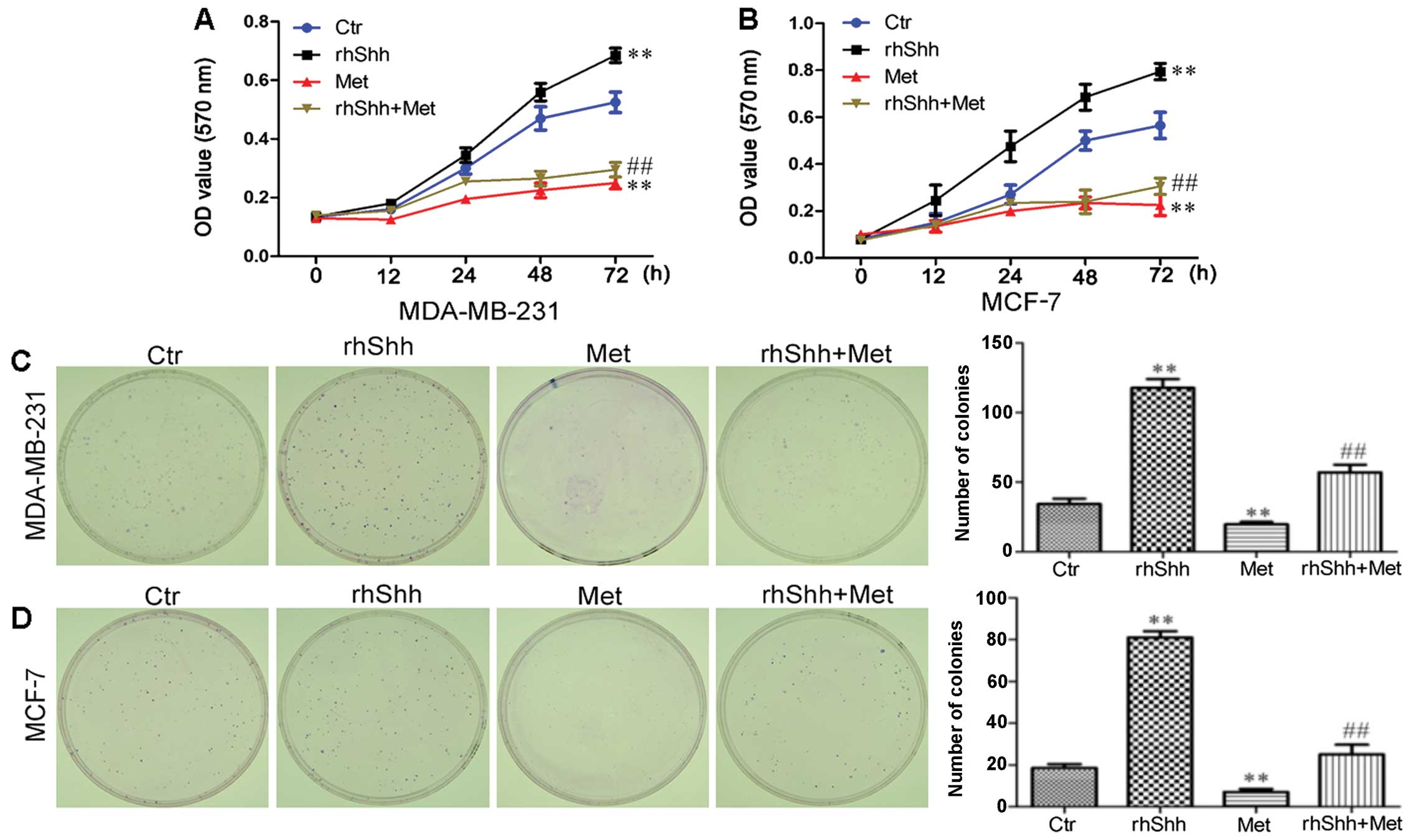
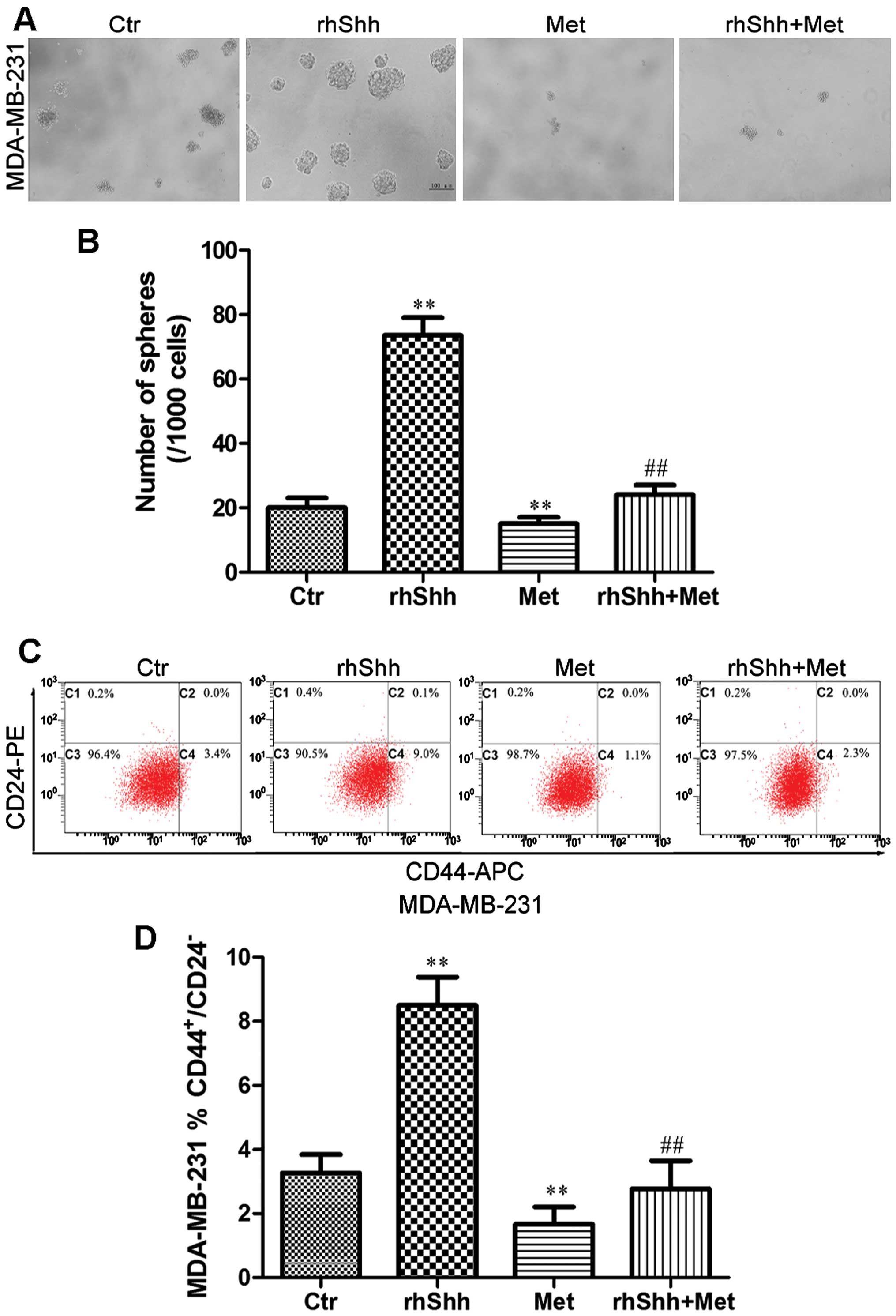
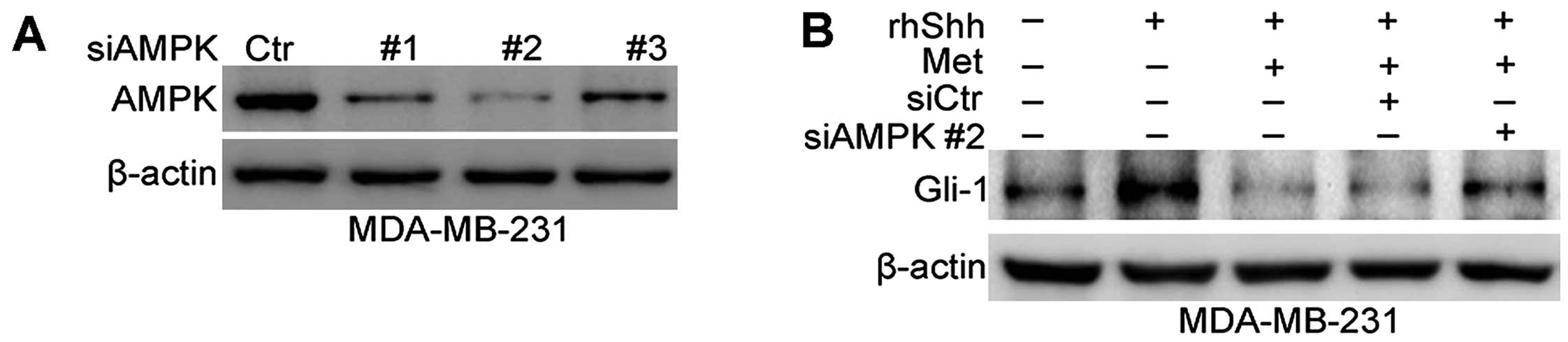
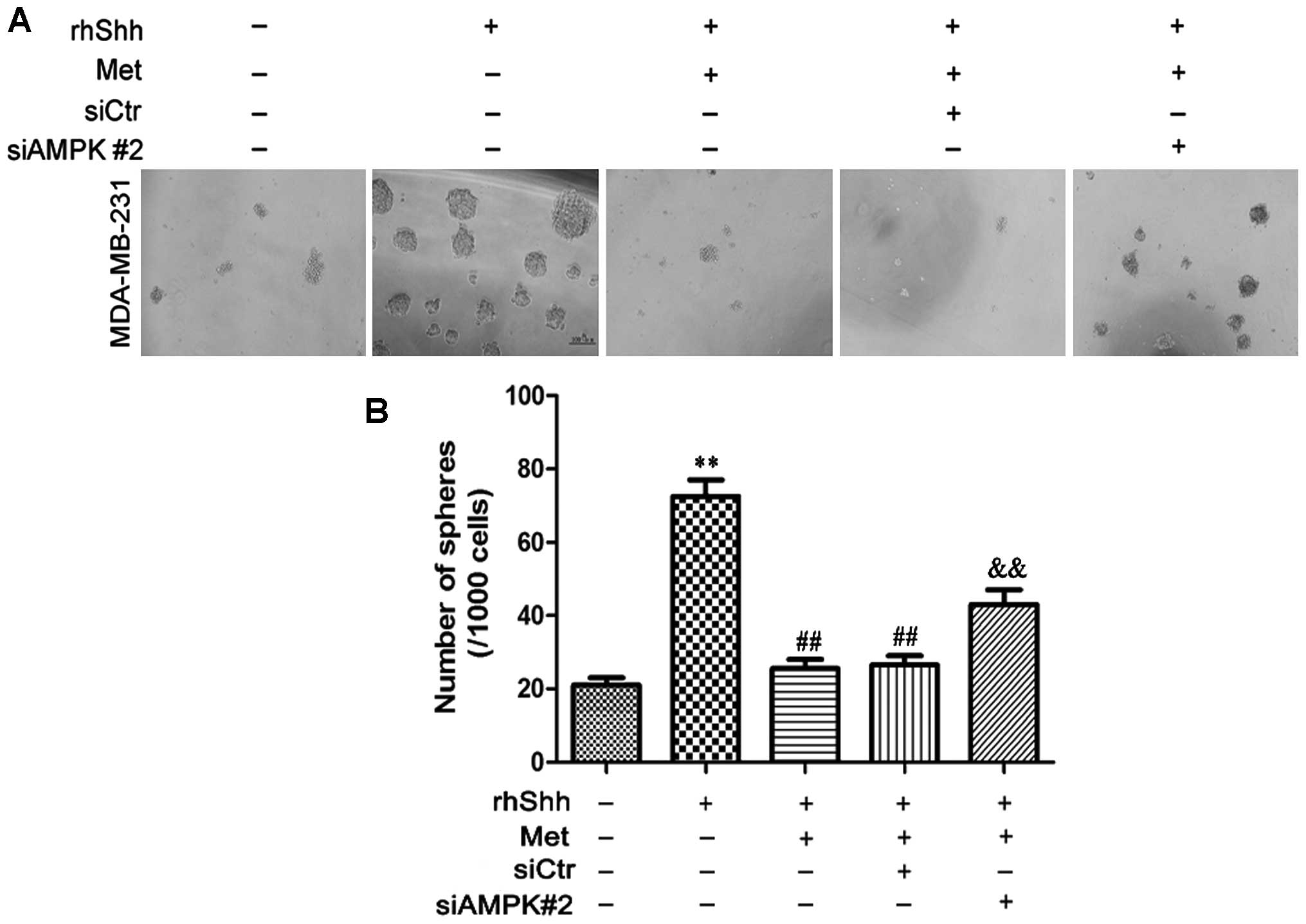
|
1
|
Alexander GC, Sehgal NL, Moloney RM and
Stafford RS: National trends in treatment of type 2 diabetes
mellitus, 1994–2007. Arch Intern Med. 168:2088–2094. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bosco JL, Antonsen S, Sørensen HT,
Pedersen L and Lash TL: Metformin and incident breast cancer among
diabetic women: A population-based case-control study in Denmark.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 20:101–111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kisfalvi K, Eibl G, Sinnett-Smith J and
Rozengurt E: Metformin disrupts crosstalk between G protein-coupled
receptor and insulin receptor signaling systems and inhibits
pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Res. 69:6539–6545. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hosono K, Endo H, Takahashi H, Sugiyama M,
Sakai E, Uchiyama T, Suzuki K, Iida H, Sakamoto Y, Yoneda K, et al:
Metformin suppresses colorectal aberrant crypt foci in a short-term
clinical trial. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 3:1077–1083. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Azoulay L, Dell’Aniello S, Gagnon B,
Pollak M and Suissa S: Metformin and the incidence of prostate
cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 20:337–344. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A,
Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Colosetti P, Auberger P, Tanti JF, Le
Marchand-Brustel Y and Bost F: The antidiabetic drug metformin
exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a
decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene. 27:3576–3586. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Tsichlis PN and
Struhl K: Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells, and acts
