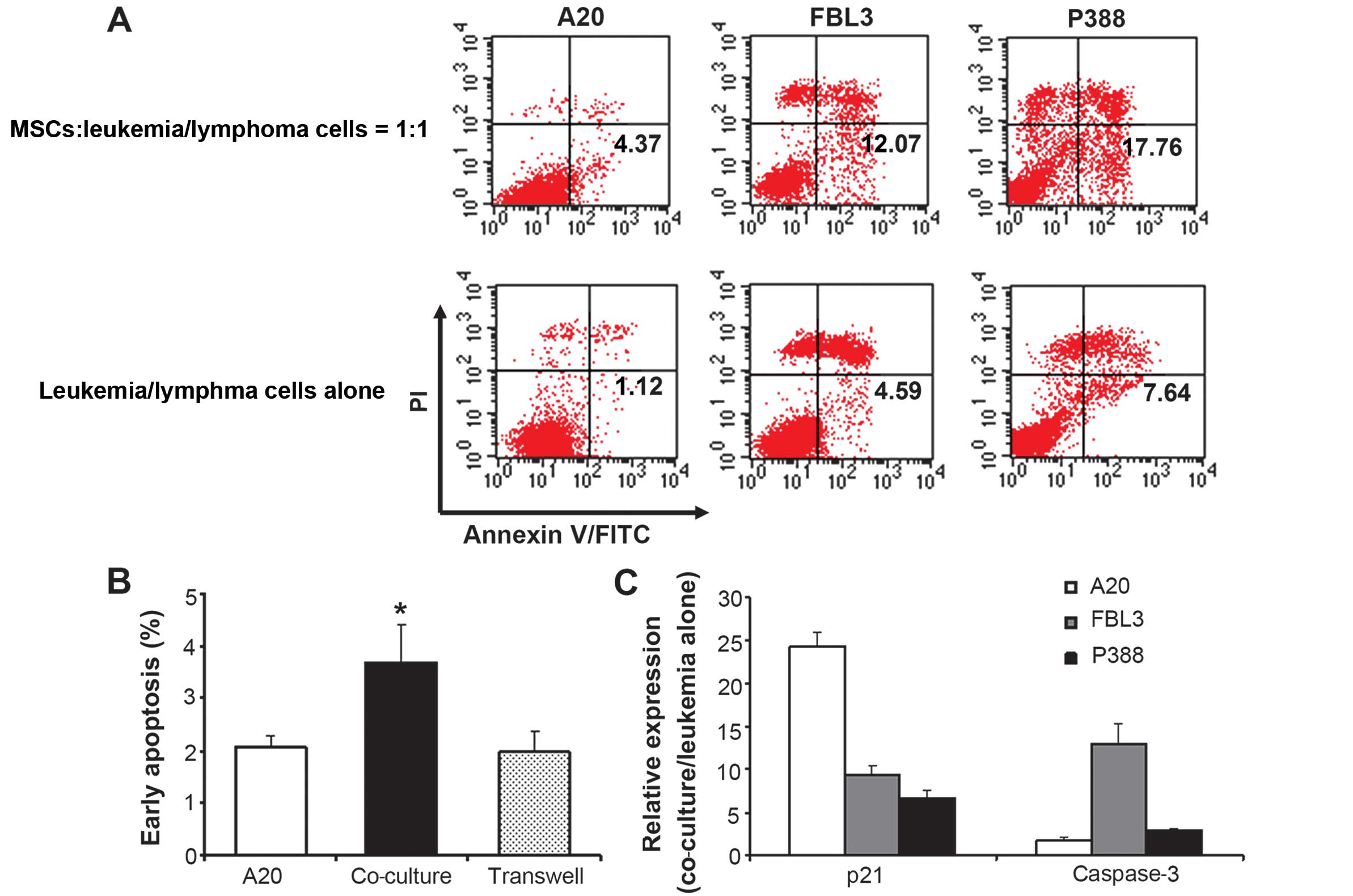
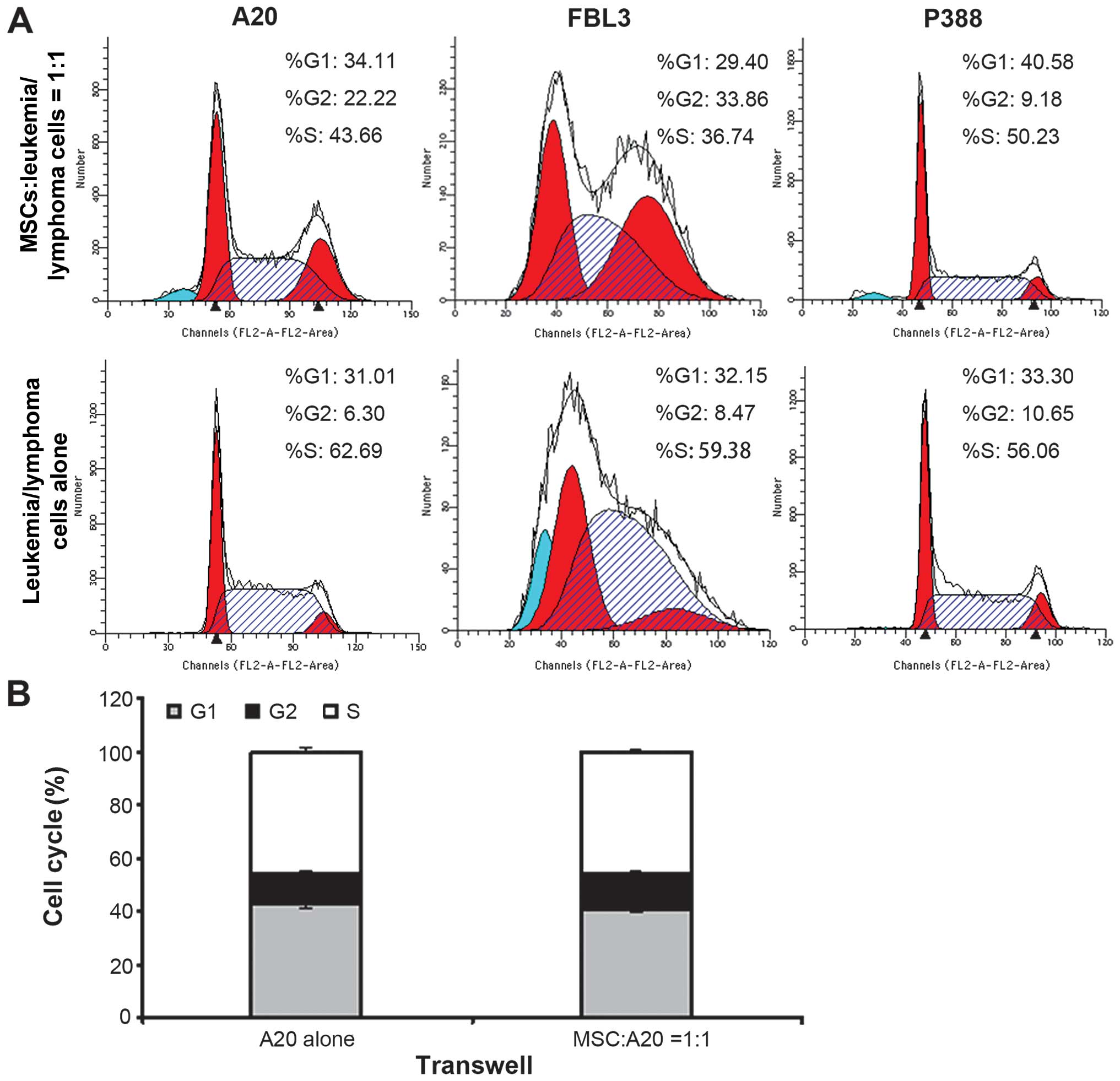
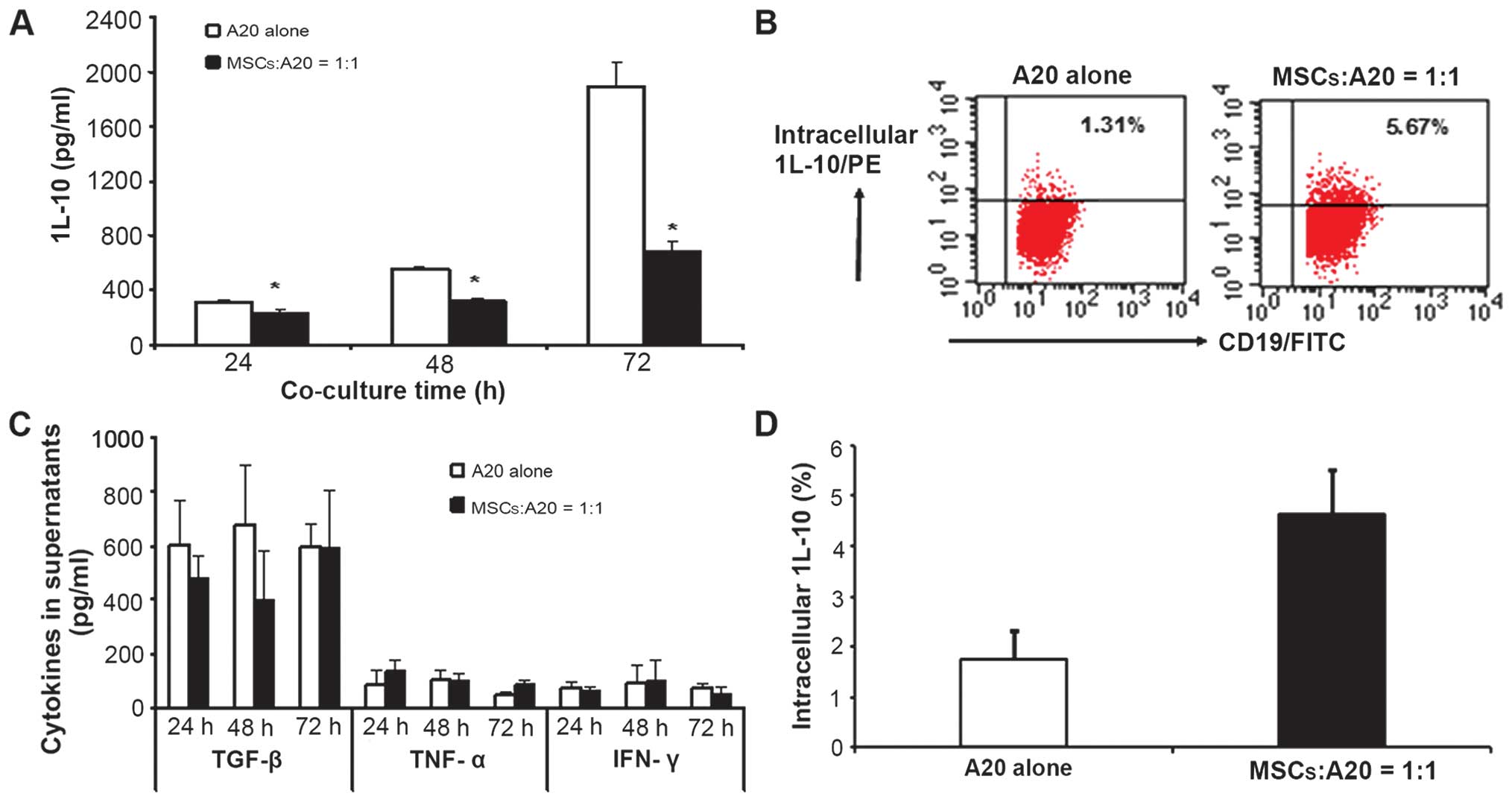
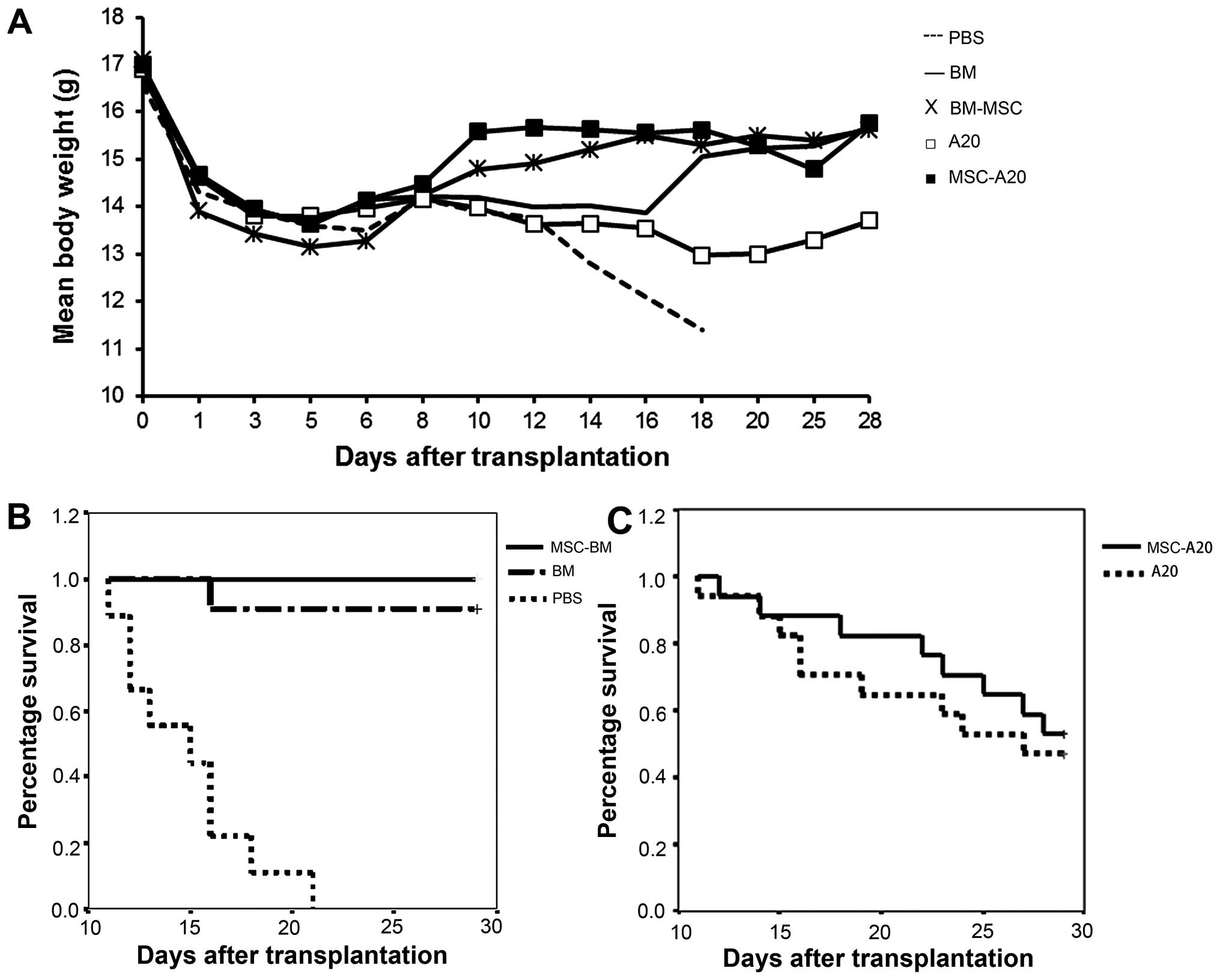
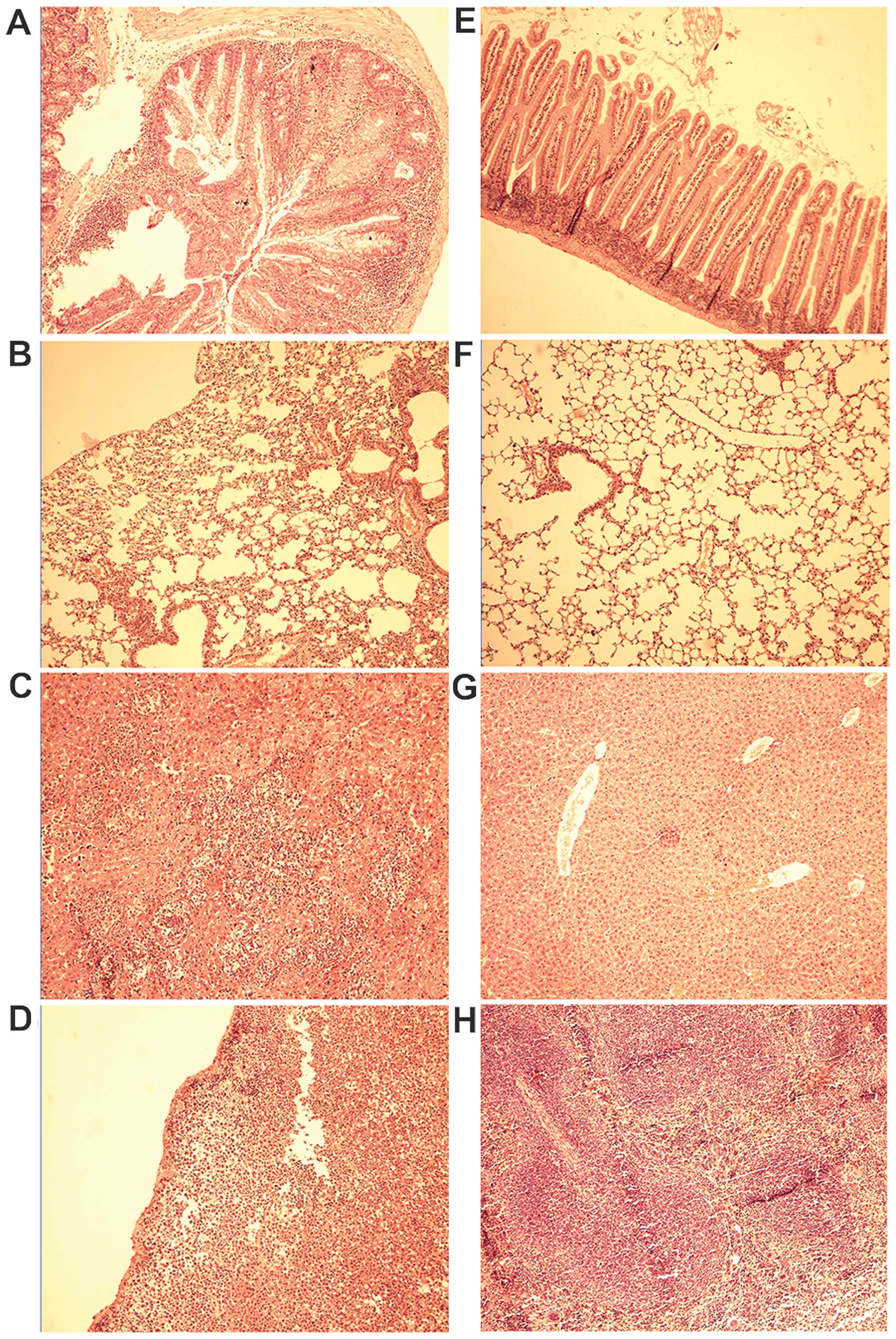
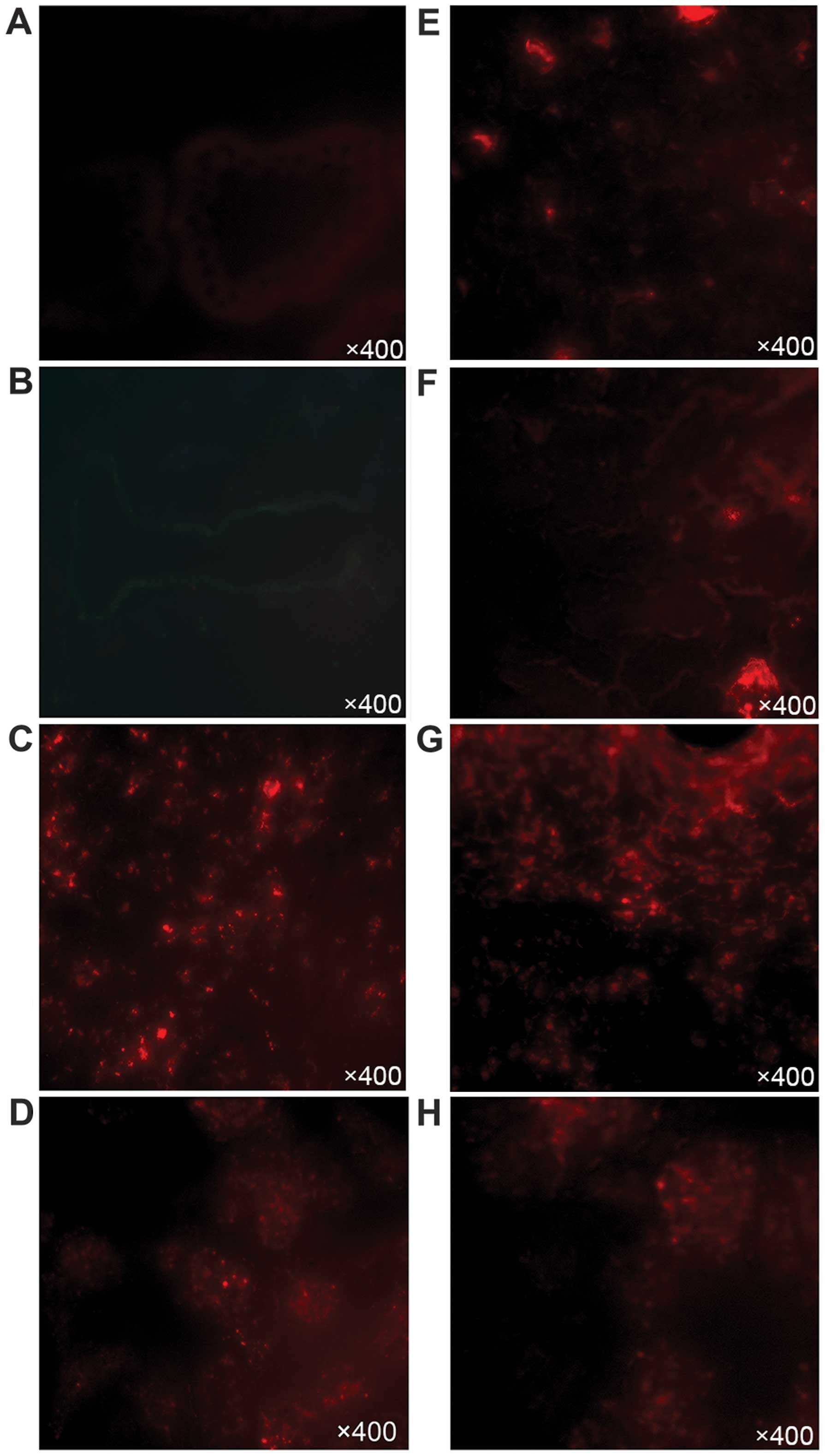
|
1
|
Sorrentino A, Ferracin M, Castelli G,
Biffoni M, Tomaselli G, Baiocchi M, Fatica A, Negrini M, Peschle C
and Valtieri M: Isolation and characterization of CD146+
multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Exp Hematol. 36:1035–1046.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Le Blanc K, Samuelsson H, Gustafsson B,
Remberger M, Sundberg B, Arvidson J, Ljungman P, Lönnies H, Nava S
and Ringdén O: Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells to enhance
engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia. 21:1733–1738.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herrmann RP and Sturm MJ: Adult human
mesenchymal stromal cells and the treatment of graft versus host
disease. Stem Cells Cloning. 7:45–52. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shlomchik WD: Graft-versus-host disease.
Nat Rev Immunol. 7:340–352. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Otsu K, Das S, Houser SD, Quadri SK,
Bhattacharya S and Bhattacharya J: Concentration-dependent
inhibition of angiogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells. Blood.
113:4197–4205. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Khakoo AY, Pati S, Anderson SA, et al:
Human mesenchymal stem cells exert potent antitumorigenic effects
in a model of Kaposi’s sarcoma. J Exp Med. 203:1235–1247. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu Y, Sun Z, Han Q, et al: Human
mesenchymal stem cells inhibit cancer cell proliferation by
secreting DKK-1. Leukemia. 23:925–933. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang PP, Xie DY, Liang XJ, Peng L, Zhang
GL, Ye YN, Xie C and Gao ZL: HGF and direct mesenchymal stem cells
contact synergize to inhibit hepatic stellate cells activation
through TLR4/NF-kB pathway. PLoS One. 7:e434082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Menge T, Gerber M, Wataha K, Reid W, Guha
S, Cox CS Jr, Dash P, Reitz MS Jr, Khakoo AY and Pati S: Human
mesenchymal stem cells inhibit endothelial proliferation and
angiogenesis via cell-cell contact through modulation of the
VE-Cadherin/β-catenin signaling pathway. Stem Cells Dev.
