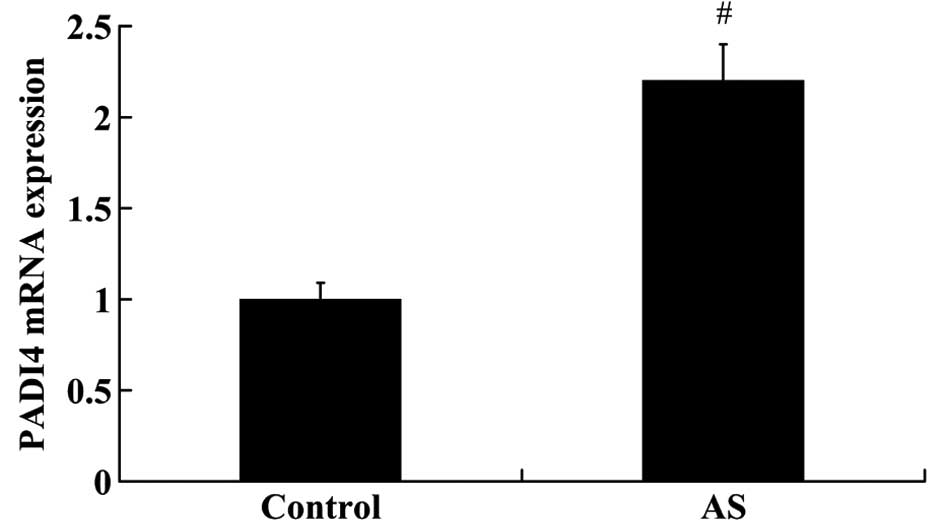
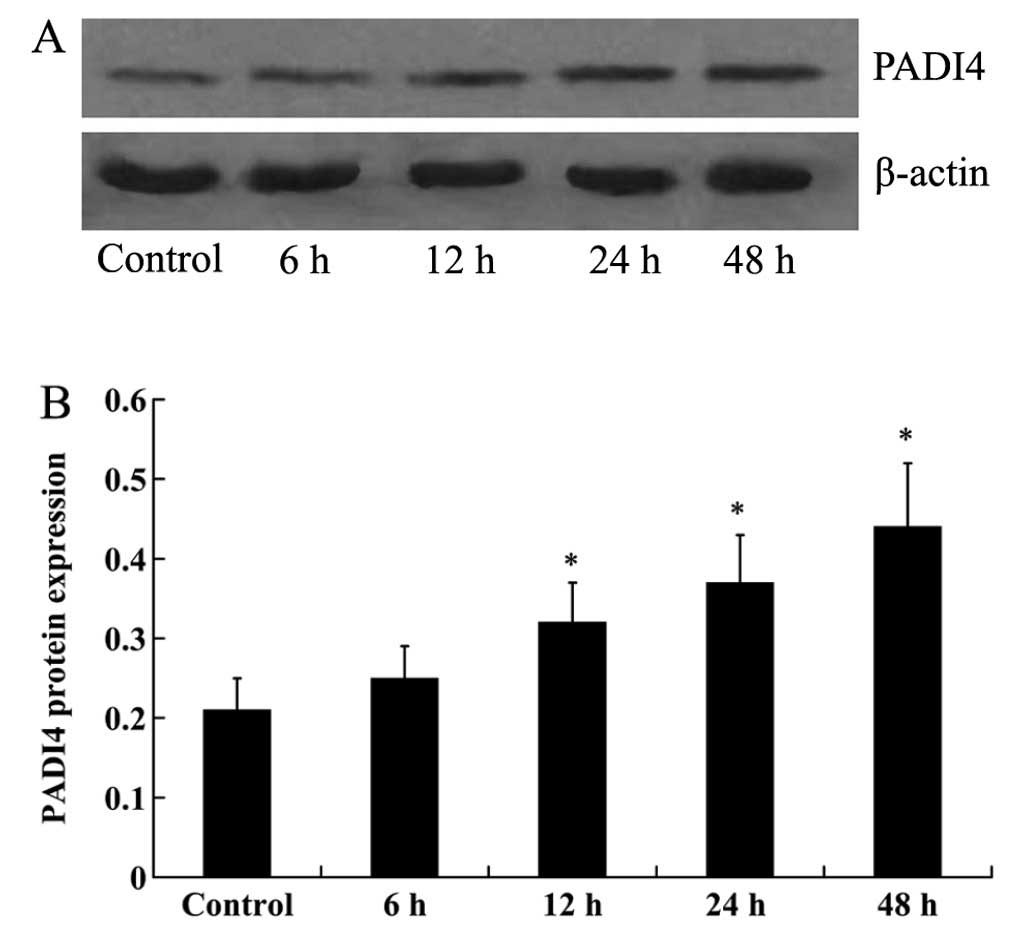
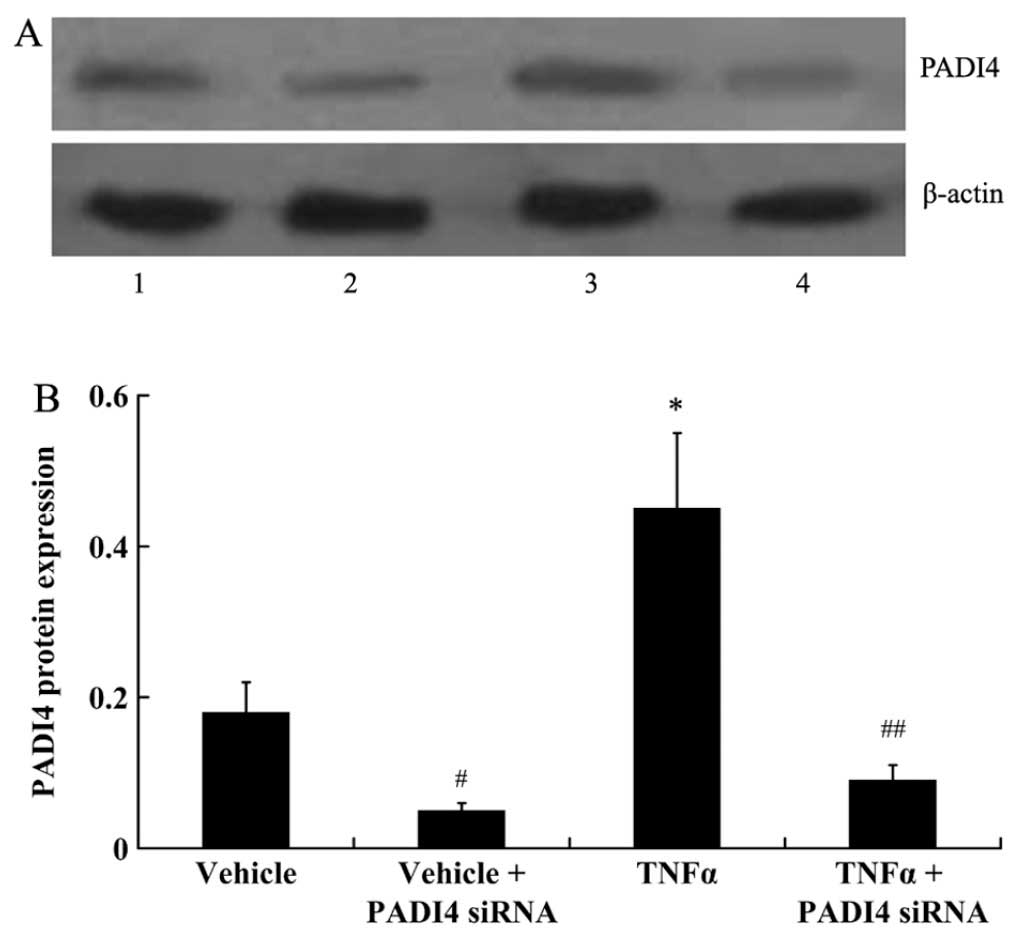
|
1
|
McHugh K and Bowness P: The link between
HLA-B27 and SpA - new ideas on an old problem. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 51:1529–1539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhang X, Aubin JE and Inman RD: Molecular
and cellular biology of new bone formation: insights into the
ankylosis of ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
15:387–393. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schett G: Bone formation versus bone
resorption in ankylosing spondylitis. Adv Exp Med Biol.
