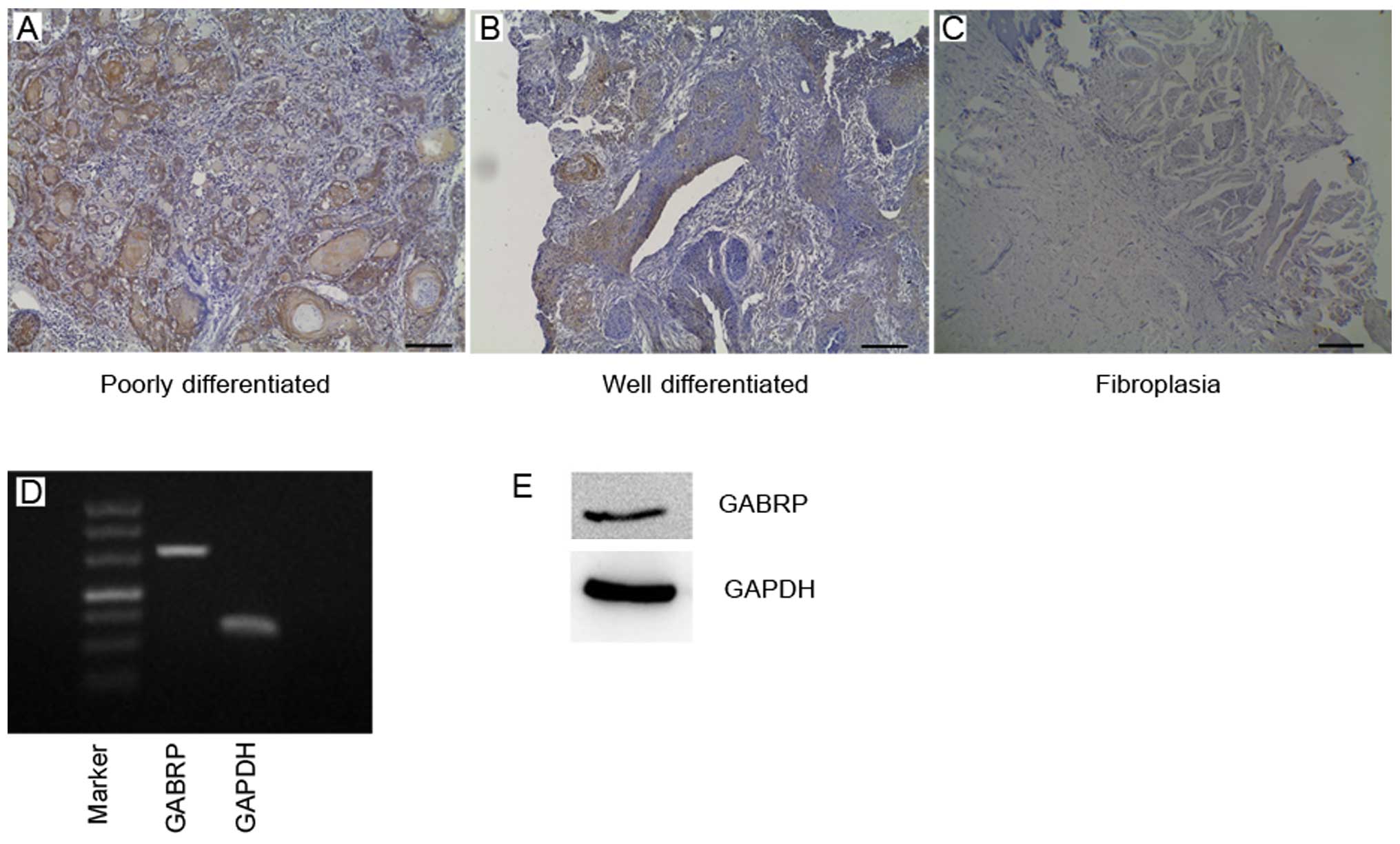
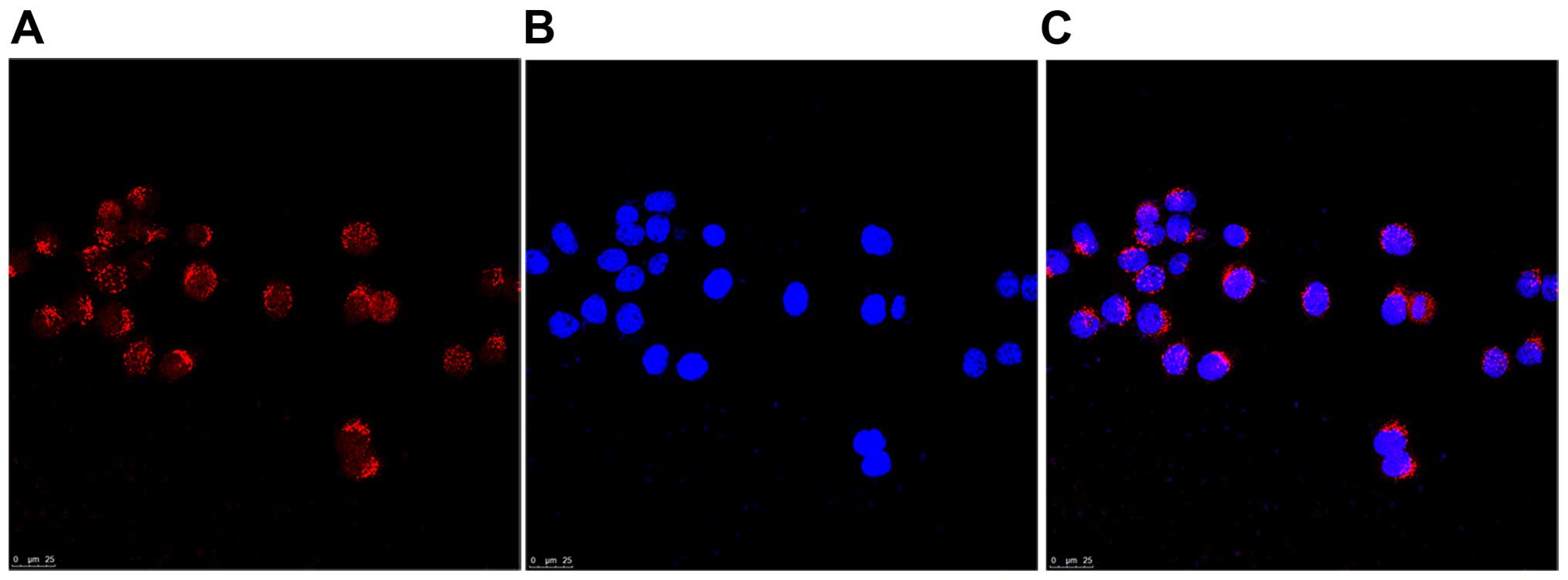
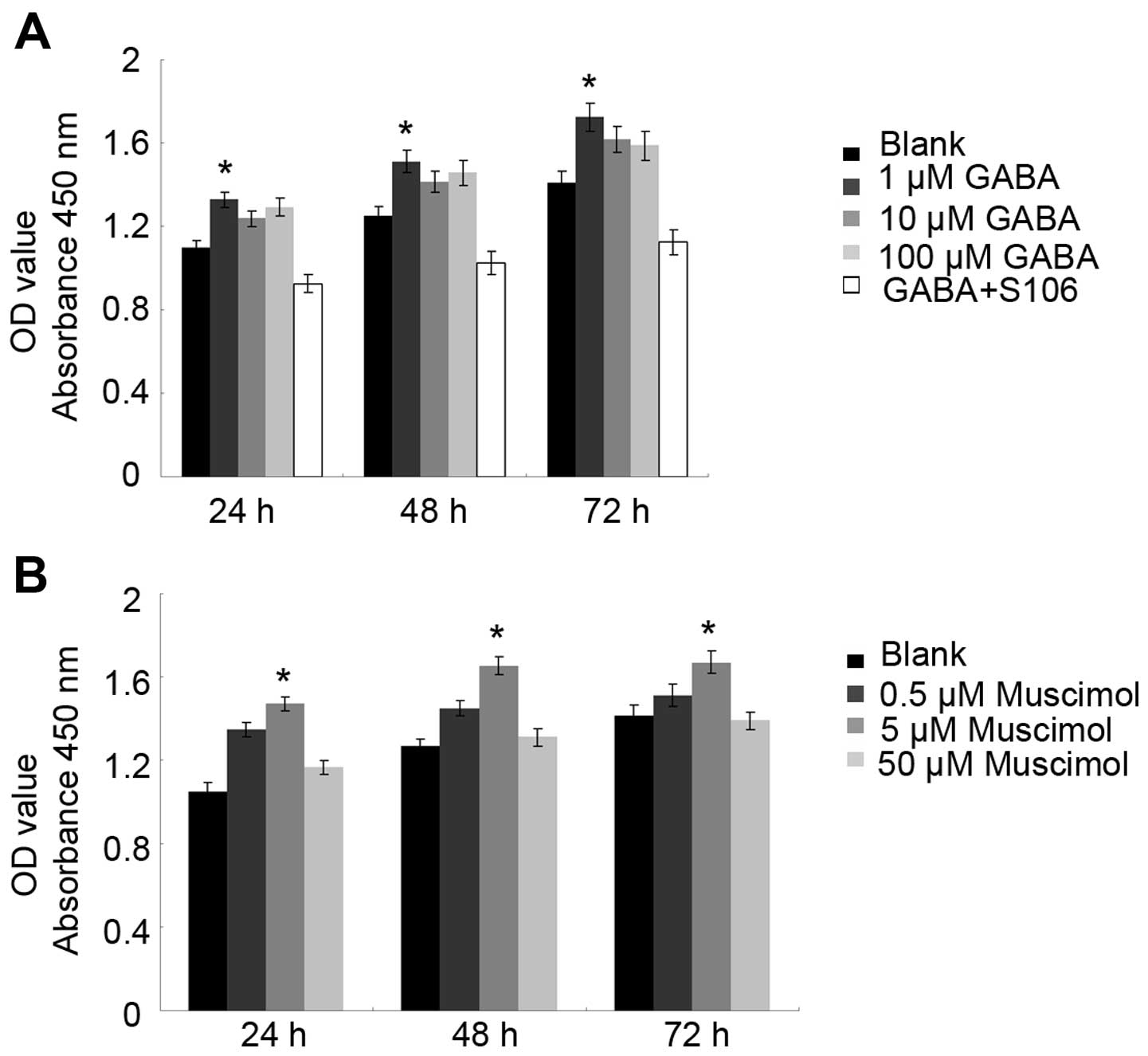
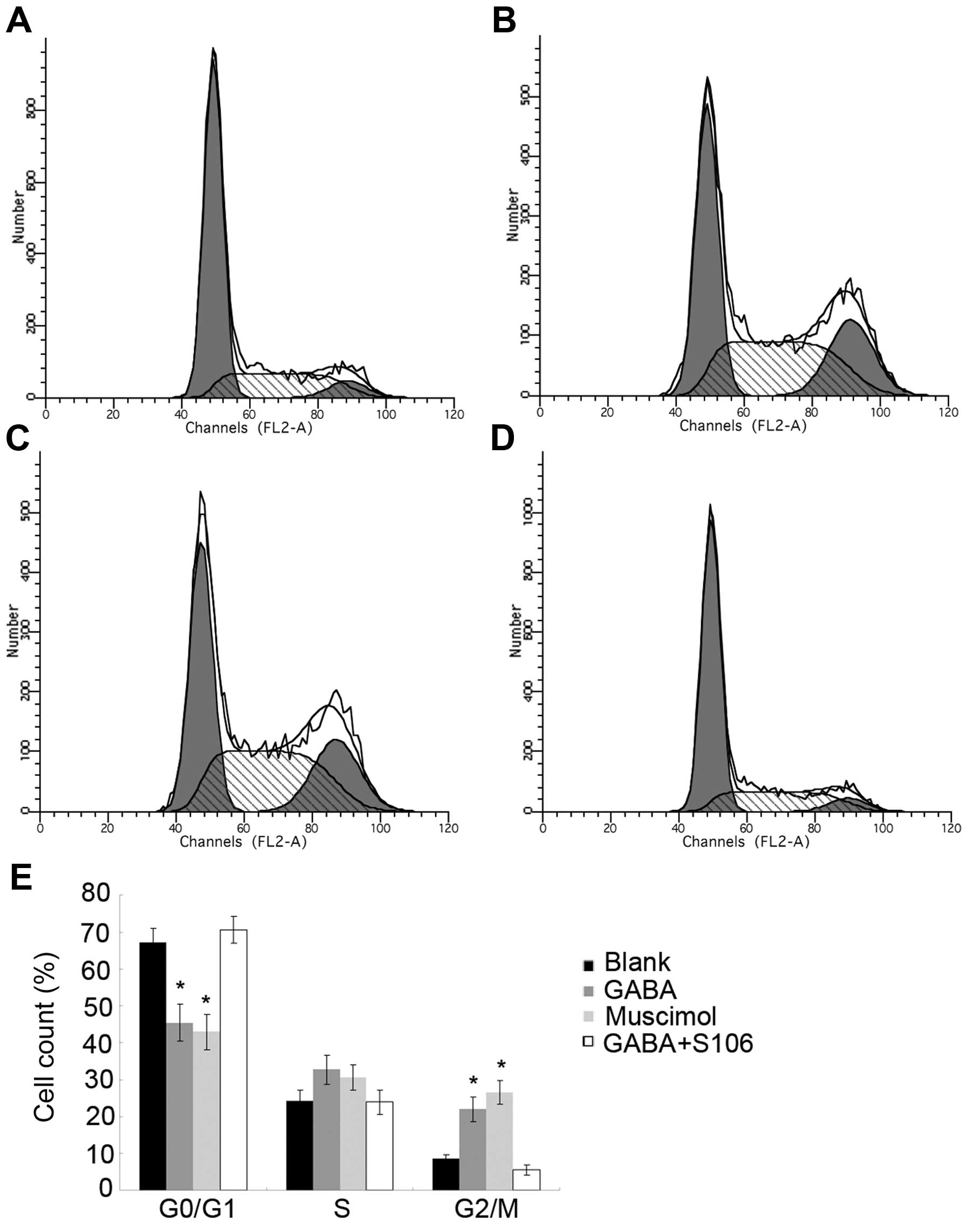
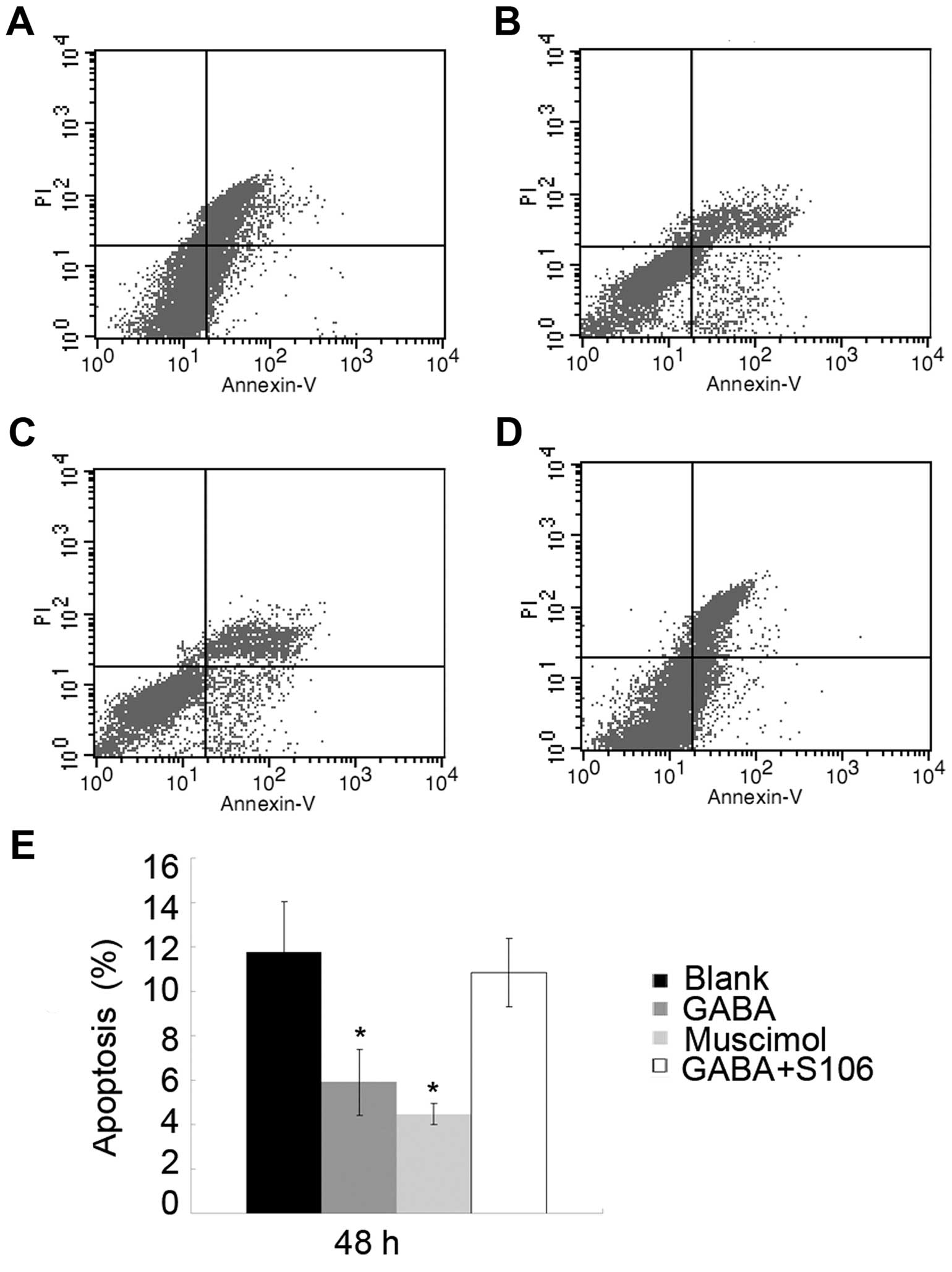
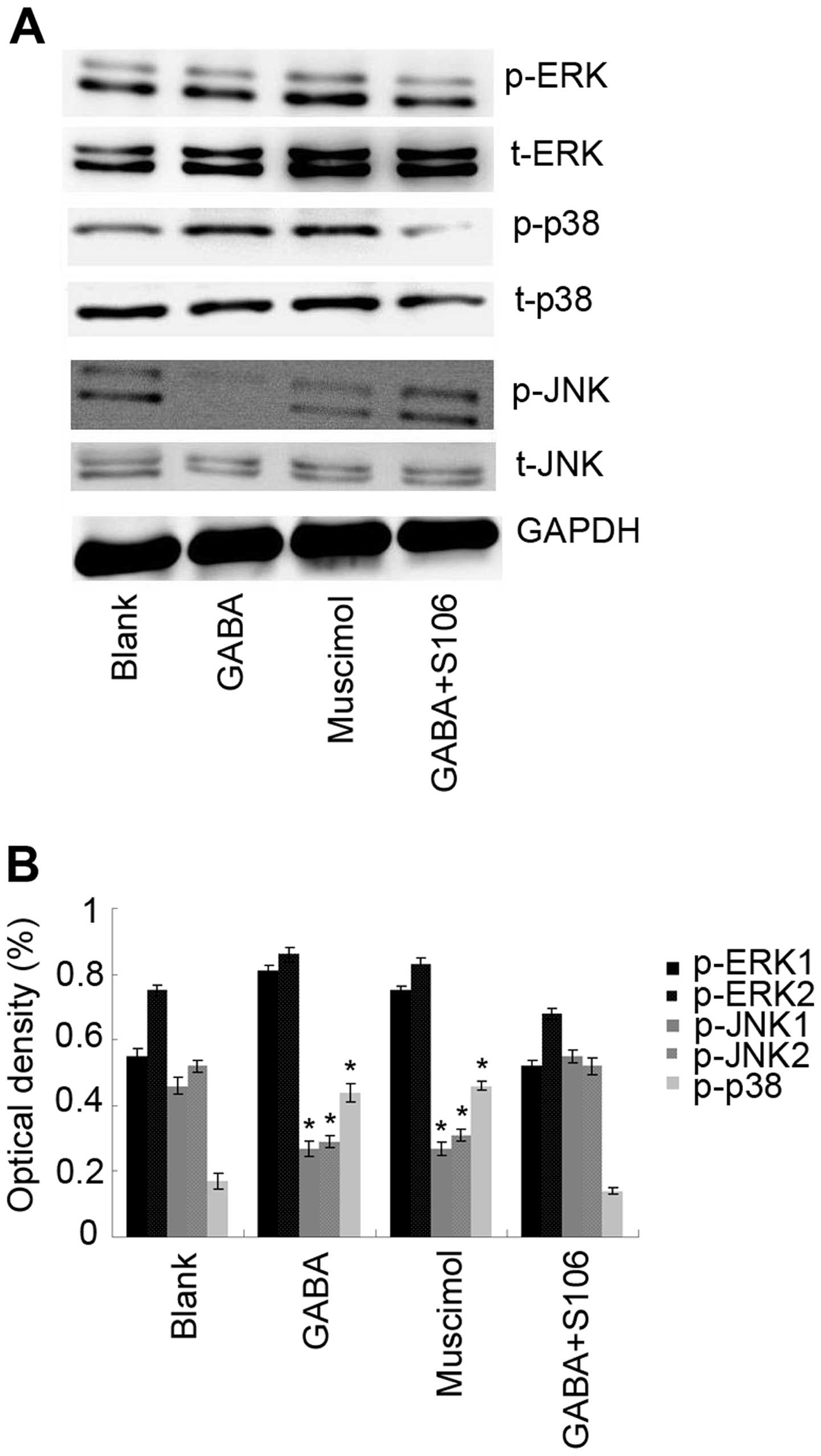
|
1
|
Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, Winn DM, Austin
DF, Greenberg RS, Preston-Martin S, Bernstein L, Schoenberg JB,
Stemhagen A and Fraumeni JF Jr: Smoking and drinking in relation to
oral and pharyngeal cancer. Cancer Res. 48:3282–3287.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rentoft M, Coates PJ, Loljung L, Wilms T,
Laurell G and Nylander K: Expression of CXCL10 is associated with
response to radiotherapy and overall survival in squamous cell
carcinoma of the tongue. Tumour Biol. 35:4191–4198. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fu X and Feng Y: QKI-5 suppresses cyclin
