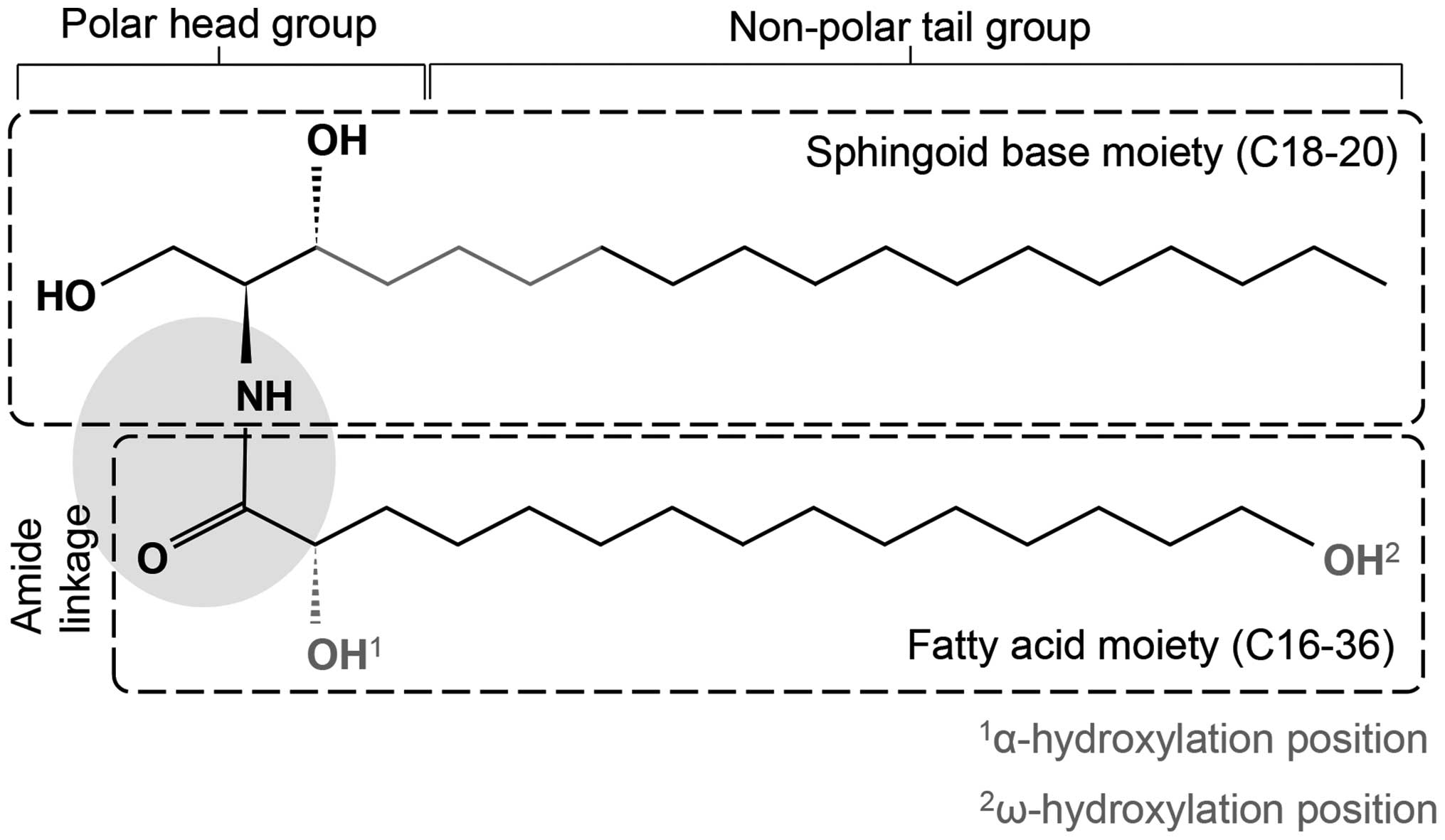
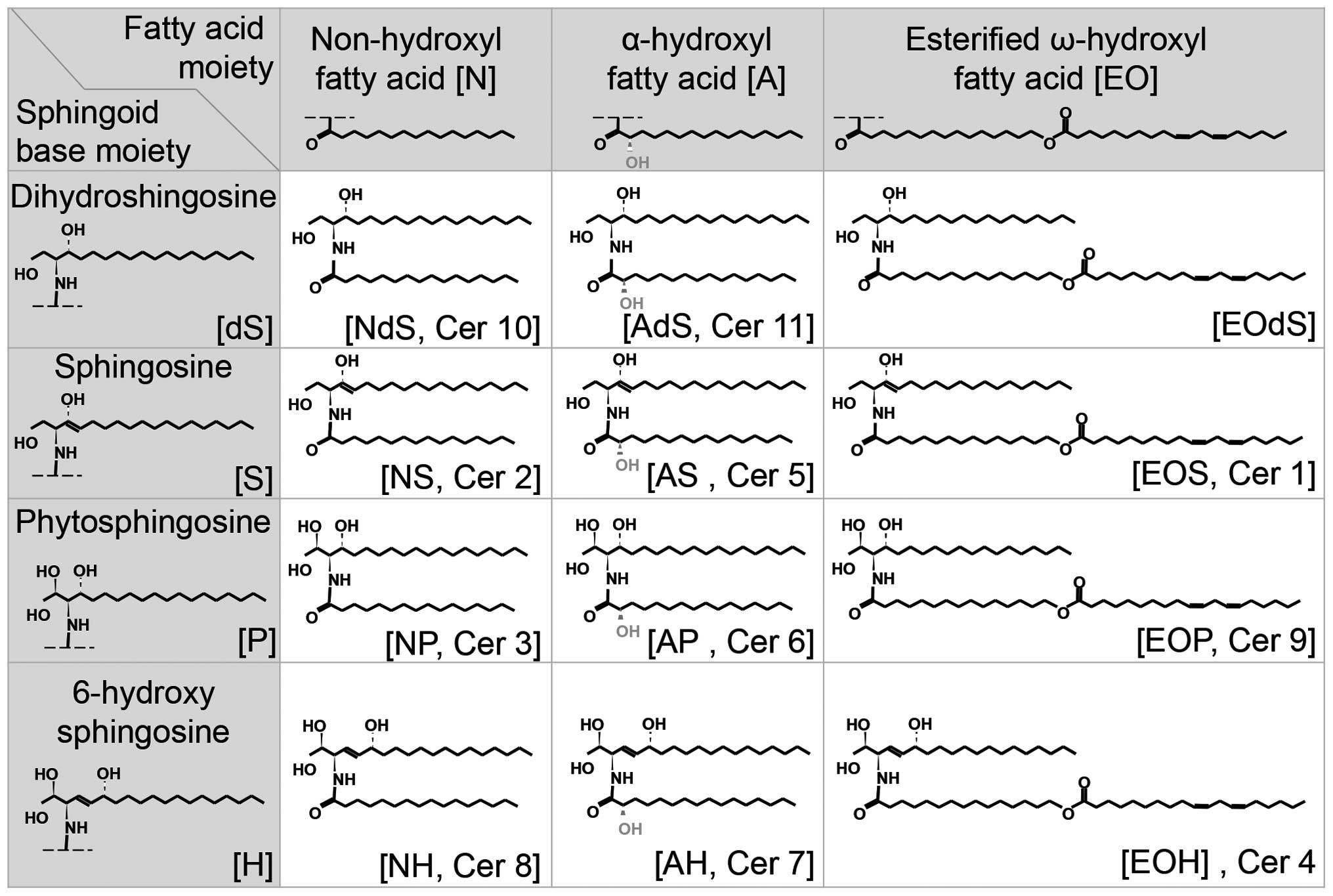
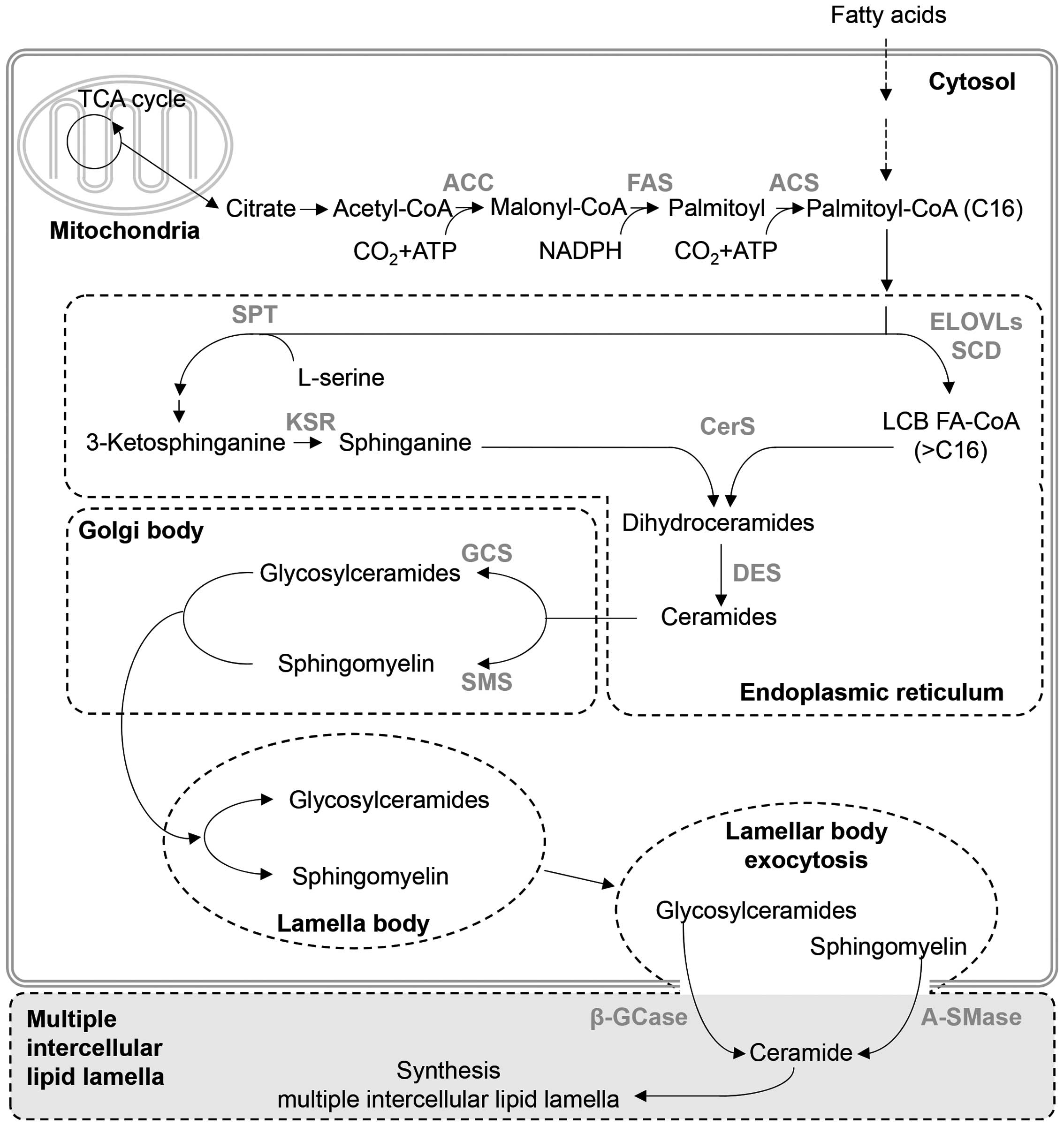
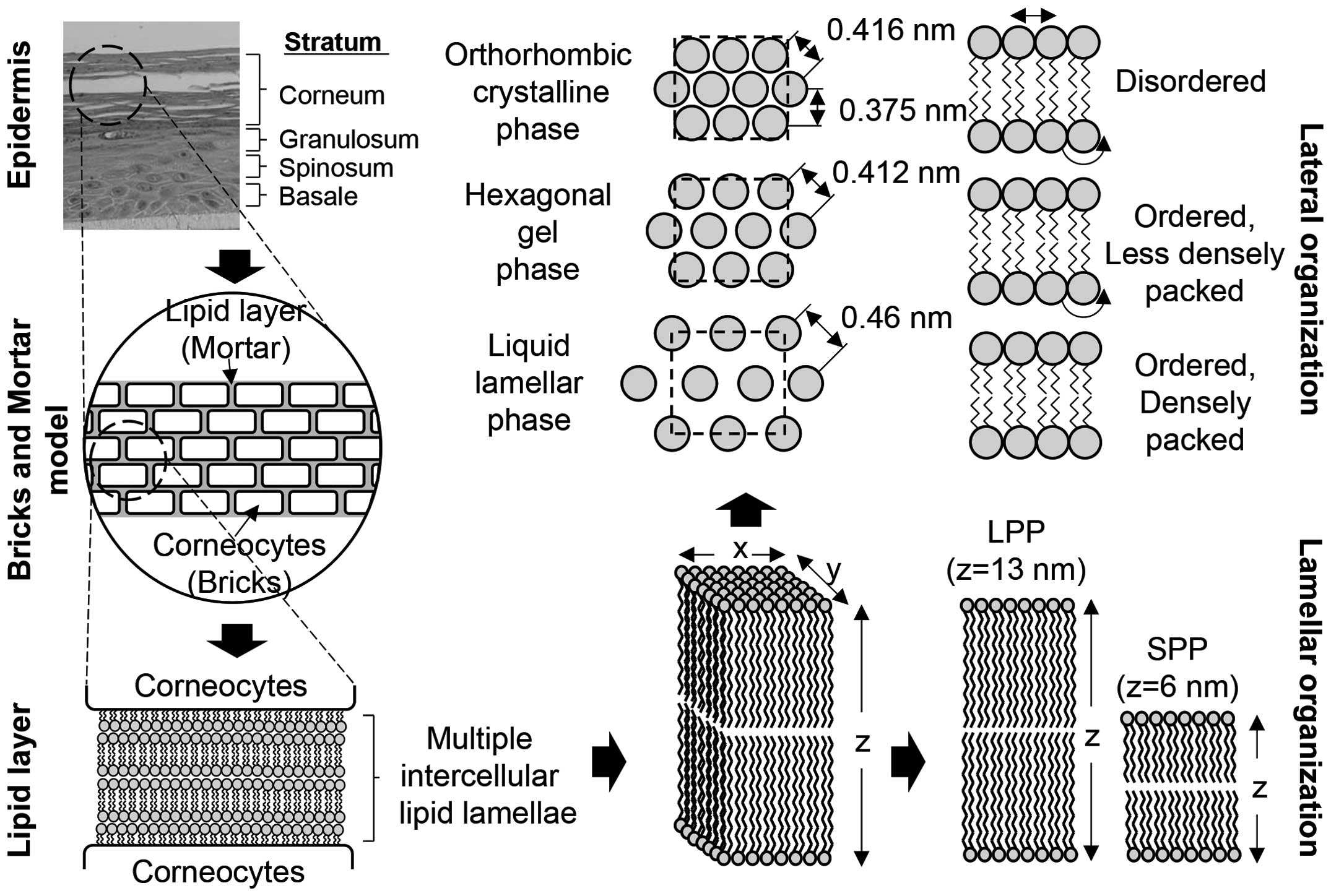
|
1
|
Natarajan VT, Ganju P, Ramkumar A, Grover
R and Gokhale RS: Multifaceted pathways protect human skin from UV
radiation. Nat Chem Biol. 10:542–551. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rawlings AV and Harding CR: Moisturization
and skin barrier function. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 17(Suppl 1):
43–48. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wertz PW: Current understanding of skin
biology pertinent to skin penetration: skin biochemistry. Skin
Pharmacol Physiol. 26:217–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Del Rosso JQ and Levin J: Clinical
relevance of maintaining the structural and functional integrity of
the stratum corneum: why is it important to you? J Drugs Dermatol.
10(Suppl): s5–s12. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jacobi OT: About the mechanism of moisture
regulation in the horny layer of the skin. Proc Sci Sect Toilet
Goods Assoc. 31:22–24. 1959.
|
|
6
|
Blank IH: Factors which influence the
water content of the stratum corneum. J Invest Dermatol.
