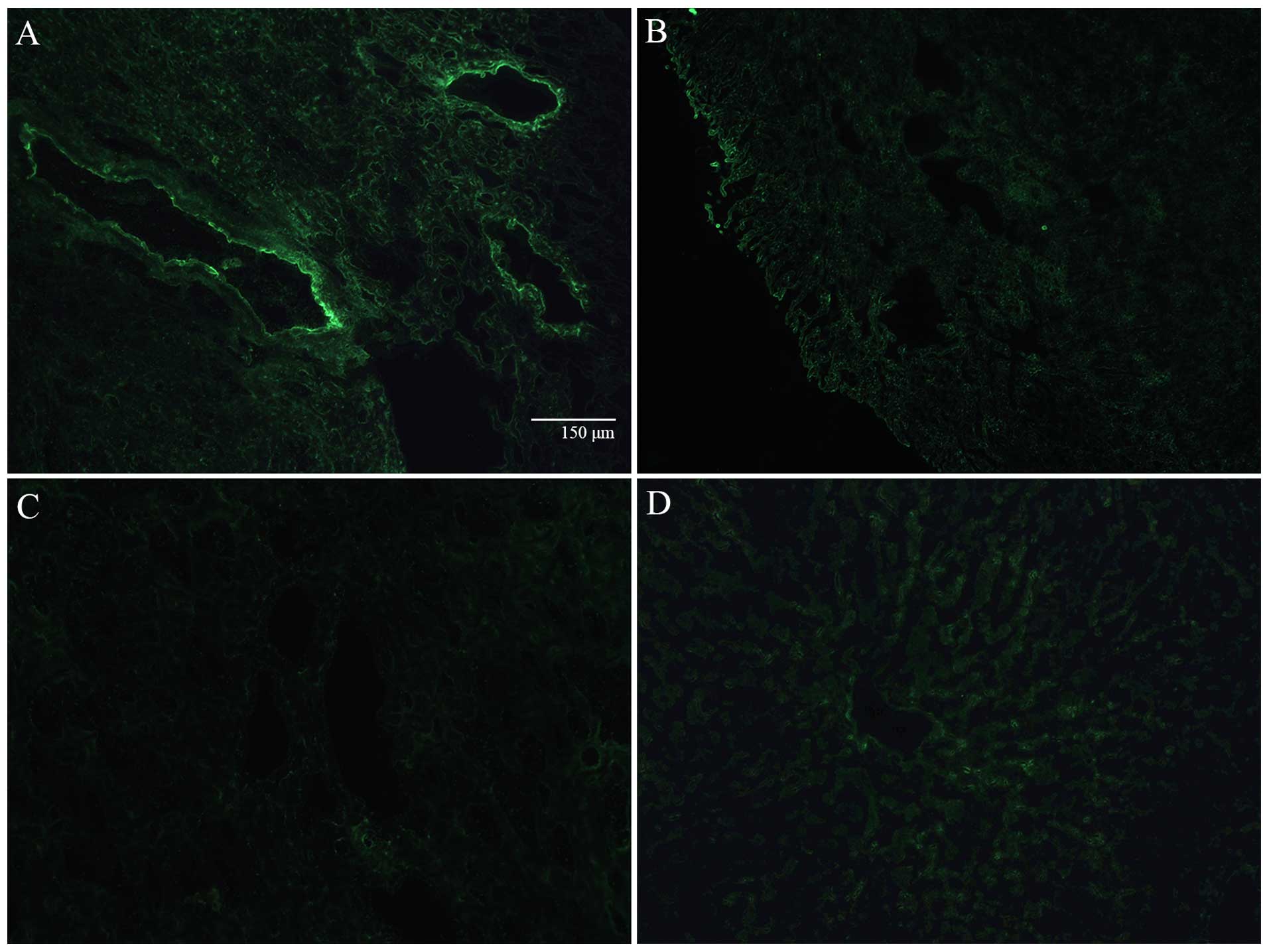
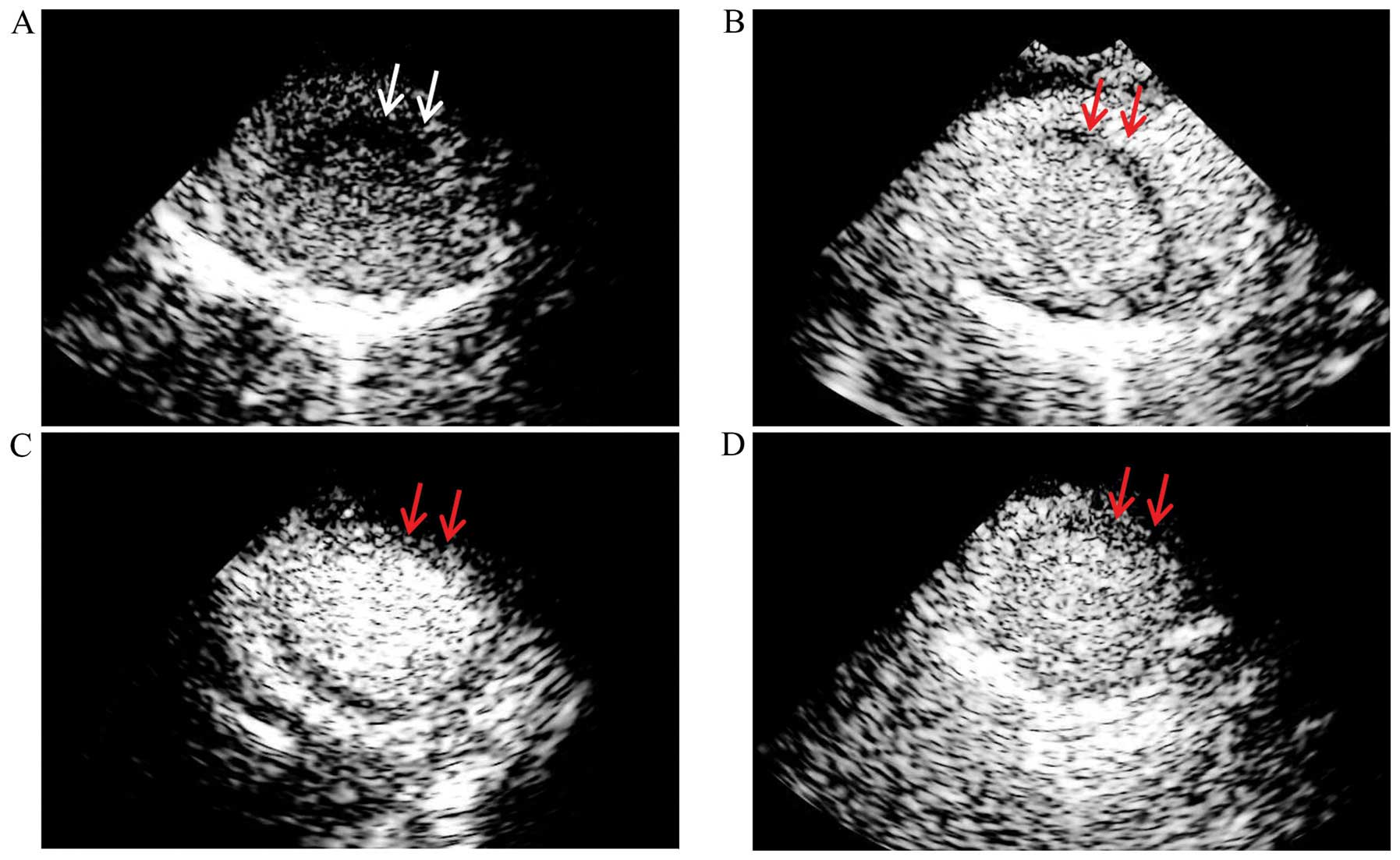
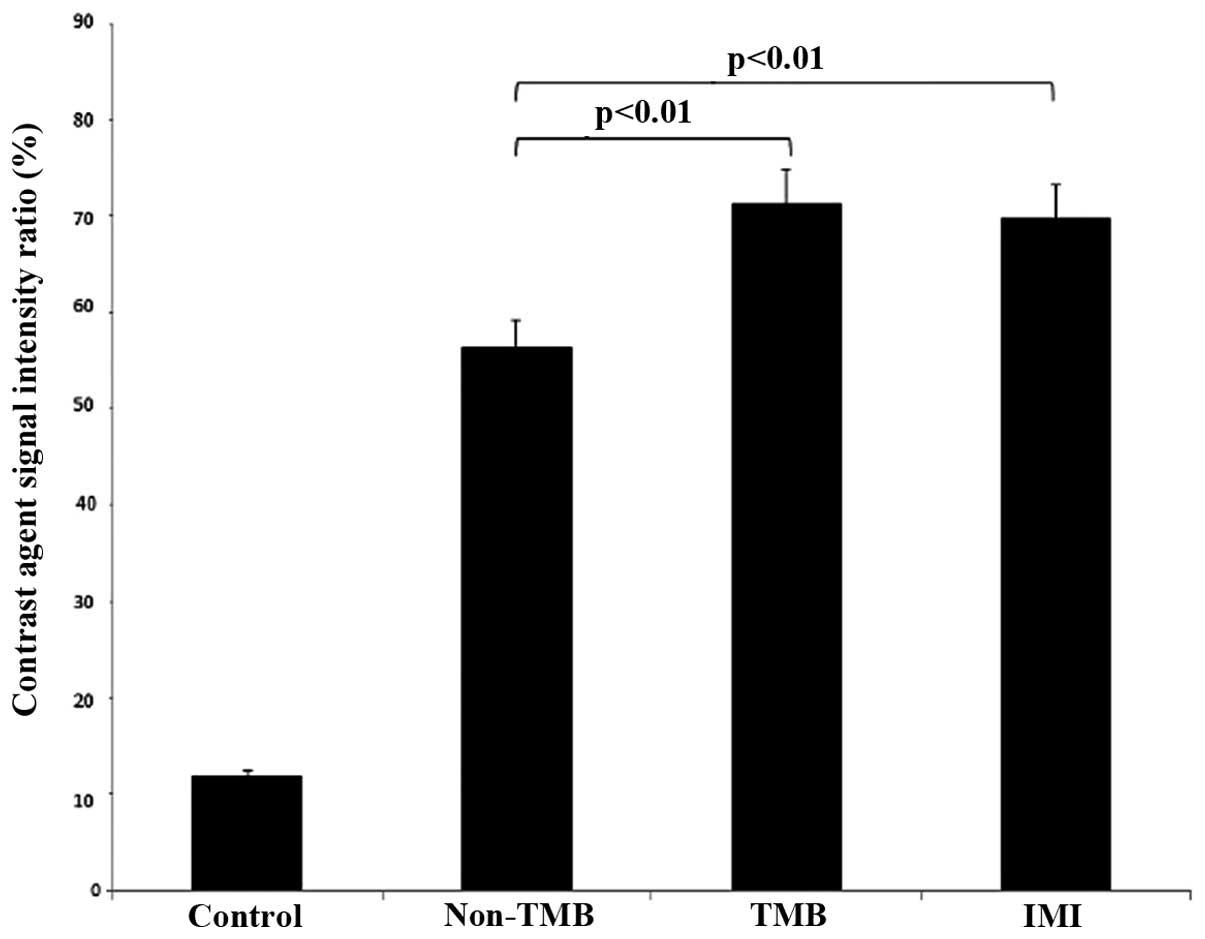
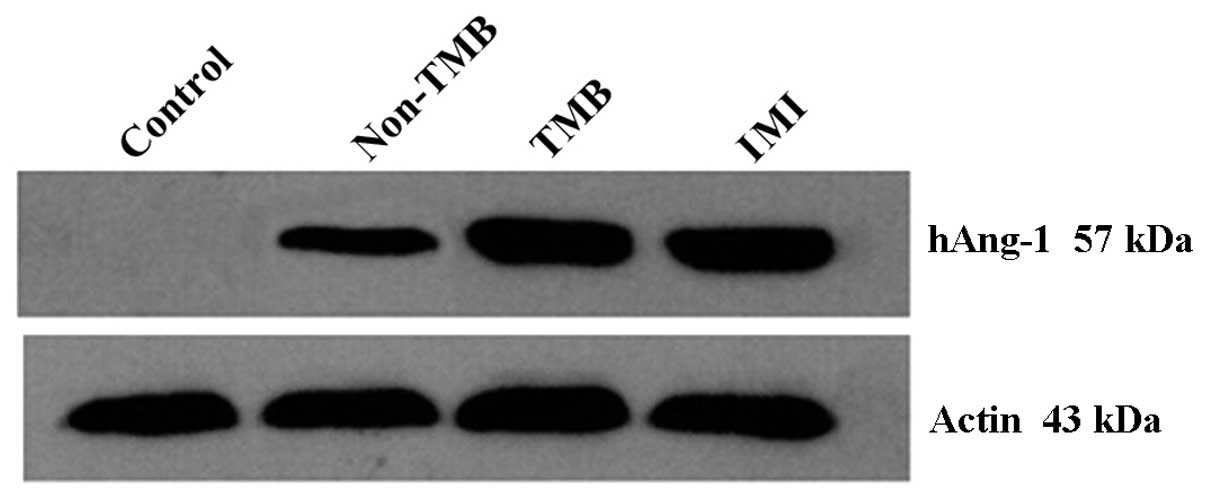