22:148–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Galiè M, Konstantinidou G, Peroni D, et
al: Mesenchymal stem cells share molecular signature with
mesenchymal tumor cells and favor early tumor growth in syngeneic
mice. Oncogene. 27:2542–2551. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, Sullivan A,
Brooks MW, Bell GW, Richardson AL, Polyak K, Tubo R and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast
cancer metastasis. Nature. 449:557–563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cirone M, Lucania G, Aleandri S, Borgia G,
Trivedi P, Cuomo L, Frati L and Faggioni A: Suppression of
dendritic cell differentiation through cytokines released by
Primary Effusion Lymphoma cells. Immunol Lett. 120:37–41. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Zhao Y, Qian J, Sun L, Lu Y, Li H,
Li Y, Yang J, Cai Z and Yi Q: Toll-like receptor-4 signaling in
mantle cell lymphoma: effects on tumor growth and immune evasion.
Cancer. 119:782–791. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shen L, Chiang AK, Liu WP, Li GD, Liang RH
and Srivastava G: Expression of HLA class I, beta(2)-microglobulin,
TAP1 and IL-10 in Epstein-Barr virus-associated nasal
NK/T-celllymphoma: Implications for tumor immune escape mechanism.
Int J Cancer. 92:692–696. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Djouad F, Plence P, Bony C, Tropel P,
Apparailly F, Sany J, Noël D and Jorgensen C: Immunosuppressive
effect of mesen-chymal stem cells favors tumor growth in allogeneic
animals. Blood. 102:3837–3844. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen WJ, Huang JW, Niu CC, Chen LH, Yuan
LJ, Lai PL, Yang CY and Lin SS: Use of fluorescence labeled
mesenchymal stem cells in pluronic F127 and porous hydroxyapatite
as a bone substitute for posterolateral spinal fusion. J Orthop
Res. 27:1631–1636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Chen X, Cao W and Shi Y:
Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation:
Pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol.
15:1009–1016. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dalal J, Gandy K and Domen J: Role of
mesenchymal stem cell therapy in Crohn’s disease. Pediatr Res.
71:445–451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cohen JA: Mesenchymal stem cell
transplantation in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 333:43–49.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu YR, Yuan Y, Wang XJ, et al: The growth
inhibitory effect of mesenchymal stem cells on tumor cells in vitro
and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:245–251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ilmer M, Vykoukal J, Recio Boiles A,
Coleman M and Alt E: Two sides of the same coin: Stem cells in
cancer and regenerative medicine. FASEB J. 28:2748–2761. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ramasamy R, Lam EW, Soeiro I, Tisato V,
Bonnet D and Dazzi F: Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation
and apoptosis of tumor cells: Impact on in vivo tumor growth.
Leukemia. 21:304–310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Elpek KG, Lacelle C, Singh NP, Yolcu ES
and Shirwan H: CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells
dominate multiple immune evasion mechanisms in early but not late
phases of tumor development in a B cell lymphoma model. J Immunol.
178:6840–6848. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu W, Xu W, Jiang R, Qian H, Chen M, Hu
J, Cao W, Han C and Chen Y: Mesenchymal stem cells derived from
bone marrow favor tumor cell growth in vivo. Exp Mol Pathol.
80:267–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Djouad F, Bony C, Apparailly F,
Louis-Plence P, Jorgensen C and Noël D: Earlier onset of syngeneic
tumors in the presence of mesenchymal stem cells. Transplantation.
82:1060–1066. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baron F, Lechanteur C, Willems E, et al:
Cotransplantation of mesenchymal stem cells might prevent death
from graft-versus- host disease (GVHD) without abrogating
graft-versus-tumor effects after HLA-mismatched allogeneic
transplantation following nonmyeloablative conditioning. Biol Blood
Marrow Transplant. 16:838–847. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B,
Götherström C, Hassan M, Uzunel M and Ringdén O: Treatment of
severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party
haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 363:1439–1441. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ning H, Yang F, Jiang M, et al: The
correlation between cotrans-plantation of mesenchymal stem cells
and higher recurrence rate in hematologic malignancy patients:
Outcome of a pilot clinical study. Leukemia. 22:593–599. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|