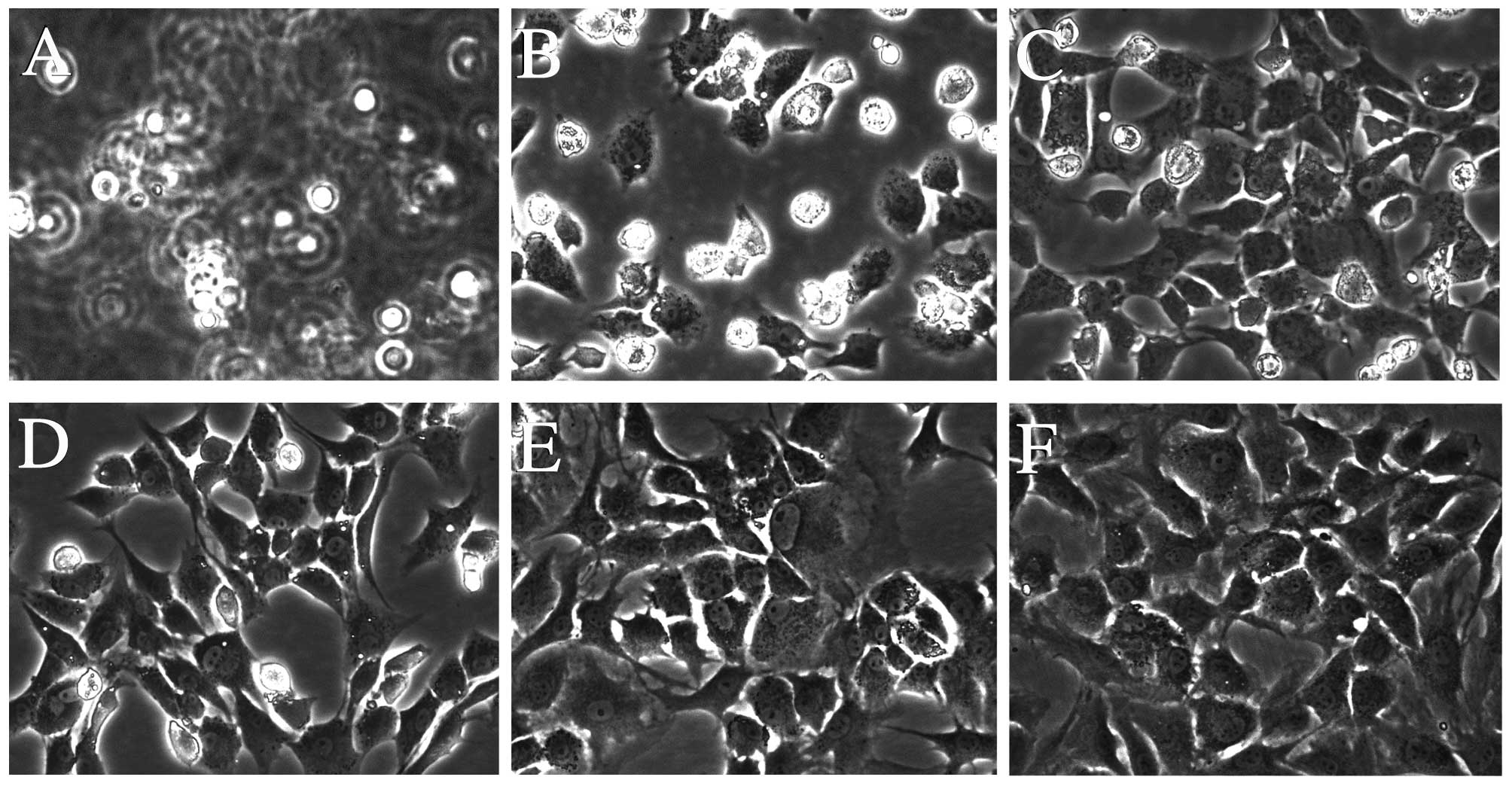
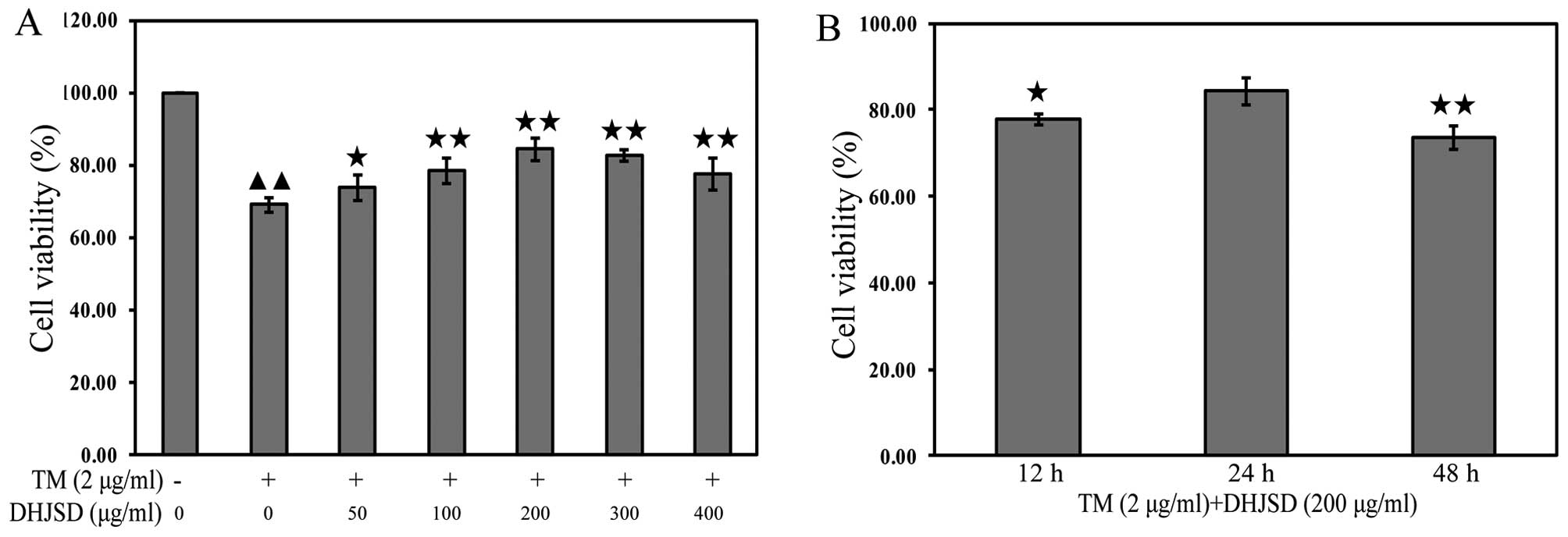
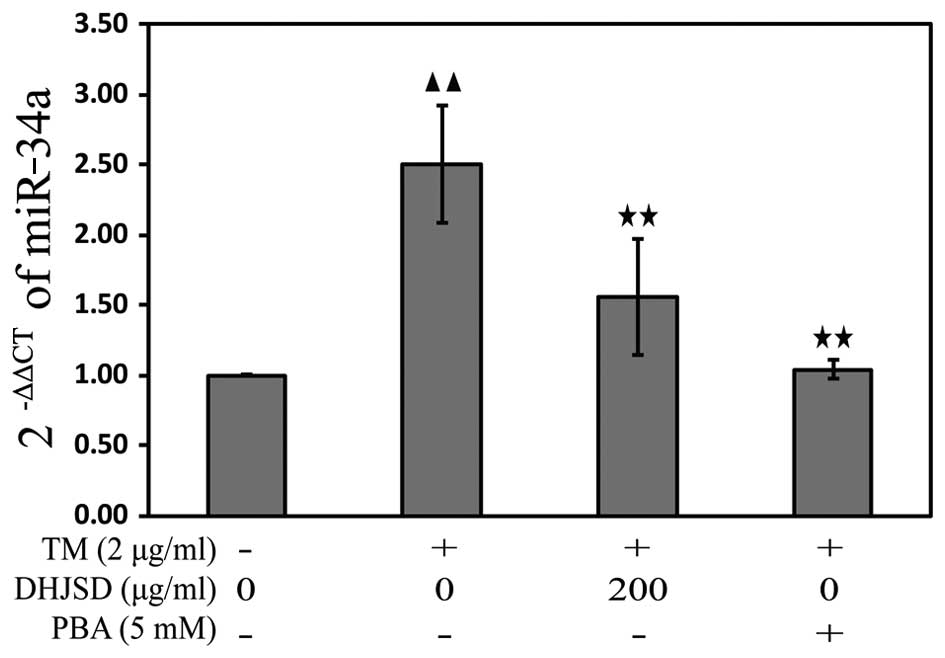
|
1
|
Bijlsma JW, Berenbaum F and Lafeber FP:
Osteoarthritis: An update with relevance for clinical practice.
