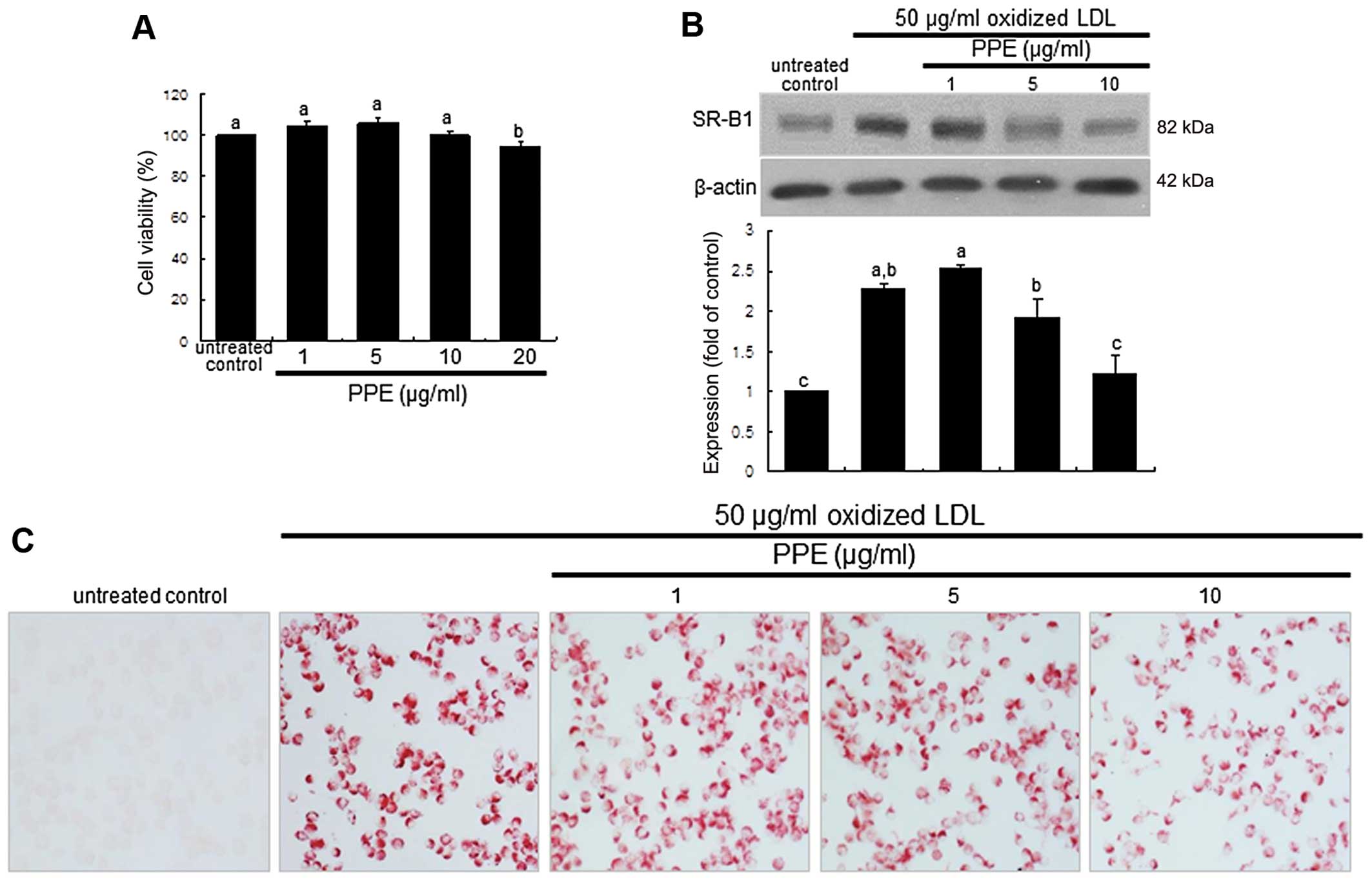
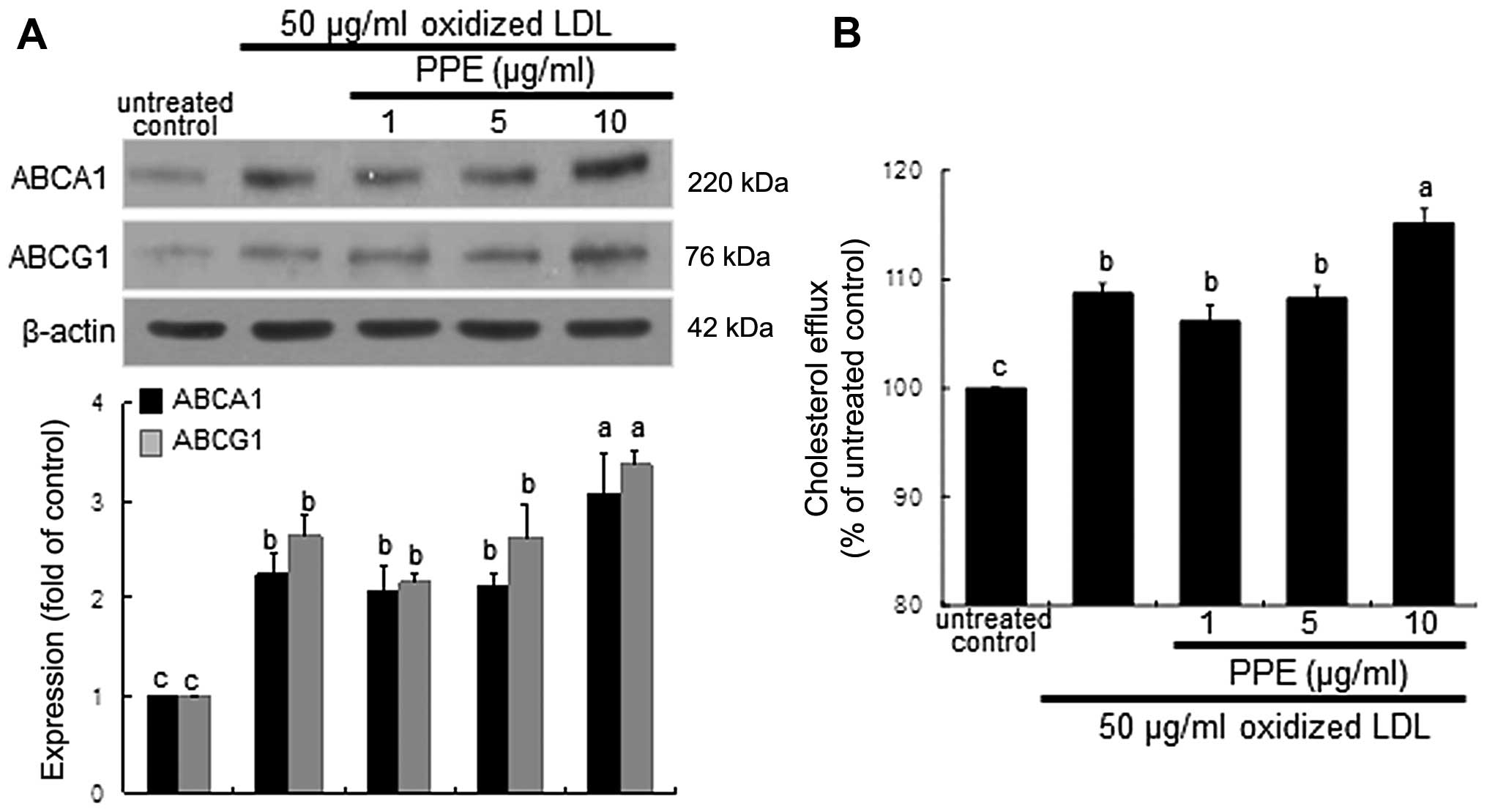
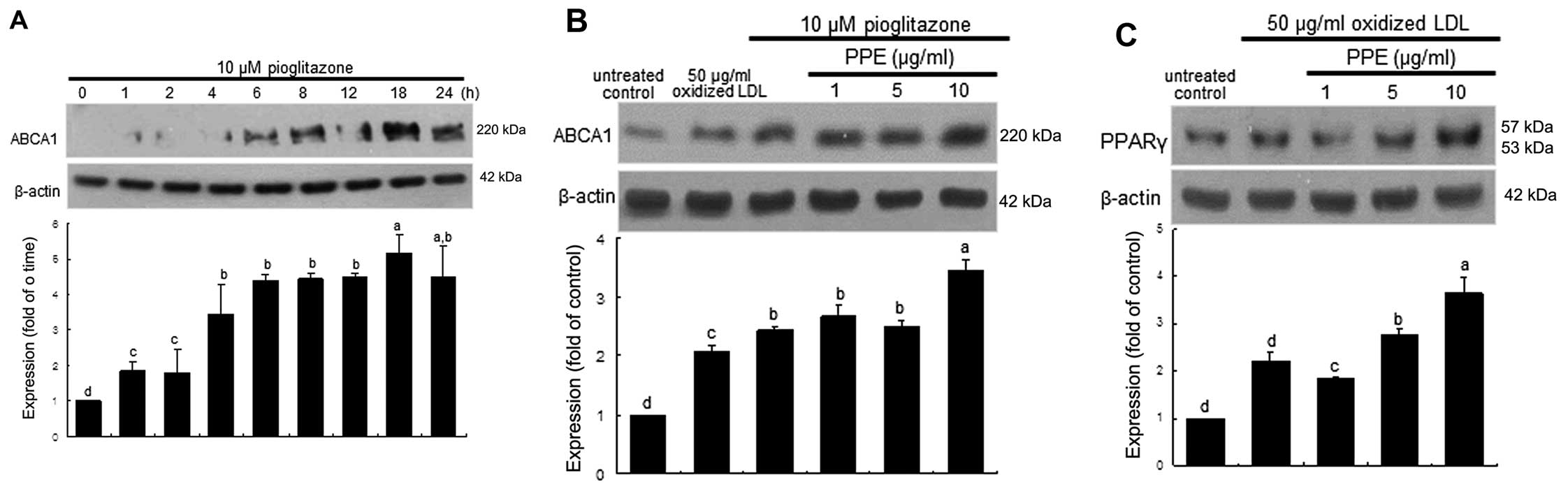
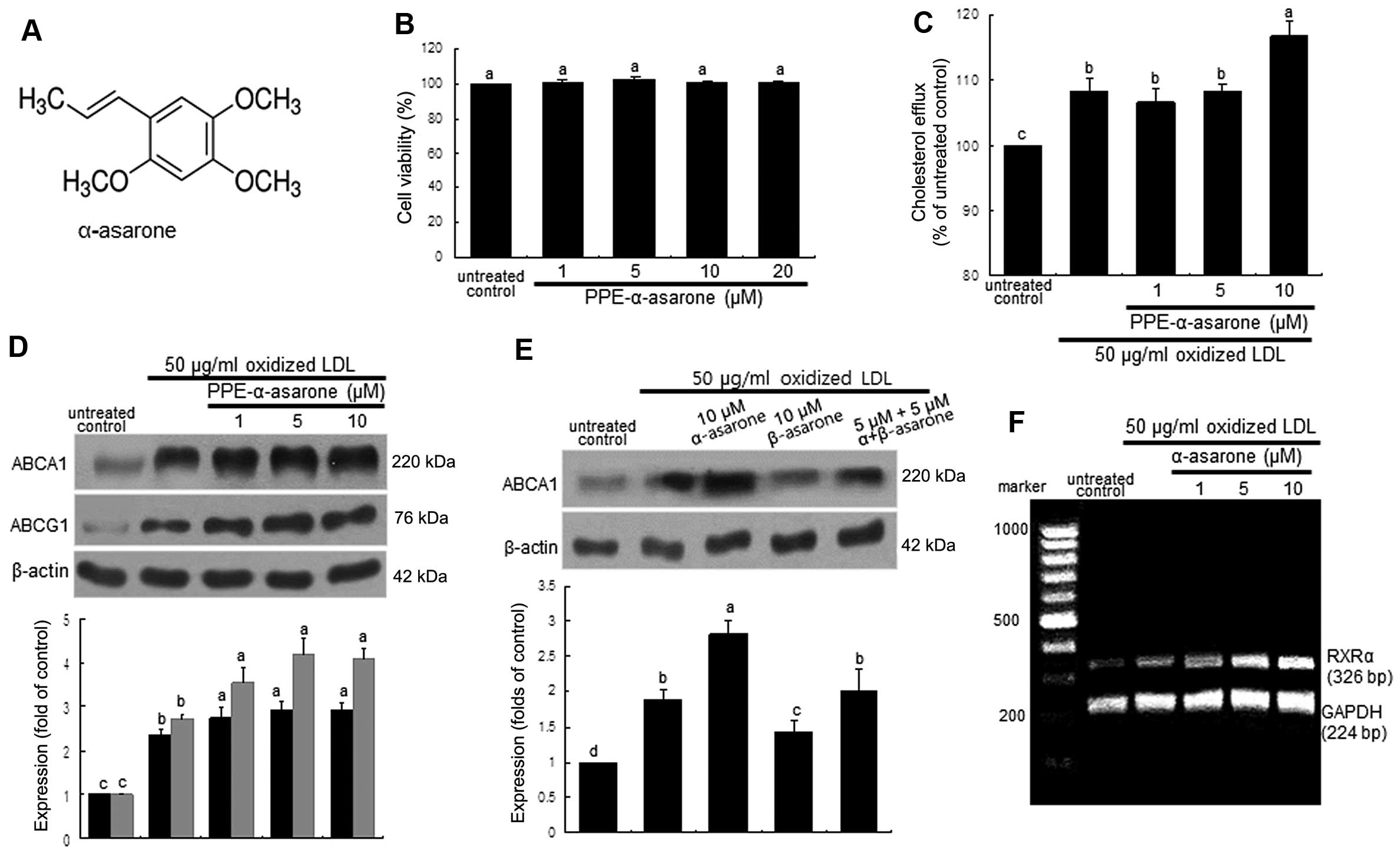
|
1
|
Li G, Gu HM and Zhang DW: ATP-binding
cassette transporters and cholesterol translocation. IUBMB Life.
65:505–512. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cruz PM, Mo H, McConathy WJ, Sabnis N and
Lacko AG: The role of cholesterol metabolism and cholesterol
transport in carcinogenesis: A review of scientific findings,
relevant to future cancer therapeutics. Front Pharmacol. 4:1192013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yue P, Chen Z, Nassir F, Bernal-Mizrachi
C, Finck B, Azhar S and Abumrad NA: Enhanced hepatic apoA-I
secretion and peripheral efflux of cholesterol and phospholipid in
