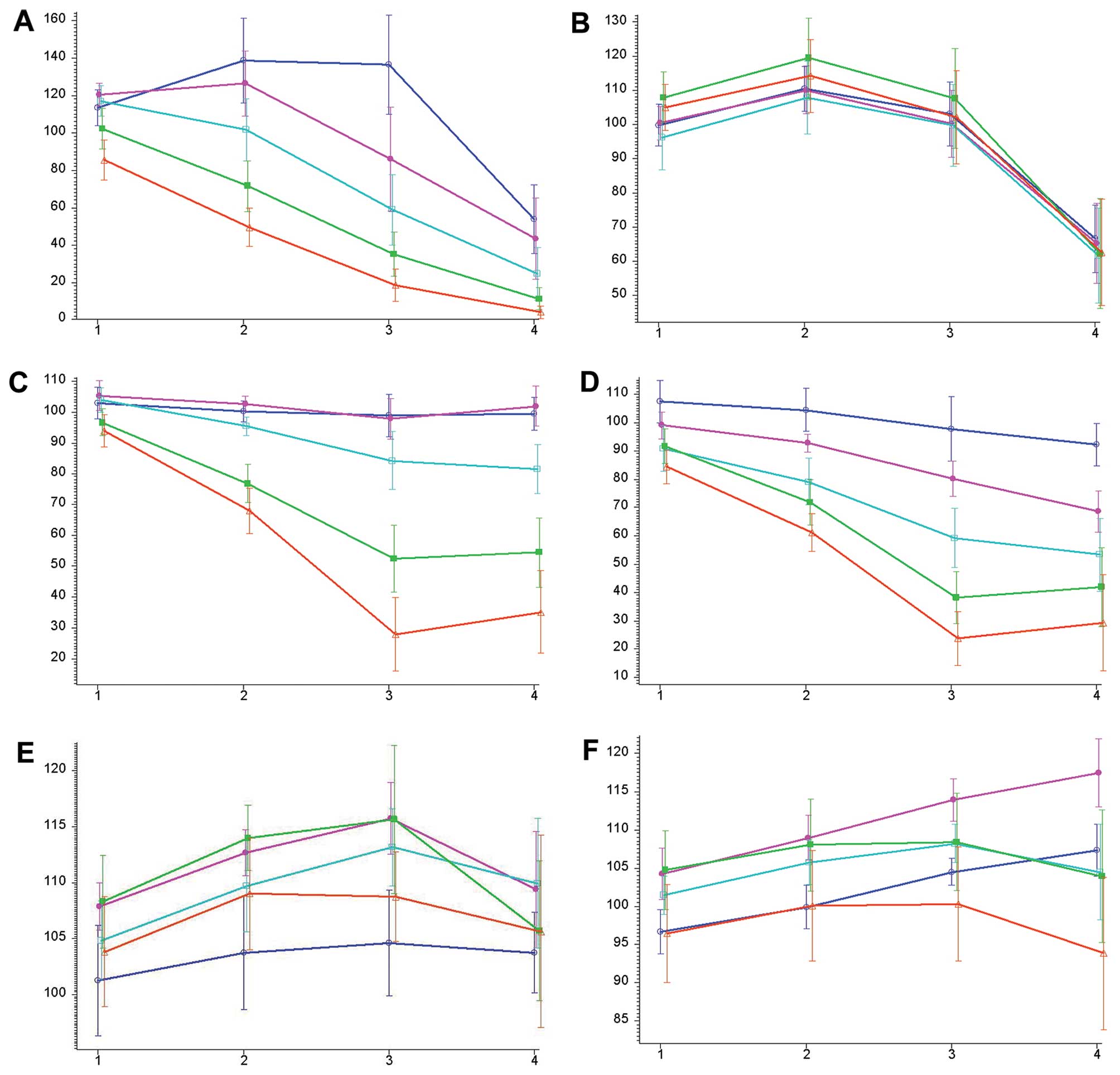
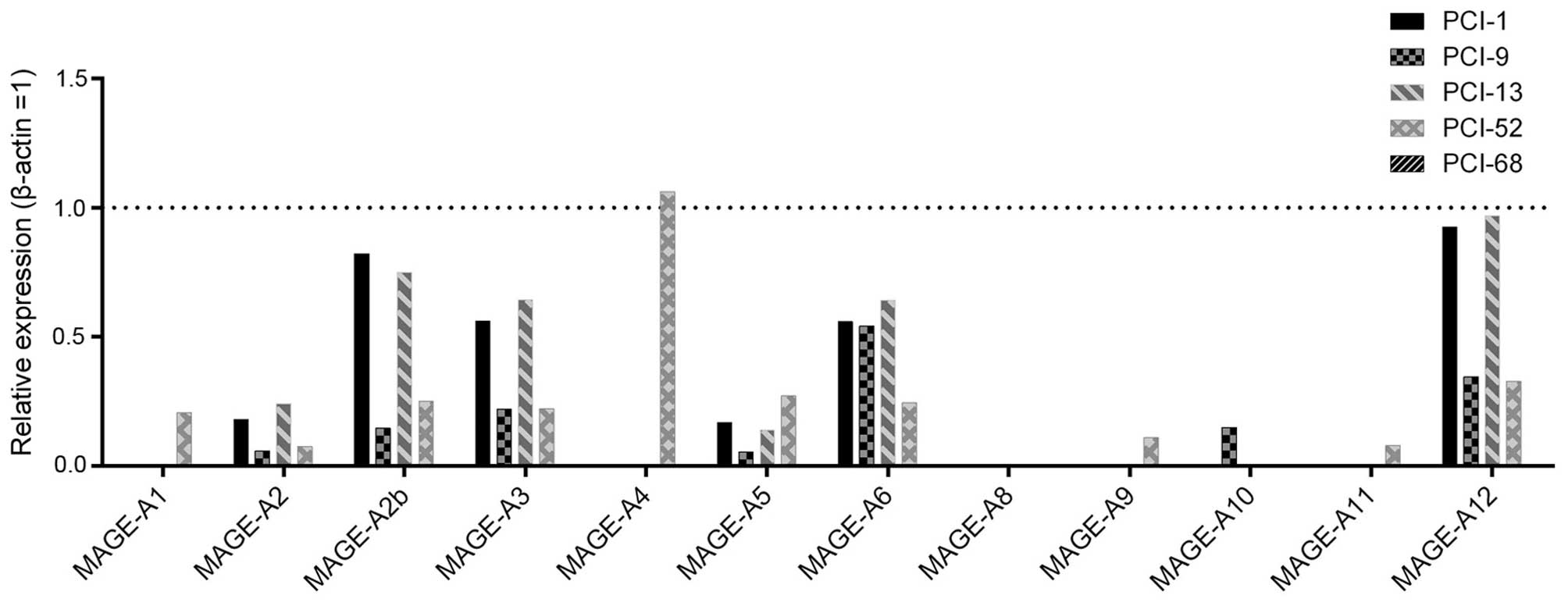
|
1
|
Gupta S, Kong W, Peng Y, Miao Q and
Mackillop WJ: Temporal trends in the incidence and survival of
cancers of the upper aerodigestive tract in Ontario and the United
States. Int J Cancer. 125:2159–2165. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Simpson AJ, Caballero OL, Jungbluth A,
Chen YT and Old LJ: Cancer/testis antigens, gametogenesis and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:615–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van der Bruggen P, Traversari C, Chomez P,
Lurquin C, De Plaen E, Van den Eynde B, Knuth A and Boon T: A gene
encoding an antigen recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes on a
human melanoma. Science. 254:1643–1647. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abd-Elsalam EA and Ismaeil NA:
Melanoma-associated antigen genes: A new trend to predict the
prognosis of breast cancer patients. Med Oncol. 31:2852014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li G, Song P and Zhang B: Expression and
significance of MAGE genes in human lung cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za
Zhi. 16:308–313. 2013.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dyrskjøt L, Zieger K, Kissow Lildal T,
Reinert T, Gruselle O, Coche T, Borre M and Ørntoft TF: Expression
of MAGE-A3, NY-ESO-1, LAGE-1 and PRAME in urothelial carcinoma. Br
J Cancer. 107:116–122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang QM, He SJ, Shen N, Luo B, Fan R, Fu
J, Luo GR, Zhou SF, Xiao SW and Xie XX: Overexpression of MAGE-D4
in colorectal cancer is a potentially prognostic biomarker and
