipoprotein as a therapeutic target: a systematic
review. JAMA. 298:786–798. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brewer HB Jr: High-density lipoproteins: a
new potential therapeutic target for the prevention of
cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:387–391.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Attie AD, Kastelein JP and Hayden MR:
Pivotal role of ABCA1 in reverse cholesterol transport influencing
HDL levels and susceptibility to atherosclerosis. J Lipid Res.
42:1717–1726. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zannis VI, Chroni A and Krieger M: Role of
apoA-I, ABCA1, LCAT, and SR-BI in the biogenesis of HDL. J Mol Med
(Berl). 84:276–294. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Trigatti BL, Krieger M and Rigotti A:
Influence of the HDL receptor SR-BI on lipoprotein metabolism and
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:1732–1738. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ji Y, Wang N, Ramakrishnan R, et al:
Hepatic scavenger receptor BI promotes rapid clearance of high
density lipoprotein free cholesterol and its transport into bile. J
Biol Chem. 274:33398–33402. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ueda Y, Royer L, Gong E, et al: Lower
plasma levels and accelerated clearance of high density lipoprotein
(HDL) and non-HDL cholesterol in scavenger receptor class B type I
transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 274:7165–7171. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nolan JJ, Ludvik B, Beerdsen P, Joyce M
and Olefsky J: Improvement in glucose tolerance and insulin
resistance in obese subjects treated with troglitazone. N Engl J
Med. 331:1188–1193. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi D, Kim SK, Choi SH, et al:
Preventative effects of rosiglitazone on restenosis after coronary
stent implantation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care.
27:2654–2660. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gerstein HC, Ratner RE, Cannon CP, et al:
Effect of rosiglitazone on progression of coronary atherosclerosis
in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery
disease: the assessment on the prevention of progression by
rosiglitazone on atherosclerosis in diabetes patients with
cardiovascular history trial. Circulation. 121:1176–1187. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kelly AS and Bank AJ: The cardiovascular
effects of the thiazolidinediones: a review of the clinical data. J
Diabetes Complications. 21:326–334. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sidhu JS, Kaposzta Z, Markus HS and Kaski
JC: Effect of rosiglitazone on common carotid intima-media
thickness progression in coronary artery disease patients without
diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:930–934. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Marx N, Duez H, Fruchart JC and Staels B:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and atherogenesis:
regulators of gene expression in vascular cells. Circ Res.
94:1168–1178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Malerød L, Sporstol M, Juvet LK, Mousavi
A, Gjøen T and Berg T: Hepatic scavenger receptor class B, type I
is stimulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
305:557–565. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Llaverias G, Rebollo A, Pou J, et al:
Effects of rosiglitazone and atorvastatin on the expression of
genes that control cholesterol homeostasis in differentiating
monocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 71:605–614. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carreon-Torres E, Rendon-Sauer K,
Monter-Garrido M, et al: Rosiglitazone modifies HDL structure and
increases HDL-apoAI synthesis and catabolic rates. Clin Chim Acta.
401:37–41. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fan JG, Chen LH, Xu ZJ and Zeng MD:
Overexpression of hepatic plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1
mRNA in rabbits with fatty liver. World J Gastroenterol. 7:710–712.
2001.
|
|
23
|
Zhao SP, Yang J, Li J, Dong SZ and Wu ZH:
Effect of niacin on LXRalpha and PPARgamma expression and
HDL-induced cholesterol efflux in adipocytes of
hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Int J Cardiol. 124:172–178. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Troutt JS, Alborn WE, Mosior MK, et al: An
apolipoprotein A-I mimetic dose-dependently increases the formation
of prebeta1 HDL in human plasma. J Lipid Res. 49:581–587. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Havel RJ, Eder HA and Bragdon JH: The
distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally
separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 34:1345–1353.
1955. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pirillo A, Norata GD, Zanelli T and
Catapano AL: Overexpression of inducible heat shock protein 70 in
Cos-1 cells fails to protect from cytotoxicity of oxidized ldls.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 21:348–354. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pirillo A, Uboldi P, Kuhn H and Catapano
AL: 15-Lipoxygenase-mediated modification of high-density
lipoproteins impairs SR-BI- and ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux
from macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1761:292–300. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhong JK, Guo ZG, Li C, et al: Probucol
alleviates atherosclerosis and improves high density lipoprotein
function. Lipids Health Dis. 10(210): 2011
|
|
29
|
Speidl WS, Cimmino G, Ibanez B, et al:
Recombinant apolipoprotein A-I Milano rapidly reverses aortic valve
stenosis and decreases leaflet inflammation in an experimental
rabbit model. Eur Heart J. 31:2049–2057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Beltowski J, Jamroz-Wisniewska A,
Borkowska E and Wojcicka G: Differential effect of antioxidant
treatment on plasma and tissue paraoxonase activity in
hyperleptinemic rats. Pharmacol Res. 51:523–532. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fan J and Watanabe T: Transgenic rabbits
as therapeutic protein bioreactors and human disease models.
