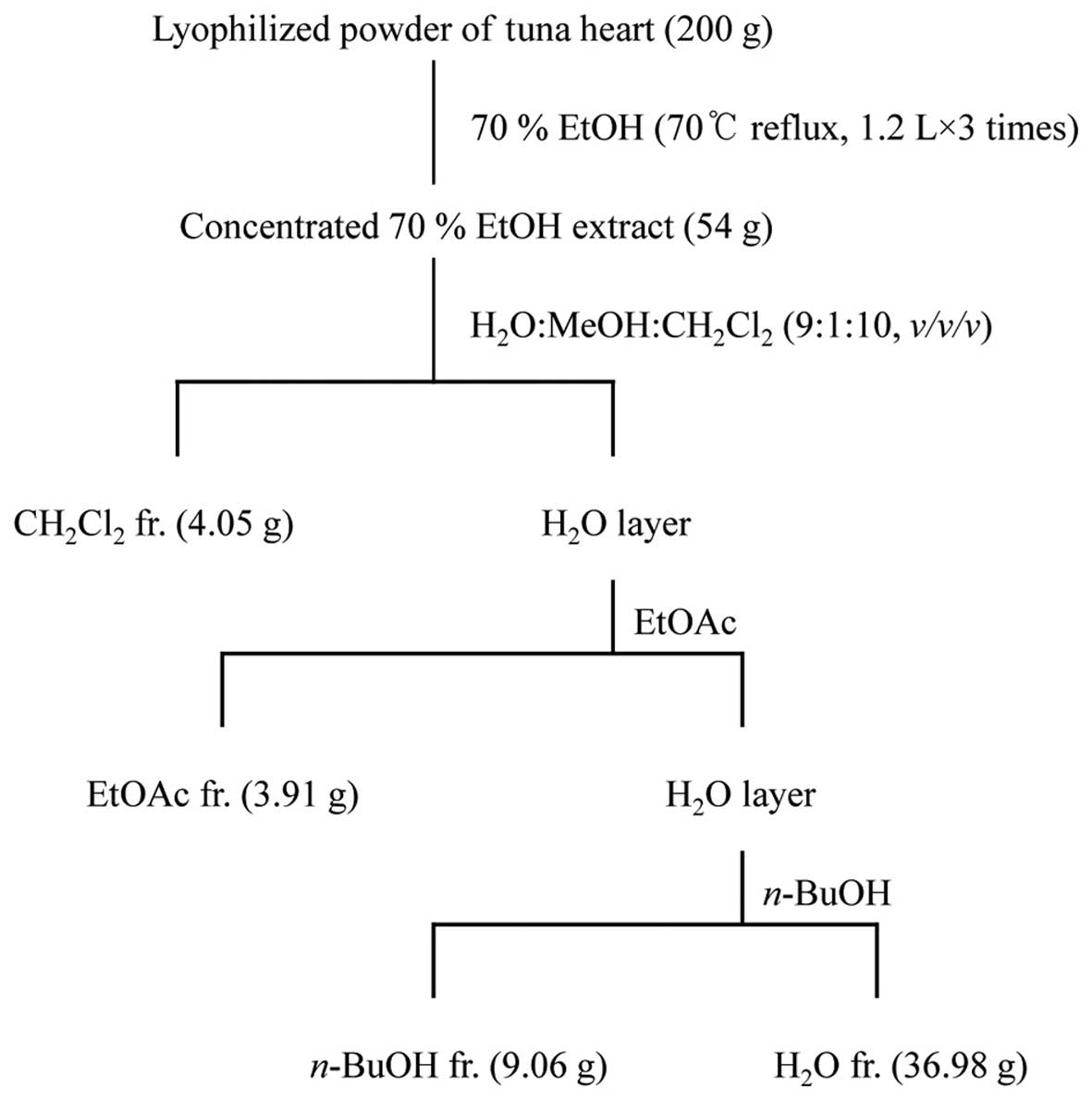
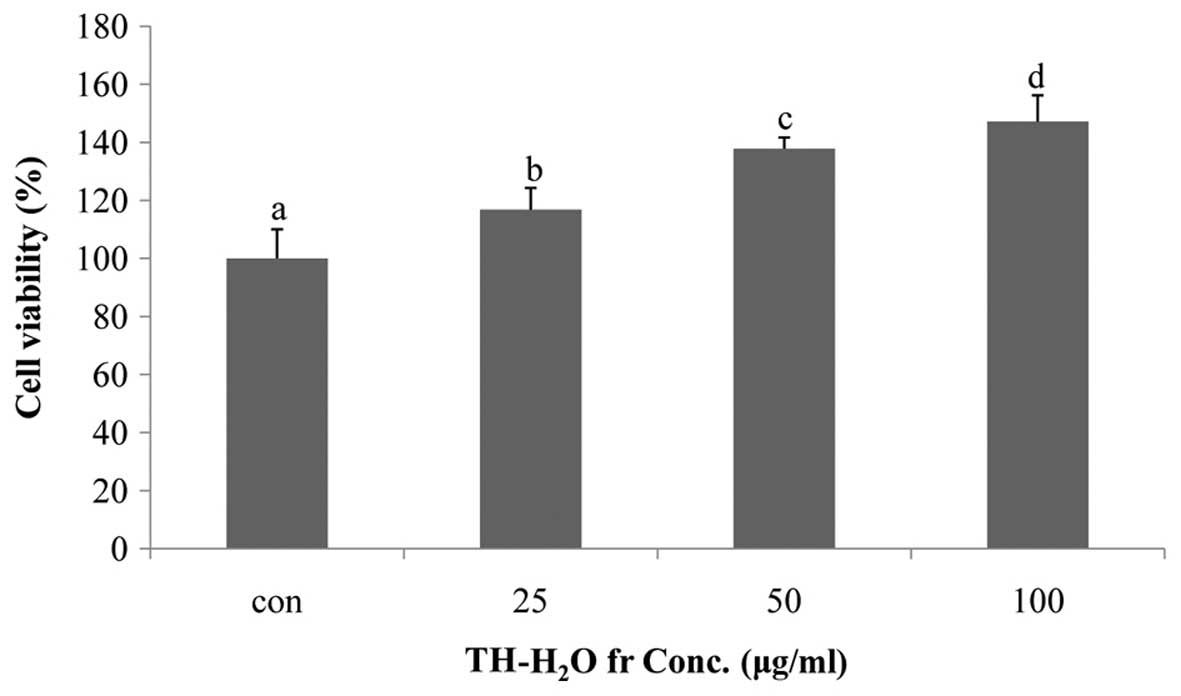
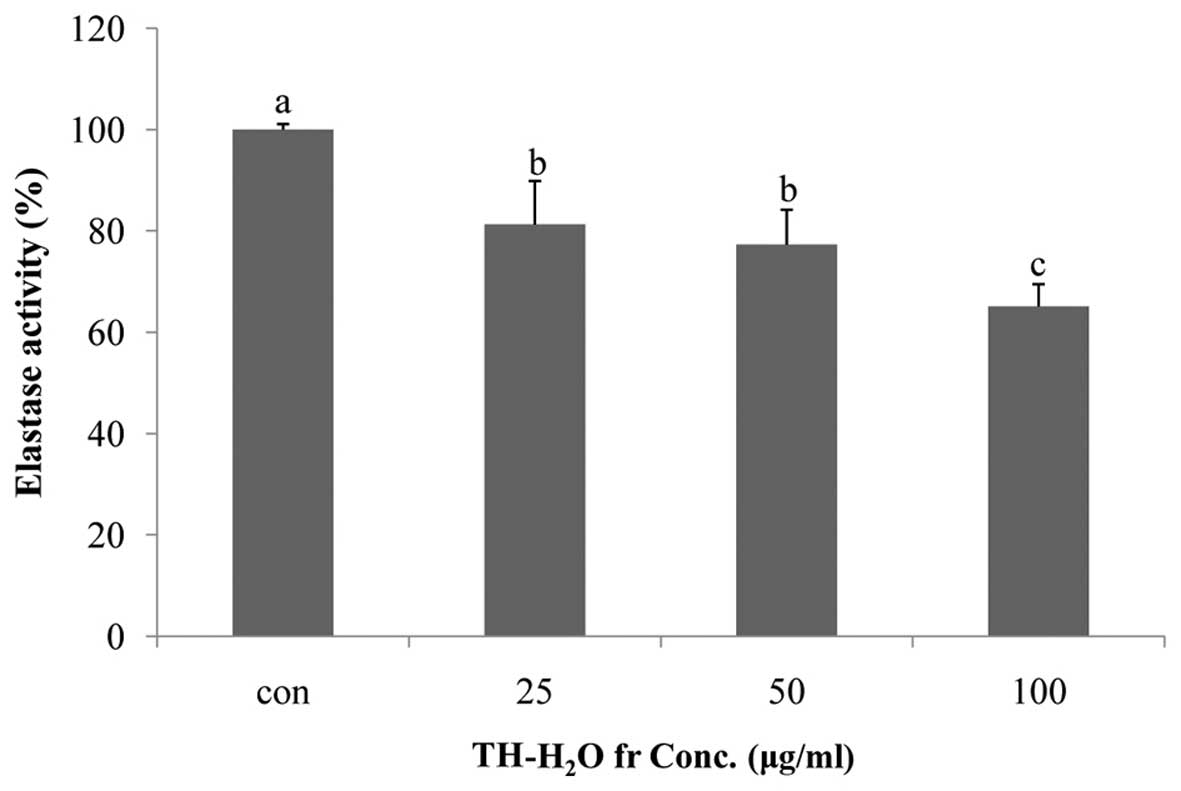
