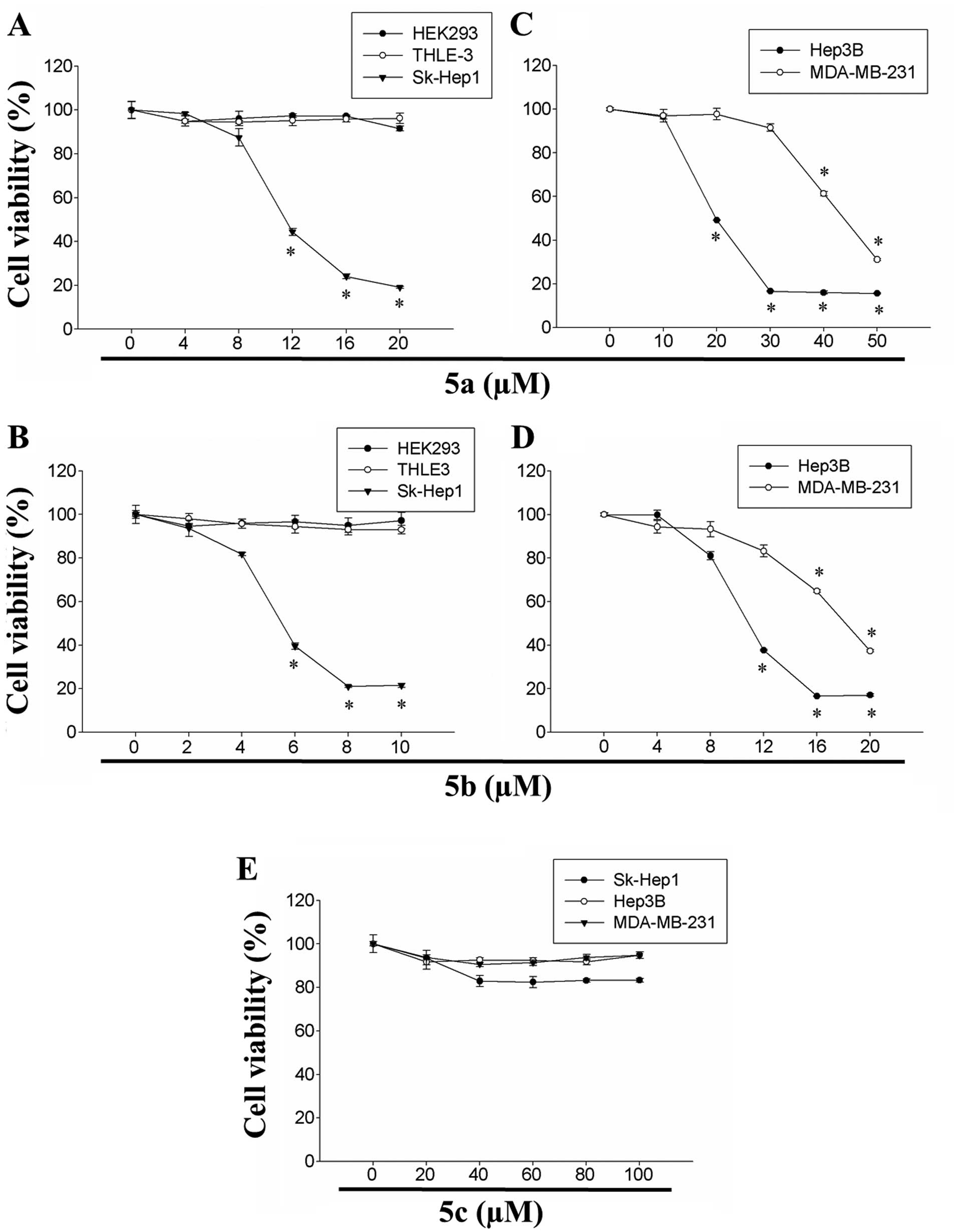
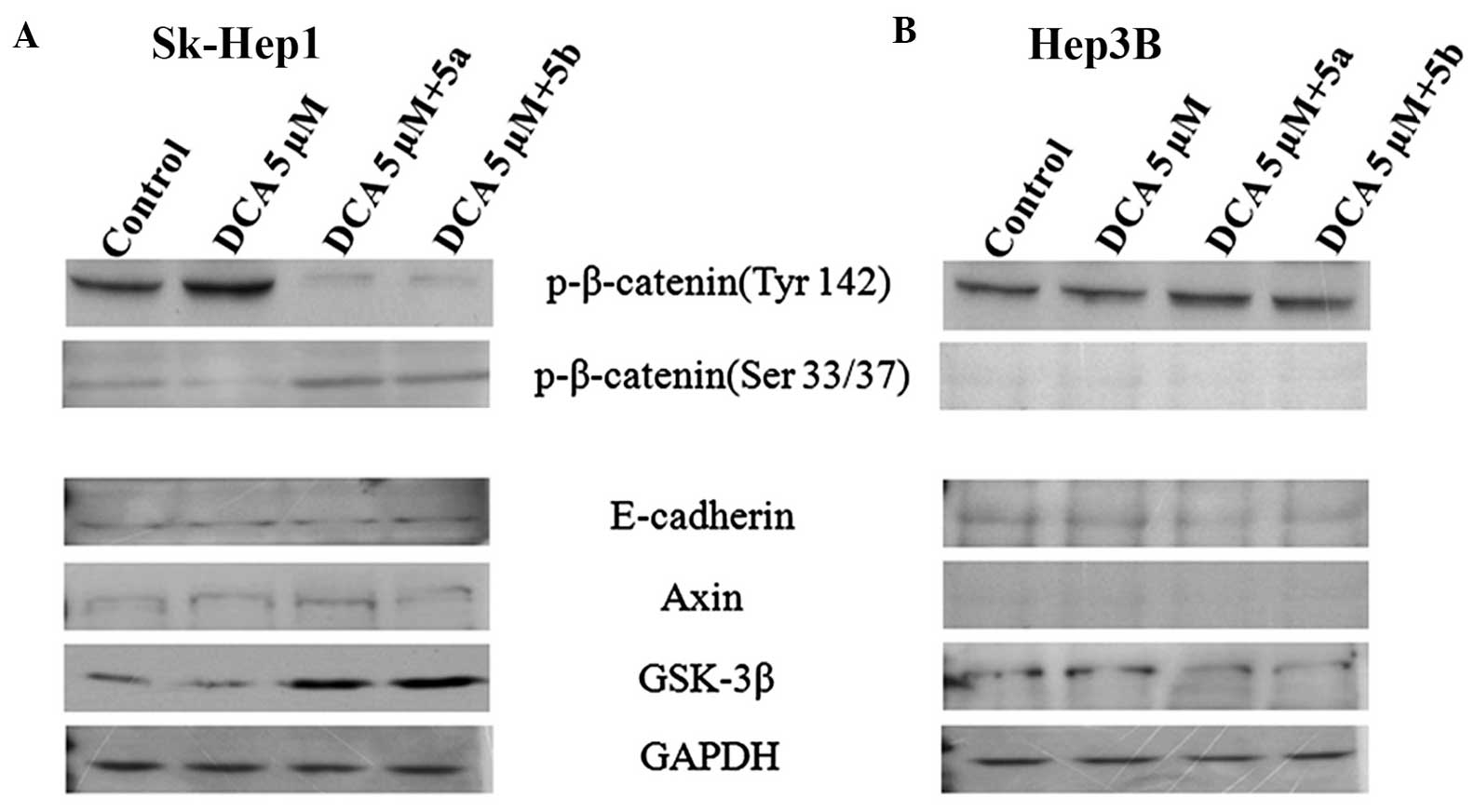
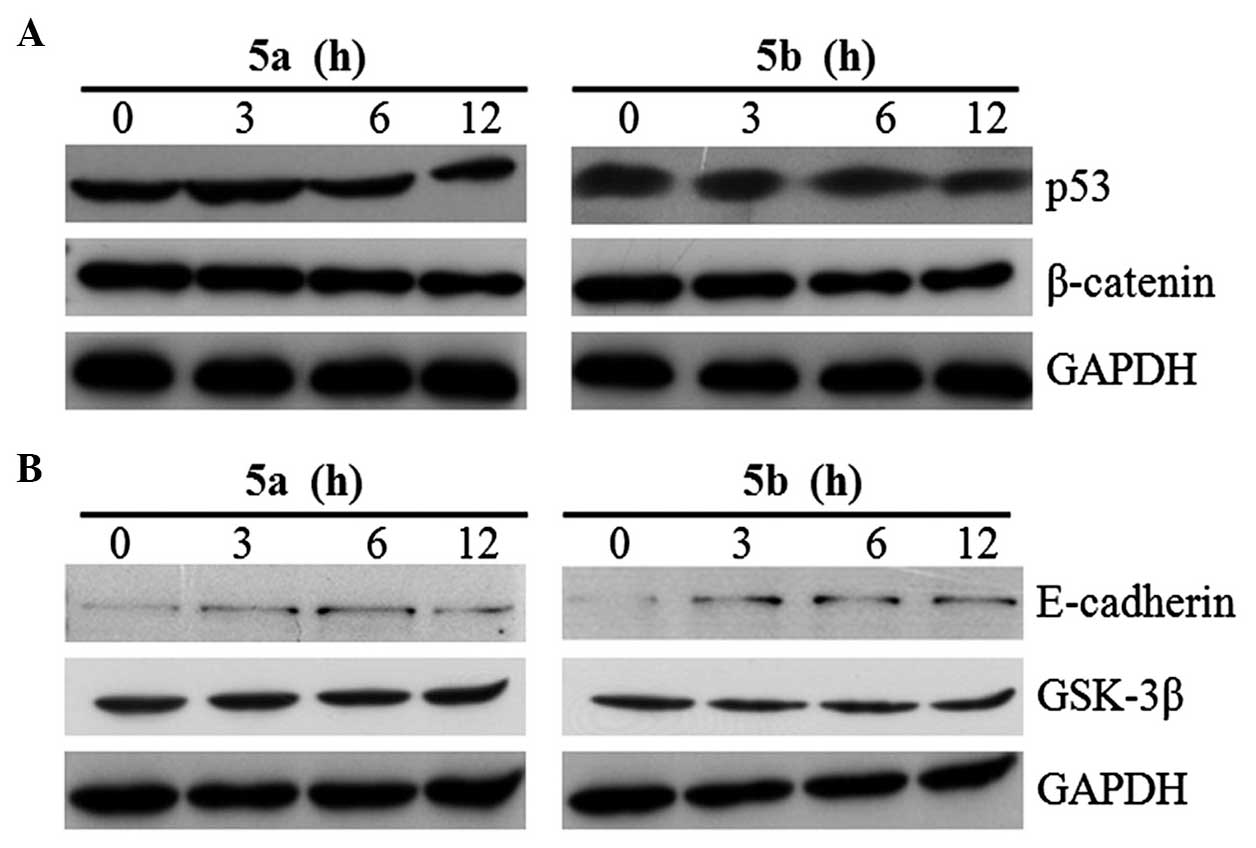
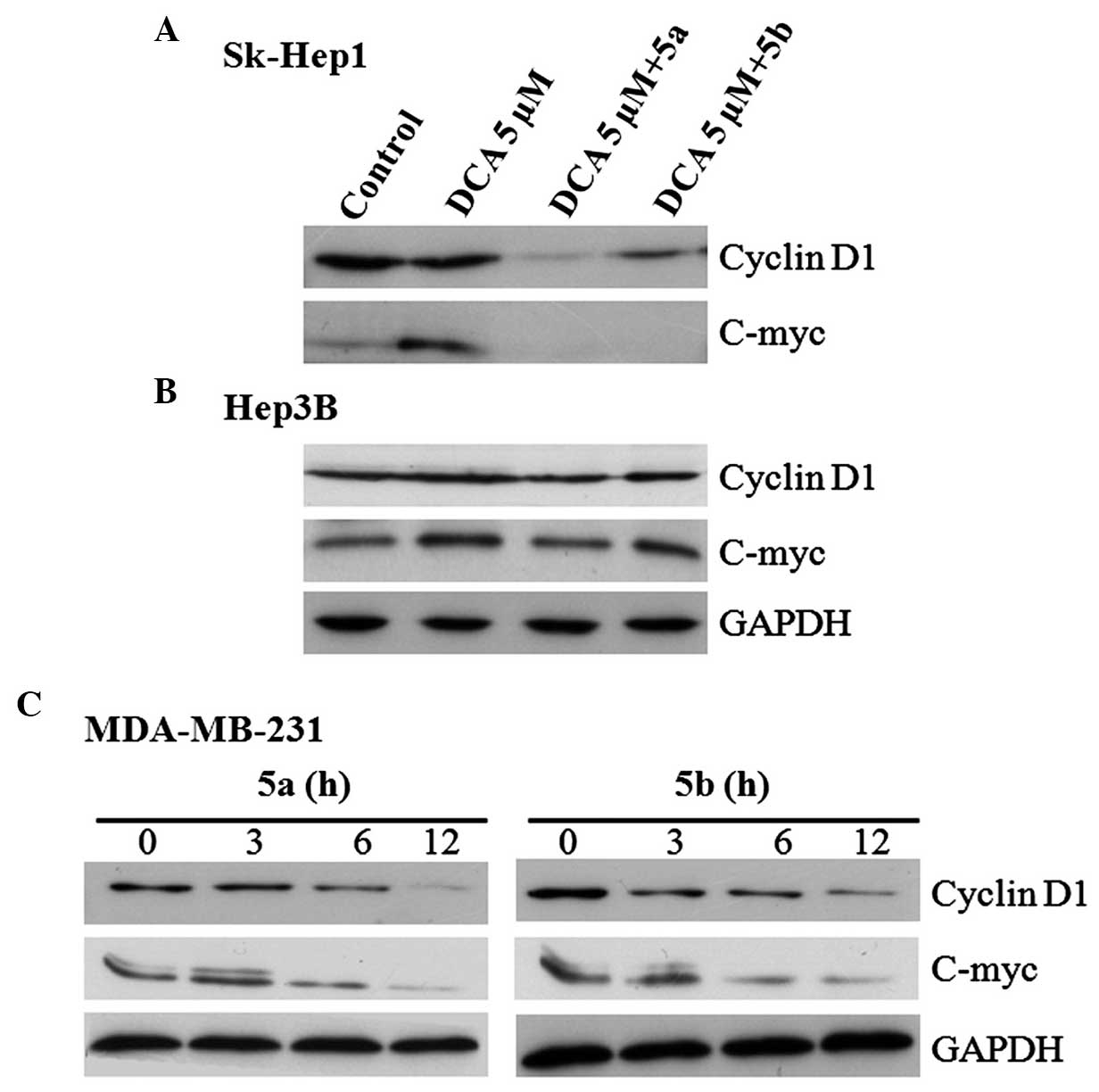
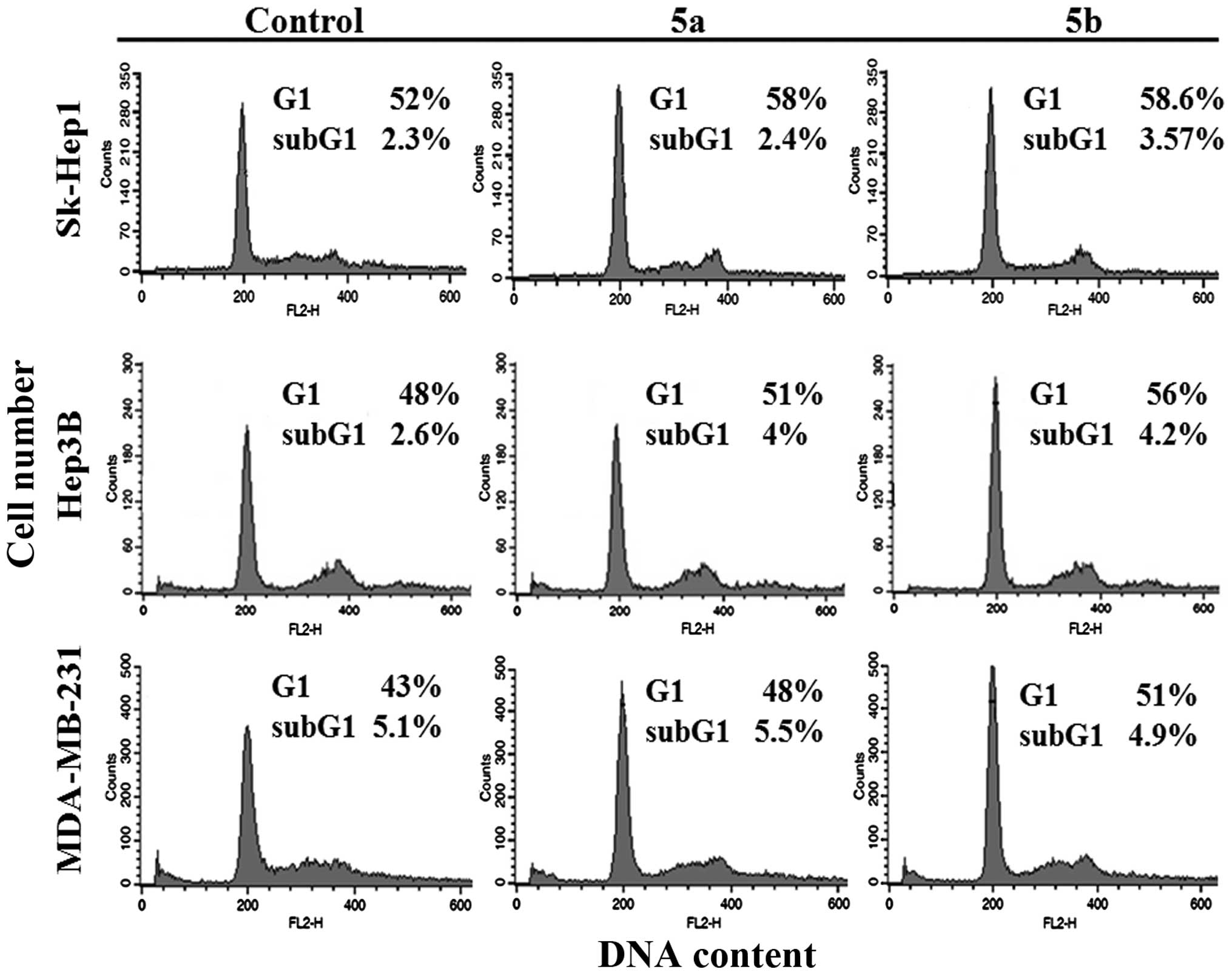
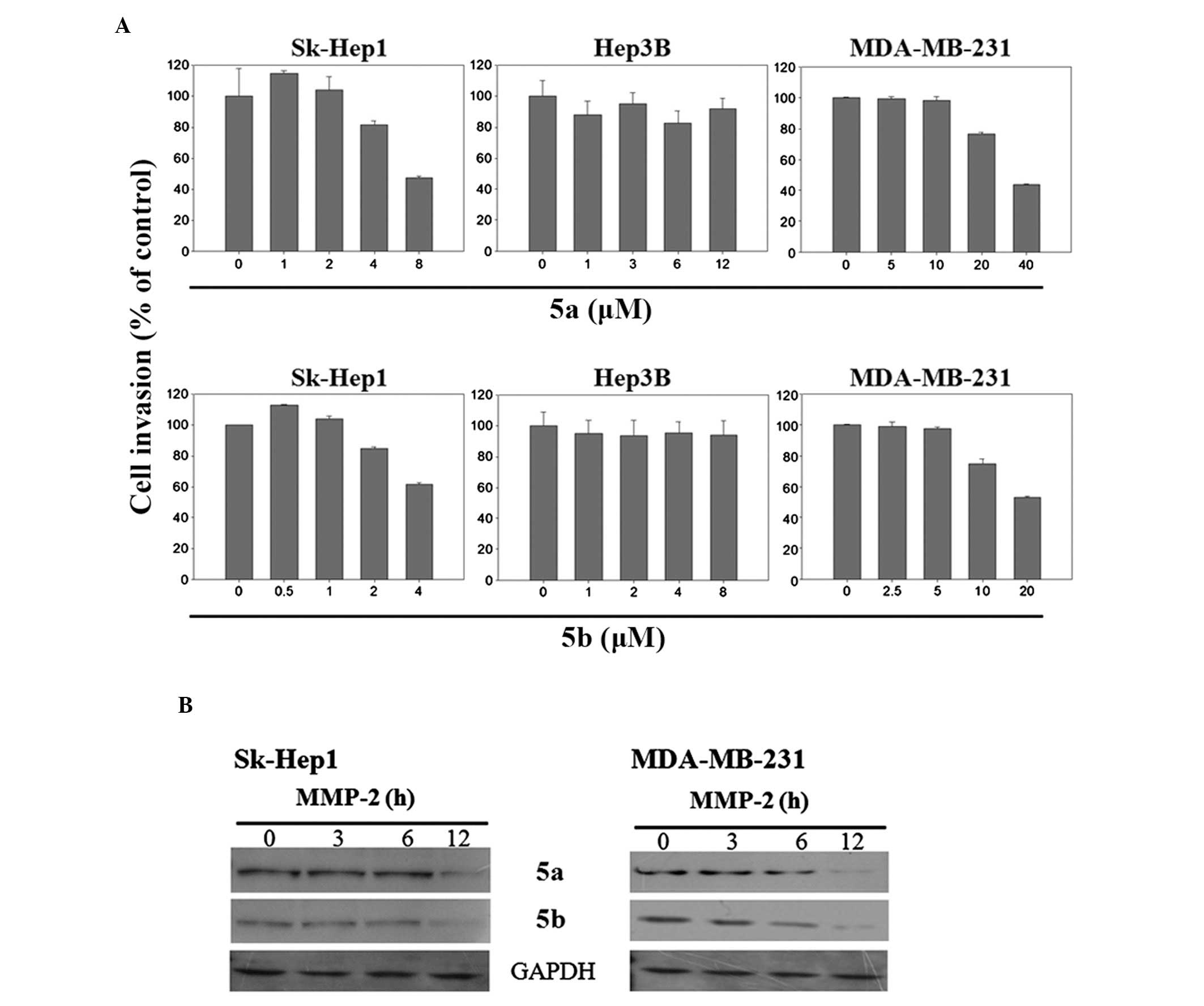
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ries L, Melbert D, Krapcho M, Stinchcomb
D, Howlader N, Horner M, Mariotto A, Miller B, Feuer E and
Altekruse S: SEER Cancer Statistics Review. Based on November 2007
SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site. National Cancer
Institute; Bethesda, MD: 2008
