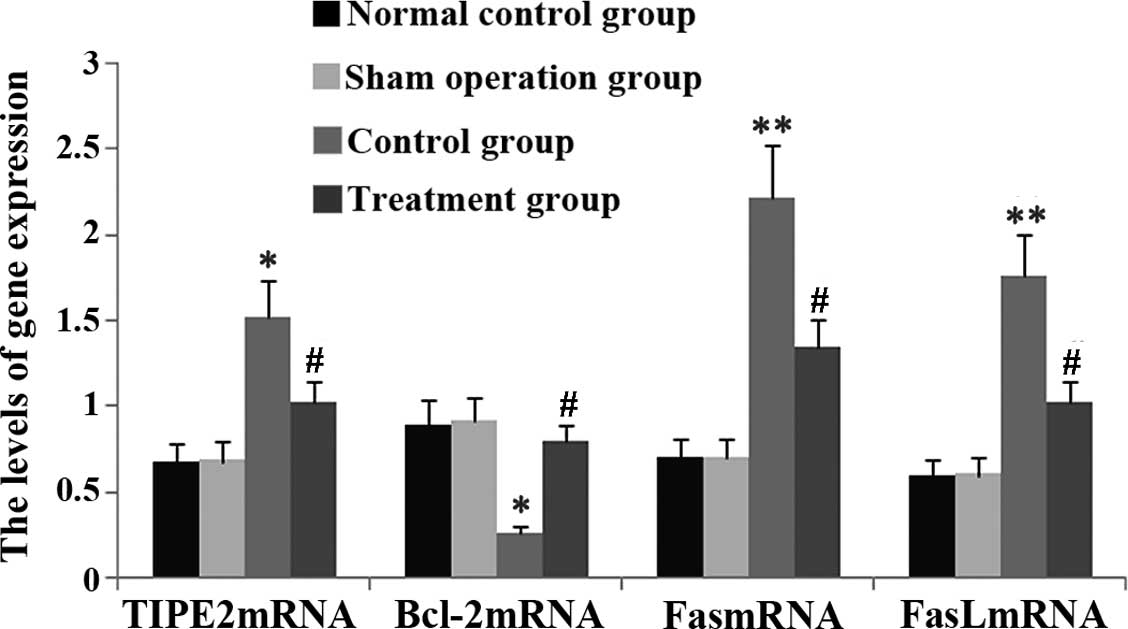
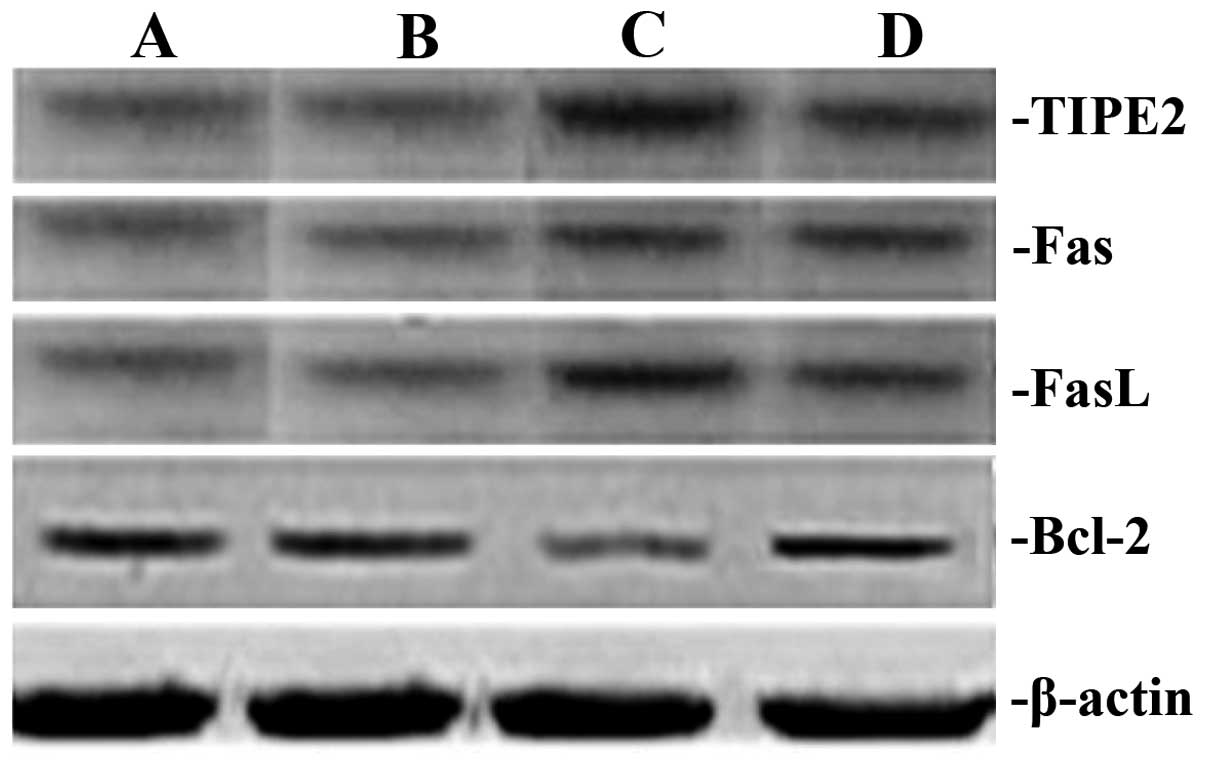
