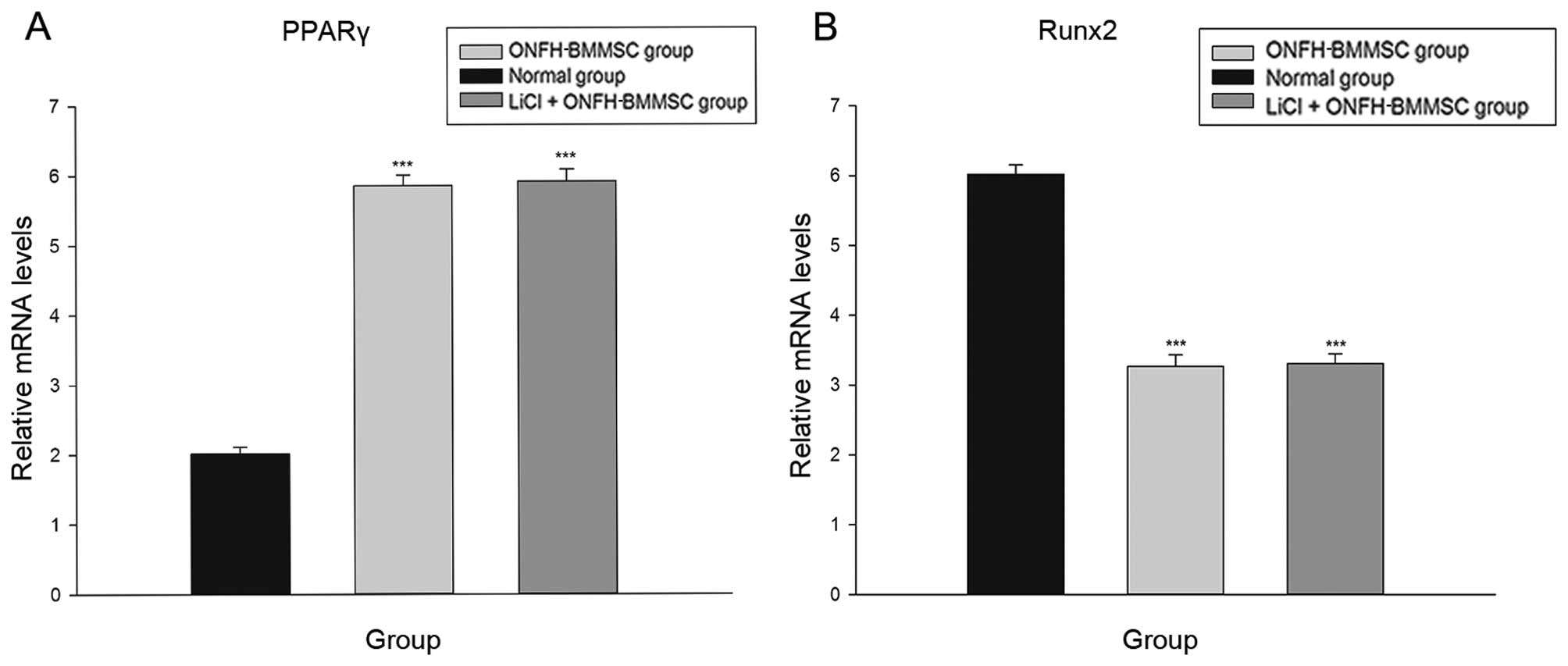
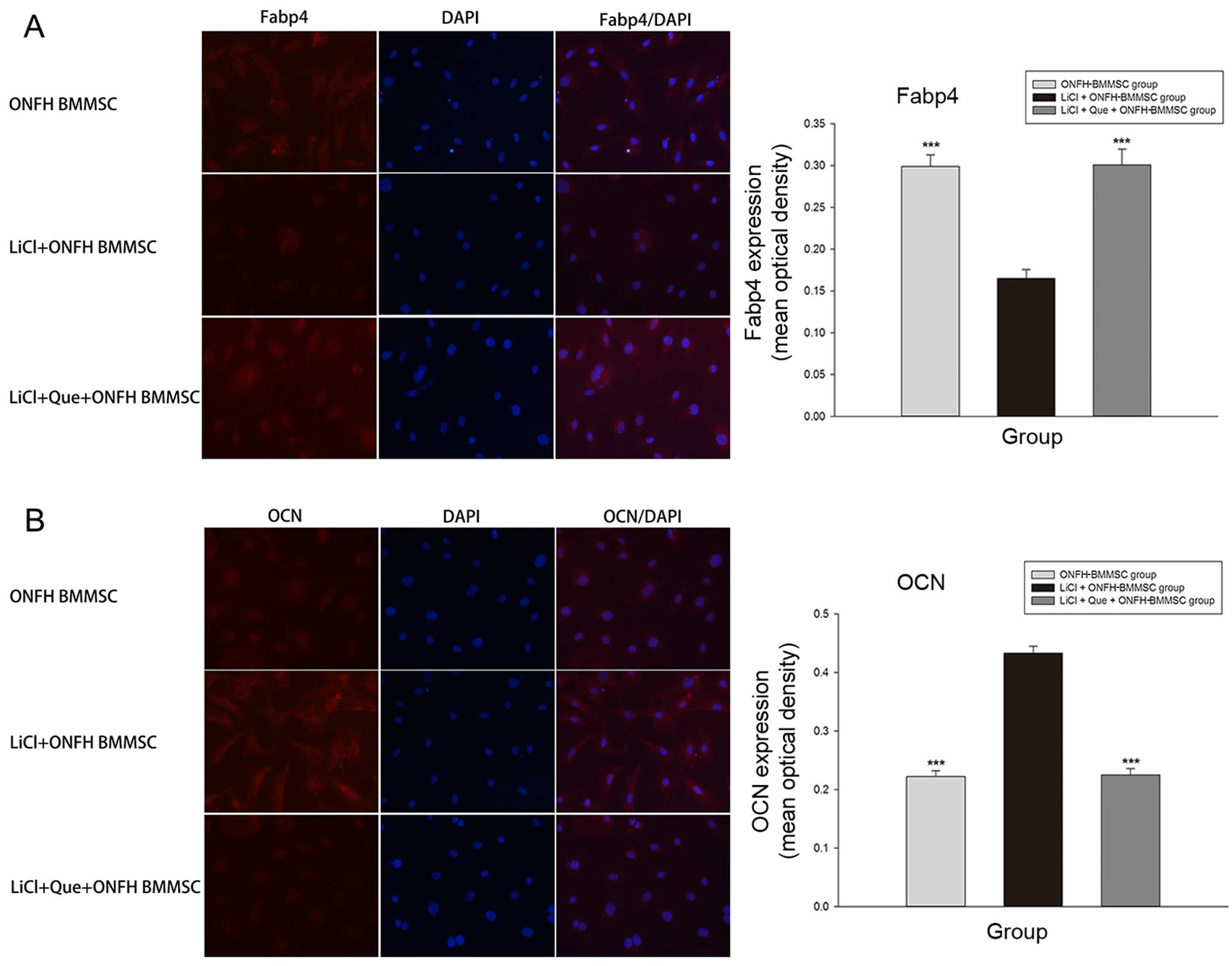
|
1
|
Sun Z, Yang S, Ye S, Zhang Y, Xu W, Zhang
B, Liu X, Mo F and Hua W: Aberrant CpG islands' hypermethylation of
ABCB1 in mesenchymal stem cells of patients with steroid-associated
osteonecrosis. J Rheumatol. 40:1913–1920. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lieberman JR, Berry DJ, Mont MA, Aaron RK,
Callaghan JJ, Rajadhyaksha AD and Urbaniak JR: Osteonecrosis of the
hip: management in the 21st century. Instr Course Lect. 52:337–355.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Webster RA, Blaber SP, Herbert BR, Wilkins
MR and Vesey G: The role of mesenchymal stem cells in veterinary
therapeutics - a review. N Z Vet J. 60:265–272. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hernigou P and Beaujean F: Abnormalities
in the bone marrow of the iliac crest in patients who have
osteonecrosis secondary to corticosteroid therapy or alcohol abuse.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 79:1047–1053. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seamon J, Keller T, Saleh J and Cui Q: The
pathogenesis of nontraumatic osteonecrosis. Arthritis (Egypt).
2012:6017632012.
|
|
6
|
Abdallah BM and Kassem M: New factors
controlling the balance between osteoblastogenesis and
adipogenesis. Bone. 50:540–545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sheng H, Sheng CJ, Cheng XY, Zhang G, Lee
KM, Leung KS, Qu S and Qin L: Pathomorphological changes of bone
marrow adipocytes in process of steroid-associated osteonecrosis.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 6:1046–1050. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Taipaleenmäki H, Abdallah BM, AlDahmash A,
Säämänen AM and Kassem M: Wnt signalling mediates the cross-talk
between bone marrow derived pre-adipocytic and pre-osteoblastic
cell populations. Exp Cell Res. 317:745–756. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Franceschi RT and Xiao G: Regulation of
the osteoblast-specific transcription factor, Runx2: responsiveness
to multiple signal transduction pathways. J Cell Biochem.
88:446–454. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg GH,
Tan Y, Zhang Z, Lin X and He X: Control of beta-catenin
phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell.