|
|
3
|
Roayaie S, Blume IN, Thung SN, Guido M,
Fiel MI, Hiotis S, Labow DM, Llovet JM and Schwartz ME: A system of
classifying microvascular invasion to predict outcome after
resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 137:850–855. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lang L: FDA approves sorafenib for
patients with inoperable liver cancer. Gastroenterology.
134:3792008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cadigan KM: Wnt-β-catenin signaling. Curr
Biol. 18:R943–R947. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kemler R: From cadherins to catenins:
cytoplasmic protein interactions and regulation of cell adhesion.
Trends Genet. 9:317–321. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jamora C and Fuchs E: Intercellular
adhesion, signalling and the cytoskeleton. Nat Cell Biol.
4:E101–E108. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Polakis P: The many ways of Wnt in cancer.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 17:45–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zucman-Rossi J, Benhamouche S, Godard C,
Boyault S, Grimber G, Balabaud C, Cunha A, Bioulac-Sage P and
Perret C: Differential effects of inactivated Axin1 and activated
β-catenin mutations in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncogene.
26:774–780. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fujie H, Moriya K, Shintani Y, Tsutsumi T,
Takayama T, Makuuchi M, Kimura S and Koike K: Frequent beta-catenin
aberration in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res.
20:39–51. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim YD, Park CH, Kim HS, Choi SK, Rew JS,
Kim DY, Koh YS, Jeung KW, Lee KH and Lee JS: Genetic alterations of
Wnt signaling pathway-associated genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:110–118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Laurent-Puig P and Zucman-Rossi J:
Genetics of hepatocellular tumors. Oncogene. 25:3778–3786. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aridoss G, Amirthaganesan S, Kumar NA, Kim
JT, Lim KT, Kabilan S and Jeong YT: A facile synthesis,
antibacterial, and antitubercular studies of some piperidin-4-one
and tetrahydro-pyridine derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
18:6542–6548. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aridoss G, Amirthaganesan S and Jeong YT:
Synthesis, crystal and antibacterial studies of diversely
functionalized tetrahy-dropyridin-4-ol. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
20:2242–2249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Awasthi N, Schwarz MA, Verma V, Cappiello
C and Schwarz RE: Endothelial monocyte activating polypeptide II
interferes with VEGF-induced proangiogenic signaling. Lab Invest.