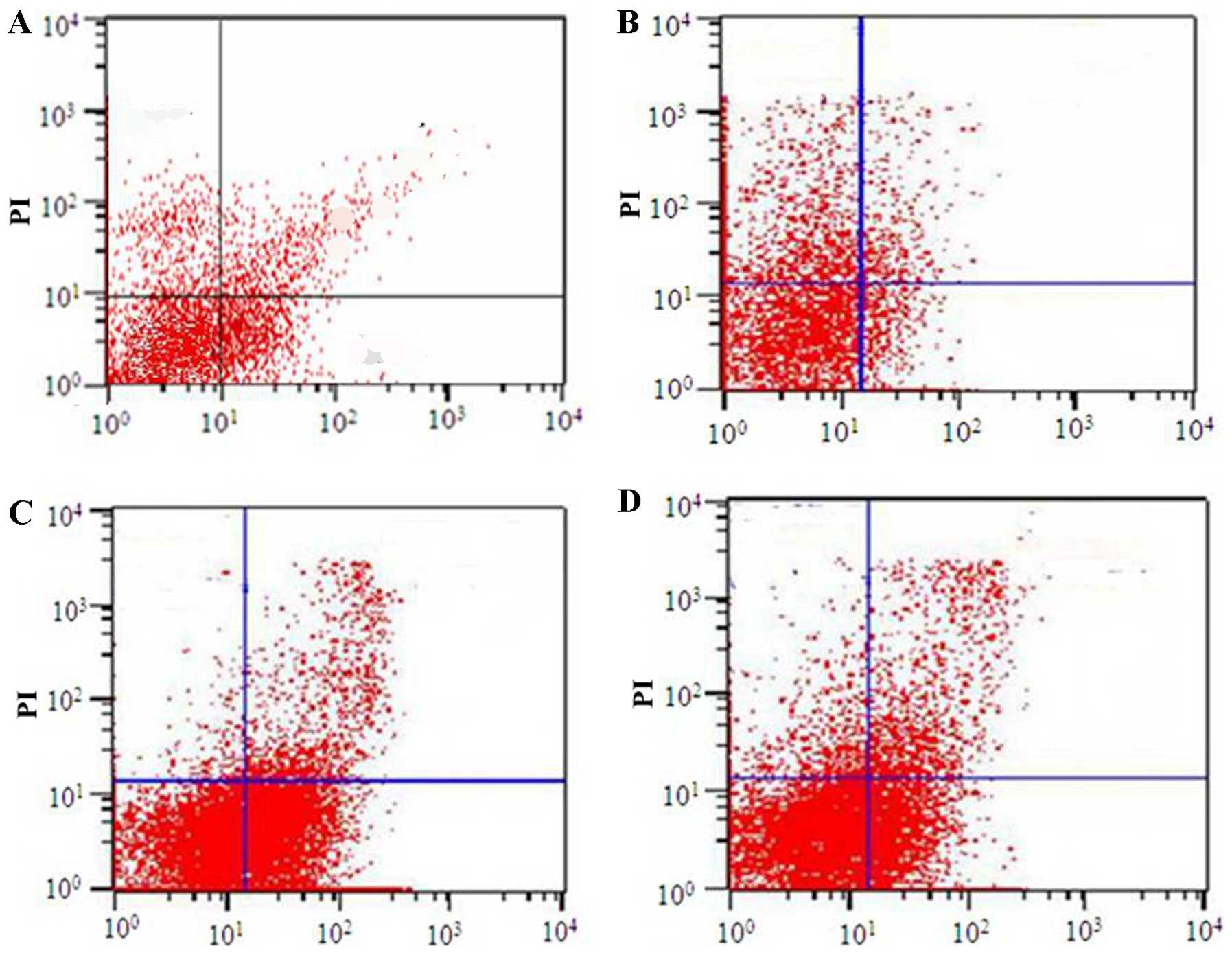
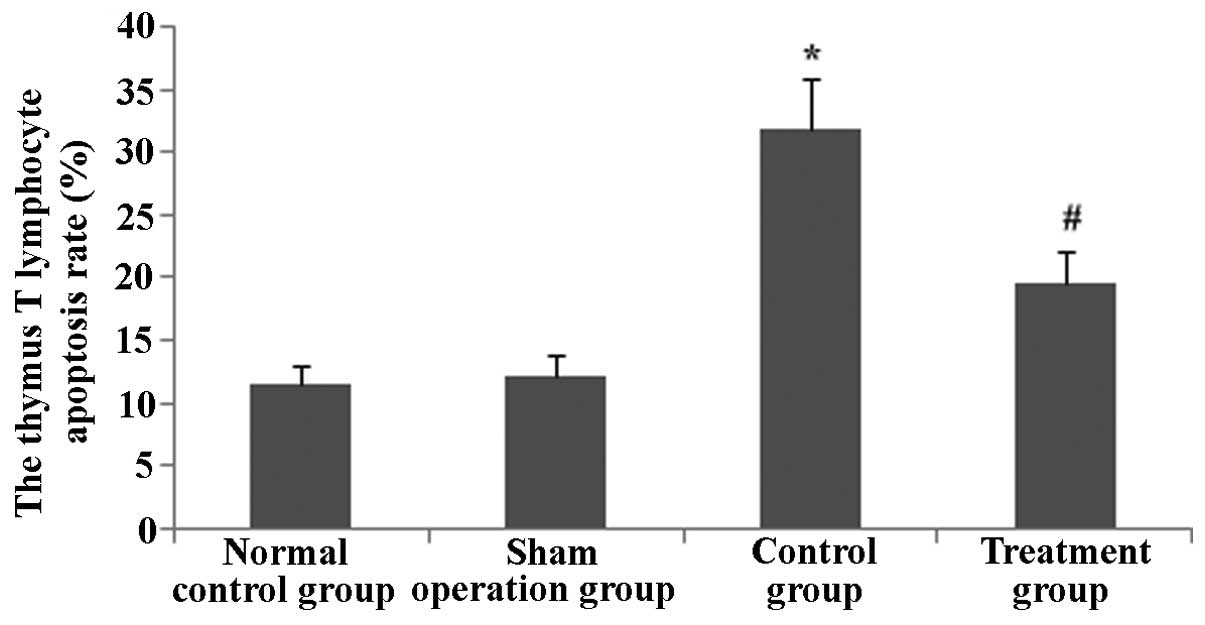
|
1
|
Cepinskas G and Wilson JX: Inflammatory
response in micro-vascular endothelium in sepsis: role of oxidants.
