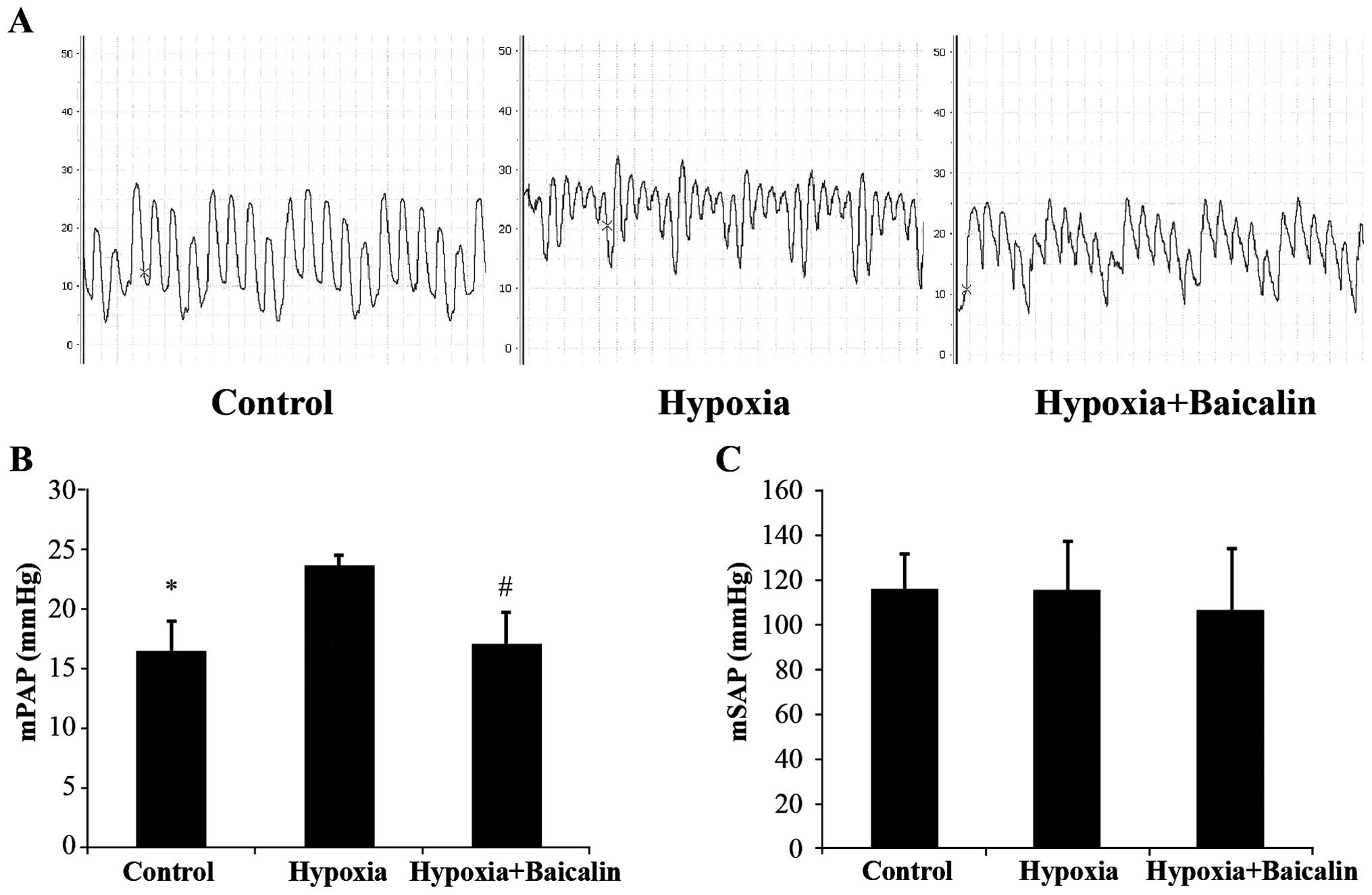
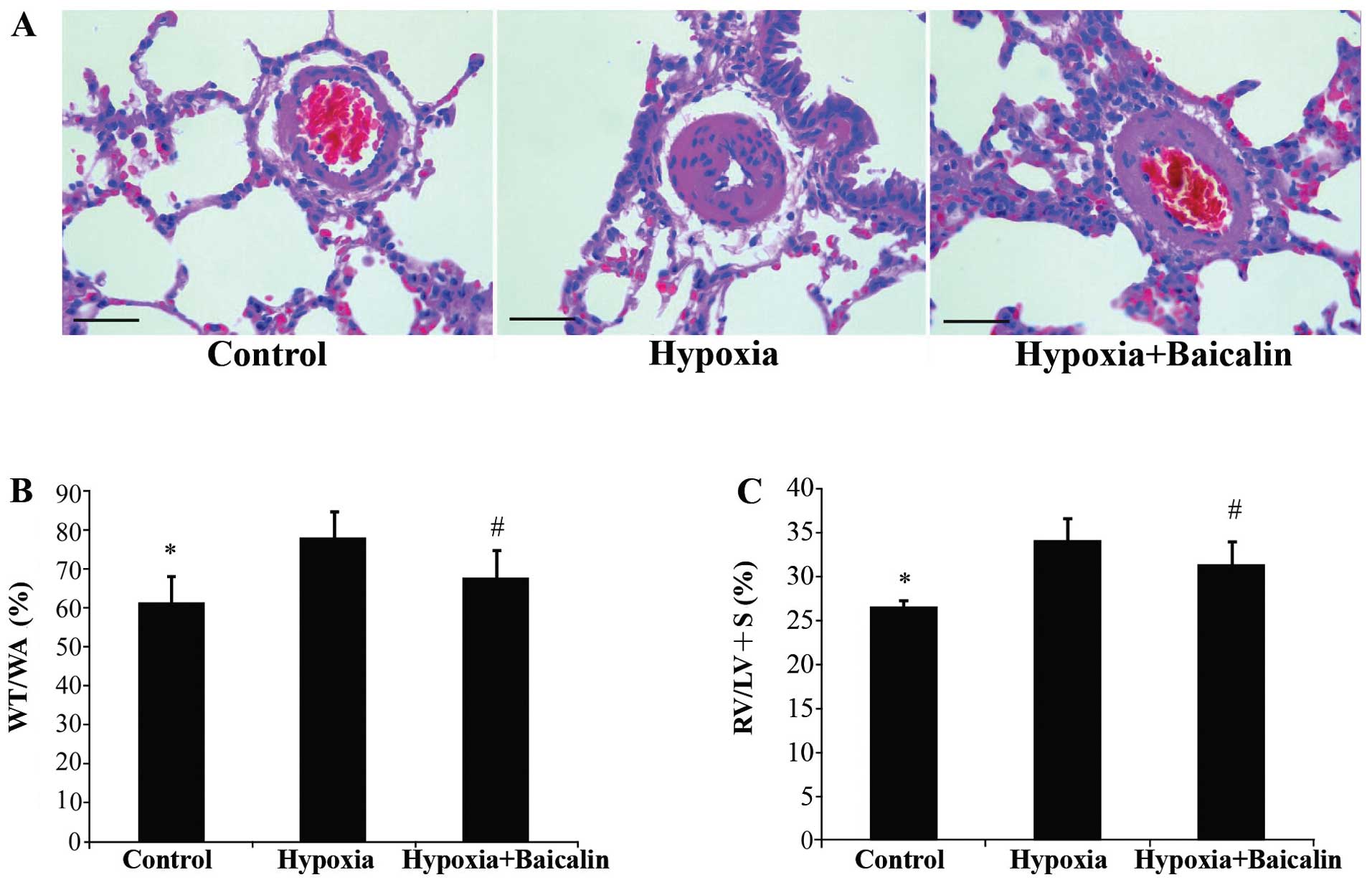
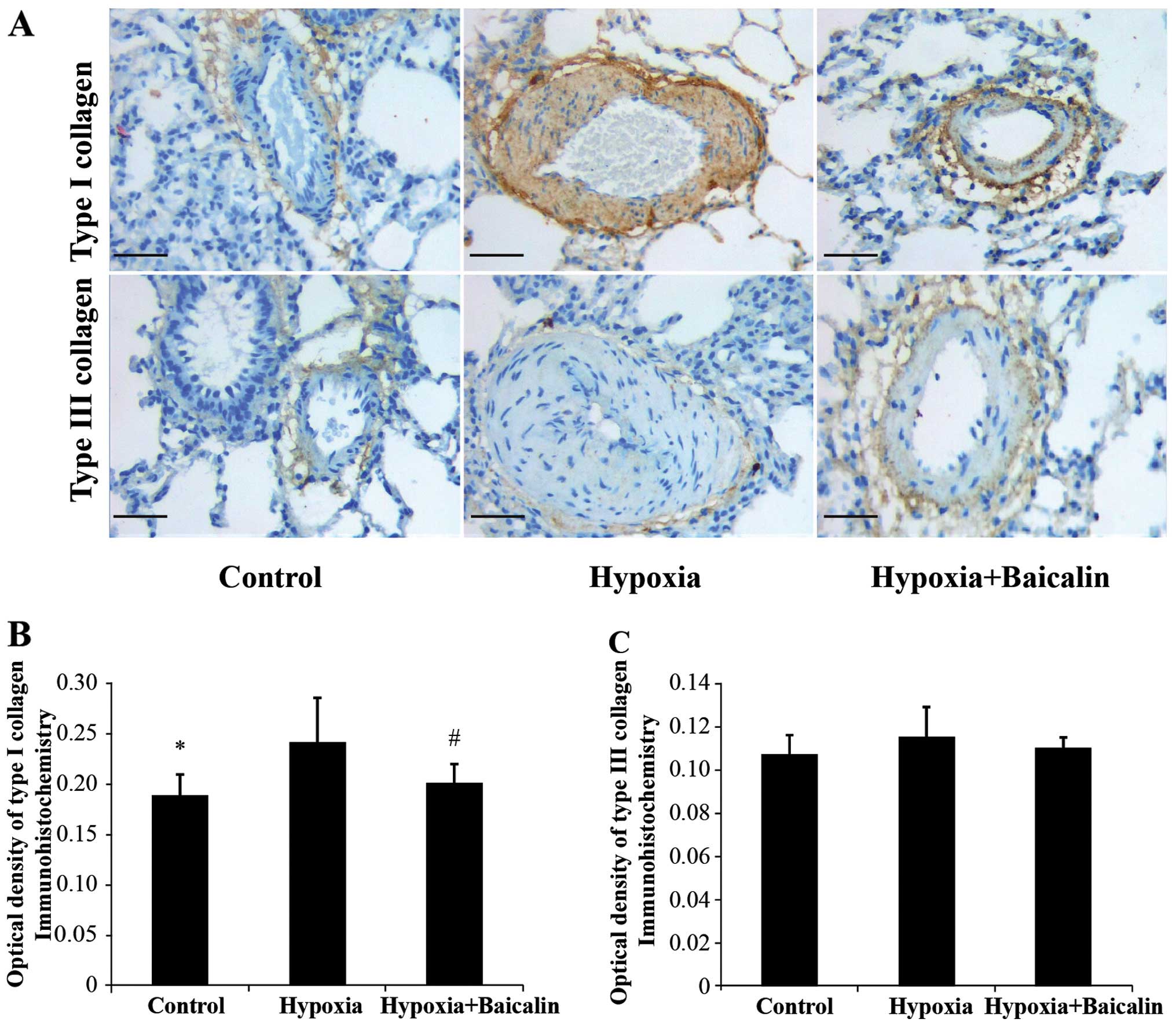
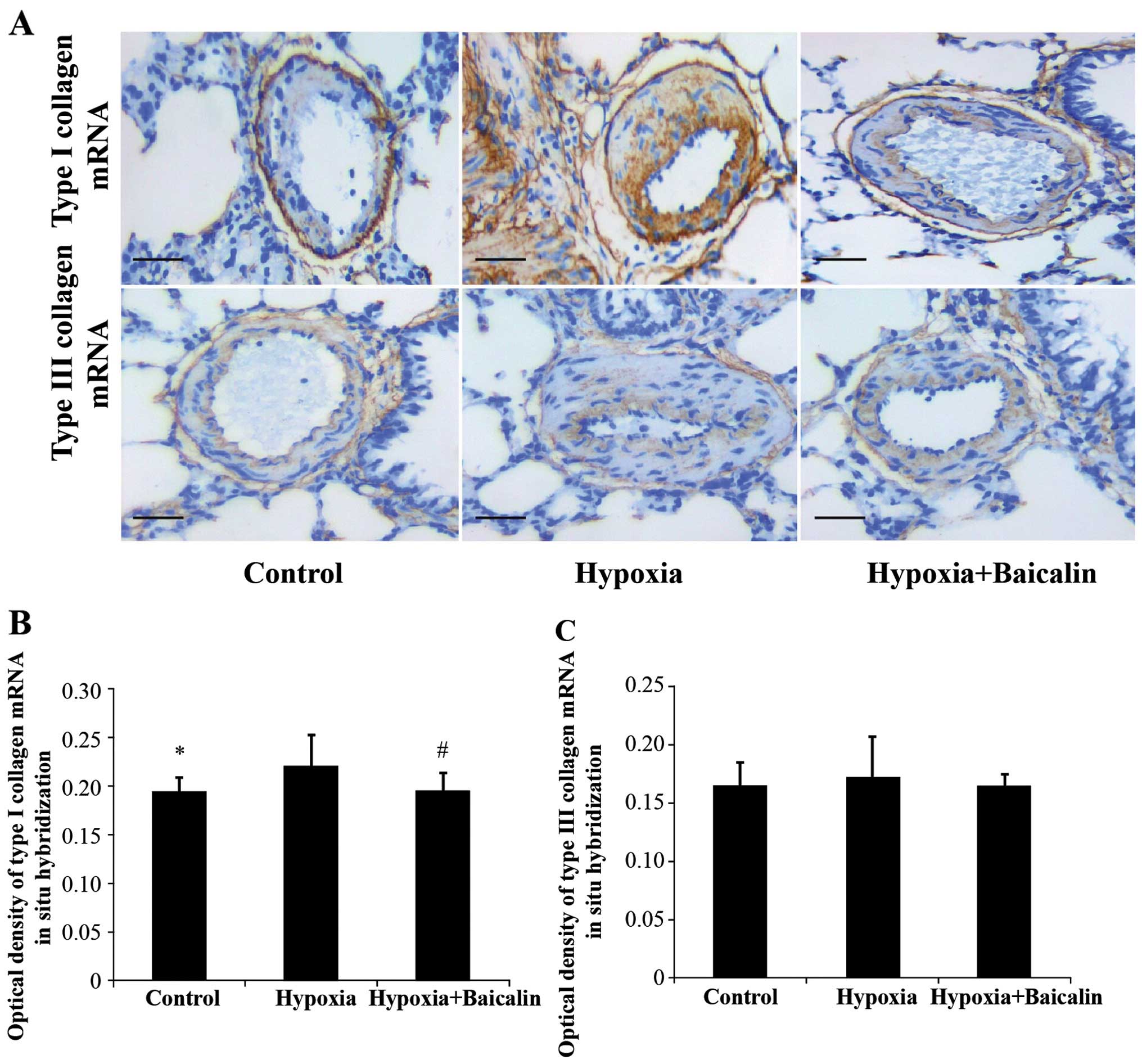
|
1
|
Safdar Z, Bartolome S and Sussman N:
Portopulmonary hypertension: an update. Liver Transpl. 18:881–891.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morales-Blanhir JE, Carmona-Rubio AE,
Rosas-Romero MJ, Vergara de Marquez GS and Arbo-Oze-de-Morvil GA:
Pulmonary arterial hypertension, a rare entity. Rev Invest Clin.
66:65–78. 2014.In Spanish. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang Z, Lakes RS, Eickhoff JC and Chesler
NC: Effects of collagen deposition on passive and active mechanical
properties of large pulmonary arteries in hypoxic pulmonary
