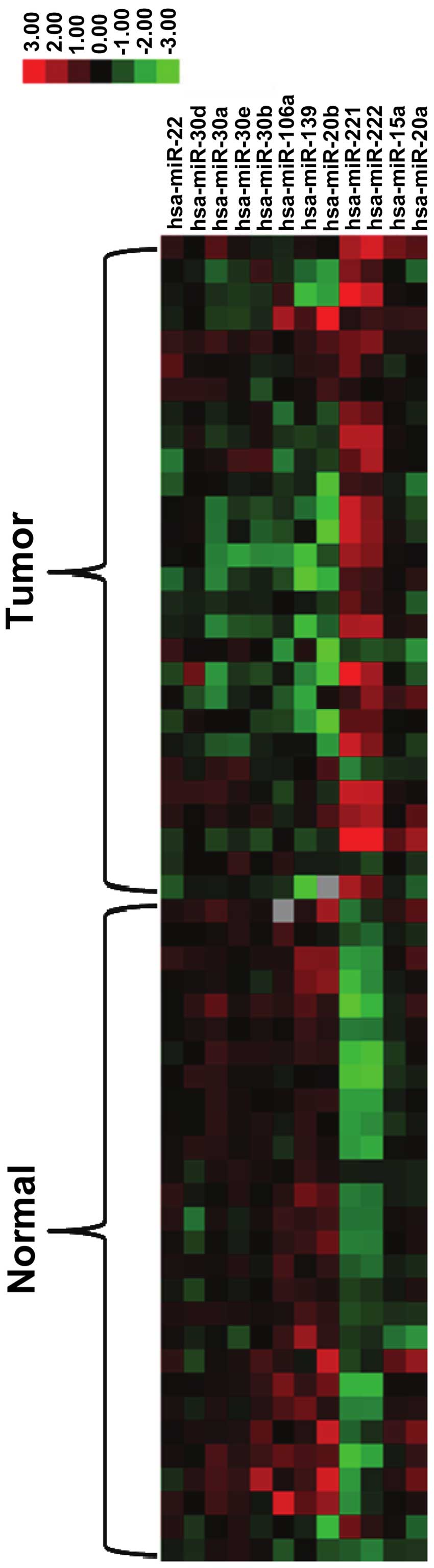
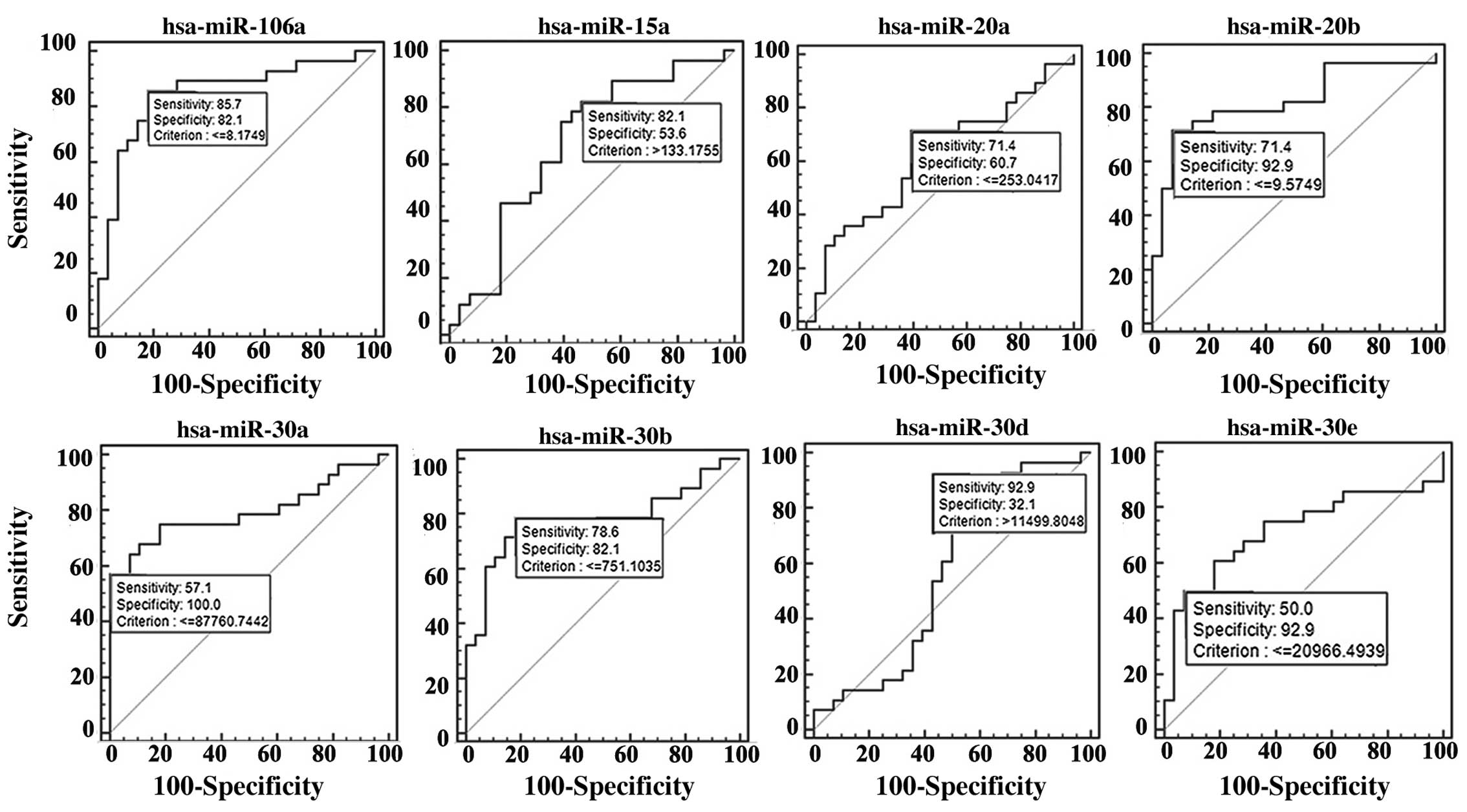
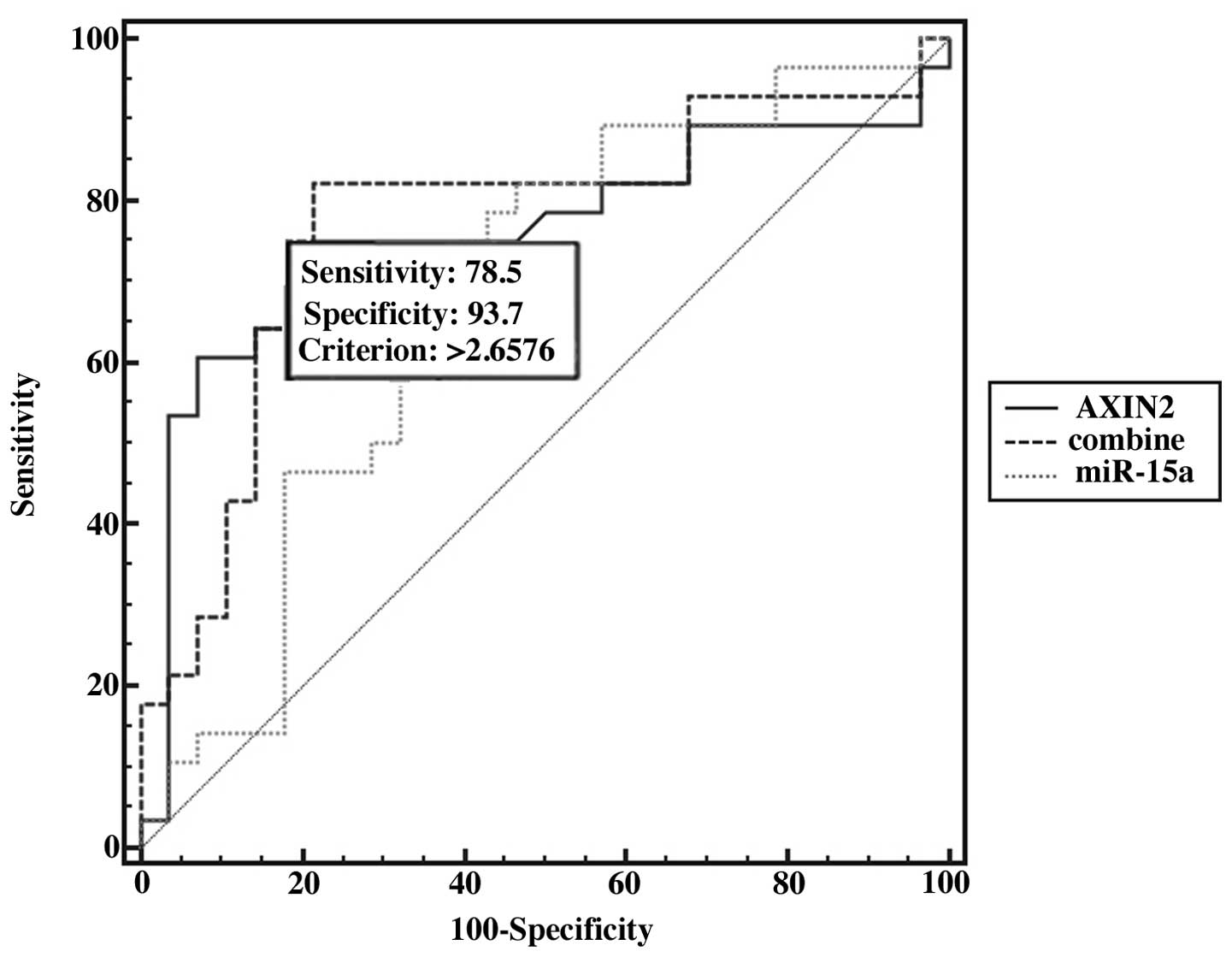
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goldfarb M and Casillas J: Unmet
information and support needs in newly diagnosed thyroid cancer:
comparison of adolescents/young adults (AYA) and older patients. J
Cancer Surviv. 8:394–401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Olaleye O, Ekrikpo U, Moorthy R, Lyne O,
Wiseberg J, Black M and Mitchell D: Increasing incidence of
differentiated thyroid cancer in South East England: 1987–2006. Eur
Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 268:899–906. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chen AY, Jemal A and Ward EM: Increasing
incidence of differentiated thyroid cancer in the United States,
1988–2005. Cancer. 115:3801–3807. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li X, Abdel-Mageed AB, Mondal D and Kandil
E: MicroRNA expression profiles in differentiated thyroid cancer, a
review. Int J Clin Exp Med. 6:74–80. 2013.
|
|
6
|
Sethi K, Sarkar S, Das S, Mohanty B and
Mandal M: Biomarkers for the diagnosis of thyroid cancer. J Exp
Ther Oncol. 8:341–352. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Torréns JI and Burch HB: Serum
thyroglobulin measurement. Utility in clinical practice. Endocrinol
Metab Clin North Am. 30:429–467. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kebebew E and Reiff E: Patients with
differentiated thyroid cancer have a venous gradient in
thyroglobulin levels. Cancer. 109:1078–1081. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weinberger PM, Adam BL, Gourin CG, Moretz
WH III, Bollag RJ, Wang BY, Liu Z, Lee JR and Terris DJ:
Association of nuclear, cytoplasmic expression of galectin-3 with
beta-catenin/Wnt-pathway activation in thyroid carcinoma. Arch