108:837–847. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Young W: Review of lithium effects on
brain and blood. Cell Transplant. 18:951–975. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wexler EM, Geschwind DH and Palmer TD:
Lithium regulates adult hippocampal progenitor development through
canonical Wnt pathway activation. Mol Psychiatry. 13:285–292. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Galli C, Piemontese M, Lumetti S, Manfredi
E, Macaluso GM and Passeri G: GSK3b-inhibitor lithium chloride
enhances activation of Wnt canonical signaling and osteoblast
differentiation on hydrophilic titanium surfaces. Clin Oral
Implants Res. 24:921–927. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Itoigawa Y, Kishimoto KN, Sano H, Kaneko K
and Itoi E: Molecular mechanism of fatty degeneration in rotator
cuff muscle with tendon rupture. J Orthop Res. 29:861–866. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sen B, Xie Z, Case N, Ma M, Rubin C and
Rubin J: Mechanical strain inhibits adipogenesis in mesenchymal
stem cells by stimulating a durable beta-catenin signal.
Endocrinology. 149:6065–6075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen S, Li J, Peng H, Zhou J and Fang H:
Administration of erythropoietin exerts protective effects against
glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats.
Int J Mol Med. 33:840–848. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Panepucci RA, Siufi JLC, Silva WA Jr,
Proto-Siquiera R, Neder L, Orellana M, Rocha V, Covas DT and Zago
MA: Comparison of gene expression of umbilical cord vein and bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 22:1263–1278.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Boku S, Nakagawa S, Masuda T, Nishikawa H,
Kato A, Kitaichi Y, Inoue T and Koyama T: Glucocorticoids and
lithium reciprocally regulate the proliferation of adult dentate
gyrus-derived neural precursor cells through GSK-3beta and
beta-catenin/TCF pathway. Neuropsychopharmacology. 34:805–815.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Park CH, Chang JY, Hahm ER, Park S, Kim HK
and Yang CH: Quercetin, a potent inhibitor against beta-catenin/Tcf
signaling in SW480 colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
328:227–234. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cui Q, Wang GJ and Balian G:
Pluripotential marrow cells produce adipocytes when transplanted
into steroid-treated mice. Connect Tissue Res. 41:45–56. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jope RS: Lithium and GSK-3: One inhibitor,
two inhibitory actions, multiple outcomes. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
24:441–443. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mai Y, Zhang Z, Yang H, Dong P, Chu G,
Yang G and Sun S: BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI)
inhibits the adipogenesis of porcine preadipocytes through
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Cell Biol. 92:172–182.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
De Boer J, Wang HJ and Van Blitterswijk C:
Effects of Wnt signaling on proliferation and differentiation of
human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 10:393–401. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gregory CA, Perry AS, Reyes E, Conley A,
Gunn WG and Prockop DJ: Dkk-1-derived synthetic peptides and
lithium chloride for the control and recovery of adult stem cells
from bone marrow. J Biol Chem. 280:2309–2323. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Makita N, Suzuki M, Asami S, Takahata R,
Kohzaki D, Kobayashi S, Hakamazuka T and Hozumi N: Two of four
alternatively spliced isoforms of RUNX2 control osteocalcin gene
expression in human osteoblast cells. Gene. 413:8–17. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin GT, Tseng HF, Chang CK, Chuang LY, Liu
CS, Yang CH, Tu CJ, Wang EC, Tan HF, Chang CC, et al: SNP
combinations in chromosome-wide genes are associated with bone
mineral density in Taiwanese women. Chin J Physiol. 51:32–41.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mackay DL, Tesar PJ, Liang LN and
Haynesworth SE: Characterizing medullary and human mesenchymal stem
cell-derived adipocytes. J Cell Physiol. 207:722–728. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang XL, Wang N, Zheng LZ, Xie XH, Yao D,
Liu MY, Yao ZH, Dai Y, Zhang G, Yao XS and Qin L: Phytoestrogenic
molecule desmethylicaritin suppressed adipogenesis via
Wnt/β-catenin 1signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 714:254–260.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Corrado A, Neve A, Macchiarola A, Gaudio
A, Marucci A and Cantatore FP: RANKL/OPG ratio and DKK-1 expression
in primary osteoblastic cultures from osteoarthritic and
osteoporotic subjects. J Rheumatol. 40:684–694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN,
Lucas PC, Erickson RL and MacDougald OA: Inhibition of adipogenesis
by Wnt signaling. Science. 289:950–953. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu J and Farmer SR: Regulating the
balance between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
and beta-catenin signaling during adipogenesis. A glycogen synthase
kinase 3beta phosphorylation-defective mutant of beta-catenin
inhibits expression of a subset of adipogenic genes. J Biol Chem.
279:45020–45027. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bennett CN, Ross SE, Longo KA, Bajnok L,
Hemati N, Johnson KW, Harrison SD and MacDougald OA: Regulation of
Wnt signaling during adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 277:30998–31004.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hughes K, Nikolakaki E, Plyte SE, Totty NF
and Woodgett JR: Modulation of the glycogen synthase kinase-3
family by tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 12:803–808.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Garza JC, Guo M, Zhang W and Lu XY: Leptin
restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a chronic unpredictable
stress model of depression and reverses glucocorticoid-induced
inhibition of GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. Mol Psychiatry.
17:790–808. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|