18:433–440. 1952. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Elias PM: Epidermal lipids, barrier
function, and desquamation. J Invest Dermatol. 80(Suppl): 44s–49s.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feingold KR: Thematic review series: skin
lipids. The role of epidermal lipids in cutaneous permeability
barrier homeostasis. J Lipid Res. 48:2531–2546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Feingold KR and Elias PM: Role of lipids
in the formation and maintenance of the cutaneous permeability
barrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:280–294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Elias PM and Wakefield JS: Mechanisms of
abnormal lamellar body secretion and the dysfunctional skin barrier
in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
134:781–791.e1. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Candi E, Schmidt R and Melino G: The
cornified envelope: a model of cell death in the skin. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 6:328–340. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Smeden J, Janssens M, Gooris GS and
Bouwstra JA: The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the
cutaneous barrier function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:295–313.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Feingold KR: The regulation and role of
epidermal lipid synthesis. Adv Lipid Res. 24:57–82. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Coderch L, López O, de la Maza A and Parra
JL: Ceramides and skin function. Am J Clin Dermatol. 4:107–129.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi MJ and Maibach HI: Role of ceramides
in barrier function of healthy and diseased skin. Am J Clin
Dermatol. 6:215–223. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ogretmen B and Hannun YA: Biologically
active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:604–616. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arana L, Gangoiti P, Ouro A, Trueba M and
Gómez-Muñoz A: Ceramide and ceramide 1-phosphate in health and
disease. Lipids Health Dis. 9:152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mimeault M, Hauke R and Batra SK: Recent
advances on the molecular mechanisms involved in the drug
resistance of cancer cells and novel targeting therapies. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 83:673–691. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Robson KJ, Stewart ME, Michelsen S, Lazo
ND and Downing DT: 6-Hydroxy-4-sphingenine in human epidermal
ceramides. J Lipid Res. 35:2060–2068. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
t'Kindt R, Jorge L, Dumont E, Couturon P,
David F, Sandra P and Sandra K: Profiling and characterizing skin
ceramides using reversed-phase liquid chromatography-quadrupole
time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 84:403–411. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Masukawa Y, Narita H, Shimizu E, Kondo N,
Sugai Y, Oba T, Homma R, Ishikawa J, Takagi Y, Kitahara T, et al:
Characterization of overall ceramide species in human stratum
corneum. J Lipid Res. 49:1466–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pruett ST, Bushnev A, Hagedorn K, Adiga M,
Haynes CA, Sullards MC, Liotta DC and Merrill AH Jr: Biodiversity
of sphingoid bases ('sphingosines') and related amino alcohols. J
Lipid Res. 49:1621–1639. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Farwanah H, Pierstorff B, Schmelzer CE,
Raith K, Neubert RH, Kolter T and Sandhoff K: Separation and mass
spectrometric characterization of covalently bound skin ceramides
using LC/APCI-MS and Nano-ESI-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol
Biomed Life Sci. 852:562–570. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stewart ME and Downing DT: Free
sphingosines of human skin include 6-hydroxysphingosine and
unusually long-chain dihydrosphingosines. J Invest Dermatol.
105:613–618. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nugteren DH: The enzymic chain elongation
of fatty acids by rat-liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta.
106:280–290. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guillou H, Zadravec D, Martin PG and
Jacobsson A: The key roles of elongases and desaturases in
mammalian fatty acid metabolism: insights from transgenic mice.
Prog Lipid Res. 49:186–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jakobsson A, Westerberg R and Jacobsson A:
Fatty acid elongases in mammals: their regulation and roles in
metabolism. Prog Lipid Res. 45:237–249. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Breiden B and Sandhoff K: The role of
sphingolipid metabolism in cutaneous permeability barrier
formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:441–452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Jennemann R, Rabionet M, Gorgas K, Epstein
S, Dalpke A, Rothermel U, Bayerle A, van der Hoeven F, Imgrund S,
Kirsch J, et al: Loss of ceramide synthase 3 causes lethal skin
barrier disruption. Hum Mol Genet. 21:586–608. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rabionet M, Gorgas K and Sandhoff R:
Ceramide synthesis in the epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1841:422–434. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Marekov LN and Steinert PM: Ceramides are
bound to structural proteins of the human foreskin epidermal
cornified cell envelope. J Biol Chem. 273:17763–17770. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wertz PW and Downing DT: Ceramides of pig
epidermis: structure determination. J Lipid Res. 24:759–765.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mizutani Y, Mitsutake S, Tsuji K, Kihara A
and Igarashi Y: Ceramide biosynthesis in keratinocyte and its role
in skin function. Biochimie. 91:784–790. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Eckl KM, Tidhar R, Thiele H, Oji V,
Hausser I, Brodesser S, Preil ML, Onal-Akan A, Stock F, Müller D,
et al: Impaired epidermal ceramide synthesis causes autosomal
recessive congenital ichthyosis and reveals the importance of
ceramide acyl chain length. J Invest Dermatol. 133:2202–2211. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Holleran WM, Takagi Y and Uchida Y:
Epidermal sphingolipids: metabolism, function, and roles in skin
disorders. FEBS Lett. 580:5456–5466. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ebel P, Imgrund S, Vom Dorp K, Hofmann K,
Maier H, Drake H, Degen J, Dörmann P, Eckhardt M, Franz T and
Willecke K: Ceramide synthase 4 deficiency in mice causes lipid
alterations in sebum and results in alopecia. Biochem J.