hypertension. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 12:1115–1125. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ooi CY, Wang Z, Tabima DM, et al: The role
of collagen in extralobar pulmonary artery stiffening in response
to hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 299:H1823–H1831. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Estrada KD and Chesler NC:
Collagen-related gene and protein expression changes in the lung in
response to chronic hypoxia. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 8:263–272.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Schreier D, Hacker T, Song G and Chesler
N: The role of collagen synthesis in ventricular and vascular
adaptation to hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. J Biomech Eng.
135:0210182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang L, Li Y, Chen M, et al:
15-LO/15-HETE mediated vascular adventitia fibrosis via p38
MAPK-dependent TGF-β. J Cell Physiol. 229:245–257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gao Z, Huang K and Xu H: Protective
effects of flavonoids in the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis
Georgi against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in
HS-SY5Y cells. Pharmacol Res. 43:173–178. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dong LH, Wen JK, Miao SB, et al: Baicalin
inhibits PDGF-BB-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation through suppressing PDGFRβ-ERK signaling and increase
in p27 accumulation and prevents injury-induced neointimal
hyperplasia. Cell Res. 20:1252–1262. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peng XD, Dai LL, Huang CQ, et al:
Correlation between anti-fibrotic effect of baicalin and serum
cytokines in rat hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol.
15:4720–4725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu Q, Noor M, Wong YF, et al: In vitro
anti-fibrotic activities of herbal compounds and herbs. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 24:3033–3041. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuno K, Kanada N, Nakashima E, et al:
Molecular cloning of a gene encoding a new type of
metalloproteinase-disintegrin family protein with thrombospondin
motifs as an inflammation associated gene. J Biol Chem.
272:556–562. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salter RC, Ashlin TG, Kwan AP and Ramji
DP: ADAMTS proteases: key roles in atherosclerosis? Mol Med (Berl).
