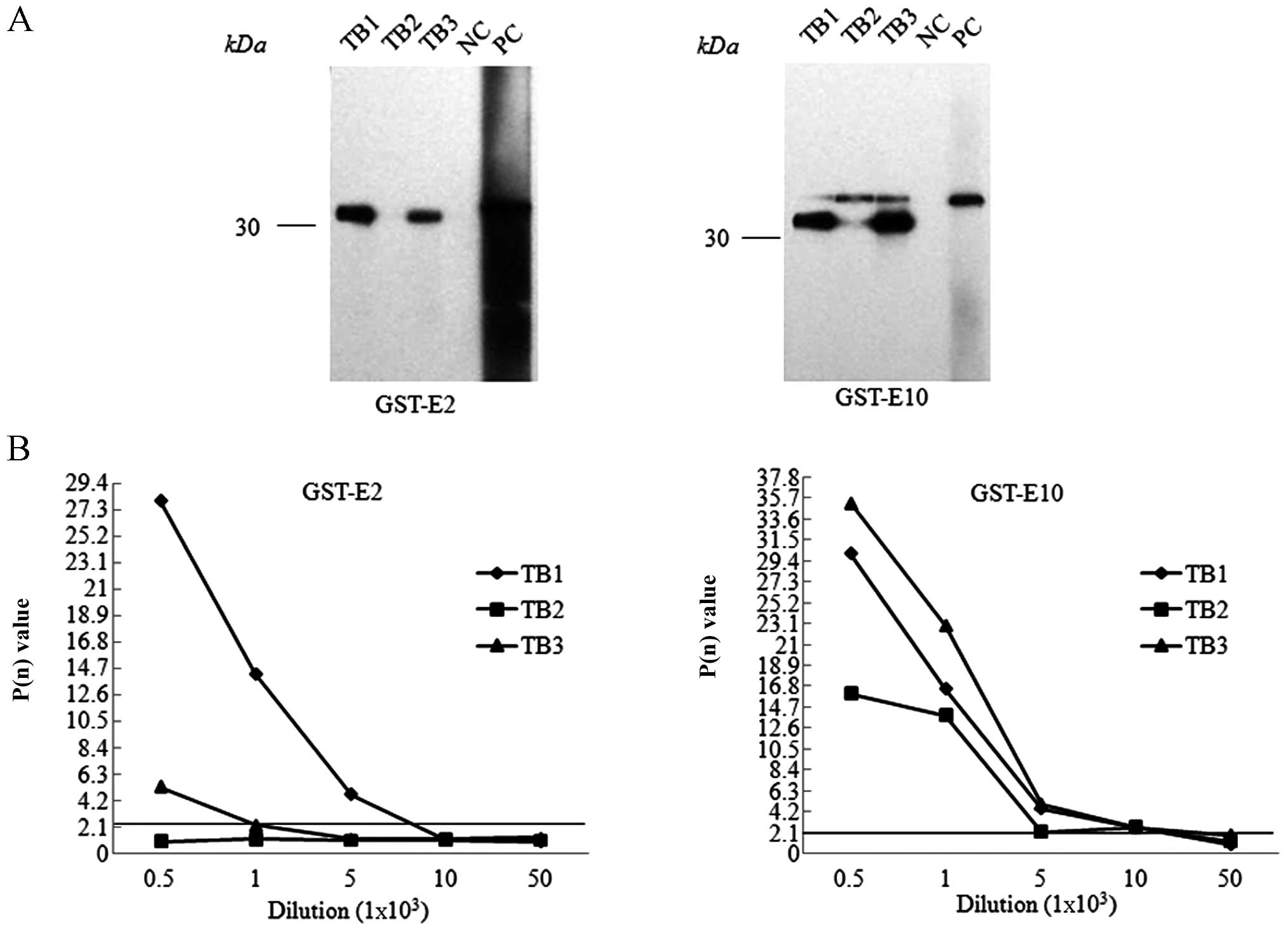
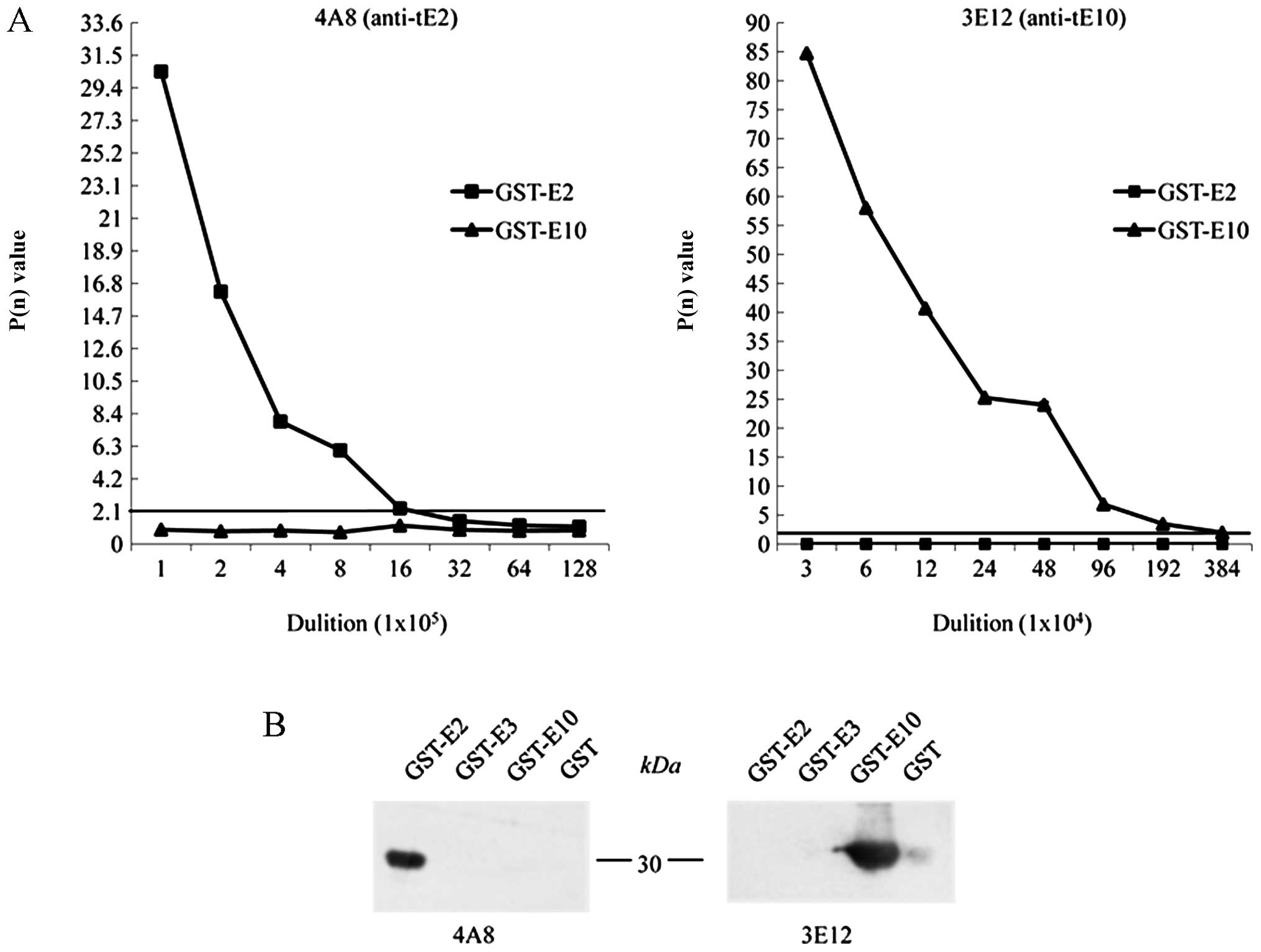
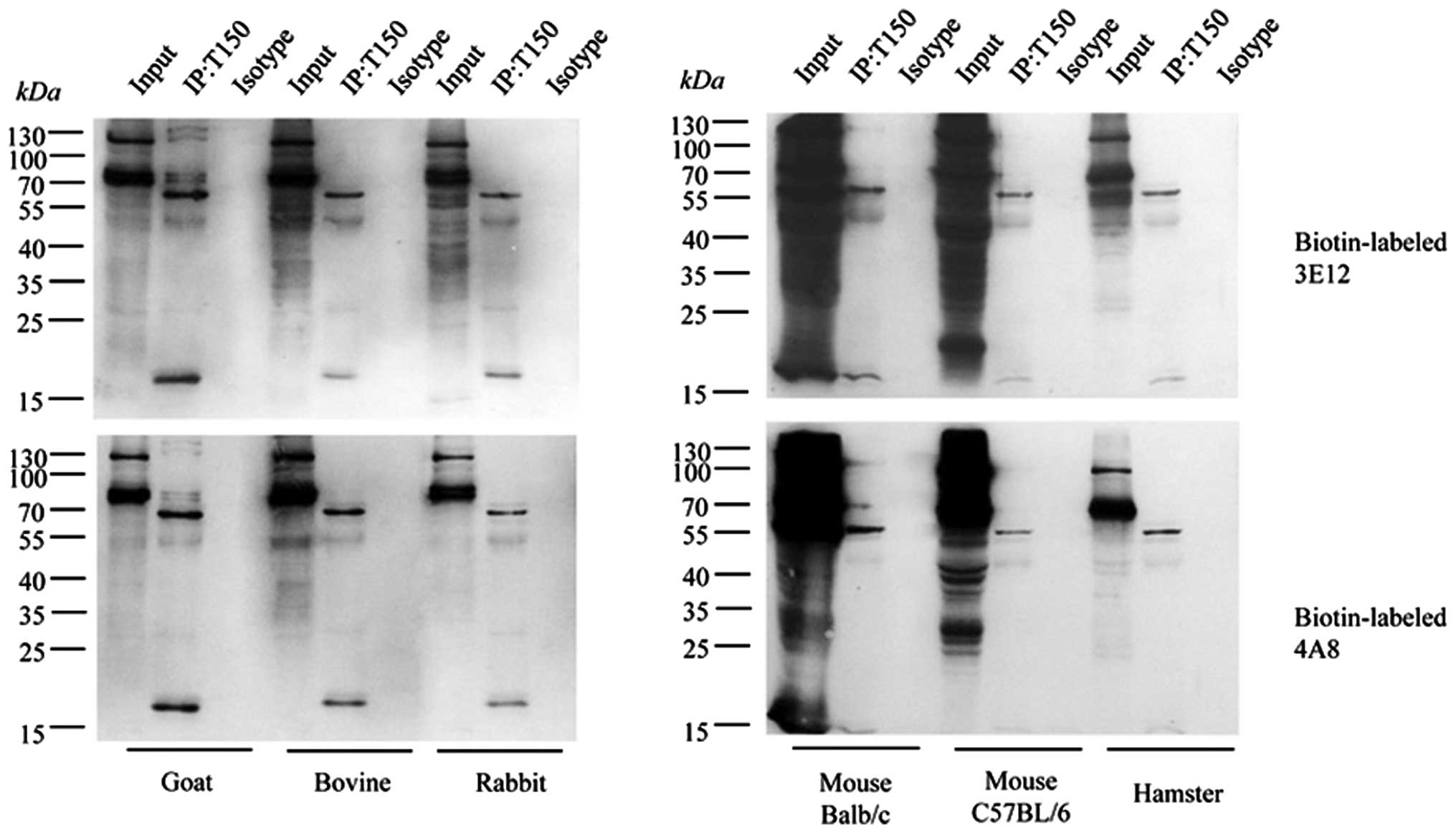
|
1
|
Goedert M: Tau protein and
neurodegeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 15:45–49. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Avila J, Lucas JJ, Perez M and Hernandez
F: Role of tau protein in both physiological and pathological
conditions. Physiol Rev. 84:361–384. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goedert M and Jakes R: Expression of
separate isoforms of human tau protein: correlation with the tau
pattern in brain and effects on tubulin polymerization. EMBO J.
