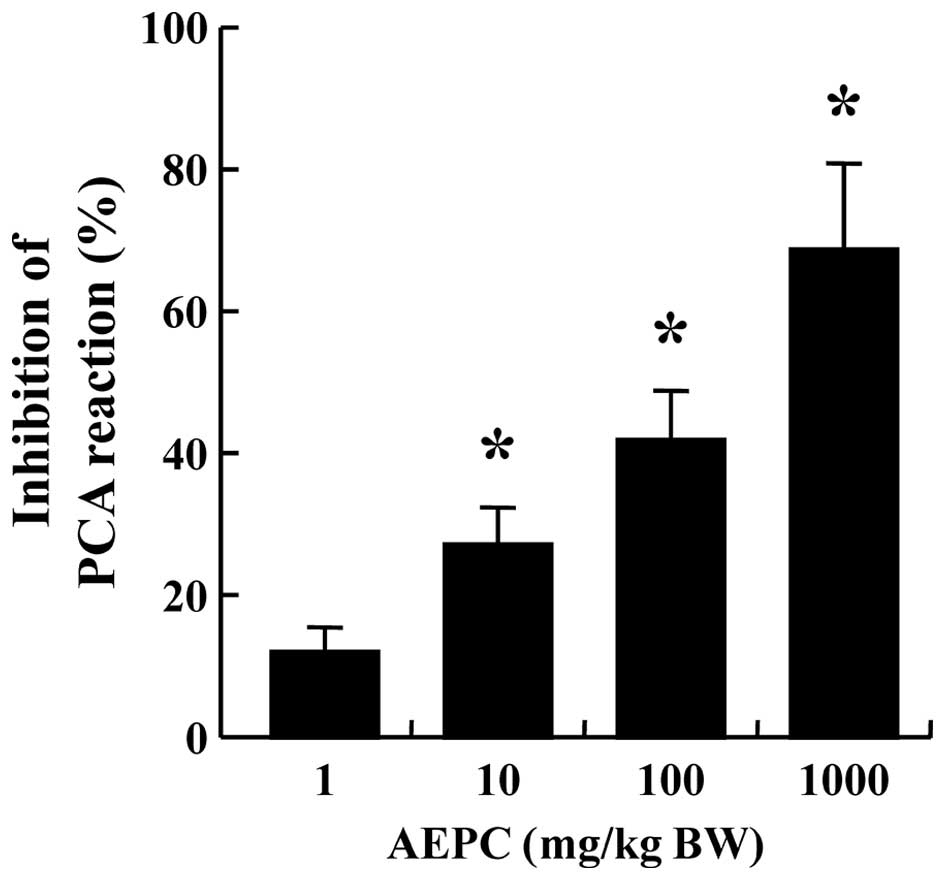
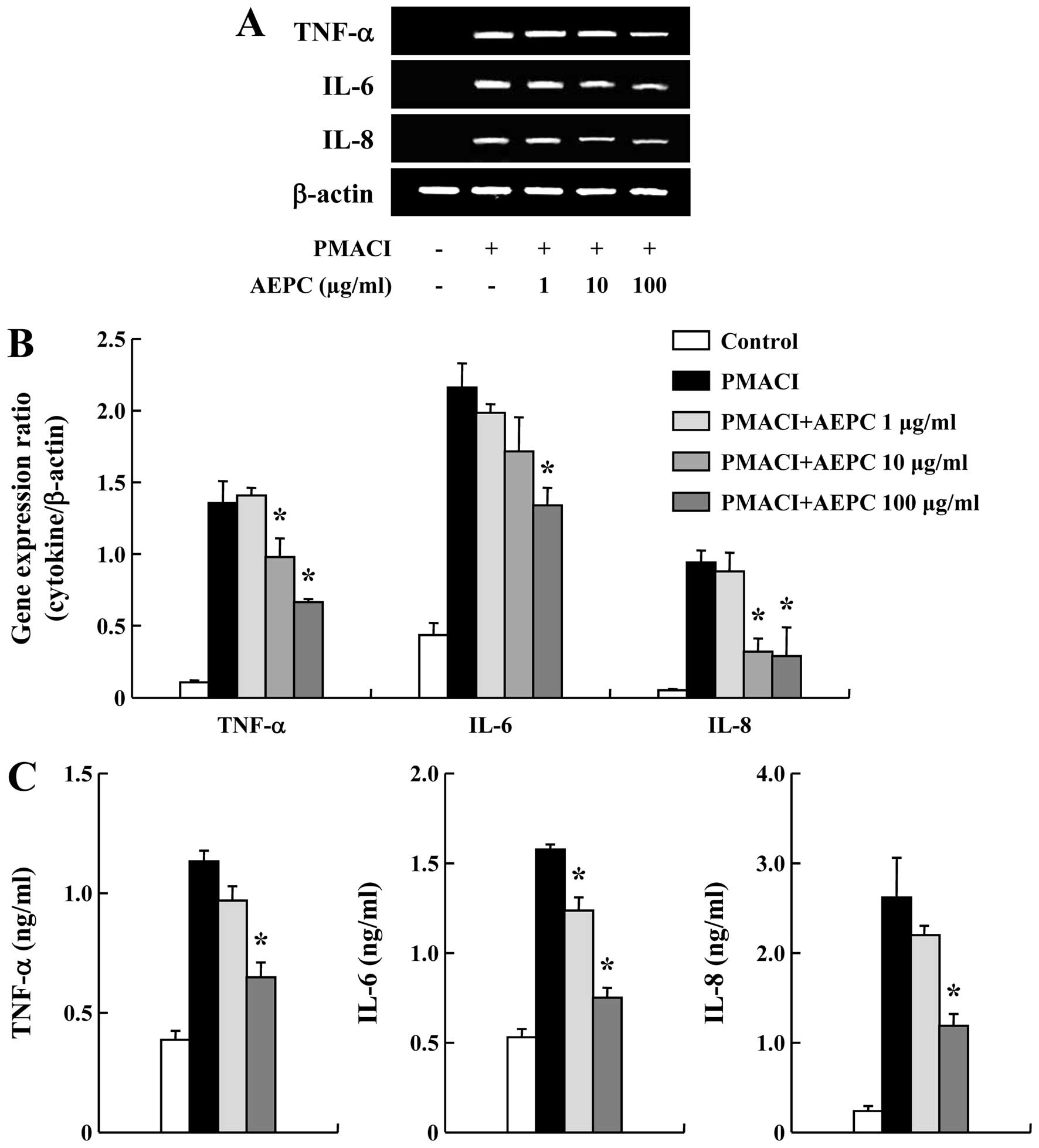
|
1
|
Takizawa H: Impact of air pollution on
allergic diseases. Korean J Intern Med. 26:262–273. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nauta AJ, Engels F, Knippels LM, Garssen
J, Nijkamp FP and Redegeld FA: Mechanisms of allergy and asthma.
Eur J Pharmacol. 585:354–360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Galli SJ, Kalesnikoff J, Grimbaldeston MA,
Piliponsky AM, Williams CM and Tsai M: Mast cells as 'tunable'
effector and immunoregulatory cells: Recent advances. Annu Rev
Immunol. 23:749–786. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jutel M, Blaser K and Akdis CA: Histamine
in allergic inflammation and immune modulation. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 137:82–92. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pandey V, Mihara S, Fensome-Green A,
Bolsover S and Cockcroft S: Monomeric IgE stimulates NFAT
translocation into the nucleus, a rise in cytosol Ca2+,
degranulation, and membrane ruffling in the cultured rat basophilic
leukemia-2H3 mast cell line. J Immunol. 172:4048–4058. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bradding P, Feather IH, Wilson S, Bardin
PG, Heusser CH, Holgate ST and Howarth PH: Immunolocalization of
cytokines in the nasal mucosa of normal and perennial rhinitic
subjects. The mast cell as a source of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6 in