88:1203–1211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Porter S, Clark IM, Kevorkian L and
Edwards DR: The ADAMTS metalloproteinases. Biochem J. 386:15–27.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Tortorella MD, Malfait F, Barve RA, et al:
A review of the ADAMTS family, pharmaceutical targets of the
future. Curr Pharm Des. 15:2359–2374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jones GC and Riley GP: ADAMTS proteinases:
a multi-domain, multi-functional family with roles in extracellular
matrix turnover and arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 7:160–169. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Taketani T, Imai Y, Morota T, et al:
Altered patterns of gene expression specific to thoracic aortic
aneurysms: microarray analysis of surgically resected specimens.
Int Heart J. 46:265–277. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jönsson-Rylander AC, Nilsson T,
Fritsche-Danielson R, et al: Role of ADAMTS-1 in atherosclerosis:
remodeling of carotid artery, immunohistochemistry, and proteolysis
of versican. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:180–185. 2005.
|
|
19
|
Sabatine MS, Ploughman L, Simonsen KL, et
al: Association between ADAMTS1 matrix metalloproteinase gene
variation, coronary heart disease, and benefit of statin therapy.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:562–567. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo C, Wang Y, Liang H and Zhang J:
ADAMTS-1 contributes to the antifibrotic effect of captopril by
accelerating the degradation of type I collagen in chronic viral
myocarditis. Eur J Pharmacol. 629:104–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Duong-Quy S, Riviere S, Bei Y, et al:
Pulmonary hypertension: from molecular pathophysiology to
haemodynamic abnormalities. Rev Mal Respir. 29:956–970. 2012.In
French. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang LY and Gao BA: Relationship between
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells and mechanism of
hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling. Zhongguo Dong Mai
Ying Hua Za Zhi. 21:177–180. 2013.In Chinese.
|
|
23
|
Juan L, Xin S and Hui B: Establishment of
on animal model of hypobaric and hypoxia pulmonary hypertension. J
Clin Cardiol. 24:297–301. 2008.
|
|
24
|
Huang X, Fan R, Lu Y, et al: Regulatory
effect of AMP-activated protein kinase on pulmonary hypertension
induced by chronic hypoxia in rats: in vivo and in vitro studies.
Mol Biol Rep. 41:4031–4041. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qian G, Cao J, Chen C, et al: Paeoniflorin
inhibits pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells proliferation via
upregulating A2B adenosine receptor in rat. PLoS ONE. 8:e691412013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sang K, Zhou Y and Li MX: Pulmonary
vascular remodeling in neonatal rats with hypoxic pulmonary
hypertension. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 14:210–214. 2012.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Z and Chesler NC: Role of collagen
content and cross-linking in large pulmonary arterial stiffening
after chronic hypoxia. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 11:279–289. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Diez J: Arterial stiffness and
extracellular matrix. Adv Cardiol. 44:76–95. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Franco CD, Hou G and Bendeck MP:
Collagens, integrins, and the discoidin domain receptors in
arterial occlusive disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 12:143–148.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tabima DM, Roldan-Alzate A, Wang Z, et al:
Persistent vascular collagen accumulation alters hemodynamic
recovery from chronic hypoxia. J Biomech. 45:799–804. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Li XW, Du J and Li YJ: The effect of
calcitonin gene-related peptide on collagen accumulation in
pulmonary arteries of rats with hypoxic pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 29:182–186.
1922013.In Chinese.
|
|
32
|
Qiao H, Tong Y, Han H, et al: A novel
therapeutic regimen for hepatic fibrosis using the combination of
mesenchymal stem cells and baicalin. Pharmazie. 66:37–43.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu W, Chen XL, Liu JH, et al: The effect
of baicalein on bleomycin-induced fibrosis in lungs of rats.
Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 25:145–149. 2009.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang S, Chen P, Shui X, et al: Baicalin
attenuates transforming growth factor-β1-induced human pulmonary
artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and phenotypic switch by
inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor-1α and aryl hydrocarbon
receptor expression. J Pharm Pharmacol. 66:1469–1477. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kaushal GP and Shah SV: The new kids on
the block: ADAMTSs, potentially multifunctional metalloproteinases
of the ADAM family. J Clin Invest. 105:1335–1337. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vo NV, Hartman RA, Yurube T, et al:
Expression and regulation of metalloproteinases and their
inhibitors in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Spine J.
13:331–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rehn AP, Birch MA, Karlström E, et al:
ADAMTS-1 increases the three-dimensional growth of osteoblasts
through type I collagen processing. Bone. 41:231–238. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|