Pharmacol Ther. 99:261–282. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ansell BJ, Fonarow GC and Fogelman AM:
High-density lipoprotein: is it always atheroprotective? Curr
Atheroscler Rep. 8:405–411. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Szapary PO, Bloedon LT, Samaha FF, et al:
Effects of pioglitazone on lipoproteins, inflammatory markers, and
adipokines in nondiabetic patients with metabolic syndrome.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:182–188. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chiesa G and Sirtori CR: Apolipoprotein
A-I(Milano): current perspectives. Curr Opin Lipidol. 14:159–163.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hiroshi N: Latest insights into
high-density lipoprotein functions. Endocrinologist. 19:179–186.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fogelman AM: When good cholesterol goes
bad. Nat Med. 10:902–903. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
von Eckardstein A, Nofer JR and Assmann G:
High density lipoproteins and arteriosclerosis. Role of cholesterol
efflux and reverse cholesterol transport. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 21:13–27. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Calpe-Berdiel L, Rotllan N, Palomer X,
Ribas V, Blanco-Vaca F and Escola-Gil JC: Direct evidence in vivo
of impaired macrophage-specific reverse cholesterol transport in
ATP-binding cassette transporter A1-deficient mice. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1738:6–9. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kozarsky KF, Donahee MH, Rigotti A, Iqbal
SN, Edelman ER and Krieger M: Overexpression of the HDL receptor
SR-BI alters plasma HDL and bile cholesterol levels. Nature.
387:414–417. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang N, Arai T, Ji Y, Rinninger F and Tall
AR: Liver-specific overexpression of scavenger receptor BI
decreases levels of very low density lipoprotein ApoB, low density
lipoprotein ApoB, and high density lipoprotein in transgenic mice.
J Biol Chem. 273:32920–32926. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kozarsky KF, Donahee MH, Glick JM, Krieger
M and Rader DJ: Gene transfer and hepatic overexpression of the HDL
receptor SR-BI reduces atherosclerosis in the cholesterol-fed LDL
receptor-deficient mouse. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
20:721–727. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Varban ML, Rinninger F, Wang N, et al:
Targeted mutation reveals a central role for SR-BI in hepatic
selective uptake of high density lipoprotein cholesterol. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 95:4619–4624. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Braun A, Trigatti BL, Post MJ, et al: Loss
of SR-BI expression leads to the early onset of occlusive
atherosclerotic coronary artery disease, spontaneous myocardial
infarctions, severe cardiac dysfunction, and premature death in
apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circ Res. 90:270–276. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang Y, Da Silva JR, Reilly M, Billheimer
JT, Rothblat GH and Rader DJ: Hepatic expression of scavenger
receptor class B type I (SR-BI) is a positive regulator of
macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in vivo. J Clin Invest.
115:2870–2874. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chawla A, Boisvert WA, Lee CH, et al: A
PPAR gamma-LXR-ABCA1 pathway in macrophages is involved in
cholesterol efflux and atherogenesis. Mol Cell. 7:161–171. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chinetti G, Lestavel S, Bocher V, et al:
PPAR-alpha and PPAR-gamma activators induce cholesterol removal
from human macrophage foam cells through stimulation of the ABCA1
pathway. Nat Med. 7:53–58. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang N, Ranalletta M, Matsuura F, Peng F
and Tall AR: LXR-induced redistribution of ABCG1 to plasma membrane
in macrophages enhances cholesterol mass efflux to HDL.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:1310–1316. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sviridov D, Mukhamedova N, Remaley AT,
Chin-Dusting J and Nestel P: Antiatherogenic functionality of high
density lipoprotein: how much versus how good. J Atheroscler
Thromb. 15:52–62. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tward A, Xia YR, Wang XP, et al: Decreased
atherosclerotic lesion formation in human serum paraoxonase
transgenic mice. Circulation. 106:484–490. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bhattacharyya T, Nicholls SJ, Topol EJ, et
al: Relationship of paraoxonase 1 (PON1) gene polymorphisms and
functional activity with systemic oxidative stress and
cardiovascular risk. JAMA. 299:1265–1276. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Holvoet P: Oxidized LDL and coronary heart
disease. Acta Cardiol. 59:479–484. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shao B, Oda MN, Oram JF and Heinecke JW:
Myeloperoxidase: an inflammatory enzyme for generating
dysfunctional high density lipoprotein. Curr Opin Cardiol.
21:322–328. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|