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 133:503–510. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ito Y, Yoshida H, Tomoda C, Miya A,
Kobayashi K, Matsuzuka F, Kakudo K, Kuma K and Miyauchi A: HBME-1
expression in follicular tumor of the thyroid: an investigation of
whether it can be used as a marker to diagnose follicular
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 25:179–182. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sassen S, Miska EA and Caldas C: MicroRNA:
implications for cancer. Virchows Archiv. 452:1–10. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Baranwal S and Alahari SK: miRNA control
of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 126:1283–1290.
2010.
|
|
15
|
Rathod SS, Rani SB, Khan M, Muzumdar D and
Shiras A: Tumor suppressive miRNA-34a suppresses cell proliferation
and tumor growth of glioma stem cells by targeting Akt and Wnt
signaling pathways. FEBS Open Bio. 4:485–495. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pencheva N and Tavazoie SF: Control of
metastatic progression by microRNA regulatory networks. Nat Cell
Biol. 15:546–554. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ell B, Qiu Q, Wei Y, Mercatali L, Ibrahim
T, Amadori D and Kang Y: The microRNA-23b/27b/24 cluster promotes
breast cancer lung metastasis by targeting metastasis-suppressive
gene prosaposin. J Biol Chem. 289:21888–21895. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu Y, Cheng Y, Song Y, Zhang Z, Deng M,
Wang C, Zheng G and He Z: MicroRNA-493 suppresses tumor growth,
invasion and metastasis of lung cancer by regulating E2F1. PLoS
One. 9:e1026022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Skinner HD, Lee JH, Bhutani MS, Weston B,
Hofstetter W, Komaki R, Shiozaki H, Wadhwa R, Sudo K, Elimova E, et