D1 expression and proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma
cells via MAPK signalling pathway. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
44:562–7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ntziachristos P, Lim JS, Sage J and
Aifantis I: From fly wings to targeted cancer therapies: a
centennial for notch signaling. Cancer Cell. 25:318–334. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kamran MZ, Patil P and Gude RP: Role of
STAT3 in cancer metastasis and translational advances. Biomed Res
Int. 2013:4218212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujii R, Imanishi Y, Shibata K, Sakai N,
Sakamoto K, Shigetomi S, Habu N, Otsuka K, Sato Y, Watanabe Y, et
al: Restoration of E-cadherin expression by selective Cox-2
inhibition and the clinical relevance of the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:40–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dalianis T: Human papillomavirus and
oropharyngeal cancer, the epidemics, and significance of additional
clinical biomarkers for prediction of response to therapy (Review).
Int J Oncol. 44:1799–1805. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nagata M, Wada K, Nakajima A, Nakajima N,
Kusayama M, Masuda T, Iida S, Okura M, Kogo M and Kamisaki Y: Role
of myeloid cell leukemia-1 in cell growth of squamous cell
carcinoma. J Pharmacol Sci. 110:344–353. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Watanabe M, Maemura K, Kanbara K, Tamayama
T and Hayasaki H: GABA and GABA receptors in the central nervous