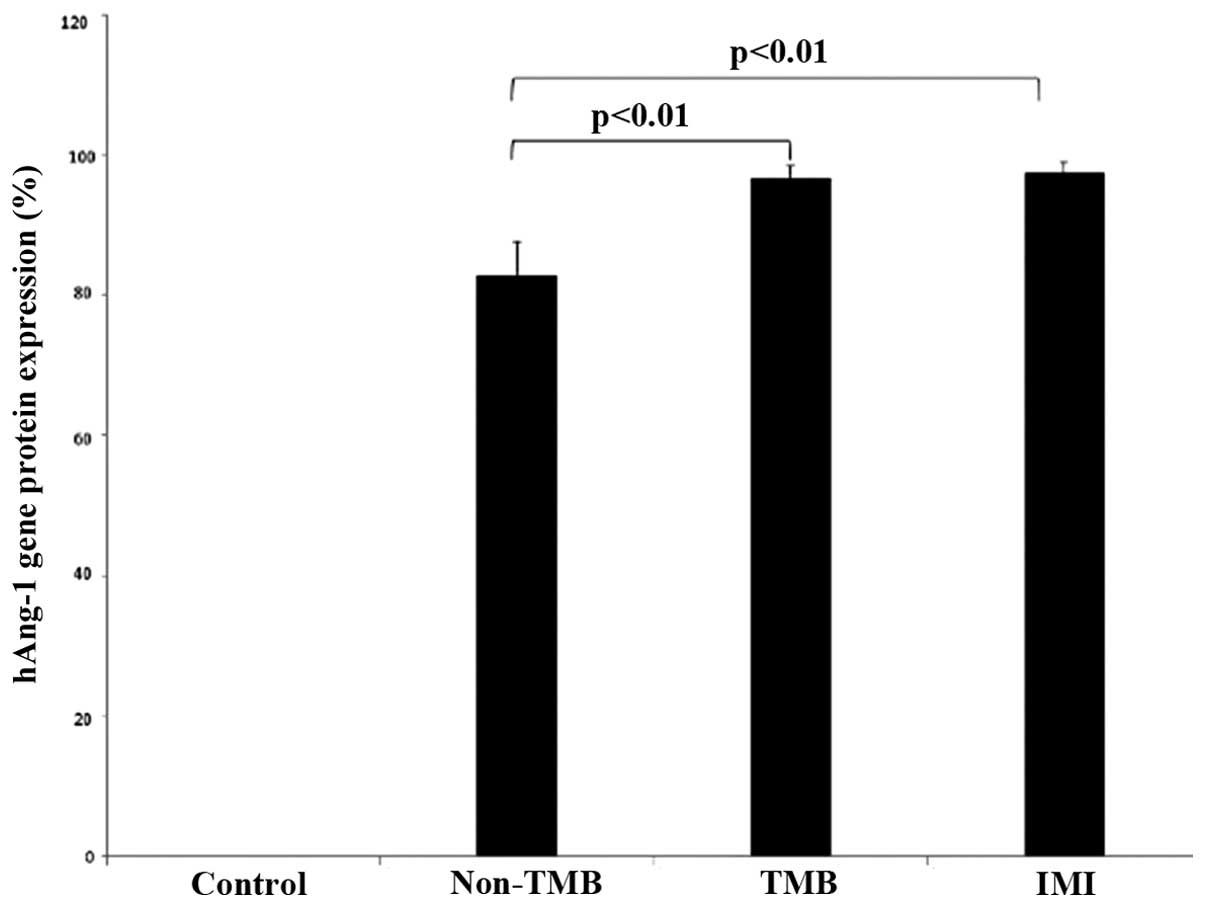
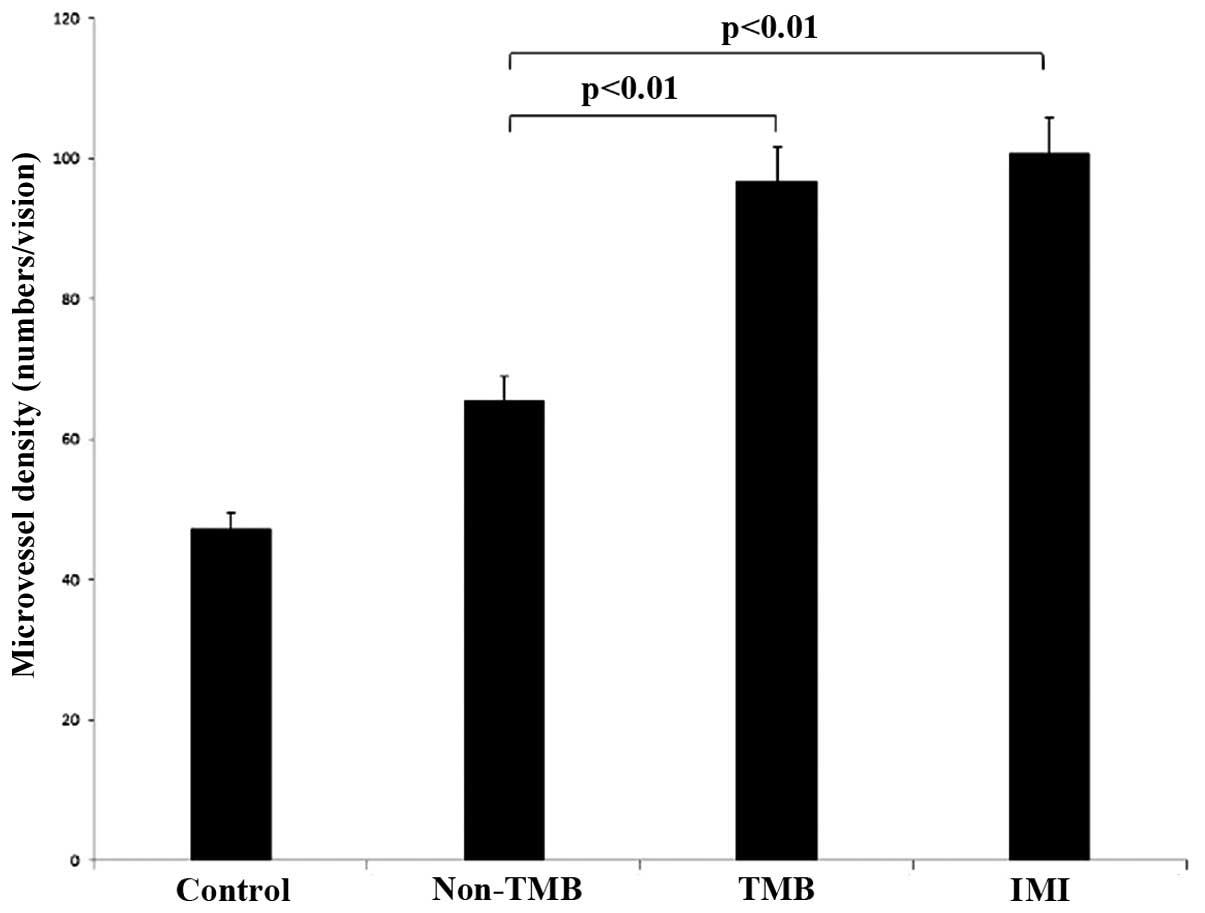
|
1
|
Phillips LC, Klibanov AL, Wamhoff BR and
Hossack JA: Targeted gene transfection from microbubbles into
vascular smooth muscle cells using focused, ultrasound-mediated
delivery. Ultrasound Med Biol. 36:1470–1480. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou J, Wang Y, Xiong Y, Wang H, Feng Y
and Chen J: Delivery of TFPI-2 using ultrasound with a microbubble
agent (SonoVue) inhibits intimal hyperplasia after balloon injury
in a rabbit carotid artery model. Ultrasound Med Biol.