CD36 null mice. PLoS One. 5:e99062010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wen Y and Leake DS: Low density
lipoprotein undergoes oxidation within lysosomes in cells. Circ
Res. 100:1337–1343. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shibata N and Glass CK: Macrophages,
oxysterols and atherosclerosis. Circ J. 74:2045–2051. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ye D, Lammers B, Zhao Y, Meurs I, Van
Berkel TJ and Van Eck M: ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and
G1, HDL metabolism, cholesterol efflux, and inflammation: Important
targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Curr Drug Targets.
12:647–660. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hafiane A and Genest J: HDL,
atherosclerosis, and emerging therapies. Cholesterol.
2013:8914032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ogata M, Tsujita M, Hossain MA, Akita N,
Gonzalez FJ, Staels B, Suzuki S, Fukutomi T, Kimura G and Yokoyama
S: On the mechanism for PPAR agonists to enhance ABCA1 gene
expression. Atherosclerosis. 205:413–419. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brewer HB Jr: HDL metabolism and the role
of HDL in the treatment of high-risk patients with cardiovascular
disease. Curr Cardiol Rep. 9:486–492. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bełtowski J: Liver X receptors (LXR) as
therapeutic targets in dyslipidemia. Cardiovasc Ther. 26:297–316.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calkin AC and Tontonoz P: Liver x receptor
signaling pathways and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 30:1513–1518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu R, Ou Z, Ruan X and Gong J: Role of
liver X receptors in cholesterol efflux and inflammatory signaling
(Review). Mol Med Rep. 5:895–900. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Neve BP, Fruchart JC and Staels B: Role of
the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in
atherosclerosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 60:1245–1250. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saita E, Kishimoto Y, Tani M, Iizuka M,
Toyozaki M, Sugihara N and Kondo K: Antioxidant activities of
Perilla frutescens against low-density lipoprotein oxidation in
vitro and in human subjects. J Oleo Sci. 61:113–120. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jun HI, Kim BT, Song GS and Kim YS:
Structural characterization of phenolic antioxidants from purple
perilla (Perilla frutescens var. acuta) leaves. Food Chem.