J Clin Biochem Nutr. 42:175–184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hotchkiss RS, Coopersmith CM, McDunn JE
and Ferguson TA: The sepsis seesaw: tilting toward
immunosuppression. Nat Med. 15:496–497. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Feng H, Guo L, Song Z, Gao H, Wang D, Fu
W, Han J, Li Z, Huang B and Li XA: Caveolin-1 protects against
sepsis by modulating inflammatory response, alleviating bacterial
burden, and suppressing thymocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
285:25154–25160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW and Karl IE: Role
of apoptotic cell death in sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis. 35:585–592.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hotchkiss RS, Osmon SB, Chang KC, Wagner
TH, Coopersmith CM and Karl IE: Accelerated lymphocyte death in
sepsis occurs by both the death receptor and mitochondrial
pathways. J Immunol. 174:5110–5118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Wei X, Liu L, Liu S, Wang Z,
Zhang B, Fan B, Yang F, Huang S, Jiang F, Chen YH and Yi F: TIPE2,
a novel regulator of immunity, protects against experimental
stroke. J Biol Chem. 287:32546–32555. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang X, Wang J, Fan C, Li H, Sun H, Gong
S, Chen YH and Shi Y: Crystal structure of TIPE2 provides insights
into immune homeostasis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 16:89–90. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang S, Zhang Y, Wei X, Zhen J, Wang Z,
Li M, Miao W, Ding H, Du P, Zhang W, He M and Yi F: Expression and
regulation of a novel identified TNFAIP8 family is associated with
diabetic nephropathy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1802:1078–1086. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu MW, Su MX, Wang YH and Qian CY: Effect
of Melilotus extract on lung injury via the upregulation of tumor
necrosis factor-α-induced protein-8-like 2 in septic mice. Mol Med
Rep. 11:1675–1684. 2015.
|
|
10
|
Guo Y, Zhao Y, Zheng C, Meng Y and Yang Y:
Synthesis, biological activity of salidroside and its analogues.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 58:1627–1629. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhu YZ, Huang SH, Tan BK, Sun J, Whiteman
M and Zhu YC: Antioxidants in Chinese herbal medicines: a
biochemical perspective. Nat Prod Rep. 21:478–489. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li F, Tang H, Xiao F, Gong J, Peng Y and
Meng X: Protective effect of salidroside from Rhodiolae Radix on
diabetes-induced oxidative stress in mice. Molecules. 16:9912–9924.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhong H, Xin H, Wu LX and Zhu YZ:
Salidroside attenuates apoptosis in ischemic cardiomyocytes: a
mechanism through a mitochondria-dependent pathway. J Pharmacol.
14:399–408. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Lee Y, Jung JC, Jang S, Kim J, Ali Z, Khan
IA and Oh S: Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of
constituents isolated from Rhodiola rosea. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:5140492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Spanakis M, Vizirianakis IS, Batzias G and
Niopas I: Pharmacokinetic interaction between losartan and Rhodiola
rosea in rabbits. Pharmacology. 91:112–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guan S, He J, Guo W, Wei J, Lu J and Deng
X: Adjuvant effects of salidroside from Rhodiola rosea L. on the
immune responses to ovalbumin in mice. Immunopharmacol
Immunotoxicol. 33:738–743. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu L, Yuan J and Zhang S: Rejuvenating
activity of salidroside (SDS): dietary intake of SDS enhances the
immune response of aged rats. Age. 35:637–646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Taylor M, Cieslak M, Rees GS, Oojageer A,
Leith C, Bristow C, Tawn EJ, Winther JF and Boice JD Jr: Comparison
of germ line minisatellite mutation detection at the CEB1 locus by
Southern blotting and PCR amplification. Mutagenesis. 25:343–349.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Z, Fayngerts S, Wang P, Sun H,
Johnson DS, Ruan Q, Guo W and Chen YH: TIPE2 protein serves as a
negative regulator of phagocytosis and oxidative burst during
infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:15413–15418. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tavernier G, Wolfrum K, Demeester J, De
Smedt SC, Adjaye J and Rejman J: Activation of
pluripotency-associated genes in mouse embryonic fibroblasts by
non-viral transfection with in vitro-derived mRNAs encoding Oct4,
Sox2, Klf4 and cMyc. Biomaterials. 33:412–417. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tassone F, Pan R, Amiri K, Taylor AK and
Hagerman PJ: A rapid polymerase chain reaction-based screening
method for identification of all expanded alleles of the fragile X
(FMR1) gene in newborn and high-risk populations. J Mol Diagn.