89:38–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hung WC and Chang HC: Indole-3-carbinol
inhibits Sp1-induced matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression to
attenuate migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. J Agric
Food Chem. 57:76–82. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pai R, Tarnawski AS and Tran T:
Deoxycholic acid activates β-catenin signaling pathway and
increases colon cell cancer growth and invasiveness. Mol Biol Cell.
15:2156–2163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev
Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: β-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H,
Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei Y, Van Nhieu JT, Prigent S,
Srivatanakul P, Tiollais P and Buendia MA: Altered expression of
E-cadherin in hepa-tocellular carcinoma: correlations with genetic
alterations, β-catenin expression, and clinical features.
Hepatology. 36:692–701. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsumura T, Makino R and Mitamura K:
Frequent down-regulation of E-cadherin by genetic and epigenetic
changes in the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinomas.
Clin Cancer Res. 7:594–599. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sakanaka C, Weiss JB and Williams LT:
Bridging of β-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase-3β by axin and
inhibition of β-catenin-mediated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:3020–3023. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Acs G, Lawton TJ, Rebbeck TR, LiVolsi VA
and Zhang PJ: Differential expression of E-cadherin in lobular and
ductal neoplasms of the breast and its biologic and diagnostic
implications. Am J Clin Pathol. 115:85–98. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rakha EA, Patel A, Powe DG, et al:
Clinical and biological significance of E-cadherin protein
expression in invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Am J Surg
Pathol. 34:1472–1479. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gould Rothberg BE and Bracken MB:
E-cadherin immunohisto-chemical expression as a prognostic factor
in infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast: a systematic review
and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Thr. 100:139–148. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Orsulic S, Huber O, Aberle H, Arnold S and
Kemler R: E-cadherin binding prevents beta-catenin nuclear
localization and beta-catenin/LEF-1-mediated transactivation. J
Cell Sci. 112:1237–1245. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Harper JW and Elledge SJ: Cdk inhibitors
in development and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 6:56–64. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yew PR: Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of
vertebrate G1- and S-phase regulators. J Cell Physiol. 187:1–10.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng YX and el-Deiry WS: Regulation of
p21WAF1/CIP1 expression by p53-independent pathways. Oncogene.
12:1557–1564. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brandi G, Paiardini M, Cervasi B, Fiorucci
C, Filippone P, De Marco C, Zaffaroni N and Magnani M: A new
indole-3-carbinol tetrameric derivative inhibits cyclin-dependent
kinase 6 expression, and induces G1 cell cycle arrest in both
estrogen-dependent and estrogen-independent breast cancer cell
lines. Cancer Res. 63:4028–4036. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nakajima M, Welch DR, Belloni PN and
Nicolson GL: Degradation of basement membrane type IV collagen and
lung subendothelial matrix by rat mammary adenocarcinoma cell
clones of differing metastatic potentials. Cancer Res.
47:4869–4876. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mareel MM, Van Roy FM and De Baetselier P:
The invasive phenotypes. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 9:45–62. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Christofori G and Semb H: The role of the
cell-adhesion molecule E-cadherin as a tumour-suppressor gene.
Trends Biochem Sci. 24:73–76. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang GJ, Yang CM, Chang YS, Amagaya S,
Wang HC, Hou WC, Huang SS and Hu ML: Hispolon suppresses SK-Hep1
human hepatoma cell metastasis by inhibiting matrix
metal-loproteinase-2/9 and urokinase-plasminogen activator through
the PI3K/Akt and ERK signaling pathways. J Agric Food Chem.
58:9468–9475. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hwang ES and Lee HJ: Inhibitory effects of
lycopene on the adhesion, invasion, and migration of SK-Hep1 human
hepatoma cells. Exp Biol Med. 231:322–327. 2006.
|
|
39
|
Meng Q, Qi M, Chen DZ, Yuan R, Goldberg
ID, Rosen E, Auborn K and Fan S: Suppression of breast cancer
invasion and migration by indole-3-carbinol: associated with
up-regulation of BRCA1 and E-cadherin/catenin complexes. J Mol Med.
78:155–165. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|