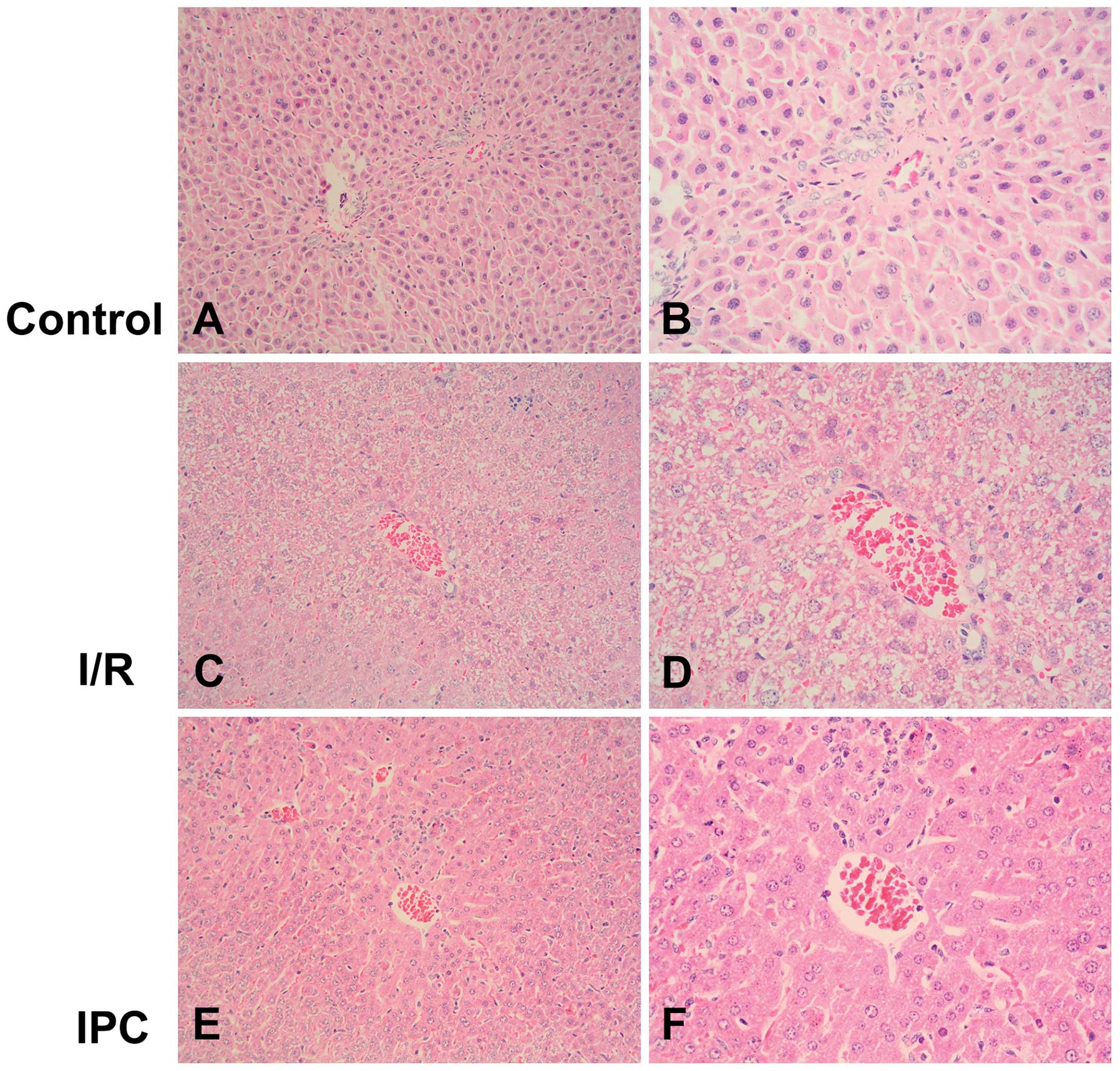
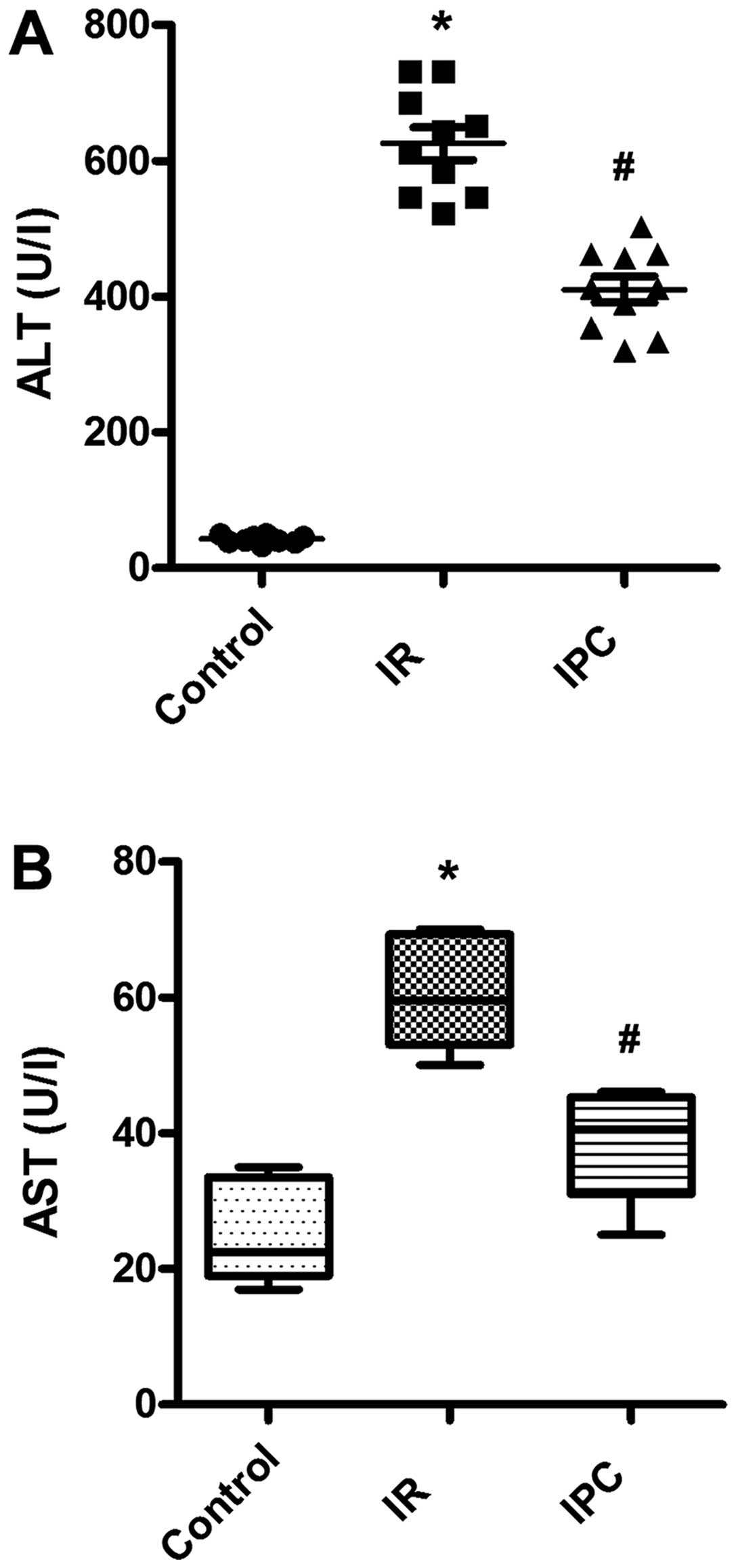
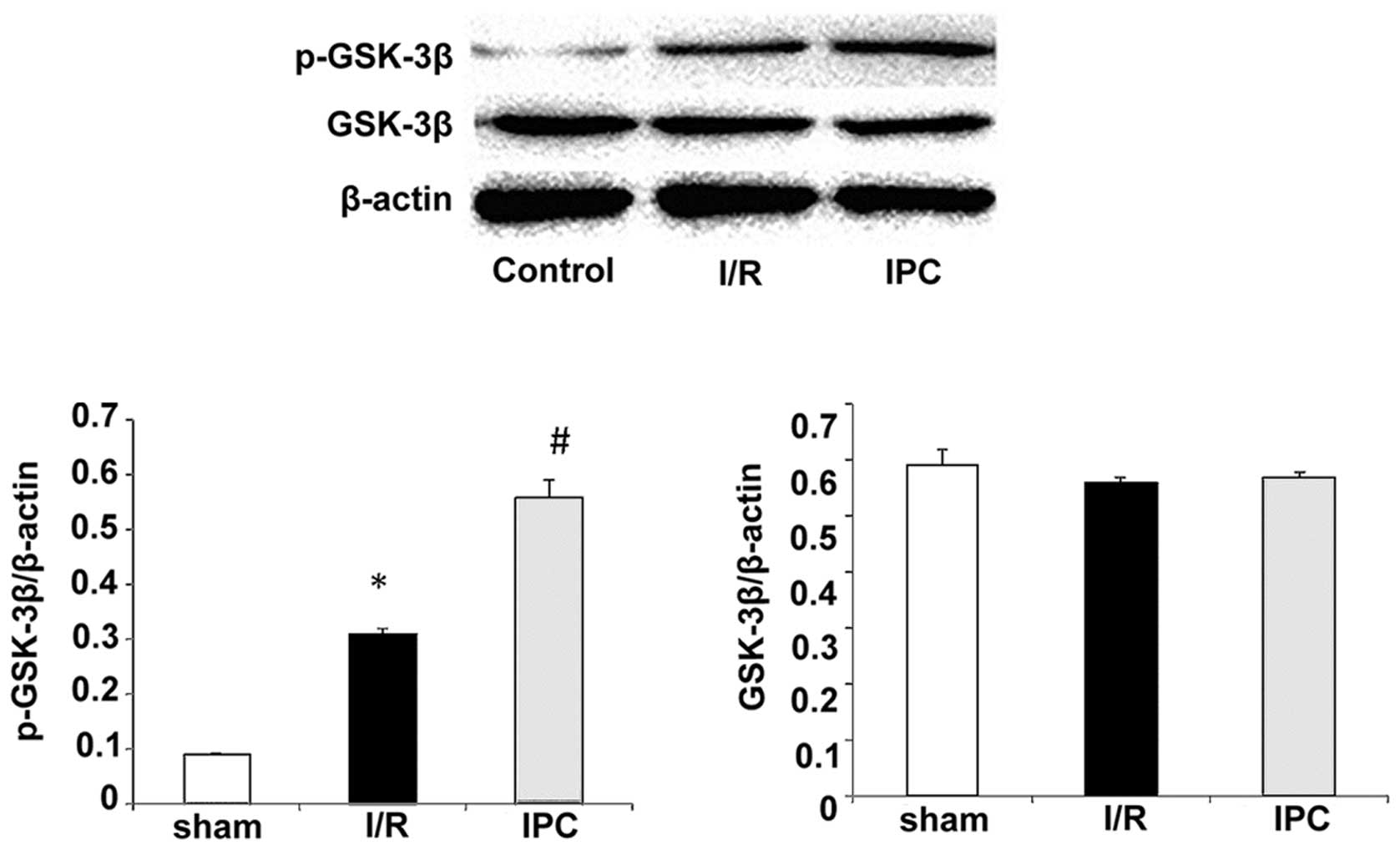
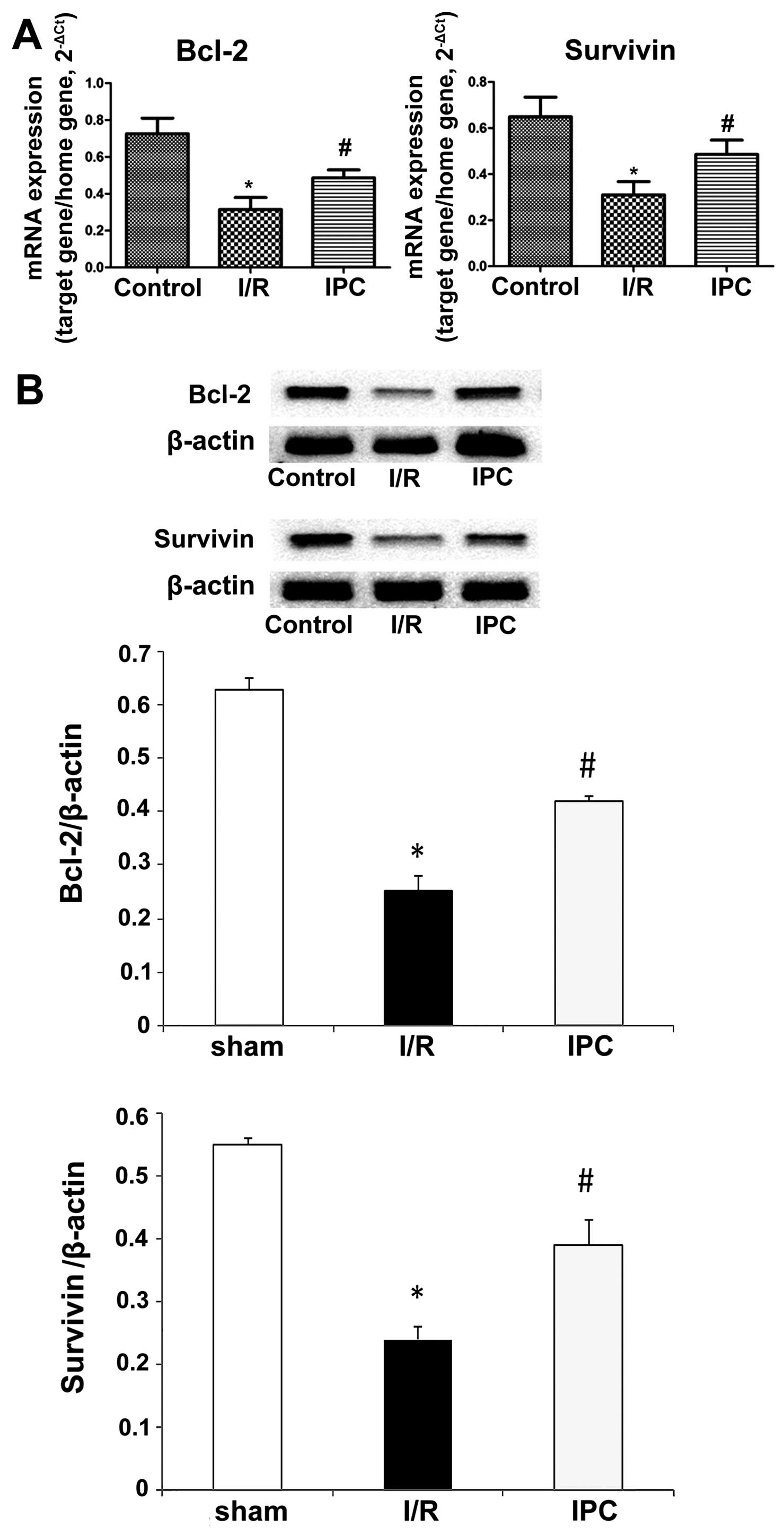
|
1
|
Burroughs AK, Sabin CA, Rolles K, et al:
3-month and 12-month mortality after first liver transplant in
adults in Europe: predictive models for outcome. Lancet.
367:225–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li Q and Li JD: Progress in liver
transplantation ischemic preconditioning. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg.
13:470–473. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
3
|
Murry CE, Jennings RB and Reimer KA:
Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in
ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 74:1124–1136. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Peralta C, Closa D, Xaus C, Gelpi E,
Rosello-Catafau J and Hotter G: Hepatic preconditioning in rats is
defined by a balance of adenosine and xanthine. Hepatology.
28:768–773. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Glazier SS, O’Rourke DM, Graham DI and
Welsh FA: Induction of ischemic tolerance following brief focal
ischemia in rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 14:545–553. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Du ZY, Hicks M, Winlaw D, Spratt P and
MacDonald P: Ischemic preconditioning enhances donor lung
preservation in the rat. J Heart Lung Transplant. 15:1258–1267.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hotter G, Closa D, Prados M,
Fernandez-Cruz L, Prats N, Gelpi E and Rosello-Catafau J:
Intestinal preconditioning is mediated by a transient increase in
nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 222:27–32. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ferdinandy P, Schulz R and Baxter GF:
Interaction of cardiovascular risk factors with myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury, preconditioning, and postconditioning.
