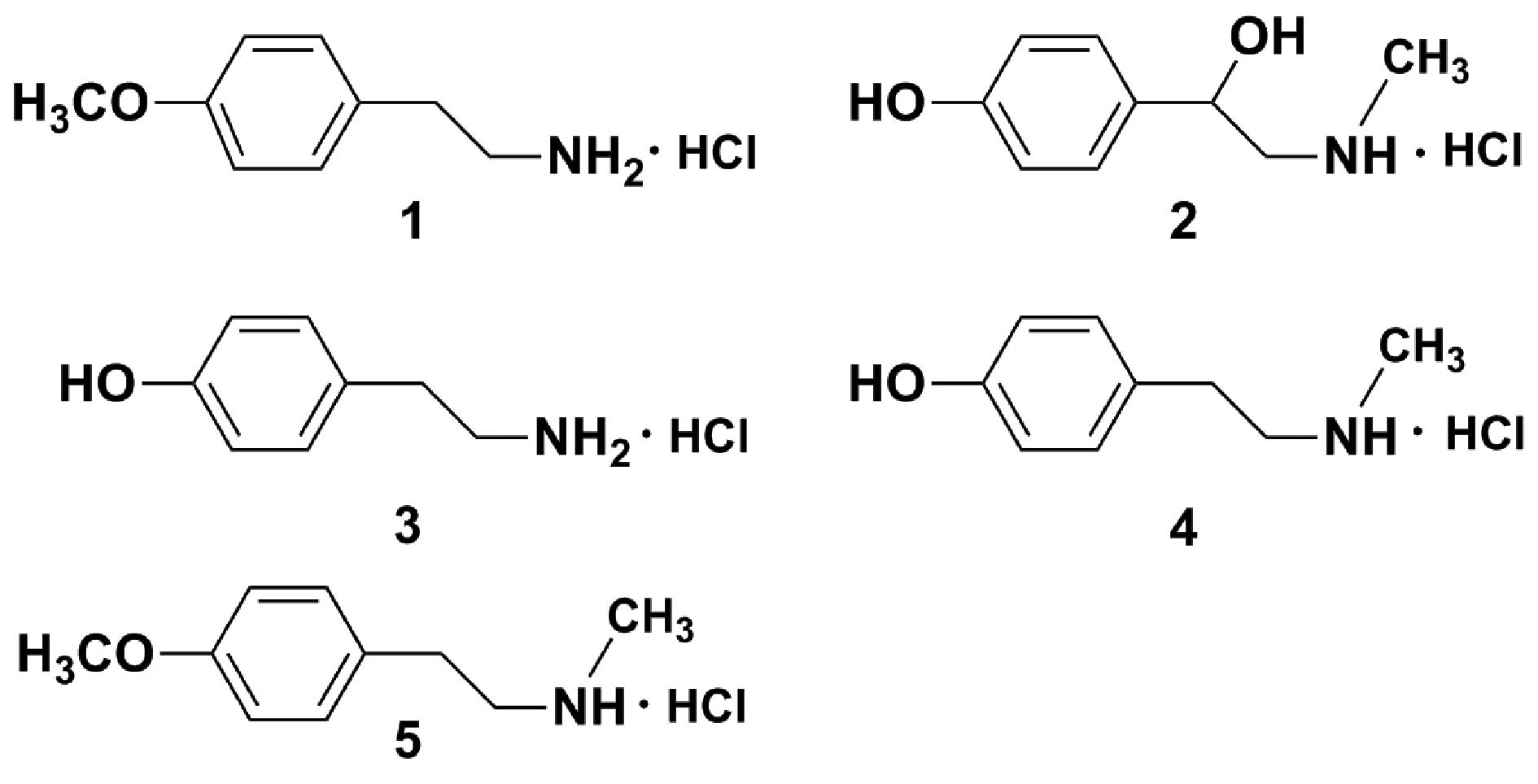
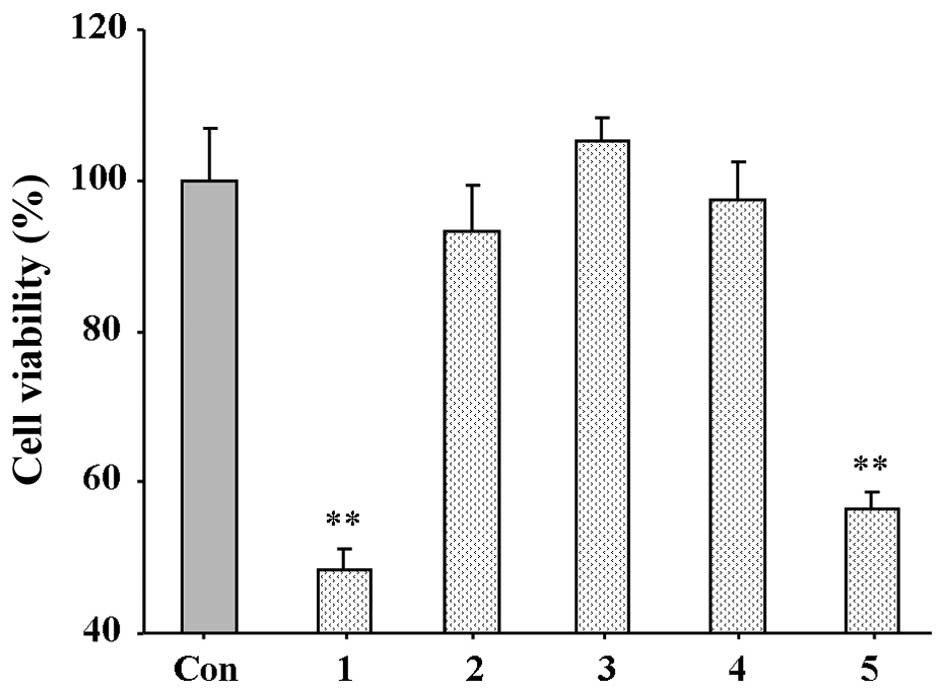
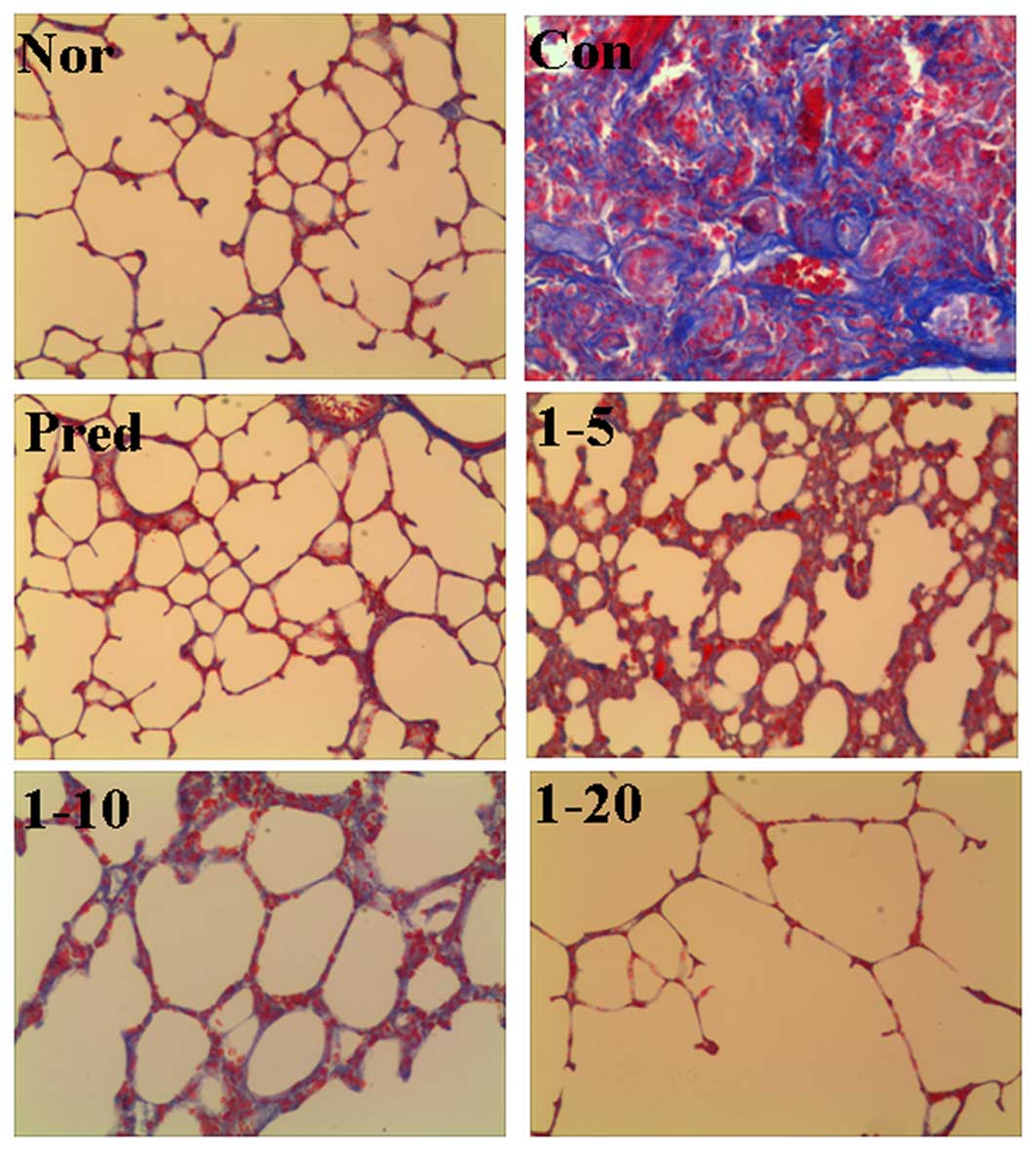
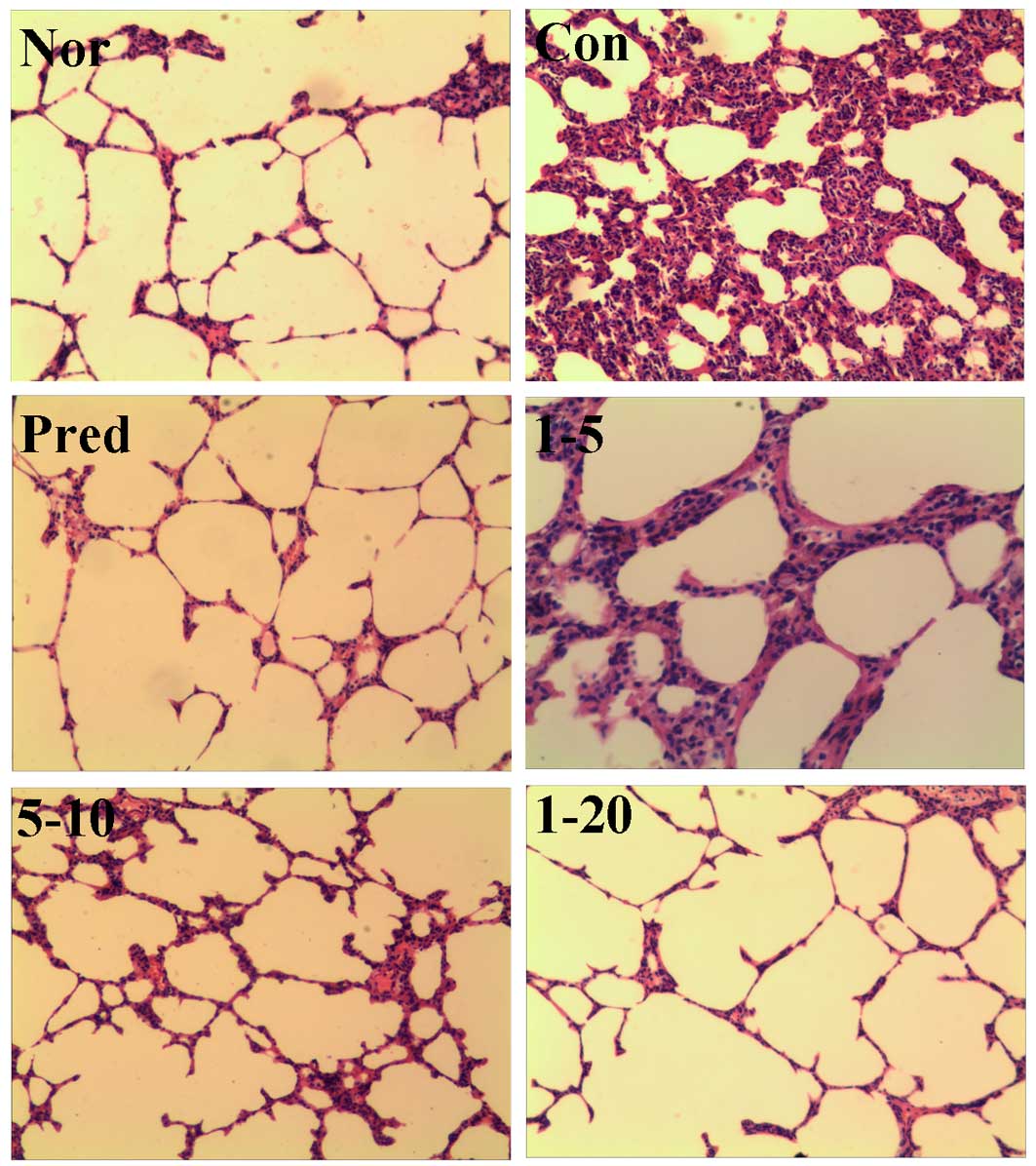
|
1
|
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ,
Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, et
al ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Committee on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: An
official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis:
evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 183:788–824. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nalysnyk L, Cid-Ruzafa J, Rotella P and
Esser D: Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis:
review of the literature. Eur Respir Rev. 21:355–361. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hilberg O, Simonsen U, du Bois R and
Bendstrup E: Pirfenidone: significant treatment effects in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Respir J. 6:131–143. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O'Connell OJ, Kennedy MP and Henry MT:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: treatment update. Adv Ther.