9:4225–4230. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Williams DR: Tauopathies: classification
and clinical update on neurodegenerative diseases associated with
microtubule-associated protein tau. Intern Med J. 36:652–660. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee VM, Goedert M and Trojanowski JQ:
Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci. 24:1121–1159.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hernández F and Avila J: Tauopathies. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 64:2219–2233. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giaccone G, Mangieri M, Capobianco R,
Limido L, Hauw JJ, Haïk S, Fociani P, Bugiani O and Tagliavini F:
Tauopathy in human and experimental variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob
disease. Neurobiol Aging. 29:1864–1873. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Alonso AD, Zaidi T, Novak M, Barra HS,
Grundke-Iqbal I and Iqbal K: Interaction of tau isoforms with
Alzheimer’s disease abnormally hyperphosphorylated tau and in vitro
phosphorylation into the disease-like protein. J Biol Chem.
276:37967–37973. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sjögren M, Davidsson P, Tullberg M,
Minthon L, Wallin A, Wikkelso C, Granérus AK, Vanderstichele H,
Vanmechelen E and Blennow K: Both total and phosphorylated tau are
increased in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
70:624–630. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hampel H, Blennow K, Shaw LM, Hoessler YC,
Zetterberg H and Trojanowski JQ: Total and phosphorylated tau
protein as biological markers of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Gerontol.
45:30–40. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Delacourte A, Robitaille Y, Sergeant N,
Buée L, Hof PR, Wattez A, Laroche-Cholette A, Mathieu J, Chagnon P
and Gauvreau D: Specific pathological Tau protein variants
char-acterize Pick’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 55:159–168.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Flament S, Delacourte A, Verny M, Hauw JJ
and Javoy-Agid F: Abnormal Tau proteins in progressive supranuclear
palsy. Similarities and differences with the neurofibrillary
degeneration of the Alzheimer type. Acta Neuropathol. 81:591–596.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ksiezak-Reding H, Morgan K, Mattiace LA,
Davies P, Liu WK, Yen SH, Weidenheim K and Dickson DW:
Ultrastructure and biochemical composition of paired helical
filaments in cortico-basal degeneration. Am J Pathol.
145:1496–1508. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen C, Shi Q, Zhang BY, Wang GR, Zhou W,
Gao C, Tian C, Mei GY, Han YL, Han J and Dong XP: The prepared tau
exon-specific antibodies revealed distinct profiles of tau in CSF
of the patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. PLoS One.
5:e118862010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi Q, Xie WL, Zhang B, Chen LN, Xu Y,
Wang K, Ren K, Zhang XM, Chen C, Zhang J and Dong XP: Brain
microglia were activated in sporadic CJD but almost unchanged in
fatal familial insomnia and G114V genetic CJD. Virol J. 10:2162013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao C, Lei YJ, Han J, Shi Q, Chen L, Guo
Y, Gao YJ, Chen JM, Jiang HY, Zhou W and Dong XP: Recombinant
neural protein PrP can bind with both recombinant and native
apolipoprotein E in vitro. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
38:593–601. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Chen L, Zhang BY, Han J, Xiao XL,
Tian HY, Li BL, Gao C, Gao JM, Zhou XB, et al: Comparison study on
clinical and neuropathological characteristics of hamsters
inoculated with scrapie strain 263K in different challenging
pathways. Biomed Environ Sci. 17:65–78. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Himmler A: Structure of the bovine tau
gene: Alternatively spliced transcripts generate a protein family.
Mol Cell Biol. 9:1389–1396. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nelson PT, Stefansson K, Gulcher J and
Saper CB: Molecular evolution of tau protein: implications for
Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 67:1622–1632. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Buée L, Bussière T, Buée-Scherrer V,
Delacourte A and Hof PR: Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and
role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev.
33:95–130. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Potier MC,
Ulrich J and Crowther RA: Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA
encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau
containing four tandem repeats: Differential expression of tau
protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 8:393–399. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hong M, Zhukareva V, Vogelsberg-Ragaglia
V, Wszolek Z, Reed L, Miller BI, Geschwind DH, Bird TD, McKeel D,
Goate A, et al: Mutation-specific functional impairments in
distinct tau isoforms of hereditary FTDP-17. Science.
282:1914–1917. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|