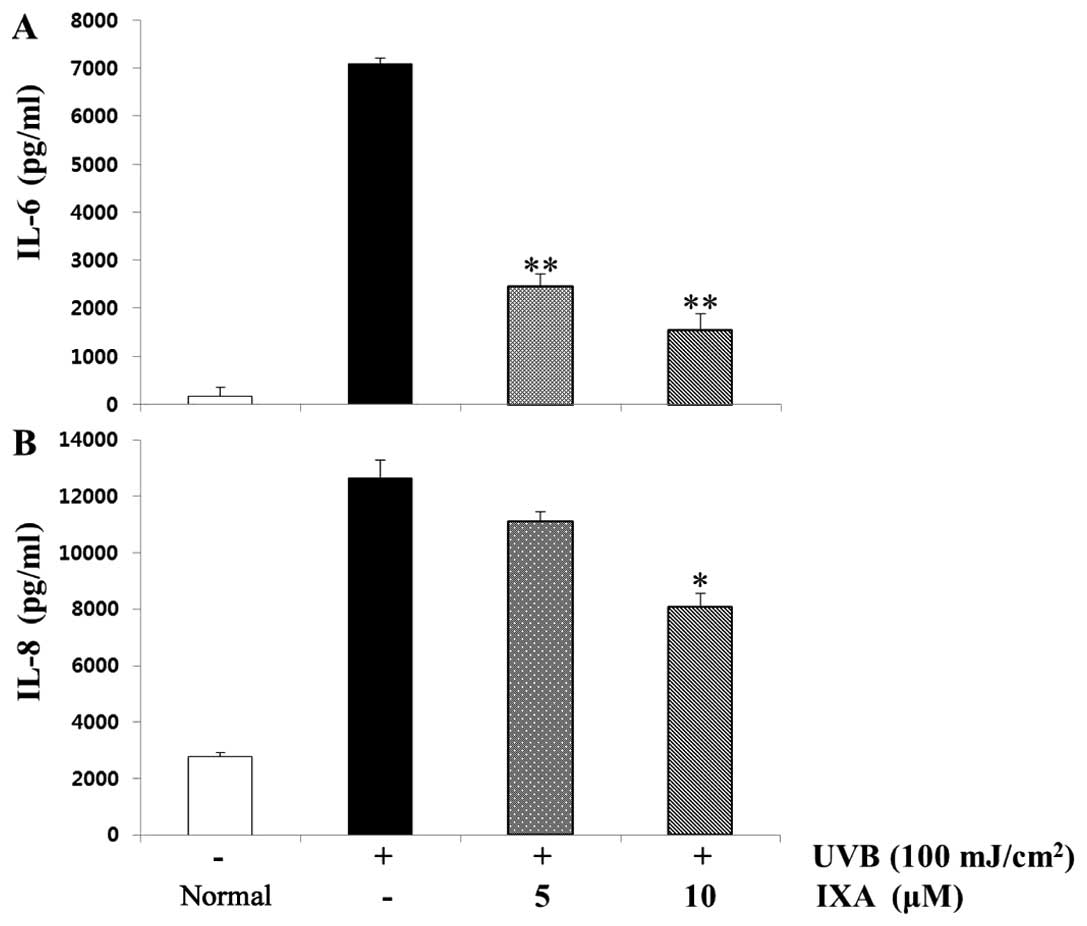
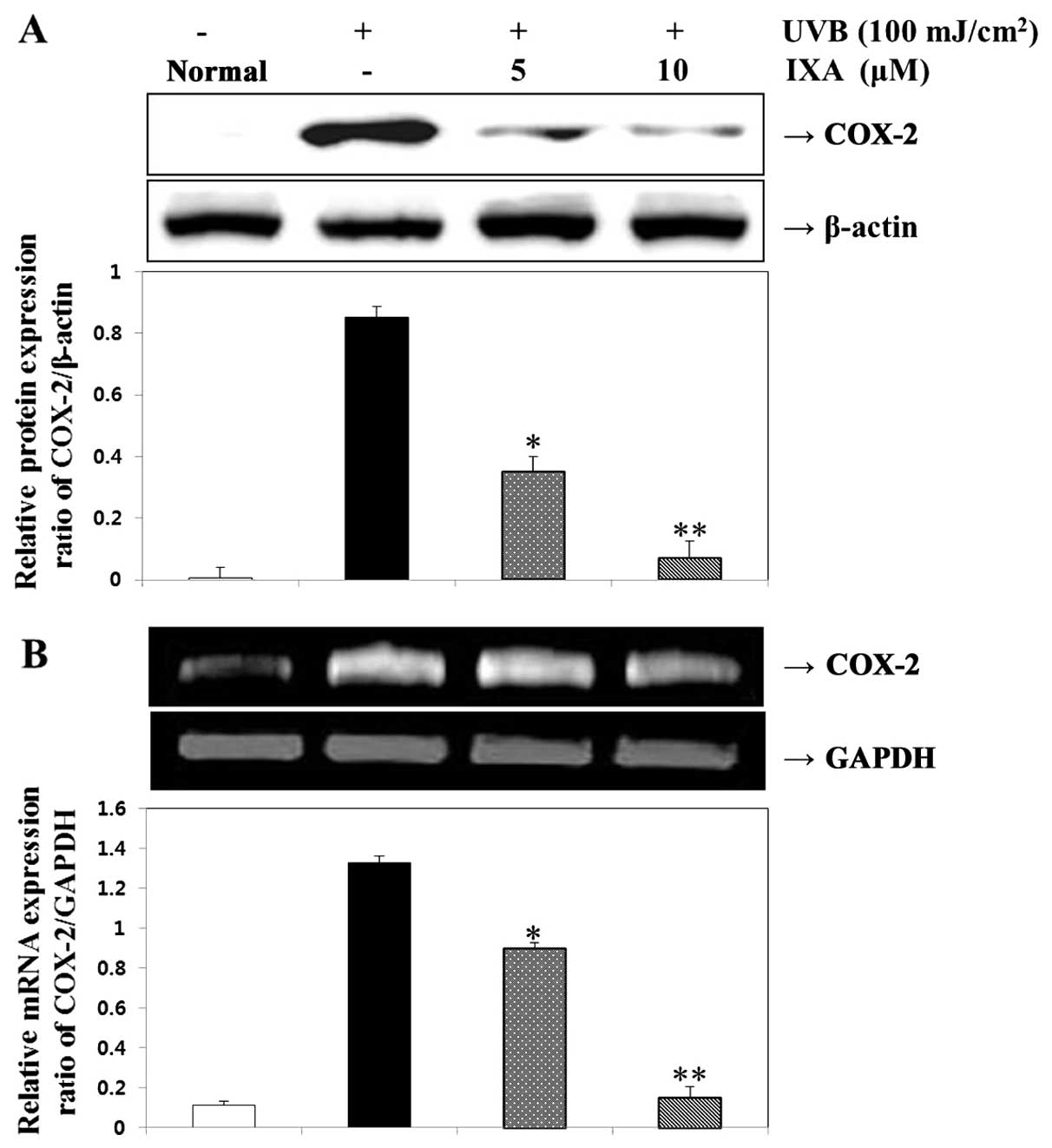
|
1
|
Muthusamy V and Piva TJ: A comparative
study of UV-induced cell signalling pathways in human
keratinocyte-derived cell lines. Arch Dermatol Res. 305:817–833.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Muthusamy V and Piva TJ: The UV response
of the skin: a review of the MAPK, NFkappaB, and TNFalpha signal
transduction pathways. Arch Dermatol Res. 302:5–17. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Duthie MS, Kimber I and Norval M: The
effects of ultraviolet radiation on the human immune system. Br J
Dermatol. 140:995–1009. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Svobodova A, Walterova D and Vostalova J:
Ultraviolet light induced alteration to the skin. Biomed Pap Med
Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czeck Repub. 150:25–38. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
de Gruijl FR and Van der Leun JC:
Environment and health: 3. Ozone depletion and ultraviolet
radiation. CMAJ. 163:851–855. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Holick MF: Vitamin D: a millenium
perspective. J Cell Biochem. 88:296–307. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Afaq F, Adhami VM and Mukhtar H:
Photochemoprevention of ultraviolet B signaling and
photocarcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 571:153–173. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Freedberg IM, Tomic-Canic M, Komine M and
Blumenberg M: Keratins and the keratinocyte activation cycle. J
Invest Dermatol. 116:633–640. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sauder DN: The role of epidermal cytokines
in inflammatory skin diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 95(Suppl 5):
S27–S28. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ziegler A, Jonason AS, Leffell DJ, Simon
JA, Sharma HW, Kimmelman J, Remington L, Jacks T and Brash DE:
Sunburn and p53 in the onset of skin cancer. Nature. 372:773–776.
