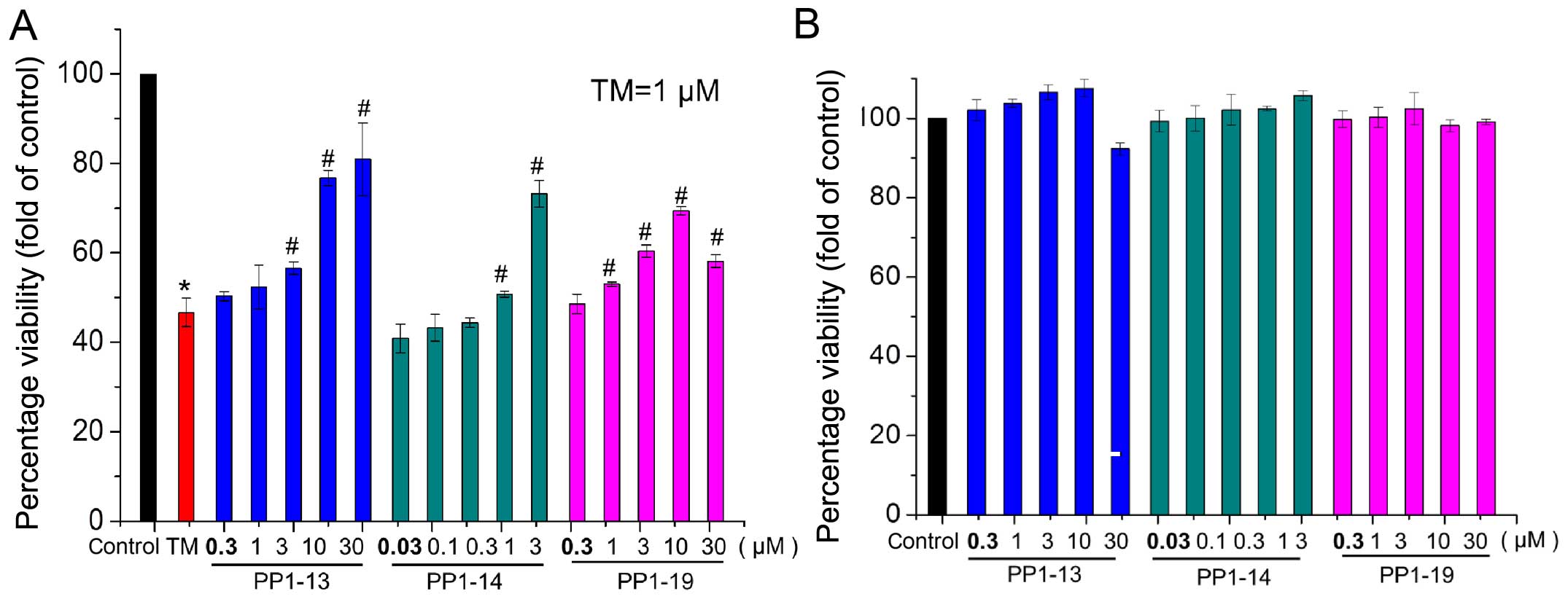
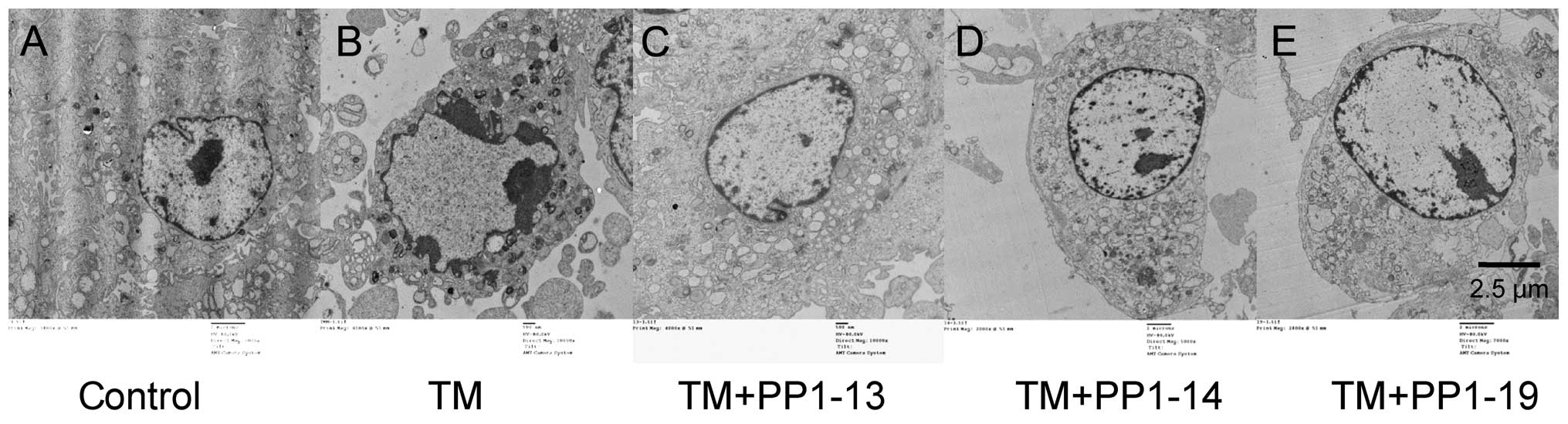
|
1
|
Wiseman RL and Balch WE: A new
pharmacology - drugging stressed folding pathways. Trends Mol Med.
