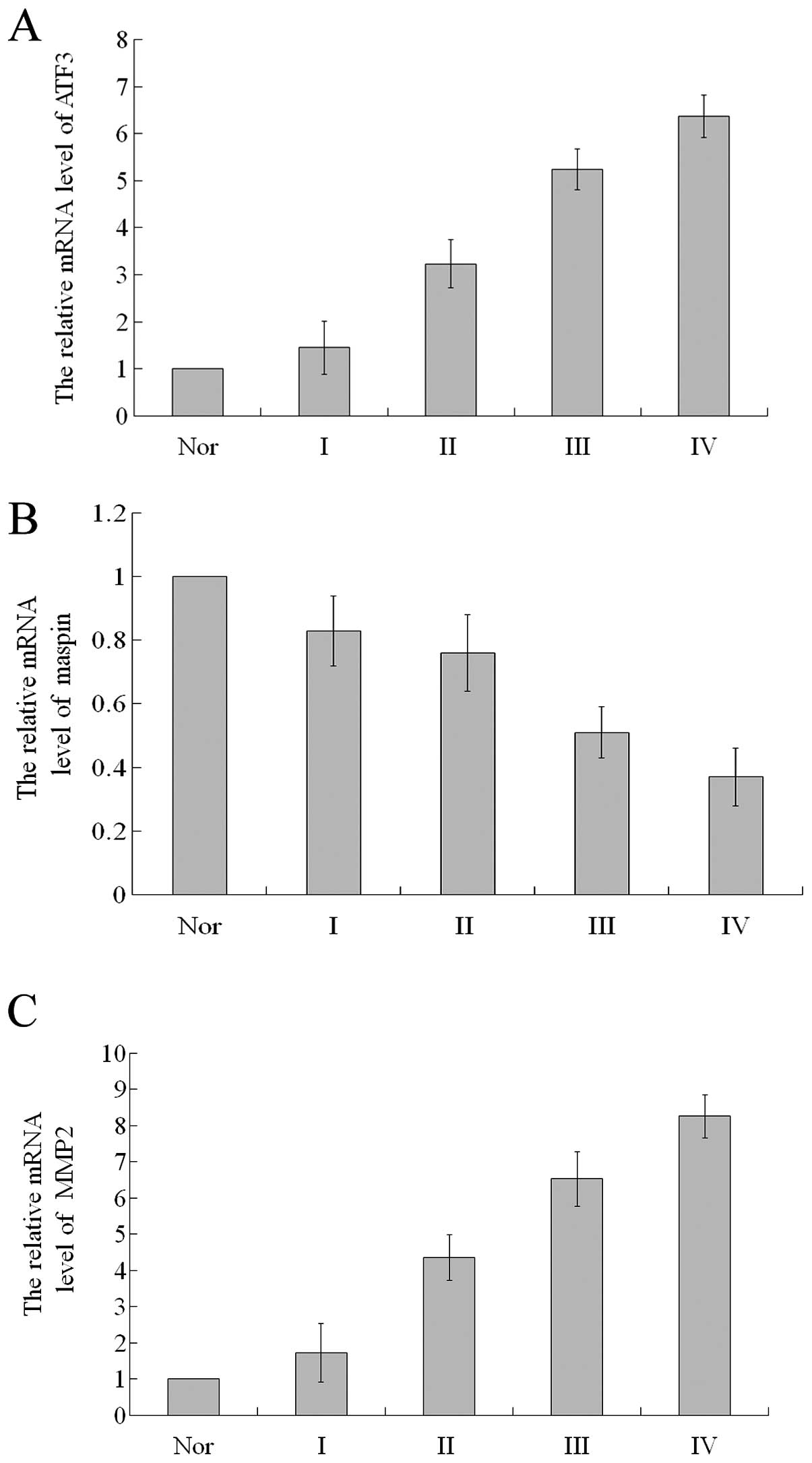
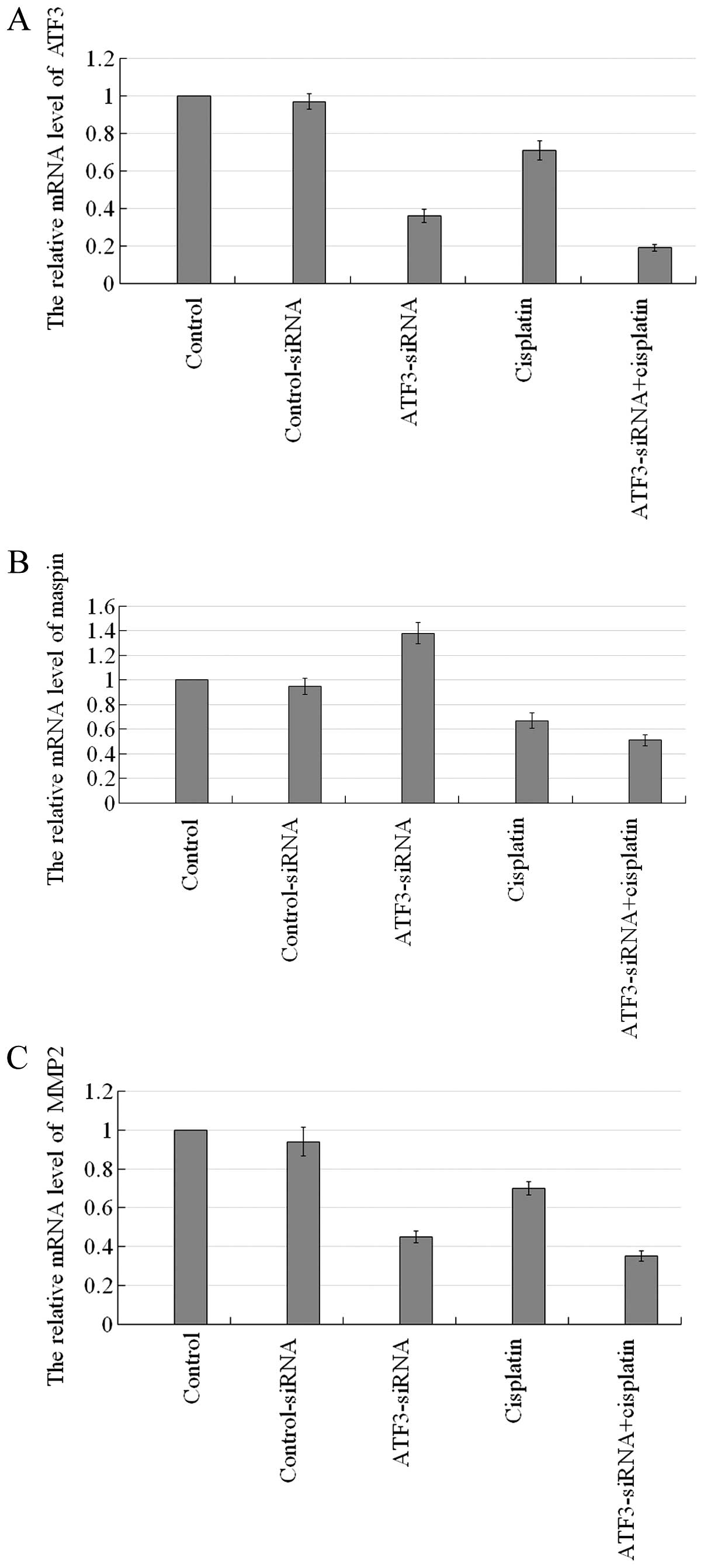
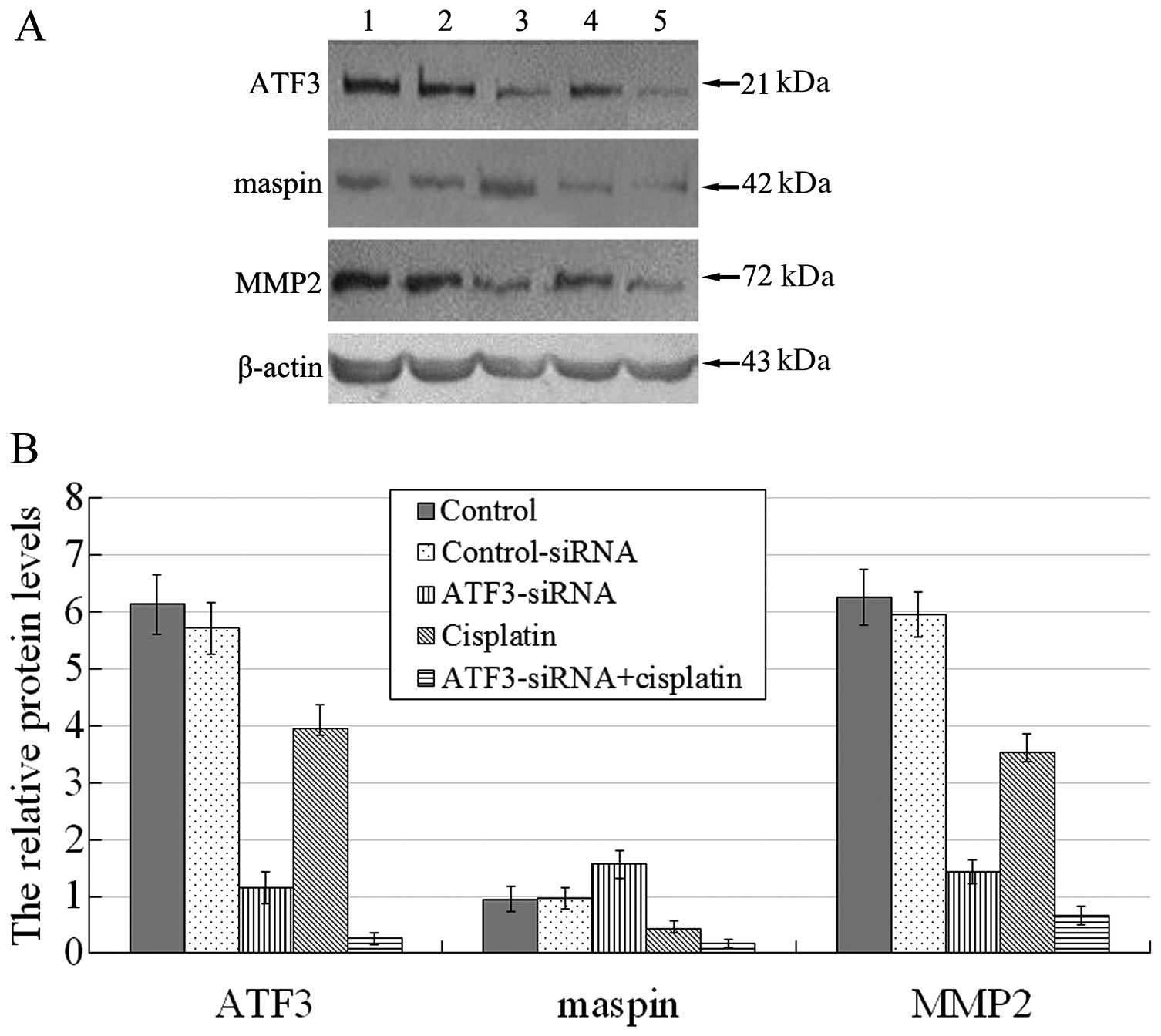
|
1
|
Pelzer AE, Bektic J, Haag P, Berger AP,
Pycha A, Schäfer G, Rogatsch H, Horninger W, Bartsch G and Klocker
H: The expression of transcription factor activating transcription
factor 3 in the human prostate and its regulation by androgen in
prostate cancer. J Urol. 175:1517–1522. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Janz M, Hummel M, Truss M, et al:
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma is characterized by high constitutive
expression of activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), which
promotes viability of Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells. Blood.
107:2536–2539. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Iyengar P, Combs TP, Shah SJ, et al:
Adipocyte-secreted factors synergistically promote mammary
tumorigenesis through induction of anti-apoptotic transcriptional
programs and protooncogene stabilization. Oncogene. 22:6408–6423.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hai T and Curran T: Cross-family
dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters
DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:3720–3724.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wolfgang CD, Chen BP, Martindale JL,
Holbrook NJ and Hai T: gadd153/Chop10, a potential target gene of
the transcriptional repressor ATF3. Mol Cell Biol. 17:6700–6707.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen BPC, Liang G, Whelan J and Hai T:
ATF3 and ATF3 delta Zip. Transcriptional repression versus
activation by alternatively spliced isoforms. J Biol Chem.
269:15819–15826. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen Z, Fan Z, McNeal JE, Nolley R,
Caldwell MC, Mahadevappa M, Zhang Z, Warrington JA and Stamey TA:
Hepsin and maspin are inversely expressed in laser capture
microdissectioned prostate cancer. J Urol. 169:1316–1319. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Forsyth PA, Wong H, Laing TD, et al:
Gelatinase-A (MMP-2), gelatinase-B (MMP-9) and membrane type matrix
metallopro-teinase-1 (MT1-MMP) are involved in different aspects of
the pathophysiology of malignant gliomas. Br J Cancer.
79:1828–1835. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Louis David N, Ohgaki Hiroko, Wiestler
Otmar D, Cavenee Webster K, et al: Astrocytic tumours. Who
Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. World
Health Organization; Geneva: pp. 13–45. 2007
|
|
10
|
Gatalica Z, Lele SM, Rampy BA and Norris
BA: The expression of Fhit protein is related inversely to disease
progression in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer.
88:1378–1383. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yin X, Dewille JW and Hai T: A potential
dichotomous role of ATF3, an adaptive-response gene, in cancer
development. Oncogene. 27:2118–2127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ishiguro T, Nakajima M, Naito M, Muto T
and Tsuruo T: Identification of genes differentially expressed in
B16 murine melanoma sublines with different metastatic potentials.
Cancer Res. 56:875–879. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bandyopadhyay S, Wang Y, Zhan R, et al:
The tumor metastasis suppressor gene Drg-1 down-regulates the
expression of activating transcription factor 3 in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 66:11983–11990. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ishiguro T, Nagawa H, Naito M and Tsuruo
T: Inhibitory effect of ATF3 antisense oligonucleotide on ectopic
growth of HT29 human colon cancer cells. Jpn J Cancer Res.