together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong
remission. Cancer Res. 69:7507–7511. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, Lum JJ,
DeBerardinis RJ, Zhao F, Viollet B and Thompson CB: Systemic
treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs
p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 67:6745–6752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shackelford DB and Shaw RJ: The LKB1-AMPK
pathway: Metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:563–575. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng L, Yang W, Wu F, Wang C, Yu L, Tang
L, Qiu B, Li Y, Guo L, Wu M, et al: Prognostic significance of AMPK
activation and therapeutic effects of metformin in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5372–5380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D and Hardie
DG: AMP-activated protein kinase: Ancient energy gauge provides
clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1:15–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rocha GZ, Dias MM, Ropelle ER,
Osório-Costa F, Rossato FA, Vercesi AE, Saad MJ and Carvalheira JB:
Metformin amplifies chemotherapy-induced AMPK activation and
antitumoral growth. Clin Cancer Res. 17:3993–4005. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak
M and Sonenberg N: Metformin inhibits mammalian target of
rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 67:10804–10812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ingham PW and McMahon AP: Hedgehog
signaling in animal development: Paradigms and principles. Genes
Dev. 15:3059–3087. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Varjosalo M and Taipale J: Hedgehog:
Functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 22:2454–2472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu AJ, Zheng L, Suyama K and Scott MP:
Altered localization of Drosophila Smoothened protein activates