649:114–121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Grisar J, Bernecker PM, Aringer M, Redlich
K, Sedlak M, Wolozcszuk W, Spitzauer S, Grampp S, Kainberger F,
Ebner W, et al: Ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and
reactive arthritis show increased bone resorption, but differ with
regard to bone formation. J Rheumatol. 29:1430–1436.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miossec P: IL-17 and Th17 cells in human
inflammatory diseases. Microbes Infect. 11:625–630. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koenders MI, Marijnissen RJ, Devesa I,
Lubberts E, Joosten LA, Roth J, van Lent PL, van de Loo FA and van
den Berg WB: Tumor necrosis factor-interleukin-17 interplay induces
S100A8, interleukin-1β, and matrix metalloproteinases, and drives
irreversible cartilage destruction in murine arthritis: rationale
for combination treatment during arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
63:2329–2339. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N,
Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S, Saito S, Inoue K, Kamatani N,
Gillespie MT, et al: IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with
rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis.
J Clin Invest. 103:1345–1352. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lubberts E, Joosten LA, van de Loo FA,
Schwarzenberger P, Kolls J and van den Berg WB: Overexpression of
IL-17 in the knee joint of collagen type II immunized mice promotes
collagen arthritis and aggravates joint destruction. Inflamm Res.
51:102–104. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakashima K, Hagiwara T, Ishigami A,
Nagata S, Asaga H, Kuramoto M, Senshu T and Yamada M: Molecular
characterization of peptidylarginine deiminase in HL-60 cells
induced by retinoic acid and 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3). J
Biol Chem. 274:27786–27792. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Asaga H, Nakashima K, Senshu T, Ishigami A
and Yamada M: Immunocytochemical localization of peptidylarginine
deiminase in human eosinophils and neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol.
70:46–51. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chang X, Yamada R, Suzuki A, Sawada T,
Yoshino S, Tokuhiro S and Yamamoto K: Localization of
peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) and citrullinated protein in
synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford).
44:40–50. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
György B, Tóth E, Tarcsa E, Falus A and
Buzás EI: Citrullination: a posttranslational modification in
health and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:1662–1677. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anzilotti C, Pratesi F, Tommasi C and
Migliorini P: Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 and citrullination in
health and disease. Autoimmun Rev. 9:158–160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chang X, Zhao Y, Sun S, Zhang Y and Zhu Y:
The expression of PADI4 in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatol Int. 29:1411–1416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vossenaar ER, Nijenhuis S, Helsen MM, van
der Heijden A, Senshu T, van den Berg WB, van Venrooij WJ and
Joosten LA: Citrullination of synovial proteins in murine models of
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 48:2489–2500. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki A, Yamada R, Chang X, Tokuhiro S,
Sawada T, Suzuki M, Nagasaki M, Nakayama-Hamada M, Kawaida R, Ono
M, et al: Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating
enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid
arthritis. Nat Genet. 34:395–402. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Plenge RM, Padyukov L, Remmers EF, Purcell
S, Lee AT, Karlson EW, Wolfe F, Kastner DL, Alfredsson L, Altshuler
D, et al: Replication of putative candidate-gene associations with
rheumatoid arthritis in >4,000 samples from North America and
Sweden: association of susceptibility with PTPN22, CTLA4, and
PADI4. Am J Hum Genet. 77:1044–1060. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kang CP, Lee HS, Ju H, Cho H, Kang C and
Bae SC: A functional haplotype of the PADI4 gene associated with
increased rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Koreans. Arthritis
Rheum. 54:90–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Klein-Nulend J, Bacabac RG and Bakker AD:
Mechanical loading and how it affects bone cells: the role of the
osteocyte cytoskeleton in maintaining our skeleton. Eur Cell Mater.
24:278–291. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Onal M, Xiong J, Chen X, Thostenson JD,
Almeida M, Manolagas SC and O’Brien CA: Receptor activator of
nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL) protein expression by B
lymphocytes contributes to ovariectomy-induced bone loss. J Biol
Chem. 287:29851–29860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vezeridis PS, Semeins CM, Chen Q and
Klein-Nulend J: Osteocytes subjected to pulsating fluid flow
regulate osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 348:1082–1088. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Walkley CR, Shea JM, Sims NA, Purton LE
and Orkin SH: Rb regulates interactions between hematopoietic stem
cells and their bone marrow microenvironment. Cell. 129:1081–1095.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schaffler MB and Kennedy OD: Osteocyte
signaling in bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 10:118–125. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Taylan A, Sari I, Akinci B, Bilge S,
Kozaci D, Akar S, Colak A, Yalcin H, Gunay N and Akkoc N:
Biomarkers and cytokines of bone turnover: extensive evaluation in
a cohort of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. BMC Musculoskelet
Disord. 13:1912012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aggarwal BB: Signalling pathways of the
TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:745–756.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Osta B, Benedetti G and Miossec P:
Classical and paradoxical effects of TNF-α on bone homeostasis.