al: A validated miRNA profile predicts response to therapy in
esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 120:3635–3641. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tumilson CA, Lea RW, Alder JE and Shaw L:
Circulating microRNA biomarkers for glioma and predicting response
to therapy. Mol Neurobiol. 50:545–558. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saito Y, Suzuki H, Imaeda H, Matsuzaki J,
Hirata K, Tsugawa H, Hibino S, Kanai Y, Saito H and Hibi T: The
tumor suppressor microRNA-29c is downregulated and restored by
celecoxib in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
132:1751–1760. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Zhang J, Wu J, Luo D, Su K, Shi W,
Liu J, Tian Y and Wei L: MicroRNA-610 inhibits the migration and
invasion of gastric cancer cells by suppressing the expression of
vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein. Eur J Cancer. 48:1904–1913.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Oh HK, Tan AL, Das K, Ooi CH, Deng NT, Tan
IB, Beillard E, Lee J, Ramnarayanan K, Rha SY, et al: Genomic loss
of miR-486 regulates tumor progression and the OLFM4 antiapoptotic
factor in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2657–2667. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu S, Liu Y, Wang J, Guo Z, Zhang Q, Yu F,
Zhang Y, Huang K, Li Y, Song E, et al: Circulating microRNA
profiles as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:2084–2092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Etheridge A, Lee I, Hood L, Galas D and
Wang K: Extracellular microRNA: a new source of biomarkers. Mutat
Res. 717:85–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cortez MA, Welsh JW and Calin GA:
Circulating microRNAs as noninvasive biomarkers in breast cancer.