system and other organs. Int Rev Cytol. 213:1–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Irwin RP and Allen CN: GABAergic signaling
induces divergent neuronal Ca2+ responses in the
suprachiasmatic nucleus network. Eur J Neurosci. 30:1462–1475.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Al-Wadei HA, Plummer HK III and Schuller
HM: Nicotine stimulates pancreatic cancer xenografts by systemic
increase in stress neurotransmitters and suppression of the
inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid.
Carcinogenesis. 30:506–511. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deng Y, Wang W, Yu P, Xi Z, Xu L, Li X and
He N: Comparison of taurine, GABA, Glu, and Asp as scavengers of
malondialdehyde in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale Res Lett.
8:1902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ortega A: A new role for GABA: inhibition
of tumor cell migration. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 24:151–154. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Macdonald RL and Olsen RW: GABAA receptor
channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 17:569–602. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fujii E and Mellon SH: Regulation of
uterine gamma-amino-butyric acid(A) receptor subunit expression
throughout pregnancy. Endocrinology. 142:1770–1777. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Follesa P, Serra M, Cagetti E, Pisu MG,
Porta S, Floris S, Massa F, Sanna E and Biggio G: Allopregnanolone
synthesis in cerebellar granule cells: roles in regulation of
GABA(A) receptor expression and function during progesterone
treatment and withdrawal. Mol Pharmacol. 57:1262–1270.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Majewska MD and Vaupel DB: Steroid control
of uterine motility via gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors in the
rabbit: a novel mechanism? J Endocrinol. 131:427–434. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maemura K, Shiraishi N, Sakagami K,
Kawakami K, Inoue T, Murano M, Watanabe M and Otsuki Y:
Proliferative effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on the gastric
cancer cell line are associated with extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1/2 activation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 24:688–696. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee SK, Dawson J, Lee JA, Osman G, Levitin
MO, Guzel RM and Djamgoz MB: Management of cancer pain: wider
implications of orthodox analgesics. Int J Gen Med. 7:49–58.