Lancet. 377:2115–2126. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Loeser RF: Aging and osteoarthritis: The
role of chondrocyte senescence and aging changes in the cartilage
matrix. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17:971–979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mistry D, Oue Y, Chambers MG, Kayser MV
and Mason RM: Chondrocyte death during murine osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 12:131–141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thomas CM, Fuller CJ, Whittles CE and
Sharif M: Chondrocyte death by apoptosis is associated with
cartilage matrix degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 15:27–34.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gorman AM, Healy SJ, Jäger R and Samali A:
Stress management at the ER: Regulators of ER stress-induced
apoptosis. Pharmacol Ther. 134:306–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takada K, Hirose J, Senba K, Yamabe S,
Oike Y, Gotoh T and Mizuta H: Enhanced apoptotic and reduced
protective response in chondrocytes following endoplasmic reticulum
stress in osteoarthritic cartilage. Int J Exp Pathol. 92:232–242.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bernales S, Papa FR and Walter P:
Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu Rev
Cell Dev Biol. 22:487–508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Walter P and Ron D: The unfolded protein
response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science.
334:1081–1086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K and Murakami S:
Role of the unfolded protein response in cell death. Apoptosis.
11:5–13. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang L, Carlson SG, McBurney D and Horton
WE Jr: Multiple signals induce endoplasmic reticulum stress in both
primary and immortalized chondrocytes resulting in loss of
differentiation, impaired cell growth, and apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
280:31156–31165. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang L, McBurney D, Tang SC, Carlson SG
and Horton WE Jr: A novel role for Bcl-2 associated-athanogene-1
(Bag-1) in regulation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response
in mammalian chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 102:786–800. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lafferty-Whyte K, Cairney CJ, Jamieson NB,
Oien KA and Keith WN: Pathway analysis of senescence-associated
miRNA targets reveals common processes to different senescence
induction mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1792:341–352. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abouheif MM, Nakasa T, Shibuya H, Niimoto
T, Kongcharoensombat W and Ochi M: Silencing microRNA-34a inhibits
chondrocyte apoptosis in a rat osteoarthritis model in vitro.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:2054–2060. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zheng CS, Xu XJ, Ye HZ, Wu GW, Li XH,
Huang SP and Liu XX: Computational approaches for exploring the
potential synergy and polypharmacology of Duhuo Jisheng decoction
in the therapy of osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 7:1812–1818.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu F, Liu G, Liang W, Ye H, Weng X, Lin
P, Li H, Chen J, Liu X and Li X: Duhuo Jisheng decoction treatment
inhibits the sodium nitroprussiate induced apoptosis of
chondrocytes through the mitochondrial dependent signaling pathway.
Int J Mol Med. 34:1573–1580. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li H, Li X, Liu G, Chen J, Weng X, Liu F,
Xu H, Liu X and Ye H: Bauhinia championi (Benth.) Benth.
polysaccharides upregulate Wnt/β-catenin signaling in chondrocytes.
Int J Mol Med. 32:1329–1336. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu G, Huang K, Yu J, Gopalakrishna-Pillai
S, Kong J, Xu H, Liu Z, Zhang K, Xu J, Luo Y, et al: Identification
of miRNA signatures during the differentiation of hESCs into
retinal pigment epithelial cells. PLoS One. 7:e372242012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu F, Li X, Cai L, Li H, Chen J, Wong X,
Xu H, Zheng C, Liu X and Ye H: Achyranthes bidentata
polysaccharides induce chon-drocyte proliferation via the promotion
of the G1/S cell cycle transition. Mol Med Rep. 7:935–940.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Peng J, Wu M, Ye H, Zheng C, Wu G,
Xu H, Chen X and Liu X: BMP2 promotes chondrocyte proliferation via
the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 4:621–626.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li X, Du M, Liu X, Chen W, Wu M, Lin J and
Wu G: Millimeter wave treatment promotes chondrocyte proliferation
by upregulating the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and
cyclin A. Int J Mol Med. 26:77–84. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zong WX, Li C, Hatzivassiliou G, Lindsten
T, Yu QC, Yuan J and Thompson CB: Bax and Bak can localize to the
endoplasmic reticulum to initiate apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
162:59–69. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Riedl SJ and Shi Y: Molecular mechanisms
of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:897–907. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gupta S, Cuffe L, Szegezdi E, Logue SE,
Neary C, Healy S and Samali A: Mechanisms of ER Stress-Mediated
Mitochondrial Membrane Permeabilization. Int J Cell Biol.