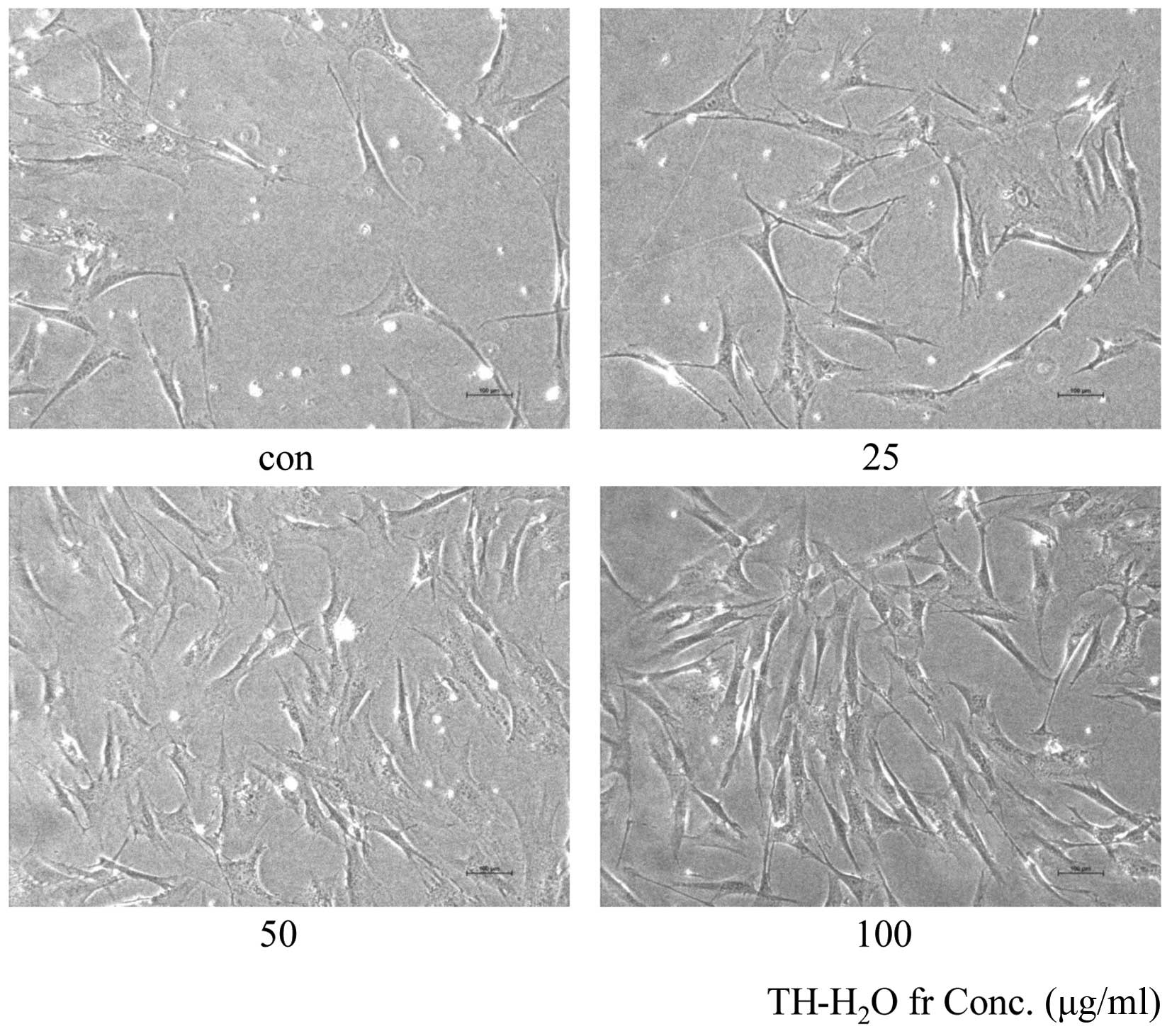
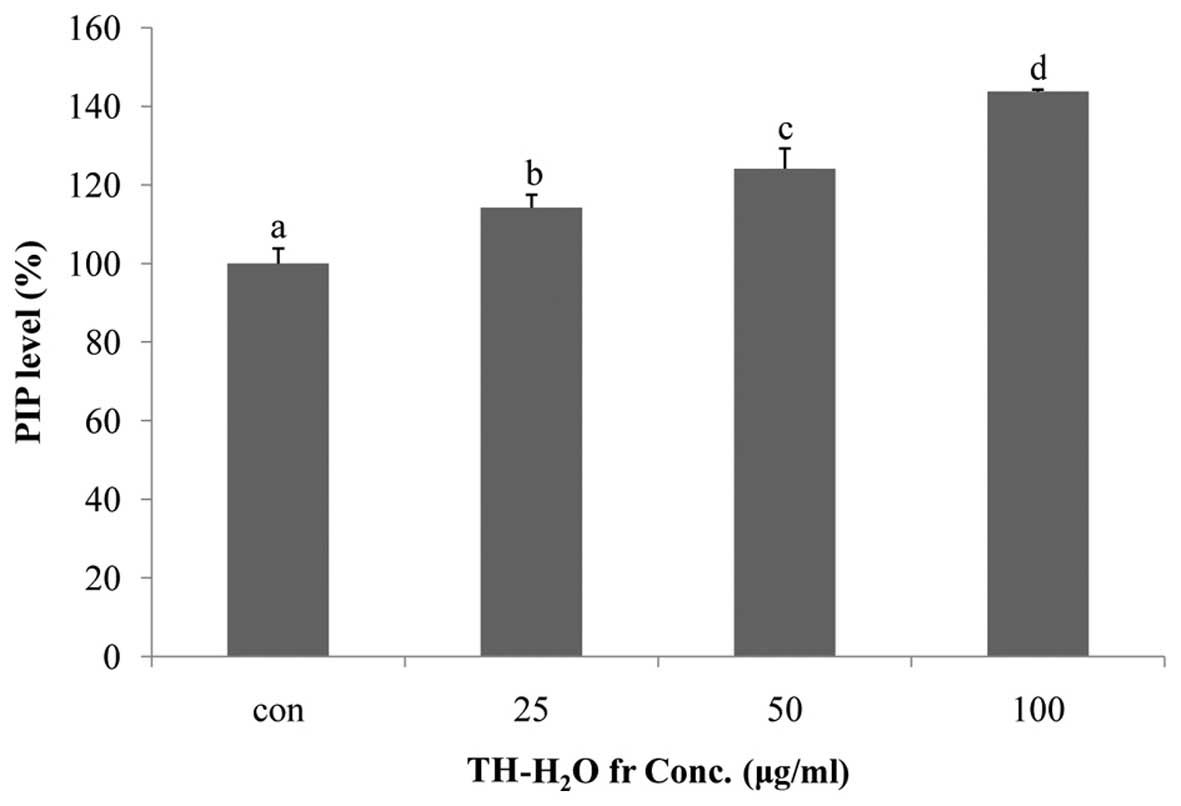
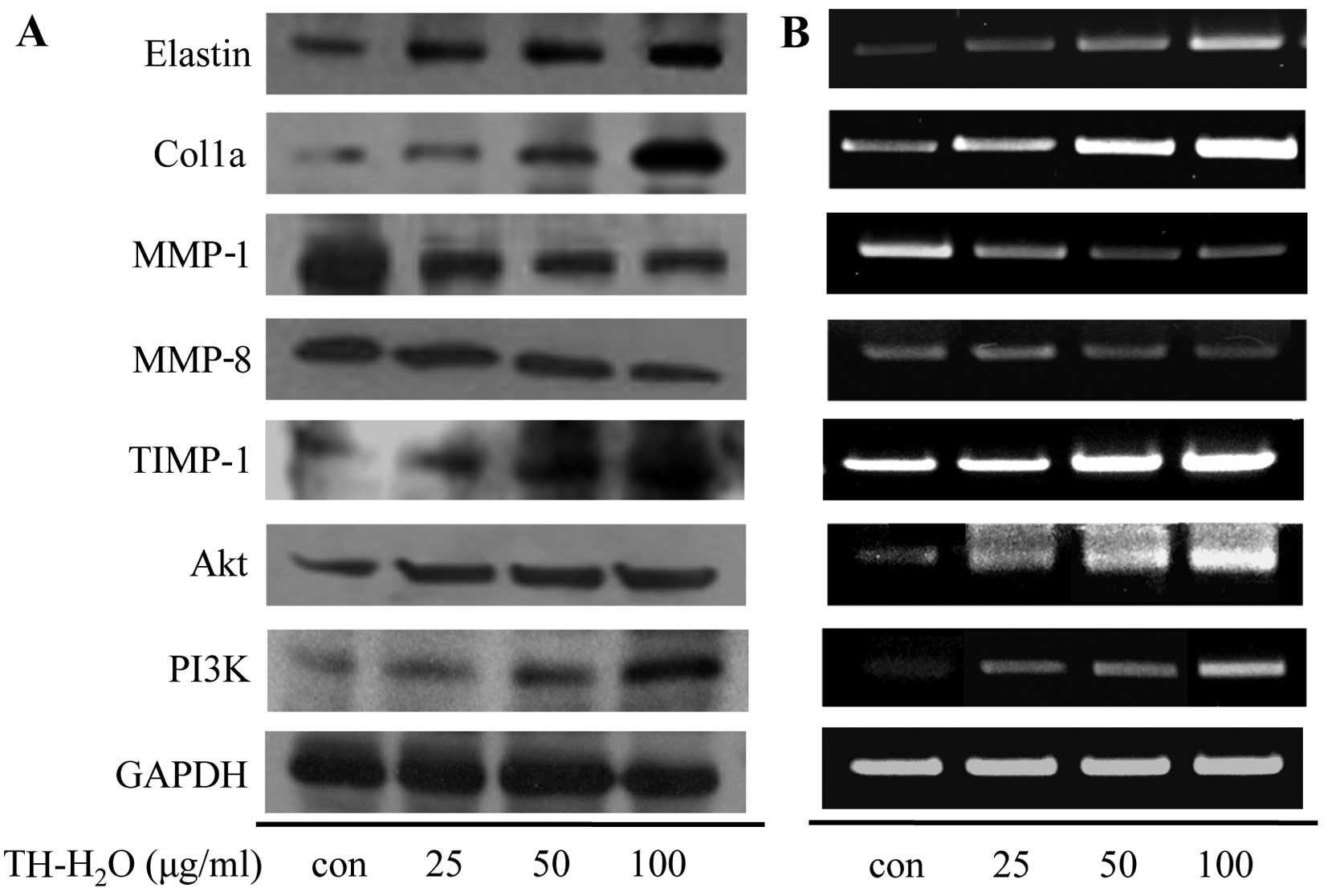
|
1
|
Kim SH, Yong HJ, Shin C and Ko SG:
Research of traditional herbal medicines for anti-aging, inhibition
effect of wrinkle and whitening effect in the skin. Korean J Ori
Physiol Pathol. 22:691–698. 2008.In Korean.
|
|
2
|
Gancevicine R, Liakou AI, Theodoridis A,
Makrantonaki E and Zouboulis CC: Skin anti-aging strategies.