2014.
|
|
20
|
Yuan L, Wang J, Xiao H, Wu W, Wang Y and
Liu X: MAPK signaling pathways regulate mitochondrial-mediated
apoptosis induced by isoorientin in human hepatoblastoma cancer
cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 53:62–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ferrari D, Codecà C, Fiore J, Moneghini L,
Bosari S and Foa P: Biomolecular markers in cancer of the tongue.
2009:4129082009.
|
|
22
|
Tamayama T, Maemura K, Kanbara K, Hayasaki
H, Yabumoto Y, Yuasa M and Watanabe M: Expression of GABA(A) and
GABA(B) receptors in rat growth plate chondrocytes: activation of
the GABA receptors promotes proliferation of mouse chondrogenic
ATDC5 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 273:117–126. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takehara A, Hosokawa M, Eguchi H, Ohigashi
H, Ishikawa O, Nakamura Y and Nakagawa H: Gamma-aminobutyric acid
(GABA) stimulates pancreatic cancer growth through overexpressing
GABAA receptor pi subunit. Cancer Res. 67:9704–9712. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Neelands TR and Macdonald RL:
Incorporation of the pi subunit into functional gamma-aminobutyric
Acid(A) receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 56:598–610. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hedblom E and Kirkness EF: A novel class
of GABAA receptor subunit in tissues of the reproductive system. J
Biol Chem. 272:15346–15350. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Gong Y, Assy N and Minuk GY:
Increased GABAergic activity inhibits alpha-fetoprotein mRNA
expression and the proliferative activity of the HepG2 human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. J Hepatol. 32:85–91. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lei YY, Wang WJ, Mei JH and Wang CL:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction in solid
tumors. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:8539–8548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cargnello M and Roux PP: Activation and
function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated
protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 75:50–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Warnakulasuriya S: Global epidemiology of
oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 45:309–316. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bitu CC, Kauppila JH, Bufalino A,
Nurmenniemi S, Teppo S, Keinänen M, Vilen ST, Lehenkari P, Nyberg
P, Coletta RD and Salo T: Cathepsin K is present in invasive oral
tongue squamous cell carcinoma in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One.
8:e709252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han X, Han Y, Jiao H and Jie Y: 14-3-3ζ
regulates immune response through Stat3 signaling in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Mol Cells. 38:112–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yan M, Xu Q, Zhang P, Zhou XJ, Zhang ZY
and Chen WT: Correlation of NF-kappaB signal pathway with tumor
metastasis of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 10:437–443. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nariai Y, Mishima K, Yoshimura Y and
Sekine J: FAP-1 and NF-κB expressions in oral squamous cell
carcinoma as potential markers for chemo-radio sensitivity and
prognosis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 40:419–426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen IC, Chiang WF, Huang HH, Chen PF,
Shen YY and Chiang HC: Role of SIRT1 in regulation of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell
carcinoma metastasis. Mol Cancer. 13:254–267. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ekshyyan O, Moore-Medlin TN, Raley MC,
Sonavane K, Rong X, Brodt MA, Abreo F, Alexander JS and Nathan CA:
Anti-lymphangiogenic properties of mTOR inhibitors in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma experimental models. BMC Cancer.
13:320–329. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Theocharis S, Kotta-Loizou I, Klijanienko
J, Giaginis C, Alexandrou P, Dana E, Rodriguez J, Patsouris E and
Sastre-Garau X: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)
expression and activation in mobile tongue squamous cell carcinoma:
associations with clinicopathological parameters and patients
survival. Tumour Biol. 35:6455–6465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Lu X, Qi H, Li X, Xiao X and Gao J:
Ursolic acid induces apoptosis through mitochondrial intrinsic
pathway and suppression of ERK1/2 MAPK in HeLa cells. J Pharmacol
Sci. 125:202–210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|