91:833–836. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu D, Wolfgang CD and Hai T: Activating
transcription factor 3, a stress-inducible gene, suppresses
Rasstimulated tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem. 281:10473–10481. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bottone FG Jr, Moon Y, Kim JS,
Alston-Mills B, Ishibashi M and Eling TE: The anti-invasive
activity of cyclooxygenase inhibitors is regulated by the
transcription factor ATF3 (activating transcription factor 3). Mol
Cancer Ther. 4:693–703. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang W and Zhang M: Tissue microarray
analysis of maspin expression and its reverse correlation with
mutant p53 in various tumors. Int J Oncol. 20:1145–1150.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zou Z, Anisowicz A, Hendrix MJ, Thor A,
Neveu M, Sheng S, Rafidi K, Seftor E and Sager R: Maspin, a serpin
with tumor-suppressing activity in human mammary epithelial cells.
Science. 263:526–529. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang DL, Wang YF, Shi GS and Huang H:
Correlation of hTERT expression to maspin and bFGF expression and
their significance in glioma. Ai Zheng. 26:601–606. 2007.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song H, Li Y, Lee J, Schwartz AL and Bu G:
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 promotes cancer
cell migration and invasion by inducing the expression of matrix
metalloproteinases 2 and 9. Cancer Res. 69:879–886. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kodera T, Nakagawa T, Kubota T, Kabuto M,
Sato K and Kobayashi H: The expression and activation of matrix
metallo-proteinase-2 in rat brain after implantation of C6 rat
glioma cells. J Neurooncol. 46:105–114. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Musso O, Théret N, Campion JP, Turlin B,
Milani S, Grappone C and Clément B: In situ detection of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2) and the metalloproteinase inhibitor
TIMP2 transcripts in human primaryhepatocellular carcinoma and in
liver metastasis. J Hepatol. 26:593–605. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mendes O, Kim HT and Stoica G: Expression
of MMP2, MMP9 and MMP3 in breast cancer brain metastasis in a rat
model. Clin Exp Metastasis. 22:237–246. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Danilewicz M, Sikorska B and
Wagrowska-Danilewicz M: Prognostic significance of the
immunoexpression of matrix metalloproteinaseMMP2 and its inhibitor
TIMP2 in laryngeal cancer. Med Sci Monit. 9:MT42–MT47.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Herbst RS, Onn A and Sandler A:
Angiogenesis and lung cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic
implications. J Clin Oncol. 23:3243–3256. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bodenstine TM, Seftor RE, Khalkhali-Ellis
Z, Seftor EA, Pemberton PA and Hendrix MJ: Maspin: Molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
31:529–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sheng S: The promise and challenge toward
the clinical application of maspin in cancer. Front Biosci.
9:2733–2745. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ngamkitidechakul C, Warejcka DJ, Burke JM,
O’Brien WJ and Twining SS: Sufficiency of the reactive site loop of
maspin for induction of cell-matrix adhesion and inhibition of cell
invasion. Conversion of ovalbumin to a maspin-like molecule. J Biol
Chem. 278:31796–31806. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zou Z, Zhang W, Young D, Gleave MG, Rennie
P, Connell T, Connelly R, Moul J, Srivastava S and Sesterhenn I:
Maspin expression profile in human prostate cancer (CaP) and in
vitro induction of Maspin expression by androgen ablation. Clin
Cancer Res. 8:1172–1177. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hai T, Wolford CC and Chang YS: ATF3, a
hub of the cellular adaptive-response network, in the pathogenesis
of diseases: Is modulation of inflammation a unifying component?
Gene Expr. 15:1–11. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McCawley LJ and Matrisian LM: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Multifunctional contributors to tumor
progression. Mol Med Today. 6:149–156. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fang J, Shing Y, Wiederschain D, Yan L,
Butterfield C, Jackson G, Harper J, Tamvakopoulos G and Moses MA:
Matrix metal-loproteinase-2 is required for the switch to the
angiogenic phenotype in a tumor model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:3884–3889. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rosenberger CM, Clark AE, Treuting PM,
Johnson CD and Aderem A: ATF3 regulates MCMV infection in mice by
modulating IFN-gamma expression in natural killer cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:2544–2549. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stearns ME, Kim G, Garcia F and Wang M:
Interleukin-10 induced activating transcription factor 3
transcriptional suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 gene
expression in human prostate CPTX-1532 Cells. Mol Cancer Res.
2:403–416. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yan C, Wang H and Boyd DD: ATF3 represses
72-kDa type IV collagenase (MMP-2) expression by antagonizing
p53-dependent trans-activation of the collagenase promoter. J Biol
Chem. 277:10804–10812. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|