Dermato-Endocrinol. 4:308–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Park KJ, Park SH and Kim JK: Anti-wrinkle
activity of Acanthopanax senticosus extract in ultraviolet B
(UBV)-induced photoaging. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 39:42–46.
2010.In Korean. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gilchrest BA: Skin aging and photoaging.
Dermatol Nurs. 2:79–82. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ha TY: Development of functional food
materials for healthy life. Korean J Crop Sci. 51:26–39. 2006.In
Korean.
|
|
6
|
Makrantonaki E and Zouboulis CC: Molecular
mechanisms of skin aging: state of the art. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1119:40–50. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seo MY, Chung SY, Choi WK, Seo YK, Jung
SH, Park JM, Seo MJ, Park JK, Kim JW and Park CS: Anti-aging effect
of rice wine in cultured human fibroblasts and keratinocytes. J
Biosci Bioeng. 107:266–271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seo JE, Kim S, Shin MH, Kim MS, Eun HC,
Park CH and Chung JH: Ultraviolet irradiation induces
thrombospondin-1 which attenuates type I procollagen downregulation
in human dermal fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci. 59:16–24. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kang TH, Park HM, Kim YB, Kim H, Kim N, Do
JH, Kang C, Cho Y and Kim SY: Effects of red ginseng extract on UVB
irradiation-induced skin aging in hairless mice. J Ethnopharmacol.
123:446–451. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsukahara K, Nakagawa H, Moriwaki S,
Takema Y, Fujimura T and Imokawa G: Inhibition of
ultraviolet-B-induced wrinkle formation by an elastase-inhibiting
herbal extract: implication for the mechanism underlying
elastase-associated wrinkles. Int J Dermatol. 45:460–468. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim MJ, Kim JY, Jung TK, Choi SW and Yoon
KS: Skin anti-aging effect of Forsythia viridissima L. extract.
Korean J Biotechnol Bioeng. 21:444–450. 2006.
|
|
12
|
Yeom MH, Lee JY, Kim JS, Park CW, Kim DH
and Kim HK: The anti-aging effects of Korean ginseng berry in the
skin. Korean J Pharmacogn. 41:26–30. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Klippel A, Reinhard C, Kavanaugh WM, Apell
G, Escobedo MA and Williams LT: Membrane localization of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is sufficient to activate multiple
signal-transducing kinase pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 16:4117–4127.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A and
Testa JR: Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: implications for
therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 94:29–86. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Long AM and Haard NF: The effect of
carotenoid-protein association on pigmentation and growth rates of
rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Bull Aquacult Assoc Can. 2:98–100.
1988.
|
|
16
|
Shahidi F and Synowiecki J: Isolation and
characterization of nutrients and value-added products from snow
crab (Chinoecetes opilio) and shrimp (Pandalus borealis) processing
discards. J Agric Food Chem. 39:1527–1532. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shahidi F, Naczk M, Pegg R and Synowiecki
J: Chemical composition and nutritional value of processing
discards of cod (Gadus morhua). Food Chem. 42:145–151. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kim YM, Kim EY, Kim IH and Nam TJ: Peptide
derived from desalinated boiled tuna extract inhibits adipogenesis
through the downregulation of C/EBP-α and PPAR-γ in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Int J Mol Med. 35:1362–1368. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim YM, Kim EH, Choi JW, Lee MK and Nam
TJ: The anti-obesity effects of a tuna peptide on 3T3-L1 adipocytes
are mediated by the inhibition of the expression of lipogenic and
adipogenic genes and by the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 36:327–334. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kang BK, Kim KBWR, Kim MJ, Bark SW, Park
WM, Kim BR, Ahn NK, Choi YU, Bae NY, Park JH, et al: Anti-atopic
activity of tuna heart ethanol extract. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr.