immunotherapy target. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:3918–3927.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gu X, Fu M, Ge Z, Zhan F, Ding Y, Ni H,
Zhang W, Zhu Y, Tang X, Xiong L, et al: High expression of MAGE-A9
correlates with unfavorable survival in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Sci Rep. 4:66252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Laban S, Atanackovic D, Luetkens T, Knecht
R, Busch CJ, Freytag M, Spagnoli G, Ritter G, Hoffmann TK, Knuth A,
et al: Simultaneous cytoplasmic and nuclear protein expression of
melanoma antigen-A family and NY-ESO-1 cancer-testis antigens
represents an independent marker for poor survival in head and neck
cancer. Int J Cancer. 135:1142–1152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sahin U, Türeci O, Chen YT, Seitz G,
Villena-Heinsen C, Old LJ and Pfreundschuh M: Expression of
multiple cancer/testis (CT) antigens in breast cancer and melanoma:
Basis for polyvalent CT vaccine strategies. Int J Cancer.
78:387–389. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krauss E, Rauthe S, Gattenlöhner S,
Reuther T, Kochel M, Kriegebaum U, Kübler AC and Müller-Richter UD:
MAGE-A antigens in lesions of the oral mucosa. Clin Oral Investig.
15:315–320. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Han L, Jiang B, Wu H, Zhang S and Lu X:
Expression and prognostic value of MAGE-A9 in laryngeal squamous
cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:6734–6742. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hartmann S, Kriegebaum U, Küchler N,
Brands RC, Linz C, Kübler AC and Müller-Richter UD: Correlation of
MAGE-A tumor antigens and the efficacy of various chemotherapeutic
agents in head and neck carcinoma cells. Clin Oral Investig.