Front Immunol. 5:482014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pacifici R: Estrogen, cytokines, and
pathogenesis of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res.
11:1043–1051. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kudo O, Fujikawa Y, Itonaga I, Sabokbar A,
Torisu T and Athanasou NA: Proinflammatory cytokine
(TNFalpha/IL-1alpha) induction of human osteoclast formation. J
Pathol. 198:220–227. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mucci JM, Scian R, De Francesco PN, García
FS, Ceci R, Fossati CA, Delpino MV and Rozenfeld PA: Induction of
osteoclastogenesis in an in vitro model of Gaucher disease is
mediated by T cells via TNF-α. Gene. 509:51–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsubara R, Kukita T, Ichigi Y, Takigawa
I, Qu PF, Funakubo N, Miyamoto H, Nonaka K and Kukita A:
Characterization and identification of subpopulations of
mononuclear preosteoclasts induced by TNF-α in combination with
TGF-β in rats. PLoS One. 7:e479302012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kagiya T and Nakamura S: Expression
profiling of microRNAs in RAW264.7 cells treated with a combination
of tumor necrosis factor alpha and RANKL during osteoclast
differentiation. J Periodontal Res. 48:373–385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Abbas S, Zhang YH, Clohisy JC and Abu-Amer
Y: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits pre-osteoblast
differentiation through its type-1 receptor. Cytokine. 22:33–41.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gilbert L, He X, Farmer P, Boden S,
Kozlowski M, Rubin J and Nanes MS: Inhibition of osteoblast
differentiation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Endocrinology.
141:3956–3964. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gilbert LC, Rubin J and Nanes MS: The p55
TNF receptor mediates TNF inhibition of osteoblast differentiation
independently of apoptosis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
288:E1011–E1018. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mukai T, Otsuka F, Otani H, Yamashita M,
Takasugi K, Inagaki K, Yamamura M and Makino H: TNF-alpha inhibits
BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation through activating SAPK/JNK
signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 356:1004–1010. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee HL, Yi T, Baek K, Kwon A, Hwang HR,
Qadir AS, Park HJ, Woo KM, Ryoo HM, Kim GS and Baek JH: Tumor
necrosis factor-α enhances the transcription of Smad ubiquitination
regulatory factor 1 in an activating protein-1- and Runx2-dependent
manner. J Cell Physiol. 228:1076–1086. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hess K, Ushmorov A, Fiedler J, Brenner RE
and Wirth T: TNFalpha promotes osteogenic differentiation of human
mesenchymal stem cells by triggering the NF-kappaB signaling
pathway. Bone. 45:367–376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Feng X1, Feng G, Xing J, Shen B, Li L, Tan
W, Xu Y, Liu S, Liu H, Jiang J, et al: TNF-α triggers osteogenic
differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells via the NF-κB
signalling pathway. Cell Biol Int. 37:1267–1275. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jaiswal N, Haynesworth SE, Caplan AI and
Bruder SP: Osteogenic differentiation of purified, culture-expanded
human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 64:295–312.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Böcker W, Docheva D, Prall WC, Egea V,
Pappou E, Rossmann O, Popov C, Mutschler W, Ries C and Schieker M:
IKK-2 is required for TNF-alpha-induced invasion and proliferation
of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 86:1183–1192.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Mastronardi FG, Wood DD, Mei J, Raijmakers
R, Tseveleki V, Dosch HM, Probert L, Casaccia-Bonnefil P and
Moscarello MA: Increased citrullination of histone H3 in multiple
sclerosis brain and animal models of demyelination: a role for
tumor necrosis factor-induced peptidylarginine deiminase 4
translocation. J Neurosci. 26:11387–11396. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|