36:1876–1883. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fujii H, Li SH, Wu J, Miyagi Y, Yau TM,
Rakowski H, Egashira K, Guo J, Weisel RD and Li RK: Repeated and
targeted transfer of angiogenic plasmids into the infarcted rat
heart via ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction enhances
cardiac repair. Eur Heart J. 32:2075–2084. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yuan QY, Huang J, Chu BC, Li XS and Si LY:
A visible, targeted high-efficiency gene delivery and transfection
strategy. BMC Biotechnol. 11:562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Henry TD, Annex BH, McKendall GR, Azrin
MA, Lopez JJ, Giordano FJ, Shah PK, Willerson JT, Benza RL, Berman
DS, et al VIVA Investigators: The VIVA trial: Vascular endothelial
growth factor in Ischemia for Vascular Angiogenesis. Circulation.
107:1359–1365. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kornowski R, Fuchs S, Leon MB and Epstein
SE: Delivery strategies to achieve therapeutic myocardial
angiogenesis. Circulation. 101:454–458. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kusumanto YH, Mulder NH, Dam WA, Losen M,
De Baets MH, Meijer C and Hospers GA: Improvement of in vivo
transfer of plasmid DNA in muscle: Comparison of electroporation
versus ultrasound. Drug Deliv. 14:273–277. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suzuki R, Takizawa T, Negishi Y, Hagisawa
K, Tanaka K, Sawamura K, Utoguchi N, Nishioka T and Maruyama K:
Gene delivery by combination of novel liposomal bubbles with
perfluoropropane and ultrasound. J Control Release. 117:130–136.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Browning RJ, Mulvana H, Tang M, Hajnal JV,
Wells DJ and Eckersley RJ: Influence of needle gauge on in vivo
ultrasound and microbubble-mediated gene transfection. Ultrasound
Med Biol. 37:1531–1537. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Laing ST and McPherson DD: Cardiovascular
therapeutic uses of targeted ultrasound contrast agents. Cardiovasc
Res. 83:626–635. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW and Entman ML:
The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res.
53:31–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Siddiqui AJ, Blomberg P, Wärdell E,
Hellgren I, Eskandarpour M, Islam KB and Sylvén C: Combination of
angiopoietin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor gene therapy
enhances arteriogenesis in the ischemic myocardium. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 310:1002–1009. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Onda T, Honmou O, Harada K, Houkin K,
Hamada H and Kocsis JD: Therapeutic benefits by human mesenchymal
stem cells (hMSCs) and Ang-1 gene-modified hMSCs after cerebral
ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 28:329–340. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Chen JX and Stinnett A: Ang-1 gene therapy
inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
(HIF-1alpha)-prolyl-4-hydroxylase-2, stabilizes HIF-1alpha
expression, and normalizes immature vasculature in db/db mice.