28:986–999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Armanios M: Telomerase and idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Mutat Res. 730:52–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Rafii R, Juarez MM, Albertson TE and Chan
AL: A review of current and novel therapies for idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. J Thorac Dis. 5:48–73. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Spagnolo P, Maher TM and Richeldi L:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: recent advances on pharmacological
therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 152:18–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A,
Brown KK, Costabel U, Cottin V, Flaherty KR, Hansell DM, Inoue Y,
et al INPULSIS Trial Investigators: efficacy and safety of
nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med.
370:2071–2082. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
King TE Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini
S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, Gorina E, Hopkins PM,
Kardatzke D, Lancaster L, et al ASCEND Study Group: A phase 3 trial
of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N
Engl J Med. 370:2083–2092. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cottin V: Current approaches to the
diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Europe:
the AIR survey. Eur Respir Rev. 23:225–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Velasco R and Licciardello C: A genealogy
of the citrus family. Nat Biotechnol. 32:640–642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Medina S, Ferreres F, García-Viguera C,
Horcajada MN, Orduna J, Savirón M, Zurek G, Martínez-Sanz JM, Gil
JI and Gil-Izquierdo A: Non-targeted metabolomic approach reveals
urinary metabolites linked to steroid biosynthesis pathway after
ingestion of citrus juice. Food Chem. 136:938–946. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nile SH and Park SW: Bioactive components
and health-promoting properties of Yuzu (Citrus ichangensis x C.
reticulate). Food Rev Int. 30:155–167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yadav L and Kalidhar SB: Chemical
components of Mandarin species: a review. J Indian Chem Soc.
88:911–926. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Khan MK, Huma ZE and Dangles O: A
comprehensive review on flavanones, the major citrus polyphenols. J
Food Compos Anal. 33:85–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Vieira SM, Theodoro KH and Glória MBA:
Profile and levels of bioactive amines in orange juice and orange
soft drink. Food Chem. 100:895–903. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Stohs SJ, Preuss HG and Shara M: The
safety of Citrus aurantium (bitter orange) and its primary
protoalkaloid p-synephrine. Phytother Res. 25:1421–1428. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaats GR, Miller H, Preuss HG and Stohs
SJ: A 60day double-blind, placebo-controlled safety study involving
Citrus aurantium (bitter orange) extract. Food Chem Toxicol.
55:358–362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stohs SJ and Preuss HG: Stereochemical and
pharmacological differences between naturally occurring
p-synephrine and synthetic p-synephrine. J Funct Foods. 4:2–5.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhou XM, Zhang GC, Li JX and Hou J:
Inhibitory effects of Hu-qi-yin on the bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 111:255–264. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhou XM, Huang MM, He CC and Li JX:
Inhibitory effects of citrus extracts on the experimental pulmonary
fibrosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 126:143–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
China Pharmacopoeia Committee: Citri
Reticulatae Pericarpium. Chinese Pharmacopeia 2010. Chemical
Industry; Press, Beijing: pp. 176–177. 2010
|
|
23
|
Zhou XM, Wen GY, Zhao Y, Liu YM and Li JX:
Inhibitory effects of alkaline extract of Citrus reticulata on
pulmonary fibrosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 146:372–378. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Camelo A, Dunmore R, Sleeman MA and Clarke
DL: The epithelium in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: breaking the
barrier. Front Pharmacol. 4:1732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kendall RT and Feghali-Bostwick CA:
Fibroblasts in fibrosis: novel roles and mediators. Front
Pharmacol. 5:1232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
B Moore B, Lawson WE, Oury TD, Sisson TH,
Raghavendran K and Hogaboam CM: Animal models of fibrotic lung
disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 49:167–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kliment CR, Englert JM, Crum LP and Oury
TD: A novel method for accurate collagen and biochemical assessment
of pulmonary tissue utilizing one animal. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
4:349–355. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huaux F, Noel S, Dhooghe B, Panin N, Lo Re
S, Lison D, Wallemacq P, Marbaix E, Scholte BJ, Lebecque P and Leal
T: Dysregulated proinflammatory and fibrogenic phenotype of
fibroblasts in cystic fibrosis. PLoS One. 8:e643412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan Z, Kui Z and Ping Z: Reviews and
prospectives of signaling pathway analysis in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Autoimmun Rev. 13:1020–1025. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Klingberg F, Hinz B and White ES: The
myofibroblast matrix: implications for tissue repair and fibrosis.
J Pathol. 229:298–309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Della Latta V, Cecchettini A, Del Ry S and
Morales MA: Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction:
from biological mechanisms to counteractions. Pharmacol Res.
97:122–130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|