2010:1702152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hua B, Abbas E, Hayes A, Ryan P, Nelson L
and O'Brien K: Reliability of Chinese medicine diagnostic variables
in the examination of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. J
Altern Complement Med. 18:1028–1037. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Wei S, Liu T, Pang J, Gao N, Ding
D, Duan T, Cao Y, Zheng Y and Zhan H: Effectiveness, medication
patterns, and adverse events of traditional chinese herbal patches
for osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2014:3431762014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin JH, Li H, Yasumura D, Cohen HR, Zhang
C, Panning B, Shokat KM, Lavail MM and Walter P: IRE1 signaling
affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science.
318:944–949. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yeung BH, Kwan BW, He QY, Lee AS, Liu J
and Wong AS: Glucose-regulated protein 78 as a novel effector of
BRCA1 for inhibiting stress-induced apoptosis. Oncogene.
27:6782–6789. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
DuRose JB, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ,
Rothblum LI and Niwa M: Phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation
initiation factor 2α coordinates rRNA transcription and translation
inhibition during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol.
29:4295–4307. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hotamisligil GS: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell.
140:900–917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sovolyova N, Healy S, Samali A and Logue
SE: Stressed to death - mechanisms of ER stress-induced cell death.
Biol Chem. 395:1–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T
and Mori K: XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in
response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription
factor. Cell. 107:881–891. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ouyang YB, Xu LJ, Emery JF, Lee AS and
Giffard RG: Overexpressing GRP78 influences Ca2+
handling and function of mitochondria in astrocytes after
ischemia-like stress. Mitochondrion. 11:279–286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Chipuk JE, Moldoveanu T, Llambi F, Parsons
MJ and Green DR: The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol Cell. 37:299–310.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Scorrano L, Oakes SA, Opferman JT, Cheng
EH, Sorcinelli MD, Pozzan T and Korsmeyer SJ: BAX and BAK
regulation of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+: A control
point for apoptosis. Science. 300:135–139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rodriguez DA, Zamorano S, Lisbona F,
Rojas-Rivera D, Urra H, Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Armisen R, Henriquez DR,
Cheng EH, Letek M, et al: BH3-only proteins are part of a
regulatory network that control the sustained signalling of the
unfolded protein response sensor IRE1α. EMBO J. 31:2322–2335. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hetz C, Bernasconi P, Fisher J, Lee AH,
Bassik MC, Antonsson B, Brandt GS, Iwakoshi NN, Schinzel A,
Glimcher LH, et al: Proapoptotic BAX and BAK modulate the unfolded
protein response by a direct interaction with IRE1α. Science.
312:572–576. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rodriguez D, Rojas-Rivera D and Hetz C:
Integrating stress signals at the endoplasmic reticulum: The BCL-2
protein family rheostat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:564–574. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen Y and Brandizzi F: IRE1: ER stress
sensor and cell fate executor. Trends Cell Biol. 23:547–555. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Takenouchi H,
Shibata T and Yasuhiko Y: An endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific
caspase cascade in apoptosis. Cytochrome c-independent activation
of caspase-9 by caspase-12. J Biol Chem. 277:34287–34294. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Costinean S and
Croce CM: MicroRNAs, the immune system and rheumatic disease. Nat
Clin Pract Rheumatol. 4:534–541. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
O'Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA and
Baltimore D: Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in
the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:111–122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dai R and Ahmed SA: MicroRNA, a new
paradigm for understanding immunoregulation, inflammation, and
autoimmune diseases. Transl Res. 157:163–179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bartoszewska S, Kochan K, Madanecki P,
Piotrowski A, Ochocka R, Collawn JF and Bartoszewski R: Regulation
of the unfolded protein response by microRNAs. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
18:555–578. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|