Recent Results Cancer Res. 195:151–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yip L, Kelly L, Shuai Y, Armstrong MJ,
Nikiforov YE, Carty SE and Nikiforova MN: MicroRNA signature
distinguishes the degree of aggressiveness of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2035–2041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fassina A, Cappellesso R, Simonato F, Siri
M, Ventura L, Tosato F, Busund LT, Pelizzo MR and Fassan M: A
4-MicroRNA signature can discriminate primary lymphomas from
anaplastic carcinomas in thyroid cytology smears. Cancer
Cytopathol. 122:274–281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nikiforova MN, Tseng GC, Steward D, Diorio
D and Nikiforov YE: MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid
tumors: biological significance and diagnostic utility. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 93:1600–1608. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hébrant A, Dom G, Dewaele M, Andry G,
Trésallet C, Leteurtre E, Dumont JE and Maenhaut C: mRNA expression
in papillary and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: molecular anatomy of
a killing switch. PLoS One. 7:e378072012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee JC, Zhao JT, Clifton-Bligh RJ, Gill A,
Gundara JS, Ip JC, Glover A, Sywak MS, Delbridge LW, Robinson BG
and Sidhu SB: MicroRNA-222 and microRNA-146b are tissue and
circulating biomarkers of recurrent papillary thyroid cancer.
Cancer. 119:4358–4365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ruggeri RM, Campennì A, Baldari S,
Trimarchi F and Trovato M: What is New on Thyroid Cancer
Biomarkers. Biomark Insights. 3:237–252. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He M, Zhao Y, Yi H, Sun H, Liu X and Ma S:
The combination of TP53INP1, TP53INP2 and AXIN2: potential
biomarkers in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocrine. 48:712–720.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu X, He M, Hou Y, Liang B, Zhao L, Ma S,
Yu Y and Liu X: Expression profiles of microRNAs and their target
genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:1415–1420.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S,
Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Franssila K, Suster S, et al:
The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:19075–19080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pallante P, Visone R, Ferracin M, Ferraro
A, Berlingieri MT, Troncone G, Chiappetta G, Liu CG, Santoro M,
Negrini M, et al: MicroRNA deregulation in human thyroid papillary
carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 13:497–508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shen R, Liyanarachchi S, Li W, Wakely PE
Jr, Saji M, Huang J, Nagy R, Farrell T, Ringel MD, de la Chapelle
A, et al: MicroRNA signature in thyroid fine needle aspiration
cytology applied to 'atypia of undetermined significance' cases.
Thyroid. 22:9–16. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Gharib H: Changing trends in thyroid
practice: understanding nodular thyroid disease. Endocr Pract.
10:31–39. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Prasad NB, Somervell H, Tufano RP, Dackiw
AP, Marohn MR, Califano JA, Wang Y, Westra WH, Clark DP, Umbricht
CB, et al: Identification of genes differentially expressed in
benign versus malignant thyroid tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
14:3327–3337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
American Thyroid Association (ATA)
Guidelines Taskforce on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid
Cancer; Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos RT, Lee SL, Mandel
SJ, Mazzaferri EL, McIver B, Pacini F, Schlumberger M, et al:
Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for
patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer.
Thyroid. 19:1167–1214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|