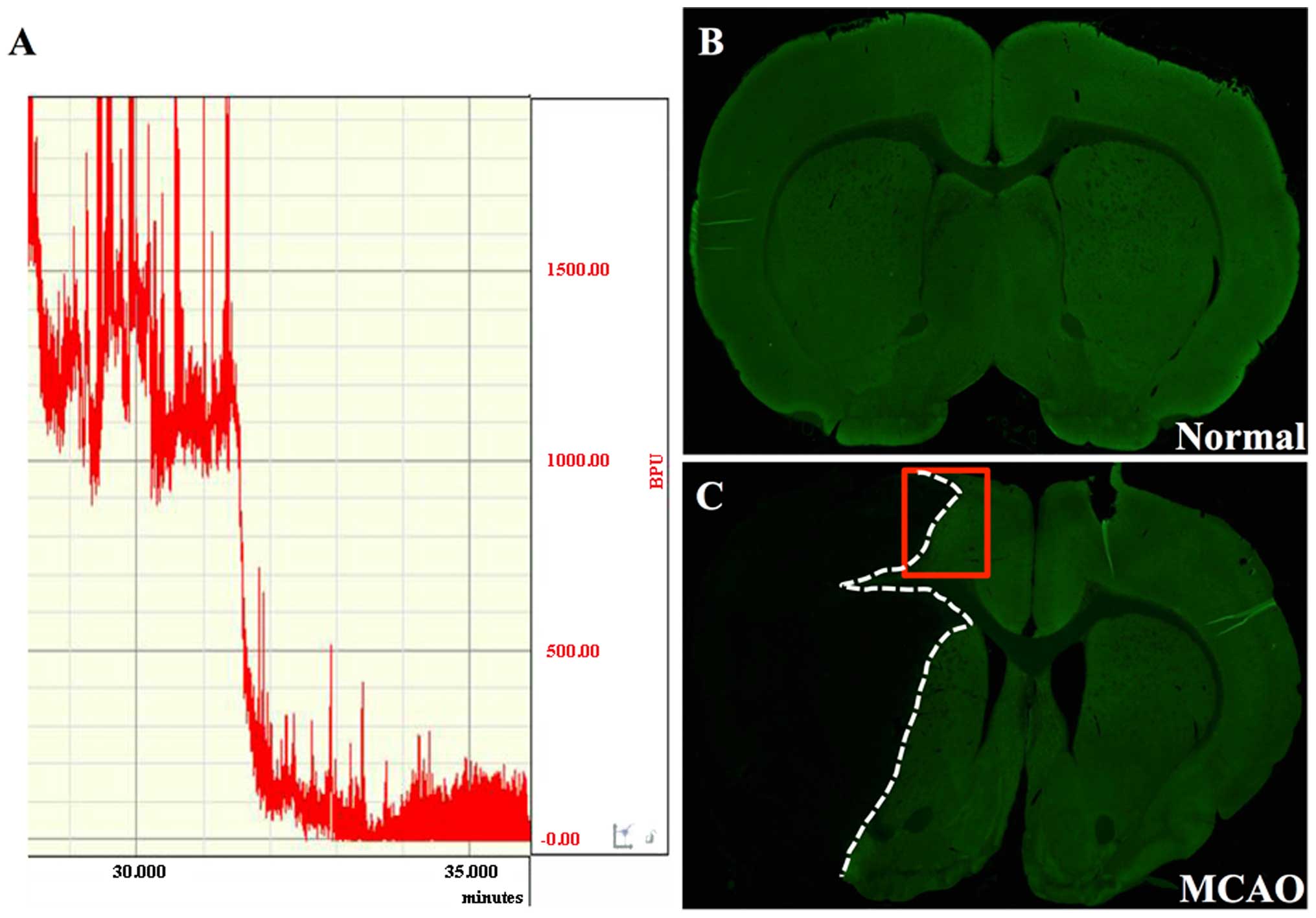
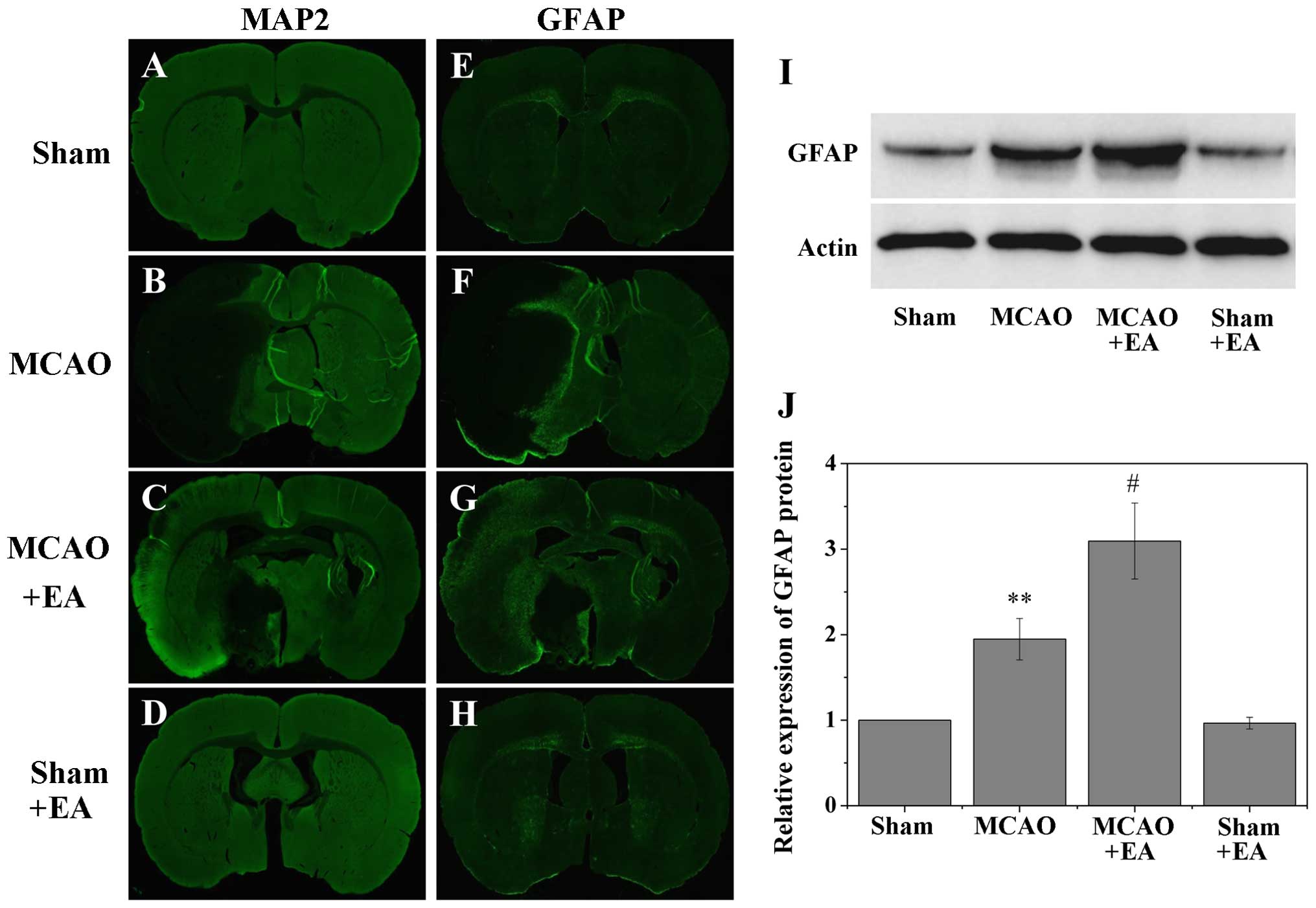
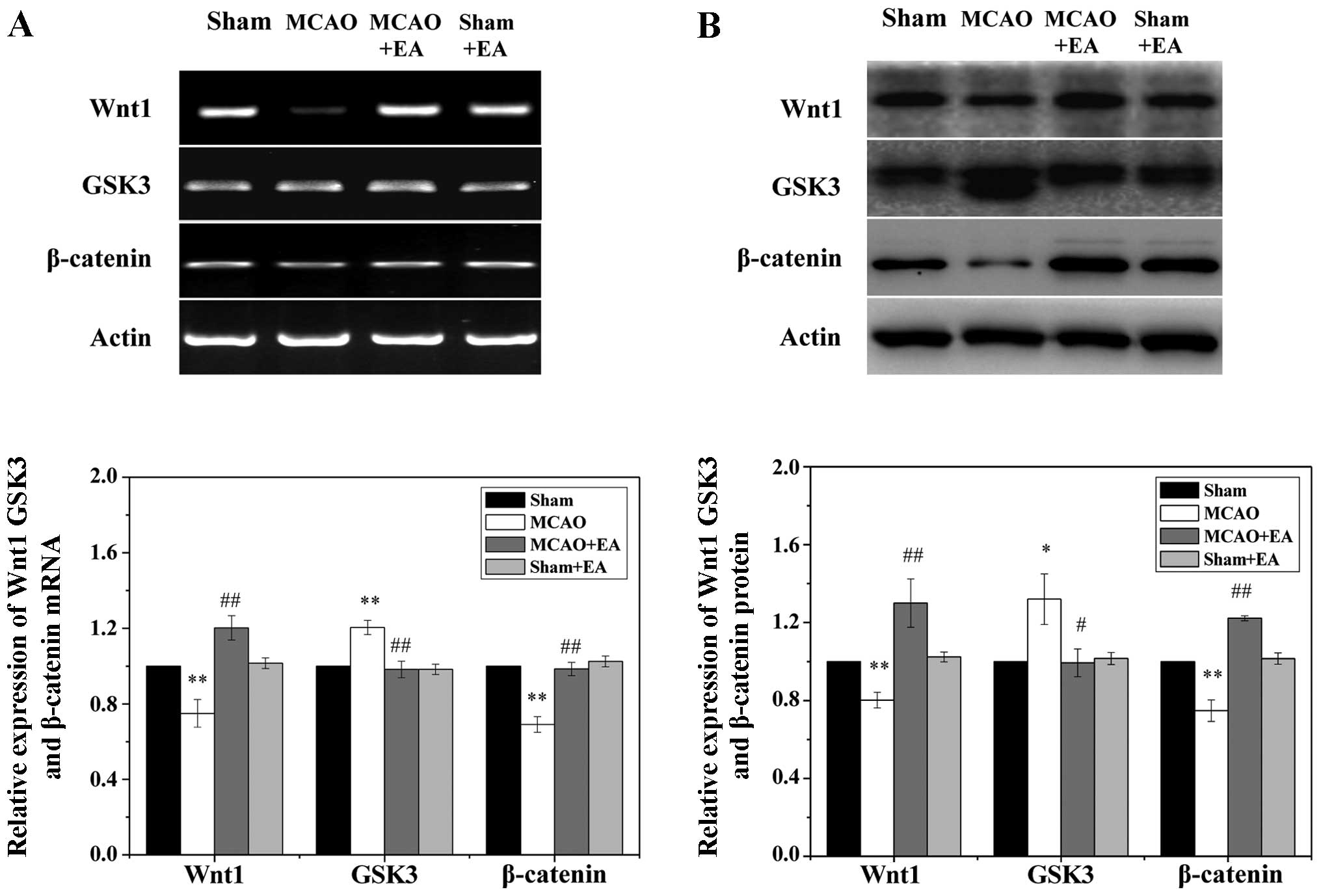
|
1
|
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M and Davis
SM: Stroke. Lancet. 371:1612–1623. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al
American Heart Association: Statistics Committee and Stroke
Statistics Subcommittee: Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2012
update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
125. pp. e2–e220. 2012, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hirabayashi Y, Itoh Y, Tabata H, Nakajima
K, Akiyama T, Masuyama N and Gotoh Y: The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway
directs neuronal differentiation of cortical neural precursor
cells. Development. 131:2791–2801. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang H, Ren C, Gao X, Takahashi T,
Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK and Zhao H: Hypothermia blocks
beta-catenin degradation after focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res.
1198:182–187. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mastroiacovo F, Busceti CL, Biagioni F,
Moyanova SG, Meisler MH, Battaglia G, Caricasole A, Bruno V and
Nicoletti F: Induction of the Wnt antagonist, Dickkopf-1,
contributes to the development of neuronal death in models of brain
focal ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:264–276. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Scott EL and Brann DW: Estrogen regulation
of Dkk1 and Wnt/β-Catenin signaling in neurodegenerative disease.