461:147–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wertz PW: Lipids and barrier function of
the skin. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 208:7–11. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Farwanah H, Raith K, Neubert RH and
Wohlrab J: Ceramide profiles of the uninvolved skin in atopic
dermatitis and psoriasis are comparable to those of healthy skin.
Arch Dermatol Res. 296:514–521. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Imokawa G, Abe A, Jin K, Higaki Y,
Kawashima M and Hidano A: Decreased level of ceramides in stratum
corneum of atopic dermatitis: an etiologic factor in atopic dry
skin? J Invest Dermatol. 96:523–526. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Houben E, Holleran WM, Yaginuma T, Mao C,
Obeid LM, Rogiers V, Takagi Y, Elias PM and Uchida Y:
Differentiation-associated expression of ceramidase isoforms in
cultured keratinocytes and epidermis. J Lipid Res. 47:1063–1070.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bouwstra JA, Gooris GS, Dubbelaar FE,
Weerheim AM, Ijzerman AP and Ponec M: Role of ceramide 1 in the
molecular organization of the stratum corneum lipids. J Lipid Res.
39:186–196. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bouwstra JA, Gooris GS, Dubbelaar FE and
Ponec M: Phase behavior of stratum corneum lipid mixtures based on
human ceramides: the role of natural and synthetic ceramide 1. J
Invest Dermatol. 118:606–617. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hanada K: Intracellular trafficking of
ceramide by ceramide transfer protein. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys
Biol Sci. 86:426–437. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ponnusamy S, Meyers-Needham M, Senkal CE,
Saddoughi SA, Sentelle D, Selvam SP, Salas A and Ogretmen B:
Sphingolipids and cancer: ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in
the regulation of cell death and drug resistance. Future Oncol.
6:1603–1624. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jensen JM, Förl M, Winoto-Morbach S, Seite
S, Schunck M, Proksch E and Schütze S: Acid and neutral
sphingomyelinase, ceramide synthase, and acid ceramidase activities
in cutaneous aging. Exp Dermatol. 14:609–618. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jensen JM, Fölster-Holst R, Baranowsky A,
Schunck M, Winoto-Morbach S, Neumann C, Schütze S and Proksch E:
Impaired sphingomyelinase activity and epidermal differentiation in
atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 122:1423–1431. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Swanbeck G and Thyresson N: A study of the
state of aggregation of the lipids in normal and psoriatic horny
layer. Acta Derm Venereol. 42:445–447. 1962.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Swanbeck G and Thyresson N: An x-ray
diffraction study of scales from different dermatoses. Acta Derm
Venereol. 41:289–296. 1961.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Breathnach AS, Goodman T, Stolinski C and
Gross M: Freeze-fracture replication of cells of stratum corneum of
human epidermis. J Anat. 114:65–81. 1973.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Breathnach AS: Aspects of epidermal
ultrastructure. J Invest Dermatol. 65:2–15. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
White SH, Mirejovsky D and King GI:
Structure of lamellar lipid domains and corneocyte envelopes of
murine stratum corneum. An X-ray diffraction study. Biochemistry.