Hedgehog signal transduction. Genes Dev. 17:1240–1252. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Murone M, Rosenthal A and de Sauvage FJ:
Hedgehog signal transduction: From flies to vertebrates. Exp Cell
Res. 253:25–33. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kubo M, Nakamura M, Tasaki A, Yamanaka N,
Nakashima H, Nomura M, Kuroki S and Katano M: Hedgehog signaling
pathway is a new therapeutic target for patients with breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 64:6071–6074. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Onishi H and Katano M: Hedgehog signaling
pathway as a therapeutic target in various types of cancer. Cancer
Sci. 102:1756–1760. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jeng KS, Sheen IS, Jeng WJ, Yu MC, Hsiau
HI and Chang FY: High expression of Sonic Hedgehog signaling
pathway genes indicates a risk of recurrence of breast carcinoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 7:79–86. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nakamura M, Ogo A, Yamura M, Yamaguchi Y
and Nakashima H: Metformin suppresses sonic hedgehog expression in
pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 34:1765–1769.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Visvader JE: Keeping abreast of the
mammary epithelial hierarchy and breast tumorigenesis. Genes Dev.
23:2563–2577. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson
KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ and Wicha MS: In vitro propagation and
transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells.
Genes Dev. 17:1253–1270. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bombonati A and Sgroi DC: The molecular
pathology of breast cancer progression. J Pathol. 223:307–317.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
O’Brien CA, Kreso A and Jamieson CH:
Cancer stem cells and self-renewal. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3113–3120.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ailles LE and Weissman IL: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumors. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 18:460–466. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kakarala M and Wicha MS: Implications of
the cancer stem-cell hypothesis for breast cancer prevention and
therapy. J Clin Oncol. 26:2813–2820. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rattan R, Graham RP, Maguire JL, Giri S
and Shridhar V: Metformin suppresses ovarian cancer growth and
metastasis with enhancement of cisplatin cytotoxicity in vivo.
Neoplasia. 13:483–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rattan R, Giri S, Hartmann LC and Shridhar
V: Metformin attenuates ovarian cancer cell growth in an AMP-kinase
dispensable manner. J Cell Mol Med. 15:166–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bodmer M, Meier C, Krähenbühl S, Jick SS
and Meier CR: Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased
risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care. 33:1304–1308. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG,
Sonenberg N and Pollak M: Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent
growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:10269–10273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Janzer A, German NJ, Gonzalez-Herrera KN,
Asara JM, Haigis MC and Struhl K: Metformin and phenformin deplete
tricarboxylic acid cycle and glycolytic intermediates during cell
transformation and NTPs in cancer stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 111:10574–10579. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ramaswamy B, Lu Y, Teng KY, Nuovo G, Li X,
Shapiro CL and Majumder S: Hedgehog signaling is a novel
therapeutic target in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer aberrantly
activated by PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancer Res. 72:5048–5059. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|