Brain Res. 1514:63–74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Sun FL, Wang W, Zuo W, Xue JL, Xu JD, Ai
HX, Zhang L, Wang XM and Ji XM: Promoting neurogenesis via
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway accounts for the neurorestorative
effects of morroniside against cerebral ischemia injury. Eur J
Pharmacol. 738:214–221. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pöschl J, Grammel D, Dorostkar MM,
Kretzschmar HA and Schüller U: Constitutive activation of β-catenin
in neural progenitors results in disrupted proliferation and
migration of neurons within the central nervous system. Dev Biol.
374:319–332. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, Désiré L,
Mira H, Consiglio A, Lein ES, Jessberger S, Lansford H, Dearie AR
and Gage FH: Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal
neurogenesis. Nature. 437:1370–1375. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhai XF, Chen Z, Li B, Shen F, Fan J, Zhou
WP, Yang YK, Xu J, Qin X, Li LQ and Ling CQ: Traditional herbal
medicine in preventing recurrence after resection of small
hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter randomized controlled
trial. J Integr Med. 11:90–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liang J, Li F, Wei C, Song H, Wu L, Tang Y
and Jia J: Rationale and design of a multicenter, phase 2 clinical
trial to investigate the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine
SaiLuoTong in vascular dementia. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis.
23:2626–2634. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang LN, Wang Y, Lu Y, Yin ZF, Zhang YH,
Aslanidi GV, Srivastava A, Ling CQ and Ling C: Pristimerin enhances
recombinant adeno-associated virus vector-mediated transgene
expression in human cell lines in vitro and murine hepatocytes in
vivo. J Integr Med. 12:20–34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ling CQ, Wang LN, Wang Y, Zhang YH, Yin
ZF, Wang M and Ling C: The roles of traditional Chinese medicine in
gene therapy. J Integr Med. 12:67–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu H, Shen X, Tang H, Li J, Xiang T and
Yu W: Using microPET imaging in quantitative verification of the
acupuncture effect in ischemia stroke treatment. Sci Rep.
3:10702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim JH, Choi KH, Jang YJ, Bae SS, Shin BC,
Choi BT and Shin HK: Electroacupuncture acutely improves cerebral
blood flow and attenuates moderate ischemic injury via an
endothelial mechanism in mice. PLoS One. 8:e567362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jin Z, Liang J, Wang J and Kolattukudy PE:
Delayed brain ischemia tolerance induced by electroacupuncture
pretreatment is mediated via MCP-induced protein 1. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tao J, Xue XH, Chen LD, Yang SL, Jiang M,
Gao YL and Wang XB: Electroacupuncture improves neurological
deficits and enhances proliferation and differentiation of
endogenous nerve stem cells in rats with focal cerebral ischemia.
Neurol Res. 32:198–204. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mazighi M, Meseguer E, Labreuche J and
Amarenco P: Bridging therapy in acute ischemic stroke: a systematic
review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 43:1302–1308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu P, Mills E, Moher D and Seely D:
Acupuncture in post-stroke rehabilitation: a systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomized trials. Stroke. 41:e171–e179. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tao J, Chen B, Gao Y, Yang S, Huang J,
Jiang X, Wu Y, Peng J, Hong Z and Chen L: Electroacupuncture
enhances hippocampal NSCs proliferation in cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via activation of notch signaling
pathway. Int J Neurosci. 124:204–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shimada IS, LeComte MD, Granger JC,
Quinlan NJ and Spees JL: Self-renewal and differentiation of
reactive astrocyte-derived neural stem/progenitor cells isolated
from the cortical peri-infarct area after stroke. J Neurosci.
32:7926–7940. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakagomi T, Taguchi A, Fujimori Y, Saino
O, Nakano-Doi A, Kubo S, Gotoh A, Soma T, Yoshikawa H, Nishizaki T,
et al: Isolation and characterization of neural stem/progenitor
cells from post-stroke cerebral cortex in mice. Eur J Neurosci.
29:1842–1852. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakagomi T, Molnár Z, Nakano-Doi A,
Taguchi A, Saino O, Kubo S, Clausen M, Yoshikawa H, Nakagomi N and
Matsuyama T: Ischemia-induced neural stem/progenitor cells in the
pia mater following cortical infarction. Stem Cells Dev.
20:2037–2051. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsao-Wu G, Savalos
RA, Davidson C and Sharp FR: A semiautomated method for measuring
brain infarct volume. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 10:290–293. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H,
Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Simcha I,
Albanese C, D'Amico M, Pestell R and Ben-Ze'ev A: The cyclin D1
gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:5522–5527. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|