10:43–49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wichterman KA, Baue AE and Chaudry IH:
Sepsis and septic shock - a review of laboratory models and a
proposal. J Surg Res. 29:189–201. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Felzmann T, Witt V, Wimmer D, Ressmann G,
Wagner D, Paul P, Hüttner K and Fritsch G: Monocyte enrichment from
leukapharesis products for the generation of DCs by plastic
adherence, or by positive or negative selection. Cytotherapy.
5:391–398. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Julius MH, Simpson E and Herzenberg LA: A
rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine
lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 3:645–649. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Celik S, Erdogan S and Tuzcu M: Caffeic
acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) exhibits significant potential as an
antidiabetic and liver-protective agent in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Pharmacol Res. 60:270–276. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Osuchowski MF, Welch K, Siddiqui J and
Remick DG: Circulating cytokine/inhibitor profiles reshape the
understanding of the SIRS/CARS continuum in sepsis and predict
mortality. J Immunol. 177:1967–1974. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim JS, Kim SJ and Lee SM: Genipin
attenuates sepsis-induced immunosuppression through inhibition of T
lymphocyte apoptosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 27:15–23. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kalil AC and Opal SM: Sepsis in the
severely immunocompromised patient. Curr Infect Dis Rep.
17:4872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C and Moldawer
LL: Sepsis syndromes: understanding the role of innate and acquired
immunity. Shock. 16:83–96. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiao D, Zhang D, Xiang D, Liu QI, Liu Y,
Lv L and Xing X: Effects of fentanyl, midazolam and their
combination on immune function and mortality in mice withsepsis.
Exp Ther Med. 9:1494–1500. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Muenzer JT, Davis CG, Chang K, Schmidt RE,
Dunne WM, Coopersmith CM and Hotchkiss RS: Characterization and
modulation of the immunosuppressive phase of sepsis. Infect Immun.
78:1582–1592. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Parker SJ and Watkins PE: Experimental
models of gram-negative sepsis. Br J Surg. 88:22–30. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wesche DE, Lomas-Neira JL, Perl M, Chung
CS and Ayala A: Leukocyte apoptosis and its significance in sepsis
and shock. J Leukoc Biol. 78:325–337. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wijnands KA, Castermans TM, Hommen MP,
Meesters DM and Poeze M: Arginine and citrulline and the immune
response in sepsis. Nutrients. 7:1426–1463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Laliberté B, Wilson AM, Nafisi H, Mao H,
Zhou YY, Daigle M and Albert PR: TNFAIP8:a new effector for
Galpha(i) coupling to reduce cell death and induce cell
transformation. J Cell Physiol. 225:865–874. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li D, Song L, Fan Y, Li X, Li Y, Chen J,
Zhu F, Guo C, Shi Y and Zhang L: Down-regulation of TIPE2mRNA
expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with
systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 33:422–427. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sun H, Gong S, Carmody RJ, Hilliard A, LI
L, Sun J, Kong L, Xu L, Hilliard B, Hu S, et al: TIPE2, a negative
regulator of innate and adaptive immunity that maintains immune
homeostasis. Cell. 133:415–426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang L, Shi Y, Wang Y, Zhu F, Wang Q, Ma
C, Chen YH and Zhang L: The unique expression profile of human
TIPE2 suggests new functions beyond its role in immune regulation.