Pharmacol Rev. 59:418–458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Halestrap AP, Clarke SJ and Khaliulin I:
The role of mitochondria in protection of the heart by
preconditioning. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1767:1007–1031. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hausenloy DJ, Tsang A and Yellon DM: The
reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway: a common target for both
ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning. Trends Cardiovasc
Med. 15:69–75. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Alchera E, Dal Ponte C, Imarisio C, Albano
E and Carini R: Molecular mechanisms of liver preconditioning.
World J Gastroenterol. 16:6058–6067. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jellestad L, Fink T, Pradarutti S, Kubulus
D, Wolf B, Bauer I, Thiemermann C and Rensing H: Inhibition of
glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3-β improves liver microcirculation
and hepatocellular function after hemorrhagic shock. Eur J
Pharmacol. 724:175–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ding VW, Chen RH and McCormick F:
Differential regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta by
insulin and Wnt signaling. J Biol Chem. 275:32475–32481. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kusano S and Raab-Traub N: I-mfa domain
proteins interact with Axin and affect its regulation of the Wnt
and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biol.
22:6393–6405. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hart MJ, de los Santos R, Albert IN,
Rubinfeld B and Polakis P: Downregulation of beta-catenin by human
Axin and its association with the APC tumor suppressor,
beta-catenin and GSK3 beta. Curr Biol. 8:573–581. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A
and Kemler R: beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway. EMBO J. 16:3797–3804. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rubinfeld B, Albert I, Porfiri E, Fiol C,
Munemitsu S and Polakis P: Binding of GSK3beta to the
APC-beta-catenin complex and regulation of complex assembly.
Science. 272:1023–1026. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bienz M: TCF: transcriptional activator or
repressor? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 10:366–372. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Easwaran V, Lee SH, Inge L, et al:
beta-Catenin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor
expression in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 63:3145–3153.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kuhl M, Bruhn L,
Wedlich D, Grosschedl R and Birchmeier W: Functional interaction of
beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature.
382:638–642. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kuroda S, Tashiro H, Igarashi Y, et al:
Rho inhibitor prevents ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat steatotic
liver. J Hepatol. 56:146–152. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nakayama H, Yamamoto Y, Kume M, et al:
Pharmacologic stimulation of adenosine A2 receptor supplants
ischemic preconditioning in providing ischemic tolerance in rat
livers. Surgery. 126:945–954. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Uysal AI, Ocmen E, Akan M, Ozkardesler S,
Ergur BU, Guneli E, Kume T, Koca U and Unal Togrul B: The effects
of remote ischemic preconditioning and N-acetylcysteine with remote
ischemic preconditioning in rat hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury
model. Biomed Res Int. 2014:8927042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qi BN, Yi JH, Tang GH, Miao JL and Guo JF:
The experimental study of n-hexane on lipid peroxidation and DNA
damage of hepatic cell in rats. J Xi’an Jiaotong Univ Med Sci.
28:145–148. 2007.In Chinese.
|
|
25
|
Jia YX and Chen ZW: The effects of
Cu2+, Cd2+ on superoxide activities in
carassius auratus. Acta Hydrobiol Sin. 27:323–325. 2003.In
Chinese.
|
|
26
|
Jiang Y, Tang JJ, Wu BQ, Yuan B and Qu Z:
The protective effects of different-time-ischemic preconditioning
on the reperfusion injury in fatty livers in rats. PLoS One.