human allergic mucosal inflammation. J Immunol. 151:3853–3865.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Azzolina A, Bongiovanni A and Lampiasi N:
Substance P induces TNF-alpha and IL-6 production through NF kappa
B in peritoneal mast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1643:75–83. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim SH, Jun CD, Suk K, Choi BJ, Lim H,
Park S, Lee SH, Shin HY, Kim DK and Shin TY: Gallic acid inhibits
histamine release and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in mast
cells. Toxicol Sci. 91:123–131. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shin TY, Kim SH, Suk K, Ha JH, Kim I, Lee
MG, Jun CD, Kim SY, Lim JP and Eun JS: Anti-allergic effects of
Lycopus lucidus on mast cell-mediated allergy model. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 209:255–262. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hsu HC, Yang WC, Tsai WJ, Chen CC, Huang
HY and Tsai YC: Alpha-bulnesene, a novel PAF receptor antagonist
isolated from Pogostemon cablin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
345:1033–1038. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu YP: Chinese Materia Medica. Harwood
Academic Publishers; The Netherlands: pp. 307–308. 1998
|
|
12
|
Kocevski D, Du M, Kan J, Jing C, Lačanin I
and Pavlović H: Antifungal effect of Allium tuberosum, Cinnamomum
cassia, and Pogostemon cablin essential oils and their components
against population of Aspergillus species. J Food Sci.