1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Masferrer JL, Leahy KM, Koki AT, Zweifel
BS, Settle SL, Woerner BM, Edwards DA, Flickinger AG, Moore RJ and
Seibert K: Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Cancer Res. 60:1306–1311.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Higashi Y, Kanekura T and Kanzaki T:
Enhanced expression of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in human skin
epidermal cancer cells: evidence for growth suppression by
inhibiting COX-2 expression. Int J Cancer. 86:667–671. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rundhaug JE and Fischer SM:
Cyclo-oxygenase-2 plays a critical role in UV-induced skin
carcinogenesis. Photochem Photobiol. 84:322–329. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Buckman SY, Gresham A, Hale P, Hruza G,
Anast J, Masferrer J and Pentland AP: COX-2 expression is induced
by UVB exposure in human skin: implications for the development of
skin cancer. Carcinogenesis. 19:723–729. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen W, Tang Q, Gonzales MS and Bowden GT:
Role of p38 MAP kinases and ERK in mediating ultraviolet-B induced
cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression in human keratinocytes. Oncogene.
20:3921–3926. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin SK, Kok SH, Yeh FT, Kuo MY, Lin CC,
Wang CC, Goldring SR and Hong CY: MEK/ERK and signal transducer and
activator of transcription signaling pathways modulate oncostatin
M-stimulated CCL2 expression in human osteoblasts through a common
transcription factor. Arthritis Rheum. 50:785–793. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mahns A, Wolber R, Stäb F, Klotz LO and
Sies H: Contribution of UVB and UVA to UV-dependent stimulation of
cyclooxygenase-2 expression in artificial epidermis. Photochem
Photobiol Sci. 3:257–262. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yi JM, Hong SH, Lee HJ, Won JH, Kim JM,
Jeong DM, Baek SH, Lim JP and Kim HM: Ixeris dentata green sap
inhibits both compound 48/80-induced aanaphylaxis-like response and
IgE-mediated anaphylactic response in murine model. Biol Pharm
Bull. 25:5–9. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seto M, Miyase T and Fukushima S:
Sesquiterpene lactones from Ixeris dentata Nakai. Chem Pharm Bull.
34:4170–4176. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lee E: Effects of Ixeris dentata ext. on
lowering lipid and anti-oxidation. Korean J Plant Res. 24:55–60.
2011.In Korean. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Park EK, Sung JH, Trinh HT, Bae EA, Yun
HK, Hong SS and Kim DH: Lactic acid bacterial fermentation
increases the anti-allergic effects of Ixeris dentata. J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 18:308–313. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chung HS: Inhibition of monamine oxidase
by a flavone and its glycoside from Ixeris dentata Nakai. Nutraceut
Food. 8:141–144. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chung HS, Jeong HJ, Han MJ, Park ST, Seong
KK, Baek SH, Jeong DM, Kim MJ and Kim HM: Nitric oxide and tumor
necrosis factor-alpha production by Ixeris dentata in mouse
peritoneal macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol. 82:217–222. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim MJ, Kim JS, Jeong DM, Ham SS and Yu
CY: Effect of antioxidant, antimutagenicity and anticancer of root
extract from Ixeris dentataNakai. Korean J Med Crop Sci.
10:222–229. 2002.In Korean.
|
|
25
|
Kim SB, Kang OH, Keum JH, Mun SH, An HJ,
Jung HJ, Hong SH, Jeong DM, Kweon KT and Kwon DY: Anti-inflammatory
effect of Ixeris dentata on ultraviolet B-induced HaCaT
keratinocytes. Nat Prod Sci. 18:60–66. 2012.
|
|
26
|
Kim SB, Kang OH, Joung DK, Mun SH, Seo YS,
Cha MR, Ryu SY, Shin DW and Kwon DY: Anti-inflammatory effects of
tectroside on UVB-induced HaCaT cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:1471–1476.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cha MR, Choi YH, Choi CW, Yoo DS, Kim YS,
Choi SU, Kim YH and Ryu SY: New guaiane sesquiterpene lactones from
Ixeris dentata. Planta Med. 77:380–382. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zidorn C: Sesquiterpene lactones and their
precursors as chemosystematic markers in the tribe Cichorieae of
the Asteraceae. Phytochemistry. 69:2270–2296. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yarilin AA and Belyakov IM: Cytokines in
the thymus: production and biological effects. Curr Med Chem.