8:e580862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jin LM, Jin SF, Liu YX, Zhou L, Xie HY,
Yan S, Xu X and Zheng SS: Ischemic preconditioning enhances
hepatocyte proliferation in the early phase after ischemia under
hemi-hepatectomy in rats. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
11:521–526. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yuan GJ, Ma JC, Gong ZJ, Sun XM, Zheng SH
and Li X: Modulation of liver oxidant-antioxidant system by
ischemic preconditioning during ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rats. World J Gastroenterol. 11:1825–1828. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yong J, Bo Y, Bao-qiang W, Jian-jun T and
Zhen Q: The optimal time window of ischemic preconditioning (IPC)
on the reperfusion injury in moderate to severe hepatocirrhosis in
rats. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 43:64–69. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Camargo CA Jr, Madden JF, Gao W, Selvan RS
and Clavien PA: Interleukin-6 protects liver against warm
ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes hepatocyte proliferation
in the rodent. Hepatology. 26:1513–1520. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Serafin A, Rosello-Catafau J, Prats N,
Xaus C, Gelpi E and Peralta C: Ischemic preconditioning increases
the tolerance of Fatty liver to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury
in the rat. Am J Pathol. 161:587–601. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Peralta C, Bulbena O, Xaus C, Prats N,
Cutrin JC, Poli G, Gelpi E and Rosello-Catafau J: Ischemic
preconditioning: a defense mechanism against the reactive oxygen
species generated after hepatic ischemia reperfusion.
Transplantation. 73:1203–1211. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peralta C, Fernandez L, Panes J, Prats N,
Sans M, Pique JM, Gelpi E and Rosello-Catafau J: Preconditioning
protects against systemic disorders associated with hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion through blockade of tumor necrosis
factor-induced P-selectin up-regulation in the rat. Hepatology.
33:100–113. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chung H, Seo S, Moon M and Park S:
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
and ERK1/2 pathways mediate protective effects of acylated and
unacylated ghrelin against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced
apoptosis in primary rat cortical neuronal cells. J Endocrinol.
198:511–521. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miller JR, Hocking AM, Brown JD and Moon
RT: Mechanism and function of signal transduction by the
Wnt/beta-catenin and Wnt/Ca2+ pathways. Oncogene.
18:7860–7872. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tong H, Imahashi K, Steenbergen C and
Murphy E: Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3bet a during
preconditioning through a phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-dependent
pathway is cardioprotective. Circ Res. 90:377–379. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kaga S, Zhan L, Altaf E and Maulik N:
Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta/beta-catenin promotes angiogenic and
anti-apoptotic signaling through the induction of VEGF, Bcl-2 and
survivin expression in rat ischemic preconditioned myocardium. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 40:138–147. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xia YX, Lu L, Wu ZS, Pu LY, Sun BC and
Wang XH: Inhibition of GSK-3beta ameliorates hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury through GSK-3beta/beta-catenin
signaling pathway in mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
11:278–284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ren F, Duan Z, Cheng Q, et al: Inhibition
of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta ameliorates liver ischemia
reperfusion injury by way of an interleukin-10-mediated immune
regulatory mechanism. Hepatology. 54:687–696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Koh PO, Won CK and Cho JH: Estradiol
prevents the injury-induced decrease of Akt/glycogen synthase
kinase 3beta phosphorylation. Neurosci Lett. 404:303–308. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Thirunavukkarasu M, Han Z, Zhan L,
Penumathsa SV, Menon VP and Maulik N: Adeno-sh-beta-catenin
abolishes ischemic preconditioning-mediated cardioprotection by
downregulation of its target genes VEGF, Bcl-2, and survivin in
ischemic rat myocardium. Antioxid Redox Signal. 10:1475–1484. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Monga SP, Monga HK, Tan X, Mule K,
Pediaditakis P and Michalopoulos GK: Beta-catenin antisense studies
in embryonic liver cultures: role in proliferation, apoptosis, and
lineage specification. Gastroenterology. 124:202–216. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ibrahim SH, Akazawa Y, Cazanave SC, et al:
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibition attenuates hepatocyte
lipoapoptosis. J Hepatol. 54:765–772. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Johnston A, Ponzetti K, Anwer MS and
Webster CR: cAMP-guanine exchange factor protection from bile
acid-induced hepatocyte apoptosis involves glycogen synthase kinase
regulation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 301:G385–G400. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gujral JS, Bucci TJ, Farhood A and
Jaeschke H: Mechanism of cell death during warm hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion in rats: apoptosis or necrosis? Hepatology.
33:397–405. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|