78:M731–M737. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jeong JB, Choi J, Lou Z, Jiang X and Lee
SH: Patchouli alcohol, an essential oil of Pogostemon cablin,
exhibits anti-tumorigenic activity in human colorectal cancer
cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 16:184–190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Y, Kinoshita K, Koyama K, Takahashi
K, Tai T, Nunoura Y and Watanabe K: Anti-emetic principles of
Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. Phytomedicine. 6:89–93. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kiuchi F, Matsuo K, Ito M, Qui TK and
Honda G: New sesquiterpene hydroperoxides with trypanocidal
activity from Pogostemon cablin. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
52:1495–1496. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ichikawa K, Kinoshita T and Sankawa U: The
screening of Chinese crude drugs for Ca2+ antagonist
activity: identification of active principles from the aerial part
of Pogostemon cablin and the fruits of Prunus mume. Chem Pharm Bull
(Tokyo). 37:345–348. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Guo JX, Kimura T, But PPH and Sung CK:
International Collation of Traditional and Folk Medicine. World
Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd; Singapore: pp. 99–100. 2001
|
|
18
|
Kim HH, Park SB, Lee S, Kwon TK, Shin TY,
Park PH, Lee SH and Kim SH: Inhibitory effect of putranjivain A on
allergic inflammation through suppression of mast cell activation.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 274:455–461. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kim HH, Kim DS, Kim SW, Lim SH, Kim DK,
Shin TY and Kim SH: Inhibitory effects of Diospyros kaki in a model
of allergic inflammation: role of cAMP, calcium and nuclear
factor-κB. Int J Mol Med. 32:945–951. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim HH, Bae Y and Kim SH: Galangin
attenuates mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation. Food Chem
Toxicol. 57:209–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Itoh T, Tsukane M, Koike M, Nakamura C,
Ohguchi K, Ito M, Akao Y, Koshimizu S, Nozawa Y, Wakimoto T, et al:
Inhibitory effects of whisky congeners on IgE-mediated
degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia RBL-2H3 cells and passive
cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction in mice. J Agric Food Chem.
58:7149–7157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bae Y, Lee S and Kim SH: Chrysin
suppresses mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation: involvement of
calcium, caspase-1 and nuclear factor-κB. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
254:56–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi JK, Oh HM, Lee S, Park JW, Khang D,
Lee SW, Lee WS, Rho MC and Kim SH: Oleanolic acid acetate inhibits
atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis in a murine
model. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 269:72–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Galli SJ and Tsai M: IgE and mast cells in
allergic disease. Nat Med. 18:693–704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kalesnikoff J and Galli SJ: New
developments in mast cell biology. Nat Immunol. 9:1215–1223. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma HT and Beaven MA: Regulators of
Ca2+ signaling in mast cells: potential targets for
treatment of mast cell-related diseases? Adv Exp Med Biol.
716:62–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Galli SJ, Tsai M and Piliponsky AM: The
development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 454:445–454. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arbabi S and Maier RV: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases. Crit Care Med. 30(Suppl 1): S74–S79. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Beyaert R, Cuenda A, Vanden Berghe W,
Plaisance S, Lee JC, Haegeman G, Cohen P and Fiers W: The p38/RK
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway regulates interleukin-6
synthesis response to tumor necrosis factor. EMBO J. 15:1914–1923.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Boden SR and Wesley Burks A: Anaphylaxis:
a history with emphasis on food allergy. Immunol Rev. 242:247–257.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jutel M, Watanabe T, Akdis M, Blaser K and
Akdis CA: Immune regulation by histamine. Curr Opin Immunol.
14:735–740. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Möller A, Henz BM, Grützkau A, Lippert U,
Aragane Y, Schwarz T and Krüger-Krasagakes S: Comparative cytokine
gene expression: regulation and release by human mast cells.
Immunology. 93:289–295. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sillaber C, Bevec D, Butterfield JH,
Heppner C, Valenta R, Scheiner O, Kraft D, Lechner K, Bettelheim P
and Valent P: Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta
mRNA expression in HMC-1 cells: differential regulation of gene
product expression by recombinant interleukin-4. Exp Hematol.
21:1271–1275. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu ZQ, Kobayashi K, Zenda N and Shimamura
T: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha- and interleukin-6-triggered mast
cell development from mouse spleen cells. Blood. 89:526–533.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Walsh LJ, Trinchieri G, Waldorf HA,
Whitaker D and Murphy GF: Human dermal mast cells contain and
release tumor necrosis factor alpha, which induces endothelial
leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
88:4220–4224. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mican JA, Arora N, Burd PR and Metcalfe
DD: Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in mouse skin is associated with
local accumulation of interleukin-6 mRNA and immunoreactive
interleukin-6 protein. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 90:815–824. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dienz O and Rincon M: The effects of IL-6
on CD4 T cell responses. Clin Immunol. 130:27–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Silvestri M, Bontempelli M, Giacomelli M,
Malerba M, Rossi GA, Di Stefano A, Rossi A and Ricciardolo FL: High
serum levels of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-8 in
severe asthma: Markers of systemic inflammation? Clin Exp Allergy.
36:1373–1381. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Karin M: NF-kappaB as a critical link
between inflammation and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0001412009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Manthey CL, Wang SW, Kinney SD and Yao Z:
SB202190, a selective inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase, is a powerful regulator of LPS-induced mRNAs in monocytes.
J Leukoc Biol. 64:409–417. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shapiro L and Dinarello CA: Osmotic
regulation of cytokine synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
92:12230–12234. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|