Diabetes. 57:3335–3343. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weller GE, Lu E, Csikari MM, Klibanov AL,
Fischer D, Wagner WR and Villanueva FS: Ultrasound imaging of acute
cardiac transplant rejection with microbubbles targeted to
intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Circulation. 108:218–224. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Q, Zhou Q, Wang YH, Wang X and Guo
RQ: Effects of ultrasound-mediated SonoVue microbubbles destruction
on the integrity and expression of hAng-1 gene. Chin J
Ultrasonography. 18:1080–1084. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Rahim A, Taylor SL, Bush NL, ter Haar GR,
Bamber JC and Porter CD: Physical parameters affecting
ultrasound/microbubble-mediated gene delivery efficiency in vitro.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 32:1269–1279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dijkmans PA, Senior R, Becher H, Porter
TR, Wei K, Visser CA and Kamp O: Myocardial contrast
echocardiography evolving as a clinically feasible technique for
accurate, rapid, and safe assessment of myocardial perfusion: The
evidence so far. J Am Coll Cardiol. 48:2168–2177. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua
P, Allred EN, Moore DH, Meli S and Gasparini G: Tumor angiogenesis:
A new significant and independent prognostic indicator in
early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 84:1875–1887.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tanaka M, Taketomi K and Yonemitsu Y:
Therapeutic angiogenesis: recent and future prospects of gene
therapy in peripheral artery disease. Curr Gene Ther. 14:300–308.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Villanueva FS: Ultrasound mediated
destruction of DNA-loaded microbubbles for enhancement of
cell-based therapies: New promise amidst a confluence of
uncertainties? JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2:880–882. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kaufmann BA, Sanders JM, Davis C, Xie A,
Aldred P, Sarembock IJ and Lindner JR: Molecular imaging of
inflammation in atherosclerosis with targeted ultrasound detection
of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Circulation. 116:276–284.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Klibanov AL: Ultrasound molecular imaging
with targeted microbubble contrast agents. J Nucl Cardiol.
14:876–884. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schumann PA, Christiansen JP, Quigley RM,
McCreery TP, Sweitzer RH, Unger EC, Lindner JR and Matsunaga TO:
Targeted-microbubble binding selectively to GPIIb IIIa receptors of
platelet thrombi. Invest Radiol. 37:587–593. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cai W and Chen X: Multimodality molecular
imaging of tumor angiogenesis. J Nucl Med. 49(Suppl 2): 113S–128S.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leong-Poi H, Christiansen J, Klibanov AL,
Kaul S and Lindner JR: Noninvasive assessment of angiogenesis by
ultrasound and microbubbles targeted to alpha(v)-integrins.
Circulation. 107:455–460. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ferrante EA, Pickard JE, Rychak J,
Klibanov A and Ley K: Dual targeting improves microbubble contrast
agent adhesion to VCAM-1 and P-selectin under flow. J Control
Release. 140:100–107. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Almenar-Queralt A, Duperray A, Miles LA,
Felez J and Altieri DC: Apical topography and modulation of ICAM-1
expression on activated endothelium. Am J Pathol. 147:1278–1288.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Benson V, McMahon AC and Lowe HC: ICAM-1
in acute myocardial infarction: A potential therapeutic target.
Curr Mol Med. 7:219–227. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lawson C and Wolf S: ICAM-1 signaling in
endothelial cells. Pharmacol Rep. 61:22–32. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wilhelmi MH, Leyh RG, Wilhelmi M and
Haverich A: Upregulation of endothelial adhesion molecules in
hearts with congestive and ischemic cardiomyopathy:
Immunohistochemical evaluation of inflammatory endothelial cell
activation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 27:122–127. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kaufmann BA and Lindner JR: Molecular
imaging with targeted contrast ultrasound. Curr Opin Biotechnol.
18:11–16. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Weller GE, Villanueva FS, Klibanov AL and
Wagner WR: Modulating targeted adhesion of an ultrasound contrast
agent to dysfunctional endothelium. Ann Biomed Eng. 30:1012–1019.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaspar BK, Roth DM, Lai NC, Drumm JD,
Erickson DA, McKirnan MD and Hammond HK: Myocardial gene transfer
and long-term expression following intracoronary delivery of
adeno-associated virus. J Gene Med. 7:316–324. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|