11:447–464. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grossman RM, Krueger J, Yourish D,
Granelli-Piperno A, Murphy DP, May LT, Kupper TS, Sehgal PB and
Gottlieb AB: Interleukin 6 is expressed in high levels in psoriatic
skin and stimulates proliferation of cultured human keratinocytes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:6367–6371. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Turksen K, Kupper TS, Degenstein L,
Williams I and Fuchs E: Interleukin 6: insights to its function in
skin by overexpression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
89:5068–5072. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sawamura D, Meng X, Ina S, Sato M, Tamai
K, Hanada K and Hashimoto I: Induction of keratinocyte
proliferation and lymphocytic infiltration by in vivo introduction
of the IL-6 gene into keratinocytes and possibility of keratinocyte
gene therapy for inflammatory skin diseases using IL-6 mutant
genes. J Immunol. 161:5633–5639. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sato M, Sawamura D, Ina S, Yaguchi T,
Hanada K and Hashimoto I: In vivo introduction of the interleukin 6
gene into human keratinocytes: induction of epidermal proliferation
by the fully spliced form of interleukin 6, but not by the
alternatively spliced form. Arch Dermatol Res. 291:400–404. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sugawara T, Gallucci RM, Simeonova PP and
Luster MI: Regulation and role of interleukin 6 in wounded human
epithilial keratinocytes. Cytokine. 15:328–336. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mohamadzadeh M, Müller M, Hultsch T, Enk
A, Saloga J and Knop J: Enhanced expression of IL-8 in normal human
kerati-nocytes and human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT in vitro
after stimulation with contact sensitizers, tolerogens and
irritants. Exp Dermatol. 3:298–303. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yen HT, Chiang LC, Wen KH, Chang SF, Tsai
CC, Yu CL and Yu HS: Arsenic induces interleukin-8 expression in
cultured keratinocytes. Arch Dermatol Res. 288:716–717. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
O’Toole AE, Mak LL, Guitart J, Woodley DT,
Hashimoto T, Amagai M and Chan LS: Induction of keratinocyte IL-8
expression and secretion by IgG autoantibodies as a novel mechanism
of epidermal neutrophil recruitment in a pemphigus variant. Clin
Exp Immunol. 119:217–224. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Schmidt E, Reimer S, Kruse N, Jainta S,
Bröcker EB, Marinkovich MP, Guidice GJ and Zillikens D:
Autoantibodies to BP180 associated with bullous pemphigoid release
interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 from cultured human keratinocytes.
J Invest Dermatol. 115:842–848. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pentland AP, Schoggins JW, Scott GA, Khan
KN and Han R: Reduction of UV-induced skin tumors in hairless mice
by selective COX-2 inhibition. Carcinogenesis. 20:1939–1944. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Athar M, An KP, Morel KD, Kim AL,
Aszterbaum M, Longley J, Epstein EH Jr and Bickers DR: Ultraviolet
B (UVB)-induced COX-2 expression in murine skin: an
immunohistochemical study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
280:1042–1047. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
An KP, Athar M, Tang X, Katiyar SK, Russo
J, Beech J, Aszterbaum M, Kopelovich L, Epstein EH Jr, Mukhtar H
and Bickers DR: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in murine and human
nonmelanoma skin cancers: Implications for therapeutic approaches.
Photochem Photobiol. 76:73–80. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Grewe M, Trefzer U, Ballhorn A, Gyufko K,
Henninger H and Krutmann J: Analysis of the mechanism of
ultraviolet (UV) B radiation-induced prostaglandin E2 synthesis by
human epidermoid carcinoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 101:528–531.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Robinson MJ and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:180–186. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lewis TS, Shapiro PS and Ahn NG: Signal
transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res.
74:49–139. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ashida M, Bito T, Budiyanto A, Ichihashi M
and Ueda M: Involvement of EGF receptor activation in the induction
of cyclooxygenase-2 in HaCaT keratinocytes after UVB. Exp Dermatol.
12:445–452. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|