11:347–350. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wiseman RL, Haynes CM and Ron D: SnapShot:
the unfolded protein response. Cell. 140:590–590.e2. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hong M, Luo S, Baumeister P, Huang JM,
Gogia RK, Li M and Lee AS: Underglycosylation of ATF6 as a novel
sensing mechanism for activation of the unfolded protein response.
J Biol Chem. 279:11354–11363. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhao L and Ackerman SL: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in health and disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
18:444–452. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boot-Handford RP and Briggs MD: The
unfolded protein response and its relevance to connective tissue
diseases. Cell Tissue Res. 339:197–211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Northington FJ, Chavez-Valdez R and Martin
LJ: Neuronal cell death in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Ann Neurol.
69:743–758. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mei J and Niu C: Alterations of Hrd1
expression in various encephalic regional neurons in 6-OHDA model
of Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 474:63–68. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chu WS, Das SK, Wang H, Chan JC, Deloukas
P, Froguel P, Baier LJ, Jia W, McCarthy MI, Ng MC, et al:
Activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) sequence polymorphisms in
type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetic traits. Diabetes. 56:856–862.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vekich JA, Belmont PJ, Thuerauf DJ and
Glembotski CC: Protein disulfide isomerase-associated 6 is an
ATF6-inducible ER stress response protein that protects cardiac
myocytes from ischemia/reperfusion-mediated cell death. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 53:259–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hotamisligil GS: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell.
140:900–917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee J, Hong SW, Park SE, Rhee EJ, Park CY,
Oh KW, Park SW and Lee WY: Exendin-4 attenuates endoplasmic
reticulum stress through a SIRT1-dependent mechanism. Cell Stress
Chaperones. 19:649–656. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsukumo Y, Tomida A, Kitahara O, Nakamura
Y, Asada S, Mori K and Tsuruo T: Nucleobindin 1 controls the
unfolded protein response by inhibiting ATF6 activation. J Biol
Chem. 282:29264–29272. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Citron M, Diehl TS, Capell A, Haass C,
Teplow DB and Selkoe DJ: Inhibition of amyloid beta-protein
production in neural cells by the serine protease inhibitor AEBSF.
Neuron. 17:171–179. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Damiano F, Tocci R, Gnoni GV and Siculella
L: Expression of citrate carrier gene is activated by ER stress
effectors XBP1 and ATF6α, binding to an UPRE in its promoter.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:23–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cox DJ, Strudwick N, Ali AA, Paton AW,
Paton JC and Schröder M: Measuring signaling by the unfolded
protein response. Methods Enzymol. 491:261–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bouck DC, Shu P, Cui J, Shelat A and Chen
T: A high-content screen identifies inhibitors of nuclear export of
forkhead transcription factors. J Biomol Screen. 16:394–404. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu J, He KL, Li X, Li RJ, Liu CL, Zhong W
and Li S: SAR, cardiac myocytes protection activity and 3D-QSAR
studies of salubrinal and its potent derivatives. Curr Med Chem.
19:6072–6079. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Toko H, Takahashi H, Kayama Y, Okada S,
Minamino T, Terasaki F, Kitaura Y and Komuro I: ATF6 is important
under both pathological and physiological states in the heart. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 49:113–120. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Adachi Y, Yamamoto K, Okada T, Yoshida H,
Harada A and Mori K: ATF6 is a transcription factor specializing in
the regulation of quality control proteins in the endoplasmic
reticulum. Cell Struct Funct. 33:75–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boyce M, Bryant KF, Jousse C, Long K,
Harding HP, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Ma D, Coen DM, Ron D and Yuan
J: A selective inhibitor of eIF2alpha dephosphorylation protects
cells from ER stress. Science. 307:935–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boyd JD, Lee-Armandt JP, Feiler MS, Zaarur
N, Liu M, Kraemer B, Concannon JB, Ebata A, Wolozin B and Glicksman
MA: A high-content screen identifies novel compounds that inhibit
stress-induced TDP-43 cellular aggregation and associated
cytotoxicity. J Biomol Screen. 19:44–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Mori T, Saito F, Yoshino T, Takeyama H and
Matsunaga T: Reporter gene assay against lipophilic chemicals based
on site-specific genomic recombination of a nuclear receptor gene,
its response element, and a luciferase reporter gene within a
stable HeLa cell line. Biotechnol Bioeng. 99:1453–1461. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gasparetto M, Gentry T, Sebti S, O'Bryan
E, Nimmanapalli R, Blaskovich MA, Bhalla K, Rizzieri D, Haaland P,
Dunne J and Smith C: Identification of compounds that enhance the
anti-lymphoma activity of rituximab using flow cytometric
high-content screening. J Immunol Methods. 292:59–71. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Starkuviene V and Pepperkok R: The
potential of high-content high-throughput microscopy in drug
discovery. Br J Pharmacol. 152:62–71. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng Y, Mitchison TJ, Bender A, Young DW
and Tallarico JA: Multi-parameter phenotypic profiling: using
cellular effects to characterize small-molecule compounds. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:567–578. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Giuliano KA, Haskins JR and Taylor DL:
Advances in high content screening for drug discovery. Assay Drug
Dev Technol. 1:565–577. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu CL, Li X, Hu GL, Li RJ, He YY, Zhong
W, Li S, He KL and Wang LL: Salubrinal protects against tunicamycin
and hypoxia induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via the PERK-eIF2α
signaling pathway. J Geriatr Cardiol. 9:258–268. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|