Mol Immunol. 48:1209–1215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lou Y and Liu S: The TIPE (TNFAIP8) family
in inflammation, immunity, and cancer. Mol Immunol. 49:4–7. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Freundt EC, Bidere N and Lenardo MJ: A
different TIPE of immune homeostasis. Cell. 133:401–402. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gus-Brautbar Y, Johnson D, Zhang L, Sun H,
Wang P, Zhang S, Zhang L and Chen YH: The anti-inflammatory TIPE2
is an inhibitor of the oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell. 45:610–618. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jadali Z, Amiri MM and Ravanbakhsh M:
Apoptosis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with
sepsis. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 53:646–650. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brudecki L, Ferguson DA, McCall CE and El
Gazzar M: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells evolve during sepsis and
can enhance or attenuate the systemic inflammatory response. Infect
Immun. 80:2026–2034. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Courtine E, Cagnard N, Mazzolini J, Antona
M, Pène F, Fitting C, Jacques S, Rousseau C, Niedergang F,
Gerondakis S, et al: Combined loss of cRel/p50 subunits of NF-κB
leads to impaired innate host response in sepsis. Innate Immun.
18:753–763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chauhan PS, Satti NK, Sharma P, Sharma VK,
Suri KA and Bani S: Differential effects of chlorogenic acid on
various immunological parameters relevant to rheumatoid arthritis.
Phytother Res. 26:1156–1165. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Muralinath M, Kuehn MJ, Roland KL and
Curtiss R: Immunization with Salmonella enterica serovar
Typhimurium-derived outer membrane vesicles delivering the
pneumococcal protein PspA confers protection against challenge with
Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 79:887–894. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Udintsev SN and Shakhov VP: The role of
humoral factors of regenerating liver in the development of
experimental tumors and the effect of Rhodiola rosea extract on
this process. Neoplasma. 38:323–331. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hu X, Lin S, Yu D, Qiu S, Zhang X and Mei
R: A preliminary study: the anti-proliferation effect of
salidroside on different human cancer cell lines. Cell Biol
Toxicol. 26:499–507. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Loo WT, Jin LJ, Chow LW, Cheung MN and
Wang M: Rhodiola algida improves chemotherapy-induced oral
mucositis in breast cancer patients. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
19:S91–S100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Skopńska-Rózewska E, Wójcik R, Siwicki AK,
Sommer E, Wasiutyński A, Furmanowa M, Malinowski M and Mazurkiewicz
M: The effect of Rhodiola quadrifida extracts on cellular immunity
in mice and rats. Pol J Vet Sci. 11:105–111. 2008.
|
|
51
|
Diwaker D, Mishra KP, Ganju L and Singh
SB: Rhodiola inhibits dengue virus multiplication by inducing
innate immune response genes RIG-I, MDA5 and ISG in human
monocytes. Arch Virol. 159:1975–1986. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li HX, Sze SC, Tong Y and Ng TB:
Production of Th1- and Th2-dependent cytokines induced by the
Chinese medicine herb, Rhodiola algida, on human peripheral blood
monocytes. J Ethnopharmacol. 123:257–266. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen SP, Huang Liu R, Lu TM, Wei JC, Wu
TC, Tsai WY, Tsai CH and Yang CC: Complementary usage of Rhodiola
crenulata (L.) in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients:
The effects on cytokines and T cells. Phytother Res. 29:518–525.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Hu B, Zou Y, Liu S, Wang J, Zhu J, Li J,
Bo L and Deng X: Salidroside attenuates concanavalin A-induced
hepatitis via modulating cytokines secretion and lymphocyte
migration in mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:3140812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|