148:367–372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Heo JC, Nam DY, Seo MS and Lee SH:
Alleviation of atopic dermatitis-related symptoms by Perilla
frutescens Britton. Int J Mol Med. 28:733–737. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang SY, Hong CO, Lee GP, Kim CT and Lee
KW: The hepato-protection of caffeic acid and rosmarinic acid,
major compounds of Perilla frutescens, against t-BHP-induced
oxidative liver damage. Food Chem Toxicol. 55:92–99. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Paek JH, Shin KH, Kang YH, Lee JY and Lim
SS: Rapid identification of aldose reductase inhibitory compounds
from Perilla frutescens. Biomed Res Int. 2013:6794632013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim MJ and Kim HK: Perilla leaf extract
ameliorates obesity and dyslipidemia induced by high-fat diet.
Phytother Res. 23:1685–1690. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park SH, Kim JL, Lee ES, Han SY, Gong JH,
Kang MK and Kang YH: Dietary ellagic acid attenuates oxidized LDL
uptake and stimulates cholesterol efflux in murine macrophages. J
Nutr. 141:1931–1937. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park SH, Kim JL, Kang MK, Gong JH, Han SY,
Shim JH, Lim SS and Kang YH: Sage weed (Salvia plebeia) extract
antagonizes foam cell formation and promotes cholesterol efflux in
murine macrophages. Int J Mol Med. 30:1105–1112. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang D, Geng Y, Fang L, Shu X, Liu J, Wang
X and Huang L: An efficient combination of supercritical fluid
extraction and high-speed counter-current chromatography to extract
and purify (E)- and (Z)-diastereomers of α-asarone and β-asarone
from Acorus tatarinowii Schott. J Sep Sci. 34:3339–3343. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lusis AJ: Atherosclerosis. Nature.
407:233–241. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tangirala RK, Bischoff ED, Joseph SB, et
al: Identification of macrophage liver X receptors as inhibitors of
atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:11896–11901. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Westerterp M, Bochem AE, Yvan-Charvet L,
Murphy AJ, Wang N and Tall AR: ATP-binding cassette transporters,
atherosclerosis, and inflammation. Circ Res. 114:157–170. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Calpe-Berdiel L, Zhao Y, de Graauw M, et
al: Macrophage ABCA2 deletion modulates intracellular cholesterol
deposition, affects macrophage apoptosis, and decreases early
atherosclerosis in LDL receptor knockout mice. Atherosclerosis.
223:332–341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu X, Lee JY, Timmins JM, et al:
Increased cellular free cholesterol in macrophage-specific Abca1
knock-out mice enhances pro-inflammatory response of macrophages. J
Biol Chem. 283:22930–22941. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kumar H, Kim BW, Song SY, Kim JS, Kim IS,
Kwon YS, Koppula S and Choi DK: Cognitive enhancing effects of
alpha asarone in amnesic mice by influencing cholinergic and
antioxidant defense mechanisms. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
76:1518–1522. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Geng Y, Li C, Liu J, Xing G, Zhou L, Dong
M, Li X and Niu Y: Beta-asarone improves cognitive function by
suppressing neuronal apoptosis in the beta-amyloid hippocampus
injection rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:836–843. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rodríguez-Páez L, Juárez-Sanchez M,
Antúnez-Solís J, Baeza I and Wong C: Alpha-asarone inhibits HMG-CoA
reductase, lowers serum LDL-cholesterol levels and reduces biliary
CSI in hypercholesterolemic rats. Phytomedicine. 10:397–404. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
De Filippis B, Giancristofaro A,
Ammazzalorso A, D’Angelo A, Fantacuzzi M, Giampietro L, Maccallini
C, Petruzzelli M and Amoroso R: Discovery of gemfibrozil analogues
that activate PPARα and enhance the expression of gene CPT1A
involved in fatty acids catabolism. Eur J Med Chem. 46:5218–5224.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|