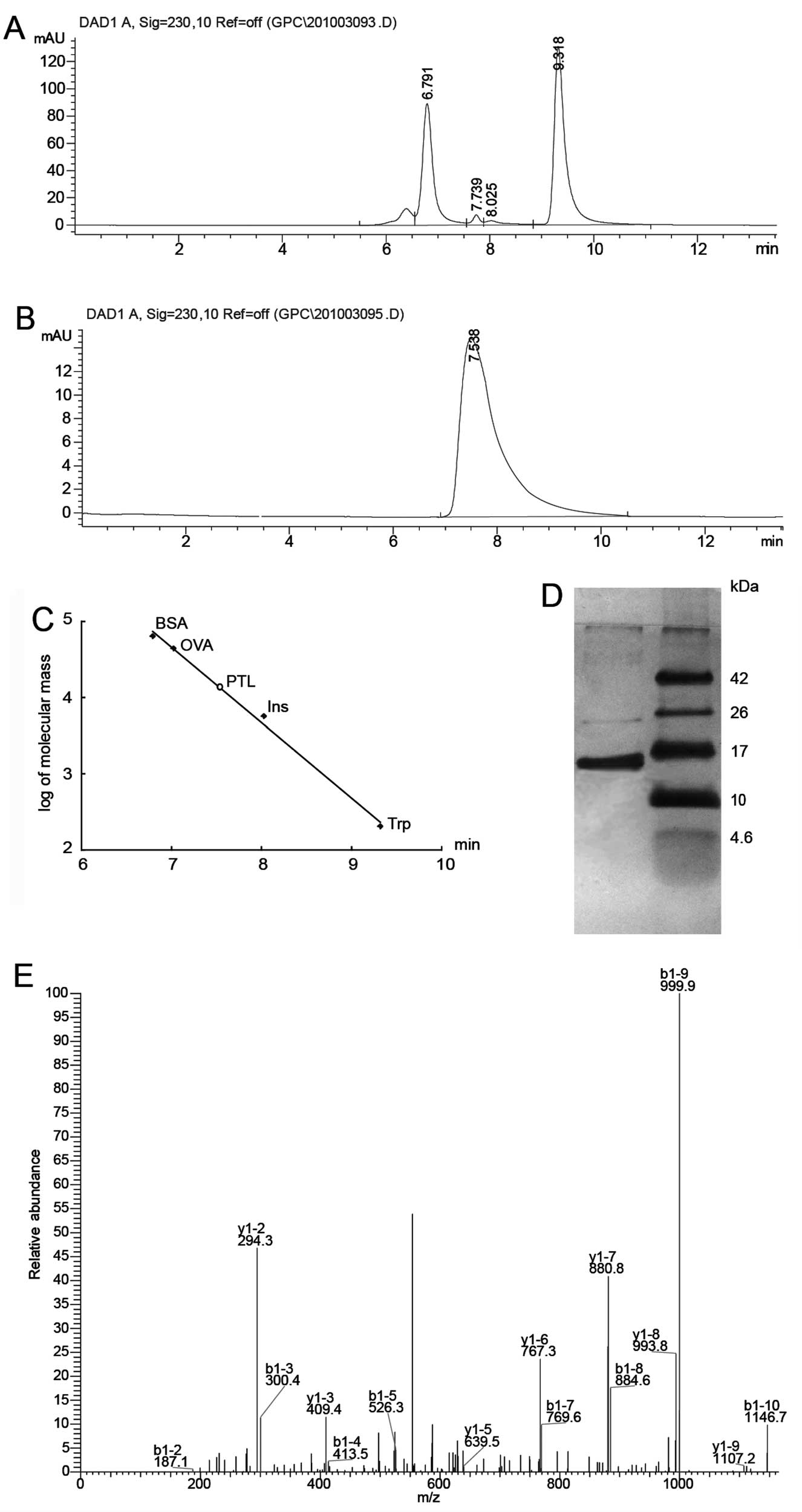
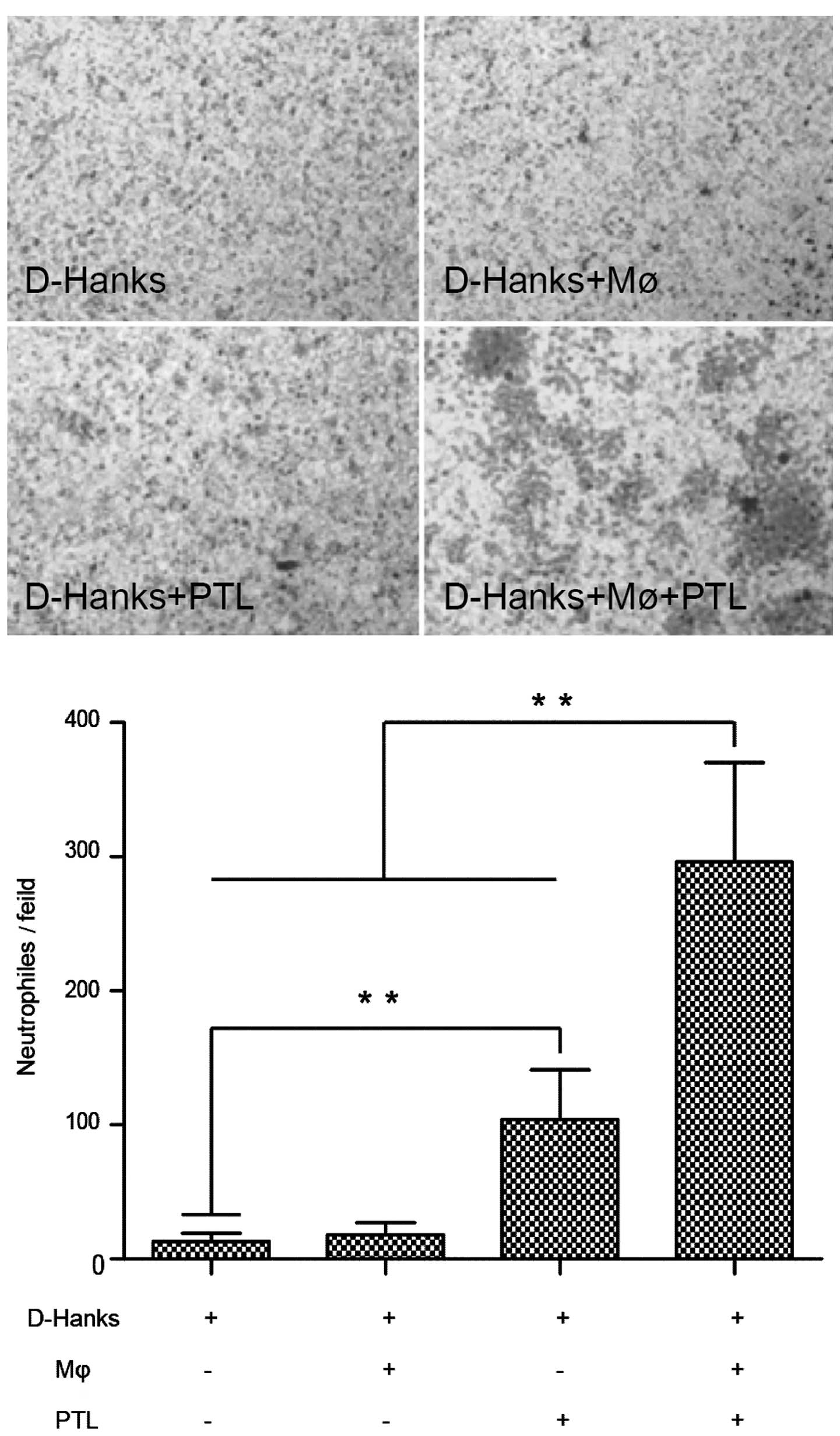
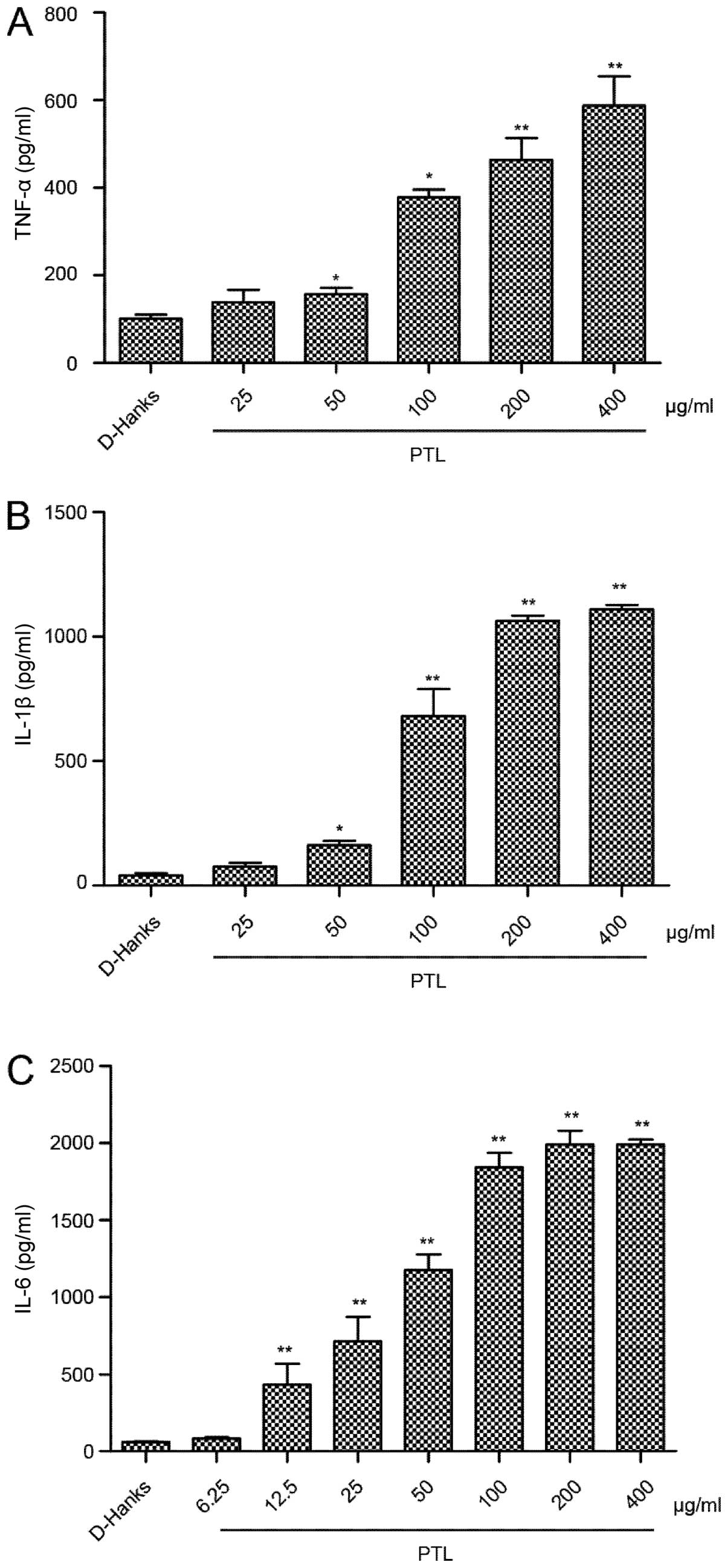
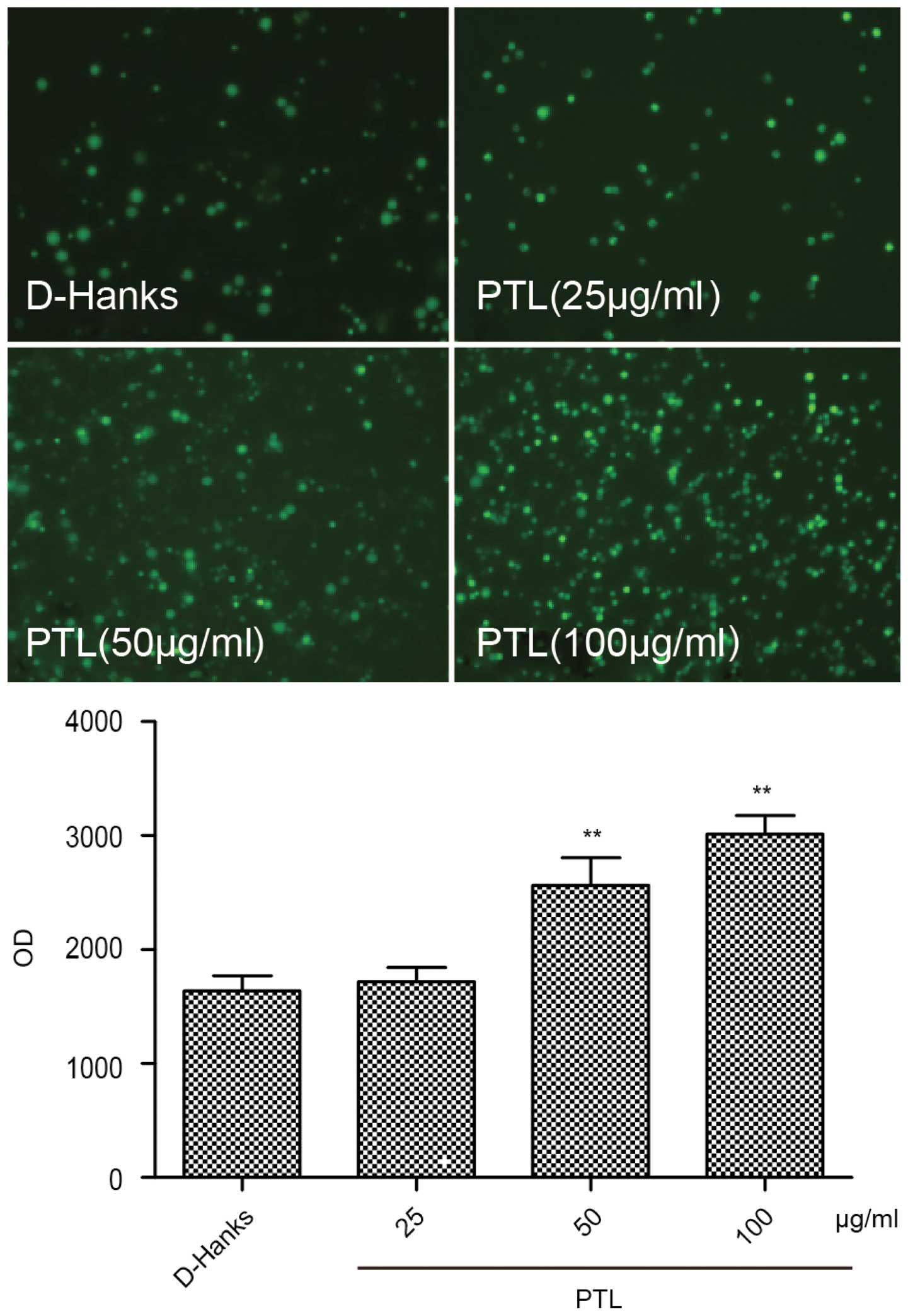
|
1
|
Peumans WJ and Van Damme EJ: Lectins as
plant defense proteins. Plant Physiol. 109:347–352. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moreira RA, Ainouz IL, De Oliveira JT and
Cavada BS: Plant lectins, chemical and biological aspects. Mem Inst
Oswaldo Cruz. 86(Suppl 2): 211–218. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cavada BS, Santos CF, Grangeiro TB, Nunes
EP, Sales PV, Ramos RL, De Sousa FA, Crisostomo CV and Calvete JJ:
Purification and characterization of a lectin from seeds of
Vatairea macrocarpa Duke. Phytochemistry. 49:675–680. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gabius HJ and Gabius S: Glycosciences:
Status and perspectives. Wiley-VCH; New York: pp. 6592002
|
|
5
|
Alencar VB, Brito GA, Alencar NM, Assreuy
AM, Pinto VP, Teixeira EH, Souza EP, Debray H, Ribeiro RA and
Cavada BS: Helianthus tuberosus agglutinin directly induces
neutrophil migration, which can be modulated/inhibited by resident
mast cells. Biochem Cell Biol. 83:659–666. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mota MR, Criddle DN, Alencar NM, Gomes RC,
Meireles AV, Santi-Gadelha T, Gadelha CA, Oliveira CC, Benevides
RG, Cavada BS, et al: Modulation of acute inflammation by a
chitin-binding lectin from Araucaria angustifolia seeds via mast
cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 374:1–10. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Santos-de-Oliveira R, Dias-Baruffi M,
Thomaz SM, Beltramini LM and Roque-Barreira MC: A neutrophil
migration-inducing lectin from Artocarpus integrifolia. J Immunol.
153:1798–1807. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Assreuy AM, Shibuya MD, Martins GJ, De
Souza ML, Cavada BS, Moreira RA, Oliveira JT, Ribeiro RA and Flores
CA: Anti-inflammatory effect of glucose-mannose binding lectins
isolated from Brazilian beans. Mediators Inflamm. 6:201–210. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Alencar NM, Teixeira EH, Assreuy AM,
Cavada BS, Flores CA and Ribeiro RA: Leguminous lectins as tools
for studying the role of sugar residues in leukocyte recruitment.
Mediators Inflamm. 8:107–113. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cavada BS, Barbosa T, Arruda S, Grangeiro
TB and Barral-Netto M: Revisiting proteus: Do minor changes in
lectin structure matter in biological activity? Lessons from and
potential biotechnological uses of the Diocleinae subtribe lectins.
Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2:123–135. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Alencar NM, Assreuy AM, Alencar VB, Melo
SC, Ramos MV, Cavada BS, Cunha FQ and Ribeiro RA: The
galactose-binding lectin from Vatairea macrocarpa seeds induces in
vivo neutrophil migration by indirect mechanism. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 35:1674–1681. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Assreuy AM, Alencar NM, Cavada BS,
Rocha-Filho DR, Feitosa RF, Cunha FQ, Calvete JJ and Ribeiro RA:
Porcine spermadhesin PSP-I/PSP-II stimulates macrophages to release
a neutrophil chemotactic substance: Modulation by mast cells. Biol
Reprod. 68:1836–1841. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alencar NM, Assreuy AM, Criddle DN, Souza
EP, Soares PM, Havt A, Aragão KS, Bezerra DP, Ribeiro RA and Cavada
BS: Vatairea macrocarpa lectin induces paw edema with leukocyte
infiltration. Protein Pept Lett. 11:195–200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alencar VB, Assreuy AM, Alencar NM,
Meireles AV, Mota MR, Aragão KS, Cajazeiras JB, Nagano CS, Brito
GA, Silva LI, et al: Lectin of Pisum arvense seeds induces in vivo
and in vitro neutrophil migration. J Pharm Pharmacol. 57:375–381.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McEver RP: Leukocyte-endothelial cell
interactions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 4:840–849. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cronstein BN and Weissmann G: The adhesion
molecules of inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 36:147–157. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Malik AB and Lo SK: Vascular endothelial
adhesion molecules and tissue inflammation. Pharmacol Rev.
48:213–229. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alencar NM, Assreuy AM, Havt A, Benevides
RG, de Moura TR, de Sousa RB, Ribeiro RA, Cunha FQ and Cavada BS:
Vatairea macrocarpa (Leguminosae) lectin activates cultured
macrophages to release chemotactic mediators. Naunyn Schmiedebergs
Arch Pharmacol. 374:275–282. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu XQ, Wu H, Yu HL, Zhao TF, Pan YZ and
Shi RJ: Purification of a lectin from Arisaema erubescens (Wall.)
Schott and its pro-inflammatory effects. Molecules. 16:9480–9494.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu HL, Zhu FG and Wu G: Toxic proteins on
Raphides from Pinellia ternata and Pinellia pedatisecta. Chin J
Tradit Chin Med Pharm. 26:1037–1042. 2011.
|
|
21
|
Sawant KV, Cho H, Lyons M, Ly LH and
McMurray DN: Guinea pig neutrophil-macrophage interactions during
infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microbes Infect.
12:828–837. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sánchez-Fidalgo S, da Silva MS, Cárdeno A,
Aparicio-Soto M, Salvador MJ, Frankland Sawaya AC, Souza-Brito AR
and de la Lastra CA: Abarema cochliacarpos reduces LPS-induced
inflammatory response in murine peritoneal macrophages regulating
ROS-MAPK signal pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 149:140–147. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim MK, Chung SW, Kim DH, Kim JM, Lee EK,
Kim JY, Ha YM, Kim YH, No JK, Chung HS, et al: Modulation of
age-related NF-kappaB activation by dietary zingerone via MAPK
pathway. Exp Gerontol. 45:419–426. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shangary S, Singh J, Kamboj SS, Kamboj KK
and Sandhu RS: Purification and properties of four monocot lectins
from the family Araceae. Phytochemistry. 40:449–455. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Anstead GM, Chandrasekar B, Zhang Q and
Melby PC: Multinutrient undernutrition dysregulates the resident
macrophage proinflammatory cytokine network, nuclear factor-kappaB
activation, and nitric oxide production. J Leukoc Biol. 74:982–991.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Silva MT: When two is better than one:
Macrophages and neutrophils work in concert in innate immunity as
complementary and cooperative partners of a myeloid phagocyte
system. J Leukoc Biol. 87:93–106. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Alencar VB, Alencar NM, Assreuy AM, Mota
ML, Brito GA, Aragão KS, Bittencourt FS, Pinto VP, Debray H,
Ribeiro RA, et al: Pro-inflammatory effect of Arum maculatum lectin
and role of resident cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:1805–1814.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gloire G, Legrand-Poels S and Piette J:
NF-kappaB activation by reactive oxygen species: Fifteen years
later. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1493–1505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim YS, Morgan MJ, Choksi S and Liu ZG:
TNF-induced activation of the Nox1 NADPH oxidase and its role in
the induction of necrotic cell death. Mol Cell. 26:675–687. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han J, Zhong CQ and Zhang DW: Programmed
necrosis: Backup to and competitor with apoptosis in the immune
system. Nat Immunol. 12:1143–1149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kung G, Konstantinidis K and Kitsis RN:
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, in the heart. Circ Res.
108:1017–1036. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McCall K: Genetic control of necrosis -
another type of programmed cell death. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
22:882–888. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|