18:189–197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hartmann S, Kriegebaum U, Küchler N,
Lessner G, Brands RC, Linz C, Schneider T, Kübler AC and
Müller-Richter UD: Efficacy of cetuximab and panitumumab in oral
squamous cell carcinoma cell lines: Prognostic value of MAGE-A
subgroups for treatment success. J Craniomaxillofac Surg.
41:623–629. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Monte M, Simonatto M, Peche LY, Bublik DR,
Gobessi S, Pierotti MA, Rodolfo M and Schneider C: MAGE-A tumor
antigens target p53 transactivation function through histone
deacetylase recruitment and confer resistance to chemotherapeutic
agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:11160–11165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Duan Z, Duan Y, Lamendola DE, Yusuf RZ,
Naeem R, Penson RT and Seiden MV: Overexpression of MAGE/GAGE genes
in paclitaxel/doxorubicin-resistant human cancer cell lines. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:2778–2785. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu W, Cheng S, Asa SL and Ezzat S: The
melanoma-associated antigen A3 mediates fibronectin-controlled
cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Res. 68:8104–8112. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vansteenkiste J, Zielinski M, Linder A, et
al: Adjuvant therapy in stage IB/II non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC): Final results of a multi-center, double-blind, randomized,
placebocontrolled phase II study evaluating the MAGE-A3 cancer
immunotherapeutic. EJC Suppl. 5:3612007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Heo DS, Snyderman C, Gollin SM, Pan S,
Walker E, Deka R, Barnes EL, Johnson JT, Herberman RB and Whiteside
TL: Biology, cytogenetics, and sensitivity to immunological
effector cells of new head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines.
Cancer Res. 49:5167–5175. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hartmann S, Seher A, Brands RC, Linz C,
Lessner G, Böhm H, Kübler AC and Müller-Richter UD: Influence of
epidermal growth factor receptor expression on the cetuximab and
pani-tumumab response rates of head and neck carcinoma cells. J
Craniomaxillofac Surg. 42:1322–1328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wheeler SE, Shi H, Lin F, Dasari S,
Bednash J, Thorne S, Watkins S, Joshi R and Thomas SM: Enhancement
of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma proliferation, invasion,
and metastasis by tumor-associated fibroblasts in preclinical
models. Head Neck. 36:385–392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Yang B, O’Herrin SM, Wu J, Reagan-Shaw S,
Ma Y, Bhat KM, Gravekamp C, Setaluri V, Peters N, Hoffmann FM, et
al: MAGE-A, mMAGE-b, and MAGE-C proteins form complexes with KAP1
and suppress p53-dependent apoptosis in MAGE-positive cell lines.
Cancer Res. 67:9954–9962. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Feng Y, Gao J and Yang M: When MAGE meets
RING: Insights into biological functions of MAGE proteins. Protein
Cell. 2:7–12. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marcar L, Maclaine NJ, Hupp TR and Meek
DW: MAGE-A cancer/testis antigens inhibit p53 function by blocking
its interaction with chromatin. Cancer Res. 70:10362–10370. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ries J, Vairaktaris E, Mollaoglu N,
Wiltfang J, Neukam FW and Nkenke E: Expression of
melanoma-associated antigens in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J
Oral Pathol Med. 37:88–93. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bandić D, Juretić A, Sarcević B, Separović
V, Kujundzić-Tiljak M, Hudolin T, Spagnoli GC, Cović D and Samija
M: Expression and possible prognostic role of MAGE-A4, NY-ESO-1,
and HER-2 antigens in women with relapsing invasive ductal breast
cancer: Retrospective immunohistochemical study. Croat Med J.
47:32–41. 2006.
|
|
27
|
Sakurai T, Itoh K, Higashitsuji H, Nagao
T, Nonoguchi K, Chiba T and Fujita J: A cleaved form of MAGE-A4
binds to Miz-1 and induces apoptosis in human cells. J Biol Chem.
279:15505–15514. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu X, Tang X, Lu M, Tang Q, Zhang H, Zhu
H, Xu N, Zhang D, Xiong L, Mao Y, et al: Overexpression of MAGE-A9
predicts unfavorable outcome in breast cancer. Exp Mol Pathol.
97:579–584. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hatiboglu G, Pritsch M, Macher-Goeppinger
S, Zöller M, Huber J, Haferkamp A, Pahernik S, Wagener N and
Hohenfellner M: Prognostic value of melanoma-associated antigen A9
in renal cell carcinoma. Scand J Urol. 47:311–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xia LP, Xu M, Chen Y and Shao WW:
Expression of MAGE-A11 in breast cancer tissues and its effects on
the proliferation of breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:254–258.
2013.
|
|
31
|
Lian Y, Sang M, Ding C, Zhou X, Fan X, Xu
Y, Lü W and Shan B: Expressions of MAGE-A10 and MAGE-A11 in breast
cancers and their prognostic significance: A retrospective clinical
study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:519–527. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|