27:3725–3732. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Schreiner V, Gooris GS, Pfeiffer S,
Lanzendörfer G, Wenck H, Diembeck W, Proksch E and Bouwstra J:
Barrier characteristics of different human skin types investigated
with X-ray diffraction, lipid analysis, and electron microscopy
imaging. J Invest Dermatol. 114:654–660. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Moore DJ, Rerek ME and Mendelsohn R: Lipid
domains and orthorhombic phases in model stratum corneum: evidence
from Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy studies. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 231:797–801. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hannun YA: Functions of ceramide in
coordinating cellular responses to stress. Science. 274:1855–1859.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ruvolo PP: Intracellular signal
transduction pathways activated by ceramide and its metabolites.
Pharmacol Res. 47:383–392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ballou LR, Laulederkind SJ, Rosloniec EF
and Raghow R: Ceramide signalling and the immune response. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1301:273–287. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Geilen CC, Wieder T and Orfanos CE:
Ceramide signalling: regulatory role in cell proliferation,
differentiation and apoptosis in human epidermis. Arch Dermatol
Res. 289:559–566. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Uchida Y: Ceramide signaling in mammalian
epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:453–462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Senkal CE, Ponnusamy S, Bielawski J,
Hannun YA and Ogretmen B: Antiapoptotic roles of
ceramide-synthase-6-generated C16-ceramide via selective regulation
of the ATF6/CHOP arm of ER-stress-response pathways. FASEB J.
24:296–308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Tonnetti L, Veri MC, Bonvini E and
D'Adamio L: A role for neutral sphingomyelinase-mediated ceramide
production in T cell receptor-induced apoptosis and
mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated signal transduction. J
Exp Med. 189:1581–1589. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gómez-Muñoz A: Ceramide-1-phosphate: a
novel regulator of cell activation. FEBS Lett. 562:5–10. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Gómez-Muñoz A, Kong JY, Salh B and
Steinbrecher UP: Ceramide-1-phosphate blocks apoptosis through
inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase in macrophages. J Lipid Res.
45:99–105. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Gomez-Muñoz A, Martin A, O'Brien L and
Brindley DN: Cell-permeable ceramides inhibit the stimulation of
DNA synthesis and phospholipase D activity by phosphatidate and
lysophosphatidate in rat fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 269:8937–8943.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gómez-Muñoz A, Kong JY, Parhar K, Wang SW,
Gangoiti P, González M, Eivemark S, Salh B, Duronio V and
Steinbrecher UP: Ceramide-1-phosphate promotes cell survival
through activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein
kinase B pathway. FEBS Lett. 579:3744–3750. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bourbon NA, Sandirasegarane L and Kester
M: Ceramide-induced inhibition of Akt is mediated through protein
kinase Czeta: implications for growth arrest. J Biol Chem.
277:3286–3292. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Schubert KM, Scheid MP and Duronio V:
Ceramide inhibits protein kinase B/Akt by promoting
dephosphorylation of serine 473. J Biol Chem. 275:13330–13335.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Grether-Beck S, Bonizzi G, Schmitt-Brenden
H, Felsner I, Timmer A, Sies H, Johnson JP, Piette J and Krutmann
J: Non-enzymatic triggering of the ceramide signalling cascade by
solar UVA radiation. EMBO J. 19:5793–5800. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wakita H, Tokura Y, Yagi H, Nishimura K,
Furukawa F and Takigawa M: Keratinocyte differentiation is induced
by cell-permeant ceramides and its proliferation is promoted by
sphingosine. Arch Dermatol Res. 286:350–354. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sayama K, Hanakawa Y, Shirakata Y,
Yamasaki K, Sawada Y, Sun L, Yamanishi K, Ichijo H and Hashimoto K:
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) is an intracellular
inducer of keratinocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem. 276:999–1004.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Jiang YJ, Kim P, Uchida Y, Elias PM, Bikle
DD, Grunfeld C and Feingold KR: Ceramides stimulate caspase-14
expression in human keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 22:113–118. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ma nggau M, K i m DS, Ruwisch L, Vogler R,
Kor ting HC, Schäfer-Kor ting M and Kleuser B:
1Alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 protects human keratinocytes from
apoptosis by the formation of sphingosine-1-phosphate. J Invest
Dermatol. 117:1241–1249. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Kim DS, Kim SY, Moon SJ, Chung JH, Kim KH,
Cho KH and Park KC: Ceramide inhibits cell proliferation through
Akt/PKB inactivation and decreases melanin synthesis in Mel-Ab
cells. Pigment Cell Res. 14:110–115. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|