44:1–6. 2015.In Korean. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu X, Zhao Y, Gao J, Pawlyk B, Starcher
B, Spencer JA, Yanagisawa H, Zuo J and Li T: Elastic fiber
homeostasis requires lysyl oxidase-like 1 protein. Nat Genet.
36:178–182. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Patel A, Fine B, Sandig M and Mequanint K:
Elastin biosynthesis: The missing link in tissue-engineered blood
vessels. Cardiovasc Res. 71:40–49. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Suganuma K, Nakajima H, Ohtsuki M and
Imokawa G: Astaxanthin attenuates the UVA-induced up-regulation of
matrix-metalloproteinase-1 and skin fibroblast elastase in human
dermal fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci. 58:136–142. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sandhu SV, Gupta S, Bansal H and Singla K:
Collagen in health and disease. J Orofac Res. 2:153–159. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim YH, Chung CB, Kim JG, Ko KI, Park SH,
Kim JH, Eom SY, Kim YS, Hwang YI and Kim KH: Anti-wrinkle activity
of ziyuglycoside I isolated from a Sanguisorba officinalis root
extract and its application as a cosmeceutical ingredient. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 72:303–311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsuji-Naito K, Ishikura S, Akagawa M and
Saeki H: Alpha-Lipoic acid induces collagen biosynthesis involving
prolyl hydroxylase expression via activation of TGF-beta-Smad
signaling in human dermal fibroblasts. Connect Tissue Re. 1–10.
2010.
|
|
27
|
Kim HH, Cho S, Lee S, Kim KH, Cho KH, Eun
HC and Chung JH: Photoprotective and anti-skin-aging effects of
eicosapentaenoic acid in human skin in vivo. J Lipid Res.
47:921–930. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rabe JH, Mamelak AJ, McElgunn PJ, Morison
WL and Sauder DN: Photoaging: mechanisms and repair. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 55:1–19. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kivirikko KI and Myllyharju J: Prolyl
4-hydroxylases and their protein disulfide isomerase subunit.
Matrix Biol. 16:357–368. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee JH, Park SM, Jung HJ, Kim HS and Yu
TS: Characteristics of Ju-back and effect of Ju-back fertilizer on
growth of crop plants. J Life Sci. 17:1562–1570. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tsuji N, Moriwaki S, Suzuki Y, Takema Y
and Imokawa G: The role of elastases secreted by fibroblasts in
wrinkle formation: implication through selective inhibition of
elastase activity. Photochem Photobiol. 74:283–290. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shin MO, Ku MJ and Bae SJ: Cytotoxicity
and quinine reductase activity stimulating effects of fin of
Thunnus thynnus extracts in various cancer cells. Korean J Nutr.
40:147–153. 2007.
|
|
33
|
DeWitt DL, Rollins TE, Day JS, Gauger JA
and Smith WL: Orientation of the active site and antigenic
determinants of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase in the
endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 256:10375–10382.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roth GJ, Siok CJ and Ozols J: Structural
characteristics of prostaglandin synthetase from sheep vesicular
gland. J Biol Chem. 255:1301–1304. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Makrantonaki E and Zouboulis CC; German
National Genome Research Network 2: The skin as a mirror of the
aging process in the human organism - state of the art and results
of the aging research in the German National Genome Research
Network 2(NGFN-2). Exp Gerontol. 42:879–886. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim SN, Lee SH, Lee BK and Jang IS:
Acompositions containing Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffmann extract or
Petroselinum sativum Miller extract for external application having
effects of improving skin wrinkle. Korea Patent 10-2002-0079594.
2002
|
|
37
|
El-Domyati M, Attia S, Saleh F, Brown D,
Birk DE, Gasparro F, Ahmad H and Uitto J: Intrinsic aging vs.
photoaging: a comparative histopathological, immunohistochemical,
and ultrastructural study of skin. Exp Dermatol. 11:398–405. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Berneburg M, Plettenberg H and Krutmann J:
Photoaging of human skin. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed.
16:239–244. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|